NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Lines and Angles are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Lines and Angles.
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Lines and Angles.
Directions: In questions 1 to 41, there are four options out of which one is correct. Write the correct one.
Question 1.
The angles between North and West and South and East are
(a) complementary
(b) supplementary
(c) both are acute
(d) both are obtuse
Solution:
(b) The angle between North and West is a right angle and angle between South and East is also a right angle.
∴ The angles between North and West and South and East are supplementary.
Question 2.
Angles between South and West and South and East are
(a) vertically opposite angles
(b) complementary angles.
(c) making a linear pair
(d) adjacent but not supplementary
Solution:
(c) The angle between South and West is a right angle and angle between South and East is also a right angle.
∴ Angles between South and West and South and East are making a linear pair.
Question 3.
In the given figure, PQ is a mirror, AB is the incident ray and BC is the reflected ray. If ∠ABC = 46°, then ∠ABP is equal to
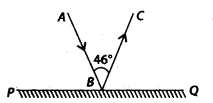
(a) 44°
(b) 67°
(c) 13°
(d) 62°
Solution:
(b) We know that angle of incident and angle of reflection is same.
∴ ∠ABP = ∠CBQ ——– (1)
As, PQ is a straight line.
∴ ∠ABP + ∠ABC + ∠CBQ = 180°
⇒ ∠ABP + 46° + ∠ABP = 180° [Using (1)
⇒ 2∠ABP = 180° – 46° = 134
\(\Rightarrow \angle A B P=\frac{134^{\circ}}{2}=67^{\circ}\)
Question 4.
If the complement of an angle is 799, then the angle will be of
(a) 10°
(b) 11°
(c) 79°
(d) 101°
Solution:
(b) Let the angle be x. Its complement -90° – x
∴ 90°- x = 79°
⇒ x = 90° – 79° ⇒ x – 11°
Thus, the required angle is 11°.
Question 5.
Angles which are both supplementary and vertically opposite are
(a) 95°, 85°
(b) 90°, 90°
(c) 100°, 60°
(d) 45°, 45°
Solution:
(b): Since, vertically opposite angles are equal.
∴ Let each angle be x.
⇒ x + x = 180° [∵Angles are supplementary]
⇒ 2x = 180° ⇒ x = 90°
Thus the required angles are 90° each.
Question 6.
The angle which makes a linear pair with an angle of 61° is of
(a) 29°
(b) 61°
(c) 122°
(d) 119°
Solution:
(d) Let the angle be x.
x + 61° = 180° [Linear pair]
⇒ x = 180° – 61° = 119°
Thus, the required angle is 119°.
Question 7.
The angle The angles x and 90° – x are
(a) supplementary
(b) complementary
(c) vertically opposite
(d) making a linear pair
Solution:
(b) Since, x + 90° = x – 90°
∴ These angles are complementary.
Question 8.
The angles x – 10° and 190° – x are
(a) interior angles on the same side of the transversal
(b) making a linear pair
(c) complementary
(d) supplementary
Solution:
(d) Since, x – 10° + 190°- x = 180°
∴These angles are supplementary.
Question 9.
In the given figure, the value of x is
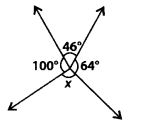
(a) 110°
(b) 46°
(c) 64°
(d) 150°
Solution:
(d) Since, sum of the angles about a point is 360°
∴ x + 64° + 46° +100° – 360°
⇒ x + 210° = 360°
⇒ x = 360°- 210°
⇒ x = 150°
Question 10.
In the given figure, if AB || CD, ∠APQ = 50° and ∠PRD = 130, then ∠QPR is
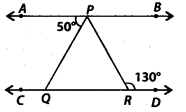
(a) 130°
(b) 50°
(c) 80
(d) 30°
Solution:
(c) Since, AB || CD and PR is a transversal
∴ ∠APR = ∠PRD [Alternate interior angles]
⇒ ∠APR = 130°
⇒∠APQ + ∠QPR = 130°
⇒ 50° + ∠QPR – 130°
⇒ ∠QPR = 130° – 50° = 80°
Question 11.
In the given figure, lines and m intersect each other at a point. Which of the following is false?
(a) ∠a = b
(b) ∠d=∠c
(c) ∠a + ∠d = 180°
(d) ∠a = ∠d
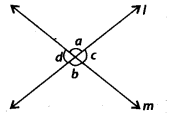
Solution:
(d) ∠a = ∠b [Vertically opposite angles]
∠d = ∠c [Vertically opposite angles]
∠a + ∠d = 180° [Linear Pair]
but ∠a ≠ ∠d
Question 12.
If angle P and angle Q are supplementary and the measure of angle P is 60°, then the measure of angle Q is
(a) 120°
(b) 60°
(c) 30°
(d) 20°
Solution:
(a) Since, ∠P + ∠Q = 180°
[∵ ∠P and ∠Q are supplementary angles]
⇒ 60° + 20 = 180°
⇒ ∠Q = 180° – 60° = 120°
Question 13.
In the given figure, POR is a line. The value of a is
(a) 40°
(b) 45°
(c) 55°
(d) 60°
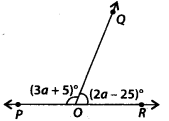
Solution:
(a) Since, POR is a straight line.
∴ ∠POQ + ∠QOR = 180° [Linear pair]
⇒ (3a + 5)° + (2a-25)° = 180°
⇒ 5a – 20° = 180°
⇒ 5a = 180° + 20° = 200°
\(\Rightarrow a=\frac{200^{\circ}}{5}=40^{\circ}\)
Question 14.
In the given figure, POQ is a line. If x= 30°, then ∠QOR is
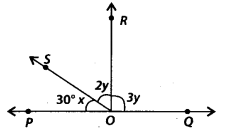
(a) 90°
(b) 30°
(c) 150°
(d) 60°
Solution:
(a) Since, POQ is a straight line.
∴ x + 2y + 3y = 180°
⇒ 30° + 5y = 180°
⇒ 5y = 180° – 30° = 150°
\(\Rightarrow y=\frac{150^{\circ}}{5}=30^{\circ}\)
∴ ∠QOR = 3y = 3× 30° = 90°
Question 15.
The measure of an angle which is four times its supplement is
(a) 36°
(b) 144°
(c) 16°
(d) 64°
Solution:
(b) Let the angle be x.
∴ Its supplement = 180° – x
According to question,
x = 4 (180° – x)
⇒ x = 720° – 4x
⇒ x + 4x = 720°
⇒ 720° = 5x
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{720^{\circ}}{5}=144^{\circ}\)
Question 16.
In the given figure, the value of y is
(a) 30°
(b) 15°
(c) 20°
(d) 22.5°
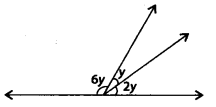
Solution:
(c) Since, angles are on a straight line.
∴ 6y + y + 2y = 180°
⇒ 9y = 180°
\(\Rightarrow \quad y=\frac{180^{\circ}}{9}=20^{\circ}\)
Question 17.
In the given figure, PA || BC || DT and AB || DC. Then, the values of a and bare respectively.
(a) 60°, 120°
(b) 50°,130°
(c) 70°, 110°
(d) 80°,100
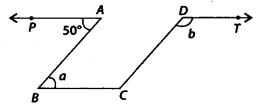
Solution:
(b) Since, PA || BC and AB is a transversal.
∴∠PAB = ∠ABC [Alternate interior angles]
⇒ 50° = a
Now, AB || DC and BC is a transversal.
∴ ∠ABC + ∠BCD = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ 50° + ∠BCD = 180°
⇒ ∠BCD = 180°- 50° = 130°
Also, BC || DT and DC is a transversal.
∴ ∠BCD = ∠CDT [Alternate interior angles]
⇒ 130° = b
Thus, a = 50° and b = 130°
Question 18.
The difference of two complementary angles is 30°. Then, the angles are
(a) 60°, 30°
(b) 70°, 40°
(c) 20°, 50°
(d) 105°, 75°
Solution:
(a) Let the angles be x and y.
∴ x + y = 90° ———(i) [Angles are complementary]
and x – y = 30° ——— (ii) [Given]
Adding (i) and (ii), we get
2x = 120°
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{120^{\circ}}{2}=60^{\circ}\)
Putting the value of x in (i), we get
60° + y = 90°
⇒ y = 90° – 60° = 30°
Thus, the required angles are 60° and 30°.
Question 19.
In the given figure, PO || SR and SP | RQ. Then, angles a and bare respectively
(a) 20°, 50°
(b) 50°, 20°
(c) 30°, 50°
(d) 45°, 35°
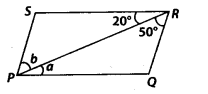
Solution:
(a) Since, PQ || SR and RP is a transversal
∴ a = 20° [Alternate interior angles]
Now, SP || RQ and PR is a transversal.
∴ b = 50° [Alternate interior angles]
Question 20.
In the given figure, a and bare
(a) alternate exterior angles
(b) corresponding angles
(c) alternate interior angles
(d) vertically opposite angles
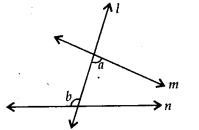
Solution:
(c) m and n are two straight lines and I is a transversal intersecting both lines m and n.
a and b are on the opposite side of transversal l.
∴ A and bare alternate interior angles.
Question 21.
If two supplementary angles are in the ratio 1 : 2, then the bigger angle is
(a) 120°
(b) 125°
(c) 110°
(d) 90°
Solution:
(a) Let the two angles be x and 2x.
Since, angles are supplementary
∴ x + 2x = 180°
⇒ 3x = 180°
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{180^{\circ}}{3}=60^{\circ}\)
∴ The bigger angle is 2x = 2 × 60° = 120°.
Question 22.
In the given figure, ∠ROS is a right angle and ∠POR and ∠QOS are in the ratio 1 : 5. Then, ∠QOS measures
(a) 150°
(b) 75°
(c) 45°
(d) 60°
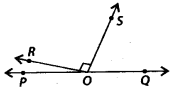
Solution:
(b) Since, POQ is a straight line
∴ ∠POR + ∠ROS + ∠QOS = 180°
⇒ ∠POR + ∠QOS = 180° – 90° = 90° ——- (i)
Given that. \(\frac{\angle P O R}{\angle Q O S}=\frac{1}{5}\)
⇒ 5 ∠POR = ∠QOS ——– (ii)
From (i) and (ii), we get
∠POR + 5 ∠POR = 90°
⇒ 6 ∠POR = 90°
\(\Rightarrow \angle P O R=\frac{90^{\circ}}{6}=15^{\circ}\)
∴ ∠QOS = 5 ∠POR = 5 × 15° = 75°
Question 23.
Statements a and bare as given below:
a: If two lines intersect, then the vertically opposite angles are equal.
b: If a transversal intersects, two other lines, then the sum of two interior angles on the same side of the transversal is 180°. Then
(a) Botha and bare true
(b) a is true and b is false
(c) a is false and b is true
(d) both a and b are false
Solution:
(b) Statement a is true but statement b is false since, if a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then the sum of two interior angles on the same side of the transversal is 180°
Question 24.
For given figure, statements p and q are given below:
p: a and bare forming a linear pair.
q: a and b are forming a pair of adjacent angles.
Then,
(a) both p and q are true
(b) p is true and q is false
(c) p is false and q is true
(d) both p and q are false
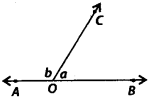
Solution:
(a) Both statements p and q are true.
Since ∠AOC and ∠BOC have a common vertex O, a common arm OC and also, their non-common arms, OA and OB, are opposite rays.
Question 25.
In the given figure, ∠AOC and ∠BOC form a pair of
(a) vertically opposite angles
(b) complementary angles
(c) alternate interior angles
(d) supplementary angles
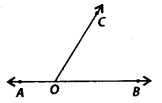
Solution:
(d) ∠AOC and ∠BOC form a pair of supplementary angles.
Question 26.
In the given figure, the value of a is
(a) 20°
(b) 15°
(c) 5°
(d) 10°
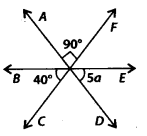
Solution:
(d) We have,
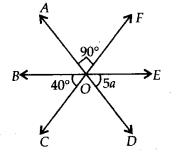
∠AOF=∠COD [Vertically opposite angles]
∴ ∠COD = 90°
Now, 40° + 90° + 5a = 180° [Angles on a straight line BOE]
⇒ 5a + 130° = 180°
⇒ 5a = 180° – 130° = 50°
\(\Rightarrow a=\frac{50^{\circ}}{5}=10^{\circ}\)
Question 27.
In the given figure, if QP || SR, the value of a is
(a) 40°
(b) 30°
(c) 90°
(d) 80°
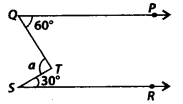
Solution:
(c) Draw a line L.M passing through T such that LM || QP || SR.
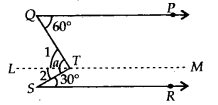
Now, LM || QP and QT is a transversal.
∴ ∠PQT = ∠LTQ [Alternate interior angles]
⇒ 60° – ∠L ——— (i)
Also, LM || SR and TS is a transversal.
∴ ∠LTS = ∠TSR [Alternate interior angles]
⇒ ∠2 = 30° ———– (ii)
From (i) and (ii), we get
a = ∠1 + ∠2 = 60° + 30° = 90°
Question 28.
In which of the following figures, a and bare forming a pair of adjacent angles?
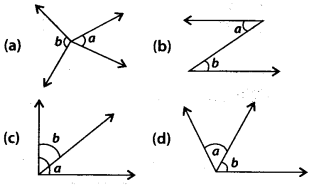
Solution:
(d) In figure (d), a and bare adjacent angles since, they have a common vertex, common arm and also, their non-common arms are on either side of common arm.
Question 29.
In a pair of adjacent angles,
(i) vertex is always common,
(ii) one arm is always common, and
(iii) uncommon arms are always opposite rays. Then
(a) All (i), (ii) and (iii) are true
(b) (iii) is false
(c) (i) is false but (ii) and (iii) are true
(d) (ii) is false
Solution:
(b) In a pair of adjacent angles, vertex is always common, one arm is always common and their non-common arms are on either side of the common arm.
Question 30.
In the given figure, lines PQ and ST intersect at O. If ∠POR = 90° and x : y = 3 : 2, then z is equal to
(a) 126°
(b) 144°
(c) 136°
(d) 154°
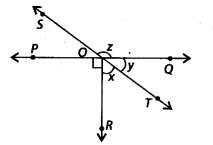
Solution:
(b) PQ is a straight line.
∴ ∠POR + ∠ROT + ∠TOQ = 180°
⇒ 90° + x + y = 180°
⇒ x + y = 180° – 90° = 90°
⇒ x+y – 90° ——- (i)
Given that \(\frac{x}{y}=\frac{3}{2}\)
Let x = 3k and y – 2k
From (i),
3k + 2k = 90° ⇒ 5k = 90°
\(\Rightarrow \quad k=\frac{90^{\circ}}{5}=18^{\circ}\)
∴ y = 2 × 18° = 36°
Now, SOT is a straight line
z + y = 180° [Linear pair]
⇒ z + 36° = 180° ⇒ z = 180° – 36° = 144°
Question 31.
In the given figure, POQ is a line, then a is equal to
(a) 35°
(b) 100°
(c) 80°
(d) 135°
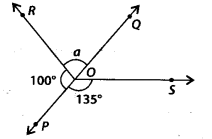
Solution:
(e) Since, POQ is a straight line.
∴ ∠POR + ∠ROQ = 180° [Linear pair]
⇒ 100° + a = 180°
⇒ a = 180° – 100° = 80°
Question 32.
Vertically opposite angles are always
(a) supplementary
(b) complementary
(c) adjacent
(d) equal
Solution:
(d) Vertically opposite angles are always equal.
Question 33.
In the given figure, a = 40°. The value of bis
(a) 20°
(b) 24°
(c) 36°
(d) 120°
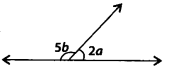
Solution:
(a) 5b + 2a = 180° [Linear pair]
⇒ 5b + 2 × 40° = 180°
⇒ 5b – 180° – 80° = 100°
\(\Rightarrow b=\frac{100^{\circ}}{5}=20^{\circ}\)
Question 34.
If an angle is 60° less than two times of its supplement, then the greater angle is
(a) 100°
(b) 80°
(c) 60°
(d) 120°
Solution:
(a) Let an angle be x.
∴ Its supplement = 180° – x
According to question,
x = 2(180° – x) – 60°
⇒ x = 360° – 2x – 60°
⇒ x + 2x = 300°
⇒ 3x = 300°
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{300^{\circ}}{3}=100^{\circ}\)
and its supplement = 180° – x= 180°- 100 = 80°
Thus, the greater angle is 100°.
Question 35.
In the given figure, PO || RS. If ∠1 = (2a + b)° and ∠6 (3a – b)°, then the measure of ∠2 in terms of b is
(a) (2 + b)°
(b) (3 – 6)°
(c) (108 – b)°
(d) (180 – b)°
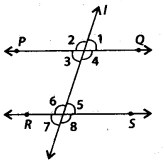
Solution:
(c) Since, PQ || RS and line 1 is a transversal.
∴ ∠2 = ∠6= (34 – b)° ——– (i)[Corresponding angles]
∠1 +∠2 = 180° [Angles on a straight line PQ]
⇒ ∠2 = 180° – (2a+ b)° ——– (ii) [∵ ∠1 = (2a + b)° (given)]
From (i) and (ii), we have
⇒ (3a – b)° = 180° – (2a + b)°
⇒ 3a – b = 180 – 2a – b
⇒ 3a – b + 2a + b = 180 ⇒ 5a = 180
\(\Rightarrow \quad a=\frac{180}{5}=36\)
∴ a = 36
Now, ∠2-(3a – b)° [From (i)]
⇒ ∠2 = (3 × 36 – b)° = (108 – b)°
Question 36.
In the given figure, PQ||RS and a : b = 3 : 2. Then, f is equal to
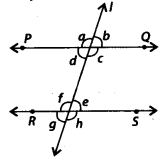
(a) 36°
(b) 108°
(c) 72°
(d) 144°
Solution:
(b) Given that a : b = 3 : 2
∴ Let a = 3x and b – 2x
Now, a + b = 180° [Angles on a straight line PQ]
⇒ 3x + 2x = 180°
⇒ 5x = 180°
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{180^{\circ}}{5}=36^{\circ}\)
∴ a = 3x = 3 × 36° = 108°
Also, PQ || RS and line I is a transversal.
∴ a = f [Corresponding angles]
⇒ f = 108°
Question 37.
In the given figure, line l intersects two parallel lines PQ and RS. Then, which one of the following is not true?
(a) ∠1 = ∠3
(b) ∠2 = ∠4
(c) ∠6 = ∠7
(d) ∠4 = ∠8
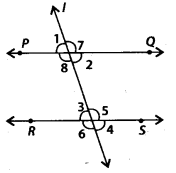
(d) Since PQ I RS and line 1 is a transversal.
∴ ∠1 = ∠3 [Corresponding angles]
∠2 = ∠4 [Corresponding angles]
∠6 = ∠7 [Alternate exterior angles]
but ∠4 ≠ ∠8
Question 38.
In the given figure, line l intersects two parallel lines PQ and RS. Then, which one of the following is not true?
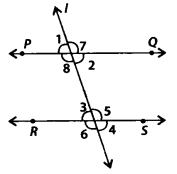
(a) ∠1 + ∠5 = 180°
(b) ∠2 + ∠5 =180°
(c) ∠3 + ∠8 = 180°
(d) ∠2 + ∠3 = 180°
Solution:
(d) Since, PQ || RS, line l is a transversal.
∴ ∠2 + ∠5 = 180° —— (i) [Co-interior angles]
∠3 + ∠8 = 180° ——– (ii) [Co-interior angles]
∠1 = ∠2 ——– (iii) [Verticallyopposite angles]
∴ ∠1 + ∠5 = 180° [By(i)and(iii)]
∠2 = ∠3 [Alternate interior angles]
but ∠2 + ∠3 = 180°
Question 39.
In the given figure, line I intersects two parallel lines PQ and RS. Then, which of the following is true?
(a) ∠1 = ∠5
(b) ∠4 = ∠8
(c) ∠5 = ∠8
(d) ∠3 = ∠7
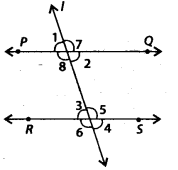
Solution:
(c) PQ || RS, line l is a transversal.
∴ ∠5 = ∠8 [Alternate interior angles]
Question 40.
In the given figure, PQ || ST. Then, the value of x + y is
(a) 125°
(b) 135°
(c) 145°
(d) 120°
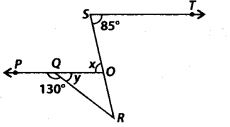
Solution:
(b) Since, PQ || ST and SO is a transversal.
∴ x = 85° [Altemate interior angles]
Now, PO is a straight line.
∴ ∠PQR + ∠RQO = 180° [Linear pair]
⇒ 130° + y = 180°
⇒ y = 180° – 30° = 50°
∴ x + y = 85° + 50° = 135°
Question 41.
In the given figure, if PQ || RS and QR || TS, then the value of a is
(a) 95°
(b) 90°
(c) 85°
(d) 75°
Solution:
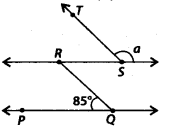
(a) Since, PQ || RS and RQ is a transversal
∴ ∠PQR – ∠QRS = 85° ———– (i) [Alternate interior angles]
Also, RQ || TS and RS is a transversal.
∴ ∠QRS – ∠TSR = 85° ———- (ii) [Using (i)] [Alternate interior angles]
Now, RS is a straight line.
∴ ∠RST + a = 180° [Linear pair]
⇒ 85° + a = 180° [Using (ii)]
⇒ a = 180° – 85° = 95°
Directions: In questions 42 to 56, fill in the blanks to make the statements true.
Question 42.
If the sum of measures of two angles is 90%, then the angles are _________
Solution:
Complementary
Question 43.
If the sum of measures of two angles is 180° then they are _________
Solution:
Supplementary
Question 44.
A transversal intersects two or more than two lines at _________ points.
Solution:
Distinct
Directions: If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then answer (Q. 45 to 48).
Question 45.
sum of interior angles on the same side of a transversal is _________
Solution:
180°
Question 46.
alternate interior angles have one common _________
Solution:
Arm
Question 47.
corresponding angles are on the _________ side of the transversal.
Solution:
Same
Question 48.
alternate Interior angles are on the _________ side of the transversal.
Solution:
Opposite
Question 49.
Two lines in a plane which do not meet at a point anywhere are called _________ lines.
Solution:
Parallel
Question 50.
Two angles forming a _________ pair are supplementary.
Solution:
Linear
Question 51.
The supplement of an acute is always _________ angle.
Solution:
Obtuse
Question 52.
The supplement of the right angle is always _________ angle.
Solution:
Right
Question 53.
The supplement of an obtuse angle is always _________ angle.
Solution:
Acute
Question 54.
In a pair of complementary angles, each angle cannot be more than _________
Solution:
90°
Question 55.
An angle is 45°. Its complementary angle will be _________
Solution:
45° : Given, angle = 45°
∴ Its complement = 90°- 45° = 45°
Question 56.
An angle which is half of its supplement is of ∴
Solution:
60°: Let the angle be x.
∴ Its supplement = 180° – x
According to question,
\(x=\frac{180^{\circ}-x}{2}\)
⇒2x = 180° – x
⇒ 2x + x = 180°
⇒ 3x = 180°
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{180^{\circ}}{3}=60^{\circ}\)
Thus, the angle which is half of its supplement is of 60°
Directions: In questions 57 to 71, state whether the statements are True or False.
Question 57.
Two right angles are complementary to each other.
Solution:
False
As two right angles are supplementary to each other.
Question 58.
One obtuse angle and one acute angle can make a pair of complementary angles.
Solution:
False
As two acute angles can make a pair of complementary angles.
Question 59.
Two supplementary angles are always obtuse angles.
Solution:
False
Question 60.
As one acute angle and one obtuse angle can make two supplementary angles. Two right angles are always supplementary to each other.
Solution:
True
Since, 90° + 90° = 180°, a supplementary angle.
Question 61.
One obtuse angle and one acute angle can make a pair of supplementary angles.
Solution:
True
Question 62.
Both angles of a pair of supplementary angles can never be acute angles.
Solution:
True
Question 63.
Two supplementary angles always form a linear pair.
Solution:
True
Question 64.
Two angles making a linear pair are always supplementary.
Solution:
True
Question 65.
Two angles making a linear pair are always adjacent angles.
Solution:
True
Question 66.
Vertically opposite angles form a linear pair.
Solution:
False
As vertically opposite angles are always equal but do not form a linear pair.
Question 67.
Interior angles on the same side of a transversal with two distinct parallel lines are complementary angles.
Solution:
False
As interior angles on the same side of a transversal with two distinct parallel lines are supplementary angles.
Question 68.
Vertically opposite angles are either both acute angles or both obtuse angles.
Solution:
True
Question 69.
A linear pair may have two acute angles.
Solution:
False
As a linear pair has one acute angle and one obtuse angle
Question 70.
An angle is more than 45°. Its complementary angle must be less than 45°.
Solution:
True
Let A and B are two angles making a complementary angle pair and A is greater than 45°
A + B = 90°
⇒ B = 90° – A
Therefore, B will be less than 45°.
Question 71.
Two adjacent angles always form a linear pair.
Solution:
False
As if both adjacent angles are acute angles, then they do not form a linear pair.
Question 72.
Write down each pair of adjacent angles shown in the following figures:
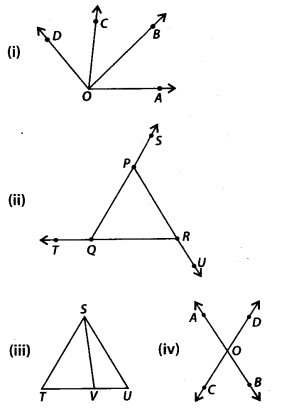
Solution:
(i) ∠AOB and ∠BOC; ∠AOC and ∠COD; ∠AOB and ∠BOD; and ∠BOC and ∠COD are adjacent angles.
(ii) ∠PQT and ∠PQR; ∠ORU and ∠QRP; ∠RPS and ∠RPQ are adjacent angles.
(iii) ∠TSV and ∠USV; ∠SVT and ∠SVU are adjacent angles.
(iv) ∠AOC and ∠AOD; ∠BOC and ∠BOD; ∠AOC and ∠BOC, ∠AOD and ∠BOD are adjacent angles.
Question 73.
In each of the following figures, write, if any,
(i) each pair of vertically opposite angles, and
(ii) each linear pair.
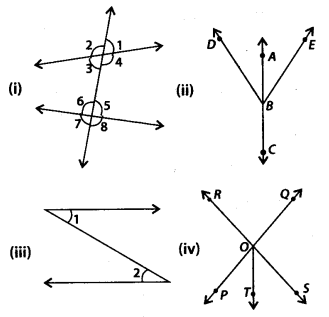
Solution:
(i) ∠1 and ∠3; ∠2 and ∠4; ∠5 and ∠7; ∠6 and ∠8 are four pairs of vertically opposite angles.
∠1 and ∠2; ∠1 and ∠4; ∠2 and ∠3; ∠3 and ∠4; ∠5 and ∠6; ∠5 and ∠8; ∠6 and ∠7; ∠7 and ∠8 are linear pairs.
(ii) There is no pair of vertically opposite angles.
∠ABD and ∠DBC; ∠ABE and ∠CBE are linear pairs.
(iii) There is no pair of vertically opposite angles and no angles are in the form of linear pair.
(iv) ∠POR and ∠QOS; ∠ROQ and ∠POS are two pairs of vertically opposite angles.
∠POR and ∠ROQ; ∠ROQ and ∠OOS; ∠QOS and ∠SOP; ∠SOP and ∠POR; ∠ROT and ∠TOS; ∠OOT and ∠POT are linear pairs.
Question 74.
Name the pairs of supplementary angles in the following figures:
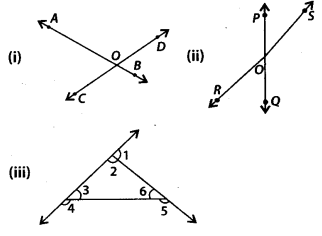
Solution:
(i) ∠AOD and ∠DOB; ∠DOB and ∠BOC, ∠BOC and ∠AOC; ∠AOC and ∠AOD are four pairs of supplementary angles.
(ii) ∠POS and ∠SOQ; ∠POR and ∠ROQ are two pairs of supplementary angles.
(iii) ∠1 and ∠2, ∠3 and ∠4, ∠5 and ∠6 are three pairs of supplementary angles.
Question 75.
In the given figure, PO || RS, TR || QU and ∠PTR = 42°. Find ∠QUR.
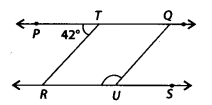
Solution:
Since, PQ || RS and TR is a transversal.
∴ ∠PTR – ∠TRU= 42° ——— (i) [Alternate interior angles]
Also, TR || QU and RS is a transversal.
∴ ∠TRU + ∠QUR = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ 42° + ∠QUR = 180° [Using (i)]
⇒ ∠QUR = 180° – 42° = 138°
Question 76.
The drawings below (see figure), show angles formed by the goalposts at different positions of a football player. The greater the angle, the better chance the player has of scoring a goal. For example, the player has a better chance of scoring a goal from Position A than from Position B.
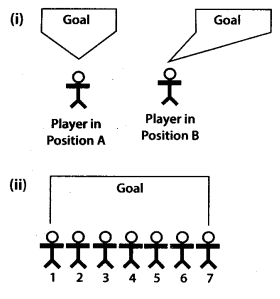
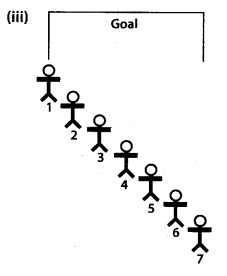
In Parts (a) and (b) given below, it may help to trace the diagrams and draw and measure angles.
(a) Seven football players are practicing their kicks. They are lined up in a straight line in front of the goalpost [See fig.(i)). Which player has the best the greatest) kicking angle?
(b) Now the players are lined up as shown in Fig. (ii). Which player has the best kicking angle?
(c) Estimate atleast two situations such that the angles formed by different positions of two players are complement to each other.
Solution:
(a) 4th player has the greatest kicking angle. So, this player has the best kicking angle.
(b) 4th player has the greatest kicking angle. So, this player has the best kicking angle.
(c) (45°, 45°) and (60°, 30°) are the two pairs of angles formed by different positions of two players such that they are complement to each other.
(∵ 45° + 45° = 90° and 60° + 30°= 90°).
Question 77.
The sum of two vertically opposite angles is 166°. Find each of the angles.
Solution:
Since, vertically opposite angles are equal.
Let each angle be x.
According to question,
x + x = 166°
⇒ 2x = 166°
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{166^{\circ}}{2}=83^{\circ}\)
Thus, both the angles are of 83°.
Question 78.
In the given figure, l || m || n. ∠OPS = 35° and ∠QRT = 55°. Find ∠PQR.
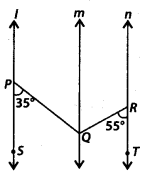
Solution:
We have,
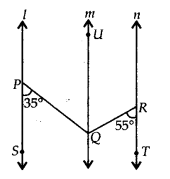
l || m and PQ is a transversal
∴ ∠SPQ = ∠PQU [Alternate interior angles]
⇒ ∠PQU = 35° ———- (i)
Also, m || n and QR is a transversal.
∴ ∠QRT = ∠RQU [Alternate interior angles]
⇒ ∠RQU = 35° ——- (ii)
Now, ∠PQR = ∠PQU + ∠UQR
= 35° + 55° [Using (6) & (ii)]
= 90°
Question 79.
In the given figure, P, Q and R are collinear points and TQ ⊥ PR,
Name;
(a) pair of complementary angles
(b) two pairs of supplementary angles.
(c) four pairs of adjacent angles.
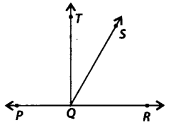
Solution:
(a) ∠TOS and ∠SQR is a pair of complementary angles.
(b) ∠PQT and ∠TOR; ∠SQR and ∠PQS are two pairs of supplementary angles.
(c) ∠PQT and ∠TQS; ∠TQS and SQR; ∠PQT and ∠TOR; ∠PQS and ∠SQR are four pairs of adjacent angles.
Question 80.
In the given figure, OR ⊥ OP.
(i) Name all the pairs of adjacent angles.
(ii) Name all the pairs of complementary angles.
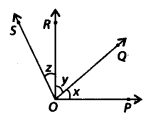
Solution:
(i) ∠x and ∠y; ∠x and ∠y + ∠z; ∠y and ∠z; ∠z and ∠x + ∠y are four pairs of adjacent angles.
(ii) ∠x and ∠y are complementary angles. If ∠x = ∠y = ∠z, then ∠x and ∠y; ∠y and ∠z; ∠z and ∠x are three pairs of complementary angles.
Question 81.
If two angles have a common vertex and their arms form opposite rays (see figure). Then,
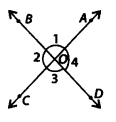
(a) how many angles are formed?
(b) how many types of angles are formed?
(c) write all the pairs of vertically opposite angles.
Solution:
(a) 13 angles are formed.
(b) 4 types of angles are formed i.e., vertically opposite angles, adjacent angles, supplementary angles and linear pairs.
(c) ∠1 and ∠3; ∠2 and ∠4 are the two pairs of vertically opposite angles.
Question 82.
In (given figures) are the following pairs of angles adjacent? Justify your answer.
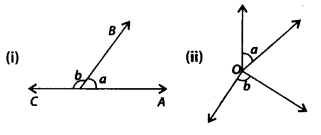
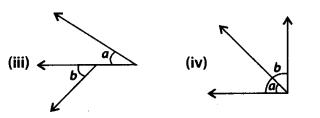
Solution:
(i) Yes, and b are the adjacent angles as they have a common vertex, one common arm and other non-common arms on the opposite side of the common arm.
(ii) No, a and b are not adjacent angles as they don’t have common arm.
(iii) No, a and b are not adjacent angles as they don’t have common vertex.
(iv) No, a and b are not adjacent angles as the arms which are not common are on the same side of common arm.
Question 83.
In the given figure, write all the pairs of supplementary angles.
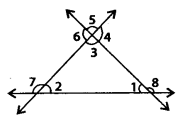
Solution:
∠1 and ∠8; ∠2 and ∠7; ∠3 and ∠4; ∠4 and ∠5; ∠5 and ∠6; ∠3 and ∠6 are six pairs of supplementary angles.
Question 84.
What is the type of other angle of a linear pair if
(a) one of its angles is acute?
(b) one of its angles is obtuse?
(c) one of its angles is right?
Solution:
(a) If one of the angles is acute, then other angle of a linear pair is obtuse.
(b) If one of the angles is obtuse, then other angle of a linear pair is acute.
(c) If one of the angles is right, then other angle of a linear pair is also right.
Question 85.
Can two acute angles form a pair of supplementary angles? Give reason in support of your answer.
Solution:
No, two acute angles cannot form a pair of supplementary angles. As if both angles are 89° and 89°, even then they cannot make the sum 180°.
Question 86.
Two lines AB and CD intersect at O (see figure). Write all the pairs of adjacent angles by taking angles 1, 2, 3, and 4 only.
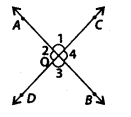
Solution:
∠1 and ∠2; ∠1 and ∠4; ∠2 and ∠3; ∠3 and ∠4 are four pairs of adjacent angles.
Question 87.
If the complement of an angle is 62°, then find its supplement.
Solution:
Let the angle be x.
∴ Its complement = 90° – x
According to question,
90° – x = 62°
⇒ 90° – 62° = x
⇒ x = 28°
∴ Supplement of x = 180° – 28° = 152°
Question 88.
A road crosses a railway line at an angle of 30° as shown in figure. Find the values of a, b and c.
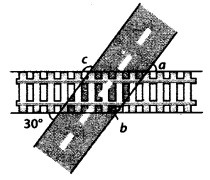
Solution:
We have,
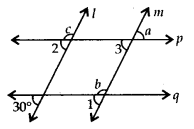
Since, l || m and q is a transversal
∴ ∠1 = 30° ——– (i) [Corresponding angles]
Also, m is a straight line.
∴ ∠b + ∠1 = 180° [Linear pair]
⇒ ∠b = 180° – 30° = 150° [Using (1)]
Now, p || q and m is a transversal.
∴ ∠1 = ∠3 = 30° ——— (ii) [Corresponding angles]
∠a = ∠3 [Vertically opposite angles]
∴ ∠a = 30° [Using (ii)]
Also, p || q and l is a transversal.
∴ ∠2 = 30° [Corresponding angles]
Now, l is a straight line.
∴ ∠c + ∠2 = 180° [Linear pair]
⇒ ∠c + 30° = 180° [Using (iii)]
⇒ ∠c = 180° – 30° = 150°
Hence, ∠a = 30°, ∠b = 150°, ∠c = 150°
Question 89.
The legs of a stool make an angle of 35″ with the floor as shown in figure. Find the angles x and y.
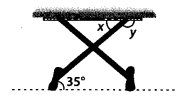
Solution:
We have,
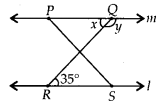
l || m and QR is a transversal.
∴ ∠x = 35° [Alternate interior angles]
and ∠y + 35° = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ ∠y = 180° – 35° = 145°
Hence, ∠x = 35° and ∠y = 145°.
Question 90.
Iron rods a, b, c, d,e and fare making a design in a bridge as shown in figure, in which a || b. c || d, e || f. Find the marked angles between
(i) b and c
(ii) d and e
(iii) d and f
(iv) c and f
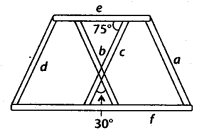
Solution:
(i) Let the angle between b and c is ∠1. and ∠1 = 30°[Vertically opposite angles]
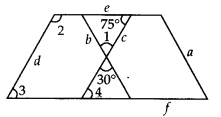
(ii) Let the angle between d and e is ∠2.
Now, c || d and e is a transversal.
∴ ∠2 + 75° = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ ∠2 = 180° – 75° = 105°
(iii) Let the angle between d and fis ∠3.
Now, e || f and d is a transversal.
∴ ∠2 + 3 = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ ∠3 – 180° – 105° = 75° [From (ii) part]
(iv) Let the angle between c and fig ∠4.
Now, e || f and c is a transversal.
∴ ∠4 = 75° [Alternate interior angles]
Question 91.
Amisha makes a star with the help of line segments a, b, d, e and f, in which a || d, b || e and c || f. Chhaya marks an angle as 120° as shown in figure, and asks Amisha to find the ∠x, ∠y and ∠z. Help Amisha in finding the angles.
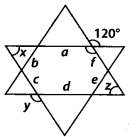
Solution:
We have
∠1 = 120° ———- (i) [Vertically opposite angles]
c || f and a is transversal.
∴ ∠1 + ∠x = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ 120° + ∠x – 180° [Using (1)]
⇒ ∠x = 180° – 120° = 60°
Now, a || d and c is a transversal.
⇒ ∠x + ∠2 = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ 60° + ∠2 = 180° [Using (ii)]
⇒ ∠2 = 180° -60° = 120°
⇒ ∠2 = ∠y = 120° [Vertically opposite angles]
Also, a || d and f is a transversal.
∴ ∠1 + ∠z = 180° (Co-interior angles)
⇒ 120° + ∠z= 180° [Using (i)]
⇒ ∠z = 180° – 120° = 60°
Thus, ∠x = 60°, ∠y = 120°and ∠z = 60°
Question 92.
In the given figure, AB || CD, AF || ED, ∠AFC = 68°and ∠FED = 42°. Find ∠EFD.
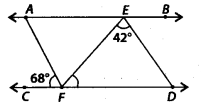
Solution:
We have,
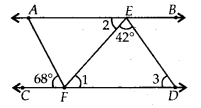
Since, AF || ED and FD is a transversal.
∴ ∠3=68° ——– (i) [Corresponding angles]
Now, AB || CD and ED is a transversal.
∴ (∠2+42°) + ∠3 = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ ∠2 = 180° – 42° – 68° [Using (i)]
⇒ ∠2 = 70° ——— (ii)
Also, AB || CD and EF is a transversal.
∴ ∠1 = ∠2 [Alternate interior angles]
⇒ ∠1 = 70° [Using (ii)]
Thus, ∠EFD = 70°
Question 93.
In figure, OB is perpendicular to OA and ∠BOC = 49°. Find ∠AOD.
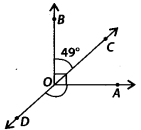
Solution:
Given that ∠AOB = 90° [∵ OB ⊥ OA]
⇒ ∠BOC + ∠COA = 90°
⇒ ∠COA = 90° – 49° [∵ ∠BOC = 49° (given)]
⇒ ∠COA – 41° ——— (i)
Now, CD is a straight line.
∴ ∠AOD + ∠AOC = 180° [Linear pair]
⇒ ∠AOD = 180°- 41° [Using (1)]
∴ ∠AOD = 139°
Question 94.
Three lines AB, CD and EF intersect each other at O. If ∠AOE = 30° and ∠DOB = 40° (see figure), find ∠COF.
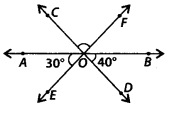
Solution:
∵ AB is a straight line.
∴ ∠AOE + ∠EOD + ∠DOB = 180°
⇒ ∠EOD = 180° -30° – 40° = 110° ——— (i)
[ ∵∠AOE = 30° and ∠DOB =40° (given)]
Now, CD and EF intersect each other at O.
∴ ∠COF = ∠EOD = 110° [Using (i)] [Vertically opposite angles]
Thus, ∠COF = 110°
Question 95.
Measures (in degrees) of two complementary angles are two consecutive even integers. Find the angles.
Solution:
Let one angle be 2x and the other angle be 2x + 2.
We know that the sum of the measures of the complementary angles is 90°
According to question,
2x + 2x + 2 = 90°
⇒ 4x = 90° – 2 = 88°
\(\Rightarrow \quad x=\frac{88^{\circ}}{4}=22^{\circ}\)
∴ 2x = 2 × 22° = 44° and 2x + 2 = 44° +2 = 46°
Thus, one angle is 44° and other is 46°
Question 96.
If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, and the difference of two interior angles on the same side of a transversal is 20°, find the angles.
Solution:
Let one angle be x and other be y.
Since, a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then interior angles on the same side of a transversal are supplementary.
∴ x + y = 180° ———– (i)
and x – y = 20° ——— (ii) [Given]
Adding (i) and (ii), we get
2x = 180° + 20° = 200°
\(\Rightarrow \quad x=\frac{200^{\circ}}{2}=100^{\circ}\)
Putting value of x in (i), we get
100° + y = 180 ⇒ y = 180° – 100° = 80°
Thus, one angle is 100° and other is 80°.
Question 97.
Two angles are making a linear pair. If one of them is one-third of the other, find the angles.
Solution:
Let one angle be x.
Since, two angles form a linear pair.
∴ Other angle is 180° – x.
According to question,
\(x=\frac{1}{3}\left(180^{\circ}-x\right)\)
⇒ 3x = 180° – x ⇒ 3x + x = 180°
⇒ 4x = 180°
\(\Rightarrow \quad x=\frac{180^{\circ}}{4}=45^{\circ}\)
Thus, one angle is 45° and other is 180° – 45° = 135°
Question 98.
Measures (in degrees) of two supplementary angles are consecutive odd integers. Find the angles.
Solution:
Let one angle be 2x + 1, then the other angle is 2x + 3.
We know that the sum of the measures of the supplementary angles is 180°.
According to question,
2x + 1 + 2x + 3 = 180°
⇒ 4x + 4 = 180° ⇒ 4x = 180°- 4 = 176°
\(\Rightarrow \quad x=\frac{176^{\circ}}{4}=44^{\circ}\)
∴ 2x + 1 = 2 × 44° + 1 = 88° + 1 = 890
and 2x + 3 = 2 × 44° + 3 = 88° + 3 = 91°
Thus, one angle is 89° and other is 91°
Question 99.
In the given figure, AE || GF || BD, AB||CG|| DF and ∠CHE = 120°. Find ∠ABC and ∠CDE.
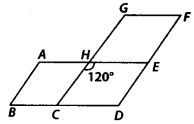
Solution:
Since, AE || BD and CH is a transversal.
∴∠CHE = ∠HCB – 120° ———- (i) [Alternate interior angles]
Now, CH || DF and CD is a transversal.
∴ ∠HCB =∠CDE [Corresponding angles]
⇒ ∠CDE-120° ——- (ii) [Using (1)]
Also, AB || DF and BD is a transversal.
∴ ∠ABC + ∠CDE = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ ∠ABC = 180° – 120° [Using (ii)]
= 60°
Thus, ∠ABC = 60° and ∠CDE = 120°
Question 100.
In the given figure, find the value of ∠BOC, if points A, O and B are collinear.
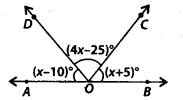
Solution:
Given points A, O and B are collinear.
∴ AOB is a straight line.
⇒ (x – 10)° +(4x – 25)° + (x + 5)° = 180° [Angles on a straight line]
⇒ (6x – 30) = 180 ⇒ 6x – 180 + 30 = 210
\(\Rightarrow \quad x=\frac{210}{6}=35\)
Now, ∠BOC = (x + 5)° = (35 + 5) = 40°
Thus, ∠BOC = 40°
Question 101.
In the given figure, if l || m, find the values of a and b.
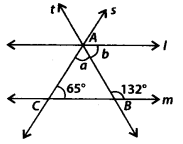
Solution:
Since, l || m and AB is a transversal.
∴ b + 132° = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ b = 180° – 132° = 48°
∴ b = 48° ——— (i)
Now, l || m and AC is a transversal.
∴ (a + b) + 65° = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ a = 180° – 65° = 48° [Using (i)]
⇒ a = 67°
Thus, a = 67° and b = 48°
Question 102.
In the given figure, 4m and a line t intersects these lines at P and Q, respectively. Find the sum 2a +b.
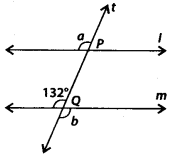
Solution:
Since, l || m and is a transversal.
∴ a = 132 [Corresponding angles]
and b = 132° [Vertically opposite angles]
Now, 2a + b = 2 × 132° + 132°
= 264° + 132° = 396°
Question 103.
In the given figure, QP || RS. Find the values of a and b.
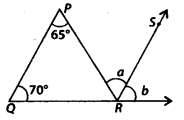
Solution:
Since, QP || RS and QR is a transversal.
∴ b = 70° [Corresponding angles]
Now, QP || RS and PR is a transversal.
∴ a = 65° [Alternate interior angles]
Hence, a = 65° and b = 70°.
Question 104.
In the given figure, PO || RT. Find the value of a + b.
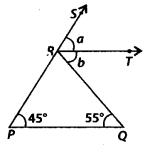
Solution:
Since, PQ || RT and PR is a transversal.
∴ a = 45° [Corresponding angles]
Now, PQ || RT and RQ is a transversal.
∴ b = 55° [Alternate interior angles]
Now, a + b = 45° + 55° = 100°
Question 105.
In the given figure, PQ, RS and UT are parallel lines.
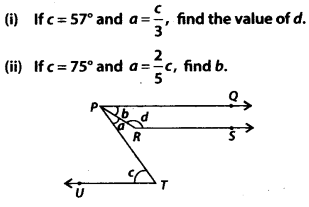
Solution:
(i) Since, PQ || UT and PT is a transversal.
∴ a + b = c [Alternate interior angles]
⇒ b = c – a
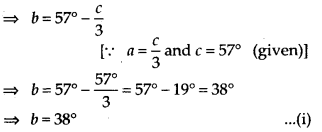
Now, PQ || RS and PR is a transversal.
∴ b + d = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ d = 180°- 38° = 142° [Using (i)]
Thus, d = 142°
(ii) PQ || UT and PT is a transversal.
∴ a + b = c [Alternate interior angles]
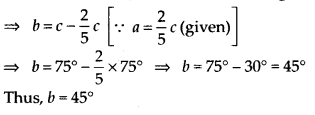
Question 106.
In the given figure, AB||CD. Find the reflex ∠EFG.
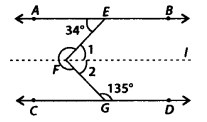
Solution:
Since, AB || l and EF is a transversal.
∴ ∠1 = 34° [Alternate interior angles]
Now, l is also parallel to CD and FG is a transversal. .
∴ ∠2 + 135° = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ ∠2 = 180° – 135° = 45°
Also, ∠EFG = ∠1 + ∠2 – 34° +45° = 79°
The reflex ∠EFG = 360° – 79° = 281°
Question 107.
In the given figure, two parallel lines l and m are cut by two transversals n and p. Find the values of x and y.
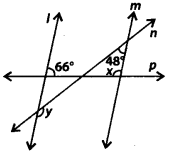
Solution:
Since, l || m and p is a transversal.
∴ x + 66° = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ x = 180° – 66° = 114°
Now, l || m and n is a transversal.
∴ y + 48° = 180° [Co-interior angles]
⇒ y = 180° – 48° = 132°
Thus, x = 114° and y = 132°
Question 108.
In the given figure, l, m and n are parallel lines, and the lines p and q are also parallel. Find the values of a, b and c.
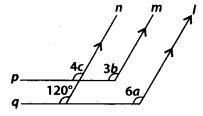
Solution:
l || n and q is a transversal.
∴ 6a = 120° [Corresponding angles]
\(\Rightarrow \quad a=\frac{120^{\circ}}{6}=20^{\circ}\)
Now, p || q and n is a transversal.
∴ 4c = 120° [Corresponding angles]
\(\Rightarrow c=\frac{120^{\circ}}{4}=30^{\circ}\) ———– (i)
Also, m || n and p is transversal.
∴ 4c = 3b [Corresponding angles]
⇒ 4 × 30° = 3b [using (i)]
\(\Rightarrow \quad b=\frac{120^{\circ}}{3}=40^{\circ}\)
Thus, a = 20°, b = 40° and c = 30°
Question 109.
In the given figure, state which pair of lines are parallel. Give reason.
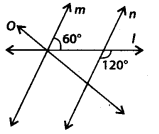
Solution:
We have,
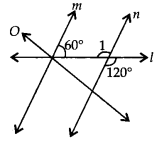
∠1 = 120° [Vertically opposite angles]
Now, 60° + ∠1 = 60° + 120° = 180° and these angles are interior angles on the same side of transversal l.
Thus, m || n as the sum of co-interior angles is 180°
Question 110.
In the given figure, examine whether the following pairs of lines are parallel or not:
(i) EF and GH
(ii) AB and CD
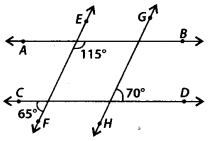
Solution:
We have,
(i)∠1 = 65° [Vertically opposite angles]
As ∠RSP and ∠QPD are corresponding angles and are not equal.
∴ EF and GH are not parallel lines.
(ii) EF is a straight line.
∴ ∠RSC + ∠CSF = 180° [Linear pair]
⇒ ∠RSC = 180° – 65° = 115°
As angles ∠QRS and ∠CSR are alternate interior angles and are equal.
∴ AB || CD.
Question 111.
In the given figure, find out which pair of lines are parallel:
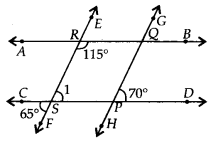
Solution:
We have,
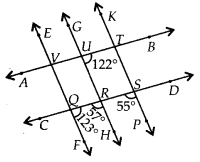
∠FOR + ∠QRH = 123° + 57° = 180°
These angles are on the same side of transversal CD.
∴ EF || GH
Now, EF || GH and AB is a transversal.
∴ ∠TUR = ∠UVQ = 122° [Corresponding angles]
As ∠UVQ and ∠ROF are corresponding angles and are not equal.
∴ AB and CD are not parallel lines.
Question 112.
In the given figure, show that
(i) AB || CD
(ii) EF || GH
Solution:
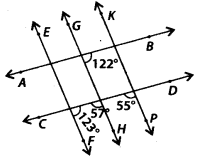
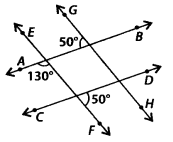
We have,
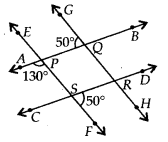
(i) ∠PSC = ∠RSF = 50° [Vertically opposite angles]
∠APS + ∠PSC = 130° + 50° = 180°
As ∠APS and ∠PSC are interior angles on the same side of transversal EF and are supplementary.
∴ AB || CD
(ii) ∠APS = ∠EPQ = 130° [Vertically opposite angles]
∠EPQ+ ∠GQP = 130° + 50° = 180°
As ∠EPQ and ∠GQP are interior angles on the same side of transversal AB and are supplementary
∴ EF || GH
Question 113.
In the given figure, two parallel lines l and m are cut by two transversals p and 4. Determine the values of x and y.
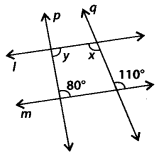
Solution:
Since, l || m and q is a transversal.
∴ x = 110° [Alternate interior angles]
Now, l || m and p is a transversal.
∴ y + 80° = 180° [Co-interior angles]
∴ y = 180° – 80° = 100°
Thus, x = 110° and y = 100°
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Lines and Angles will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Lines and Angles, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.