Maps Class 6 Extra Questions Social Science Geography Chapter 4
NCERT Extra Questions for Class 6 Social Science Geography Chapter 4 Maps
Maps Class 6 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What are the limitations of a globe?
Answer:
- Globe is of little help when we want to study only a part of the Earth, about our country, states; districts, towns and villages.
- Globe is not easy to handle.
Maps Class 6 Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is a map? Describe its major features.
Answer:
- Map is a representation of the earth’s surface or a part of it drawn on flat surfaces.
- One map contains as many facts as a big book.
- All the maps are put together to make on atlas of maps of various sizes and drawn on different scales.
- They provide more information than a globe.
Question 2.
Define Sketch.
Answer:
- A sketch is a drawing of an area or object mainly based on memory and not to the scale.
- Sometimes a rough drawing of an area is needed to know where a particular place is located with reference to other places.
- With the help of a rough sketch we may find the location of a place.
- Such a rough drawing is drawn without scale.
Question 3.
What is a Plan?
Answer:
- A plan is a drawing of a small area on a large scale.
- A large-scale map depicts much information.
- Sometimes we want to know the length and breadth of a room, which can’t be shown on a map. In such an event; we can refer drawings drawn on scale.
- It is known as a plan.
Question 4.
Describe various types of maps.
Answer:
Maps are of various types. They are:
- Physical Maps. They show natural features of the Earth like mountains, plateaus, plains, rivers, oceans etc.
Example: Physical map of the world. - Political Maps. Political maps show different countries and states of the world with their boundaries.
Example: Political map of India. - Thematic Maps. Maps showing specific information are called thematic maps. Example: Road maps, rainfall maps, forest distribution maps, industries maps etc.
Question 5.
Give historical background of maps.
Answer:
The science of map making is termed as cartography.
Ancient map makers did not know the shape of the Earth:
- Babylonians drew maps assuming that the Earth is flat.
- An Egyptian geographer, (cartographer) Ptolemy first represented the Earth as a sphere.
Maps were drawn on different materials:
- Eskimos used animal skin.
- Egyptians engraved maps on metal plates.
- Babylonians made maps of clay tablets.
Today maps are made on computers:
- These maps are very accurate.
- Improvement in technology has improved the quality of maps.
Question 6.
What are the components of maps?
Answer:
- Distance,
- Direction and
- Symbol.
Distance:
- Distance is measured with the help of a scale.
Direction.
- Direction is known by the arrow marked with ‘N’ on the map.
- It is also known by an instrument called compass.
Symbol:
- Universally accepted marks or icons to depict information on the maps are known as symbols.
Question 7.
Name the two types of maps based on scale.
Answer:
Small Scale Maps
When large areas are shown on a small map, it is called small scale map.
- These maps give very limited information.
- The map of India is a small scale map.
Large Scale Maps
- When small areas are shown on large map it is called Large scale map.
- These maps give detailed information.
- The map of Delhi, shown on large sheet of paper is a large scale map.
Question 8.
How are directions known?
Answer:
Directions are known by the following:
Maps contain an arrow marked with the letter ‘N’ on the upper right.
An Arrow with ‘N’ mark:
- This arrow shows the North direction.
- It is called north line. On the Earth one can find out directions e.g. north, east, west and south.
- There are four major directions.
- North, South, East, West. They are called cardinal points.
- Other four intermediate directions are North-East (NE), South-East (SE), South¬West (SW) and North-West (NW).
- One can locate any place more accurately with the help of these intermediate directions.
Compass. One can also know the direction with the help of compass
- It is an instrument used to find the main directions.
Maps Class 6 Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
How is distance measured? Define a scale.
Answer:
Maps reduce the entire world or its part to fit on a sheet of paper.
But this reduction is done very carefully so that distances between the places are kept true:
- Reduction of map is only possible when small distances on paper represents a large distance on the ground.
- To reduce a map, a scale is chosen.
Scale is the ratio between the actual distance on the ground and the distance shown on the map.
- The distance between school and home of student is 10 km. If he shows this 10 km distance by 2 cm on map, it means, 1 cm on the map will show 5 km on ground. Thus the scale will be 1 cm. = 5 km. In this way scale is very important in a map. If the scale is known it will be easy to calculate distance between any two places.
- Scales are used for measuring distance. For example to find out the distance between the post office and the clock tower one can measure the distance between these points on the map. (Then the same distance on the scale. Types of Maps on the Basic of Scale.)
Question 2.
What are symbols? Why do we need them?
Answer:
Symbols:
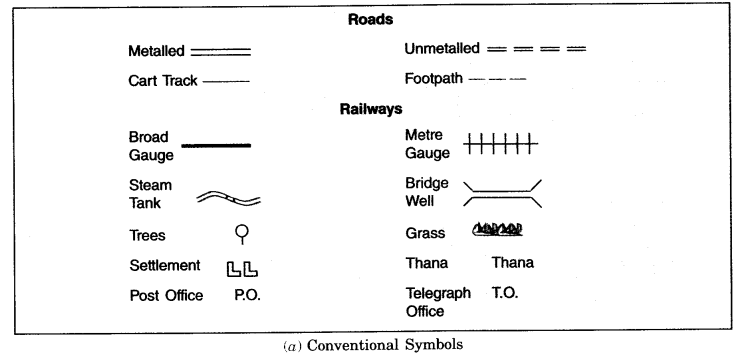
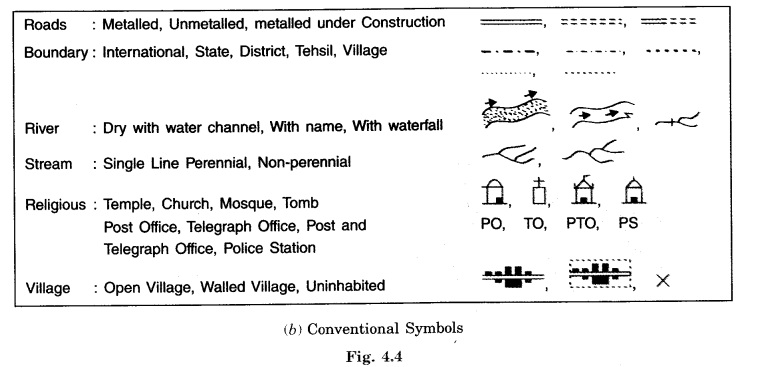
It is impossible to draw actual shape and size of different features like buildings, roads, trees, railway lines or a well on a map, so we use various symbols to show these features.
- Symbols give much information in a limited space.
- With the help of these symbols, we can draw maps and read them easily.
- Without knowing the language of a certain place, we can collect information from maps with the help of these symbols.
- Maps have a universal language – a language that can be read by all. An international agreement facilitates the use of these symbols.
- These symbols are called Conventional Symbols.
- Some of the conventional symbols are shown in the figure given below.
- Various colours in maps are also used for the same purpose.
Maps Class 6 Extra Questions Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
What is a map?
(a ) A globe
(b ) A drawing of the earth’s surface on a flat paper according to scale
(c) A projection
(d) None of these
Answer:
A drawing of the earth’s surface on a flat paper according to scale
Question 2.
What is physical map?
(a) Showing natural features of the earth
(b) Showing cities, towns and villages with boundaries
(c) Showing rainfall, distribution of forests etc.
(d) None of the above
Answer:
Showing natural features of the earth
Question 3.
Which map gives more information?
(a) Small scale map
(b) Large scale map
(c) Ordinary map
(d) None of these
Answer:
Large scale map
Question 4.
What does TV’ with arrow show?
(a) Direction of North
(b) Direction of East
(c) Direction of West
(d) Direction of South
Answer:
Direction of North
Question 5.
The blue colour is used for showing
(a) mountains
(b) plants and trees
(c) water
(d) none of these
Answer:
water
Question 6.
A scale is compulsory for
(a) a map
(b) a sketch
(c) a symbol
(d) all of these
Answer:
a map
Question 7.
For what purpose magnetic compass is used?
(a) For measuring distance
(b) For showing symbols
(c) For finding the directions
(d) For all of these
Answer:
For finding the directions
Question 8.
Plan is a drawing of
(a) small area on a large scale
(b ) large area on a small scale
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer:
small area on a large scale
Question 9.
Yellow colour is used for showing
(a) plateaus
(b) water bodies
(C) mountains
(d) plants
Answer:
plateaus