NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and its Applications
Topics and Subtopics in NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Applications:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 12 | Biotechnology and its Applications |
| 12.1 | Biotechnological Applications in Agriculture |
| 12.2 | Biotechnological Applications in Medicine |
| 12.3 | Transgenic Animals |
| 12.4 | Ethical Issues |
| 12.5 | Summary |
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK SOLVED
1. Crystals of Bt toxin produced by some bacteria do not kill the bacteria themselves because –
(a) bacteria are resistant to the toxin
(b) toxin is immature;
(c) toxin is inactive;
(d) bacteria encloses toxin in a special sac.
Ans: (c) Toxin is inactive.
2. What are transgenic bacteria? Illustrate using any one example.
Ans: Bacteria having gene or genes usually from an unrelated organism incorporated into their genome are called transgenic bacteria. For example, when human insulin gene is introduced into the isolated plasmid of E.coli bacterium and this recombinant DNA is transferred into a fresh bacterium, then the later is said to be transgenic or transformed bacterium.
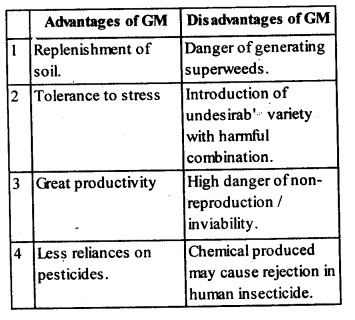
3. Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of production of genetically modified crops.
Ans:
4. What are Cry proteins? Name an organism that produces it. How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
Ans: The bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis is a common soil bacterium which produces a protein toxin that kills certain insects. The toxin is a crystal (Cry) protein. There are several kinds of Cry proteins which are toxic to different groups of insects. The gene encoding Cry protein is called cry gene. Biotechnologists have been able to isolate the gene responsible for production of toxin and to introduce it into a number of plants to produce genetically modified plants resistant to insects, e.g., Bt cotton (resistant to bollworm) and GM tobacco (resistant to hornworms).
5. What is gene therapy? Illustrate using the example of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Ans: Gene therapy is correction of malfunctioning/gen by repairing or adding correct copy. ADA (adenosine deaminase deficiency) is a very rare genetic disorder due to deletion of the gene for adenosine deaminase. The enzyme is crucial for the immune system to functions. It can be treated by gene therapy. This gene is transfected into early embryonic cells of bone marrow for permanent use.
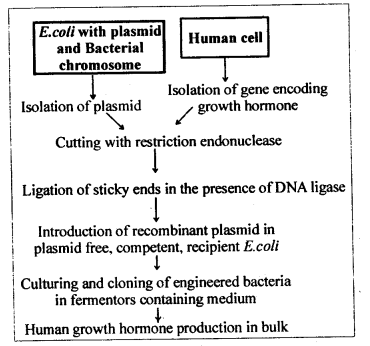
6. Digrammatically represent the experimental steps in cloning and expressing an human gene (say the gene for growth hormone) into a bacterium like E. coli?
Ans:
7. Can you suggest a method to remove oil (hydrocarbon) from seeds based on your understanding of rDNA technology and chemistry of oil?
Ans: The genes for the formation of oil in the seed should be identified. The appropriate genes should be removed with the help of restriction endonucleases. Such DNA should then be treated with DNA ligases to make seal DNA at the broken ends. These cells when grown aseptically on nutrient medium will differentiate into a new plant whose seeds will not have oil in them.
8. Find out from internet what is golden rice.
Ans: Golden rice is a transgenic variety of rice (Oryza sativa) containing good quantities of β-carotene (provitamin A) which is principle source of vitamin A. Since the grains of the rice are yellow in colour due to β-carotene, the rice is commonly called golden rice. It was developed at Swiss Federal Institute of Technology by Professor Ingo Potrykus and Peter Beyer.
9. Does our blood have proteases and nucleases?
Ans: No, blood does not have protease and nuclease. If it would have been there blood and cell would have been digested, some protease do exist in inactive form.
10. Consult internet and find out how to make orally activ&protein pharmaceutical. What is the major problem to be encountered?
Ans: Orally active protein product that is successfully manufactured is vaccines for preventions of infectious diseases such as hepatitis B, herpes, influenza, etc. Gene for antigen are isolated from bacteria and grown along with cut leaf portions of potato plant in antibiotic medium – followed by callus formation and recombinant/transgenic potato are obtained which contain those vaccines.
More Resources for CBSE Class 12: