NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number Systems are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Number Systems.
NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Number Systems
Question 1.
Every rational number is
(a) a natural number
(b) an integer
(c) a real number
(d) a whole number
Solution:
(c) Since, real numbers are the combination of rational and irrational numbers.
Hence, every rational number is a real number.
Question 2.
Between two rational numbers
(a) there is no rational number
(b) there is exactly one rational number
(c) there are infinitely many rational numbers
(d) there are only rational numbers and no irrational numbers
Solution:
(c) Between two rational numbers, there are infinitely many rational numbers.
Question 3.
Decimal representation of a rational number cannot be
(a) terminating
(b) non-terminating
(c) non-terminating repeating
(d) non-terminating non-repeating
Solution:
(d) Decimal representation of a rational number cannot be non-terminating non-repeating because the decimal expansion of rational number is either terminating or non-terminating recurring (repeating) or Non Terminating Repeating Numbers.
Question 4.
The product of any two irrational numbers is
(a) always an irrational number
(b) always a rational number
(c) always an integer
(d) sometimes rational, sometimes irrational
Solution:
(d) We know that, the product of any two irrational numbers is sometimes rational and sometimes irrational. It depends upon the given terms.
Question 5.
The decimal expansion of the number √2 is
(a) a finite decimal
(b) 1.41421
(c) non-terminating recurring
(d) non-terminating non-recurring
Solution:
The decimal expansion of the number √2 is non-terminating non-recurring. Because √2 is an irrational number.
Also, we know that an irrational number is non-terminating non-recurring.
Question 6.
Which of the following is irrational?
![]()
Solution:
(c) √7is an irrational number, because √7 non-terminating non-recurring.
Question 7.
Which of the following is irrational?
![]()
Solution:
(D) We have, 0.14, which is terminating. On the other hand 0.1416 and 0.1416 are non-terminating but recurring.
And 0.4014001400014… is non-terminating non-recurring.
∴ The term given in option (D) is an irrational number.
Question 8.
A rational number between √2 and √3 is
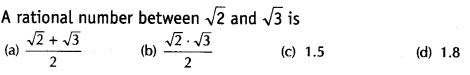
Solution:
(c) 1.5
Question 9.
The value of 1.999… in the form of p/q, where p and q are integers and q≠0, is
(a) \(\frac{19}{10}\)
(b) \(\frac{1999}{1000}\)
(c) 2
(d) \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Solution:
(c) 2
Let x = 1.999… (i)
Multiply (i) by 10, we get
10x = 19.999… (ii)
On subtracting (i) from (ii), we get
10x – x = (19.999…) – (1.999…)
⇒ 9x = 18
∴ x = 2
Question 10.
2√3 + √3 is equal to
(a) 2√6
(b) 6
(c) 3√3
(d) 4√6
Solution:
(c) 3√3
we have 2√3 + √3 = √3(2+1) = 3√3
Question 11.
√10 × √15 is equal to
(a) 6√5
(b) 5√6
(c) √25
(d) 10√5
Solution:
(b) 5√6
we have √10 × √15 = √2.√5 × √3.√5
= (√2.√3) × (√5.√5) = 5√6
Question 12.
The number obtained on rationalising the denominator of \(\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { 7 } -2 } \) is

Solution:
(A)
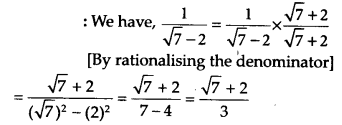
Question 13.
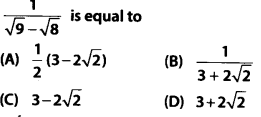
Solution:
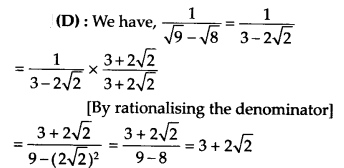
Question 14.

Solution:

Question 15.
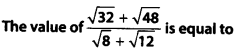
Solution:
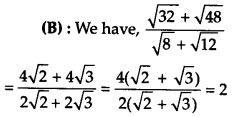
Question 16.
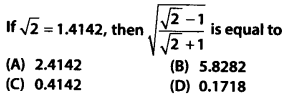
Solution:
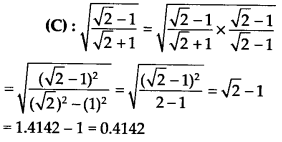
Question 17.
![]()
Solution:
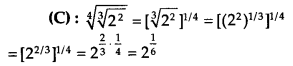
Question 18.

Solution:
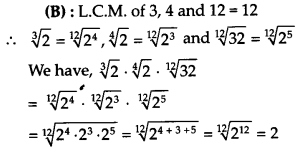
Question 19.
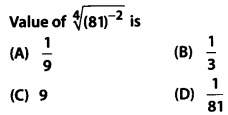
Solution:
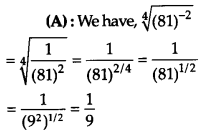
Question 20.
![]()
Solution:
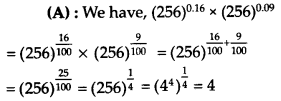
Question 21.
Which of the following is equal to x?
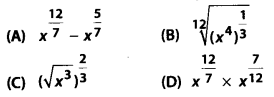
Solution:
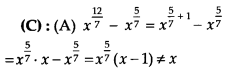
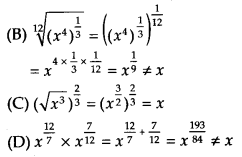
Exercise 1.2: Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Let x and y be rational and irrational numbers, respectively. Is x+y necessarily an irrational number? Give an example in support of your answer.
Solution:
Yes, (x + y) is necessarily an irrational number.
For example, let x = 2 and y = √3
Then, x + y = 2 +√3
Suppose x + y = 2+ √3 be a rational number.
Let us consider a = 2 + √3, which is rational.
On squaring both sides, we get
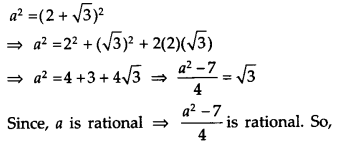
√3 is also a rational number.
The above contradicts the fact that √3 is an irrational number. Thus, our assumption was wrong. Hence, x + y is an irrational number.
Question 2.
Let x be rational and y be irrational. Is xy necessarily irrational? Justify your answer by an example.
Solution:
No, xy is necessarily irrational only when x ≠0.
Let x be a non-zero rational and y be an irrational. Then, we have to show that xy be an irrational. If possible, let xy be a rational number. Since quotient of two non-zero rational number is a rational number.
So,(xy/x) is a rational number
=> y is a rational number.
But, this contradicts the fact that y is an irrational number. Thus, our supposition is wrong. Hence, xy is an irrational number. But, when x = 0, then xy = 0, a rational number.
Question 3.
State whether the following statements are true or false? Justify your answer.
(i) \(\frac { \sqrt { 2 } }{ 3 } \) is a rational number.
(ii) There are infinitely many integers between any two integers.
(iii) Number of rational numbers between 15 and 18 is finite.
(iv)There are numbers which cannot be written in the from p/q, q≠0 p,q both are integers.
(v) The square of an irrational number is always rational.

Solution:
(i) False, here √2 is an irrational number and 3 is a rational number, we know that when we divide irrational number by non-zero rational number it will always give an irrational number.
(ii) False, because between two consecutive integers (like 1 and 2), there does not exist any other integer.
(iii) False, because between any two rational numbers there exist infinitely many rational numbers.
(iv) True, because there are infinitely many numbers which cannot be written in the form p/q, q ≠0. p,q both are integers and these numbers are called irrational numbers.

Question 4.
Classify the following numbers as rational or irrational with justification

Solution:

(vii) We have, 0.5918, whose decimal expansion is terminating and it can be written in the form of p/q, where q≠0, p and q are integers. Thus, 0.5918 is a rational number.
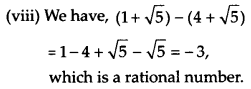
(ix) We have, 10.124124…, whose decimal expansion is non-terminating but recurring. Thus, 10.124124 is a rational number.
(x) We have 1.010010001…, whose decimal expansion is non-terminating non-recurring. Thus, 1.010010001… is an irrational number.
Exercise 1.3: Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Find which of the variables x, y, z and u represent rational numbers and which irrational numbers.
(i) x2 =5
(ii) y2 = 9
(iii) z2 = 0.04
(iv) u2 = 17/4
Solution:

Question 2.
Find three rational numbers between
(i) -1 and -2
(ii) 0.1 and 0.11
(iii) 5/7 and 6/7
(iv) 1/4 and 1/5
Solution:

(ii) Let x = 0.1 and y = 0.11
As we can write, x = 0.1 = 0.100 and y = 0.11 = 0.110
Thus, the three rational numbers between 0.100 and 0.110 are 0.101, 0.102, 0.103.

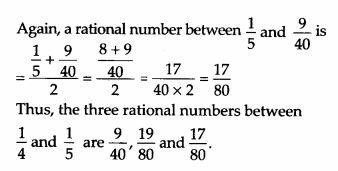
Question 3.
Insert a rational number and an irrational number between the following
(i) 2 and 3
(ii) 0 and 0.1
(iii) 1/3 and 1/2
(iv) -2/5 and -1/2
(v) 0.15 and 0.16
(vi) √2 and √3
(vii) 2.357 and 3.121
(viii) .0001 and .001
(ix) 3.623623 and 0.484848
(x) 3.375289 and 6.375738
Solution:
We know that, there are infinitely many rational and irrational values between any two numbers.
(i) A rational number between 2 and 3 is 2.1.
To find an irrational number between 2 and 3. Find a number which is non-terminating non-recurring lying between them.
Such number will be 2.040040004…………..
(ii) A rational number between 0 and 0.1 is 0.03.
An irrational number between 0 and 0.1 is 0.007000700007……….
(iii) A rational number between 1/3 and 1/2 is 5/12. An irrational number between 1/3 and 1/2 i.e., between 0-3 and 0.5 is 0.4141141114………….
(iv) A rational number between -2/5 and 1/2 is 0. An irrational number between -2/5 and 1/2 i.e., between – 0.4 and 0.5 is 0.151151115………..
(v) A rational number between 0.15 and 0.16 is 0.151. An irrational number between 0.15 and 0.16 is 0.1515515551…….
(vi) A rational number between √2 and √3 i.e.,, between 1.4142…… and 1.7320…… is 1.5.
An irrational number between √2 and √3 is 1.585585558……….
(vii) A rational number between 2.357 and 3.121 is 3. An irrational number between 2.357 and 3.121 is 3.101101110……..
(viii) A rational number between 0.0001 and 0.001 is 0.00011. An irrational number between 0.0001 and 0.001 is 0.0001131331333………..
(ix) A rational number between 3.623623 and 0.484848 is 1. An irrational number between 3.623623 and 0.484848 is 1.909009000……….
(x) A rational number between 6.375289 and 6.375738 is 6.3753. An irrational number between 6.375289 and 6.375738 is 6.375414114111………
Question 4.
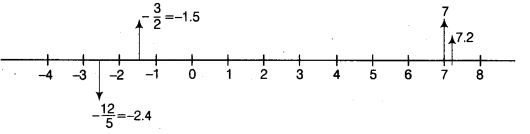
Represent the following numbers on the number line 7, 7.2, -3/2 and -12/5 .
Solution:
As we know positive numbers lies on right hand side of 0 and negative numbers lies on left hand side of 0.
Represent the given numbers on the number line as shown below:
Question5.
Locate √5, √10 and √17 on the number line.
Solution:
(i) We have, 5 = 2² +1 Now, draw a right angled ΔOAB, in which OA = 2 units and AB = 1 unit and ∠OAB = 90°. By using Pythagoras theorem, we get
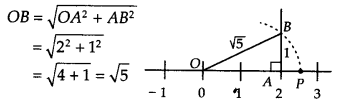
Taking OB = √5
as radius and point O as centre, draw an arc which meets the number line at point P.
Thus, point P represents √5 on the number line.
(ii) We have, 10 = 3² + 1
Now, draw a right angled ΔOAB, in which OA = 3 units and AB = 1 unit and ∠OAB = 90°. By using Pythagoras theorem, we get
![]()
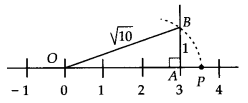
Taking OB =√10 as radius and point O as centre, draw an arc which meets the number line at point P. Thus, the point P represents
√10 on the number line.
(iii) We have, 17 = 4² +1 Now, draw a right angled ΔOAB, in which OA = 4 units and AB = 1 unit and ∠OAB = 90°. By using Pythagoras theorem, we get
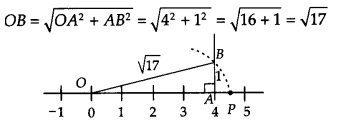
Taking OB = √17 as radius and point line at point P. Thus, the point P represents √17 on the number line.
Question 6.
Represent geometrically the following numbers on the number line:
(i) √4.5
(ii) √5.6
(iii) √8.1
(iv) √2.3
Solution:
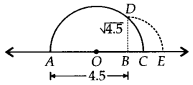
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 4.5 units and extend it to C such that BC = 1 unit. Let O be the mid-point of AC.
Now, we will draw a semi-circle with centre O and radius OA. Let us draw BD perpendicular to AC passing through a point B, intersecting the semi-circle at a point D.
∴ BD = √4.5 units.
Now, draw an arc with centre B and radius BD, meeting AC produced at E, such that
BE = BD = √4.5 units
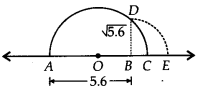
(ii) Draw a line segment AB = 5.6 units and extend it to C such that BC = 1 unit. Let O be the mid-point of AC.
Now, we will draw a semi-circle with centre O and radius OA. Let us draw BD perpendicular to AC passing through a point B, intersecting the semi-circle at a point D.
∴ BD = √5.6 units.
Now, draw an arc with centre B and radius BD, meeting AC produced at E, such that
BE = BD = √5.6 units
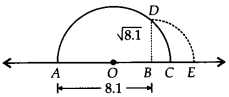
(iii) Draw a line segment AB = 8.1 units and extend it to C such that BC = 1 unit. Let O be the mid-point of AC.
Now, we will draw a semi-circle with centre O and radius OA.
Let us draw BD perpendicular to AC passing through a point B, intersecting the semi-circle at a point D.
∴ BD = √8.1 units.
Now, draw an arc with centre B and radius BD, meeting AC produced at E, such that
BE = BD = √8.1 units
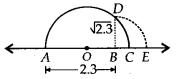
(iv) Draw a line segment AB = 2.3 units and extend it to C such that BC = 1 unit. Let O be the mid-point of AC.
Now, we will draw a semi-circle with centre O and radius OA.
Let us draw BD perpendicular to AC passing through a point B, intersecting the semi-circle at a point D.
∴ BD = √2.3 units.
Now, draw an arc with centre B and radius BD, meeting AC produced at E, such that
BE = BD = √2.3 units.
7. Express the following in the form p/q, where p and q are integers and q≠0
(i) 0.2
(ii) 0.888…
(iii) 5.2
(iv) 0.001
(v) 0.2555…
(vi) 0.134
(vii) .00323232…
(viii) .404040…
Solution:
(i) Let x = 0.2 = 2/10 = 1/5
(ii) Let x = 0.888… … (1)
On multiplying both sides of (1) by 10, we get
1Ox = 8.888… … (2)
On subtracting (1) from (2), we get
1Ox – x = (8.888…) – (0.888…) ⇒ 9x = 8
Thus, x = 8/9
(iii) Let x = \(5.\bar { 2 } \)= 5.222… …(1)
On multiplying both sides of (1) by 10, we get
10x = 52.222… …(2)
On subtracting (1) from (2), we get
10x-x = (52.222…)-(5.222…) ⇒ 9x = 47
Thus, x = 47/9
(iv) Let x= \(0.\bar {001} \) or x = 0.001001… … (1)
On multipying both sides of (1) by 1000, we get
1000x = 1.001001… … (2)
On subtracting (1) from (2), we get 1000x – x = (1.001001…) – (0.001001…)
⇒ 999 x = 1
Thus, x = 1/999
(v) Let x = 0.2555… … (1)
On multiplying both sides, of (1) by 10, we get
10x = 2.5555… … (2)
On subtracting (1) from (2), we get
10x-x = (2.555…)-(0.255…) ⇒ 9x = 2.3
Thus 23/90
(vi) Let x = \(0.1\bar { 34 } \) or x = 0.13434… …(1)
On multiplying both sides of (1) by 100, we get
100x = 13.434… …(2)
On subtracting (1) from (2), we get 100x – x = (13.434…) – (0.134…)
⇒ 99x = 13.3
Thus, x = 133/990
(vii) Let x = 0.00323232… …(1)
On multiplying both sides of (1) by 100, we get
100x = 0.3232… …(2)
On subtracting (1) from (2), we get
100x-x = (0.3232…)-(0.0032…) = 99x = 0.32
Thus x = 32/9900 = 8/2475
(viii) Let x = 0.404040… …(1)
On multiplying both sides of (1) by 100, we get
100x = 40.4040… …(2)
On subtracting (1) from (2), we get
100x – x = (40.4040…) – (0.404040…)
= 99x = 40
Thus x = 40/99
Question 8.
Show that 0.142857142857… = 1/7
Solution:

Question 9.
Simplify the following
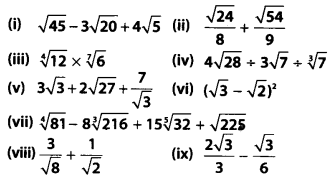
Solution:
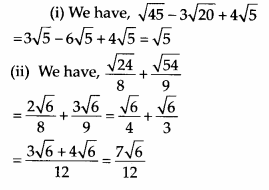
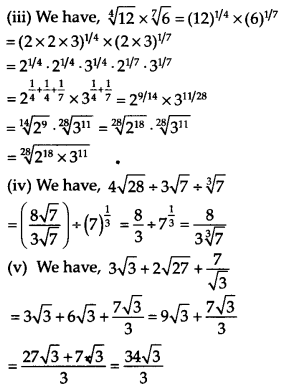

Question 10.
Rationalise the denominator of the following
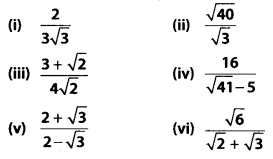
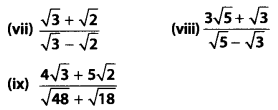
Solution:
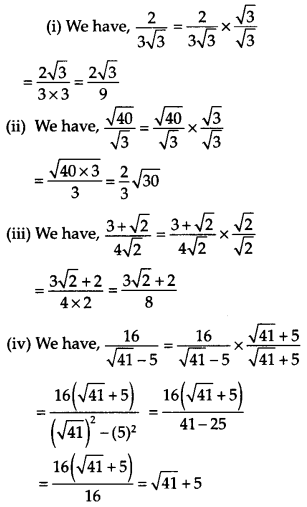
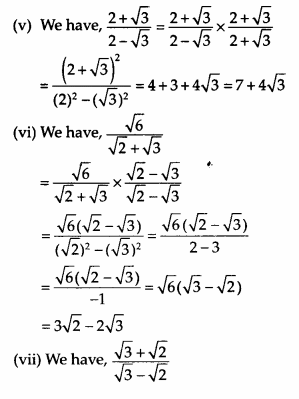
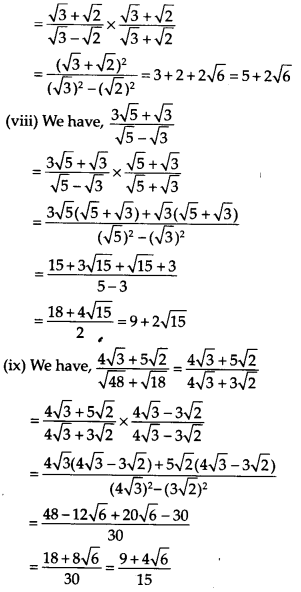
Question 11.
Find the values of a and b in each of the following
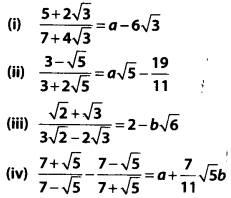
Solution:
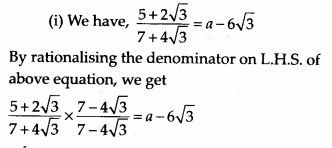
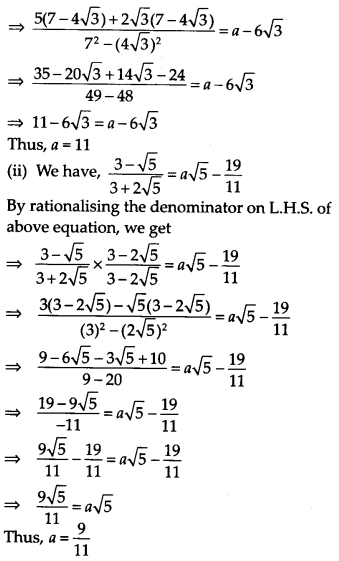
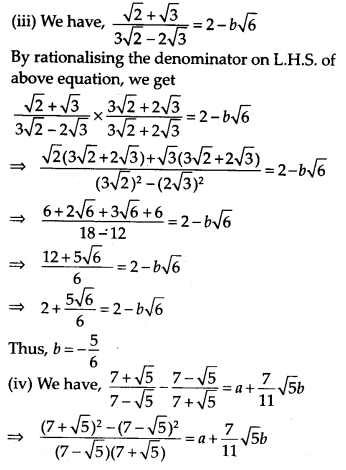
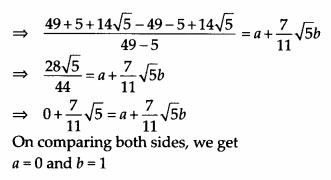
Question 12.
![]()
Solution:

Question 13.
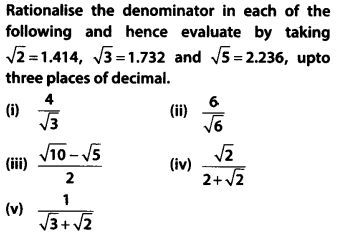
Solution:
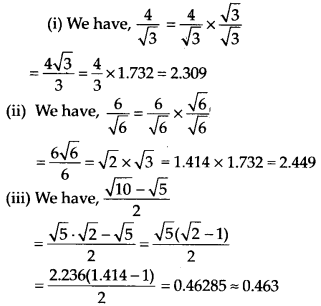
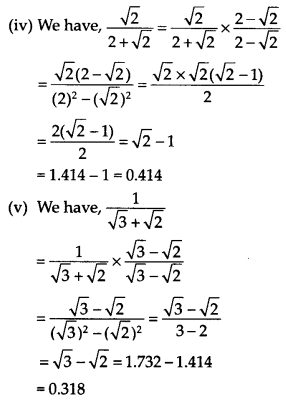
Question 14.
Simplify
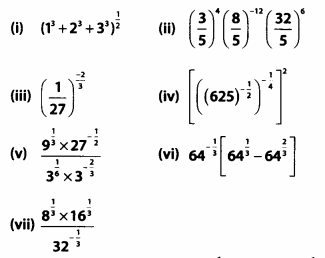
Solution:
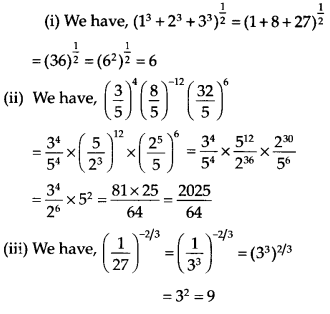
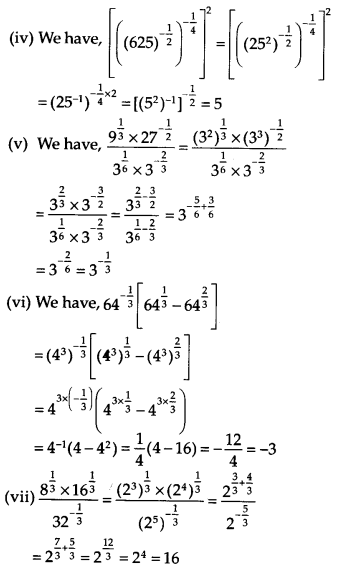
Exercise 1.4: Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Express 0.6+ \(0.\bar { 7 } \) + \(0.4\bar { 7 } \) in the form p/q , where p and q are integers and q≠0
Solution:

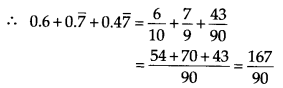
Question 2.
Simplify
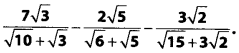
Solution:
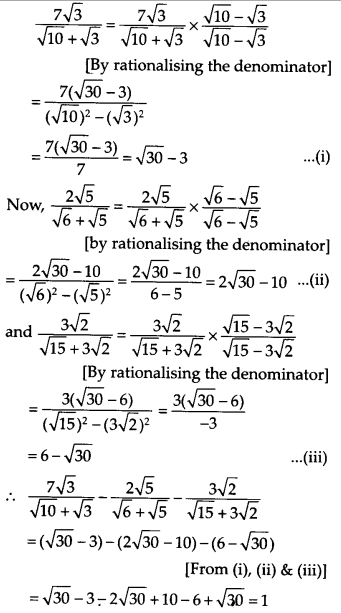
Question 3.
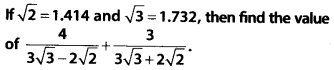
Solution:
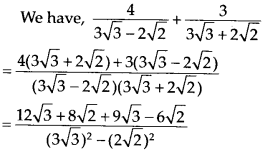
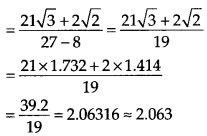
Question 4.
![]()
Solution:
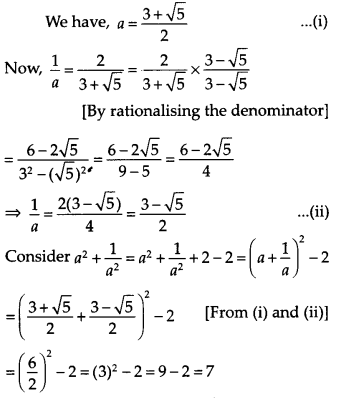
Question 5.
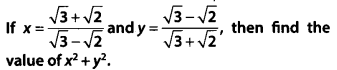
Solution:

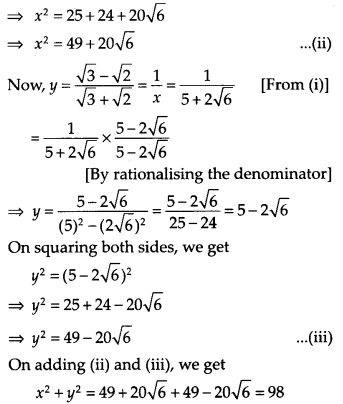
Question 6.
![]()
Solution:
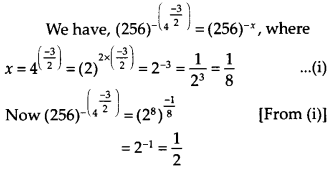
Question 7.
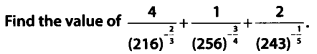
Solution:
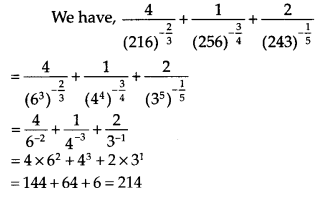
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number Systems will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Number Systems, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest