Informatics Practices Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Database is part of Informatics Practices Class 12 Important Questions. Here we have given Informatics Practices Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Database.
Informatics Practices Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Database
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Write two examples of DML commands to SQL. (All India 2014C)
Answer:
Two examples of DML commands are:
SELECT, INSERT
Question 2.
When using the LIKE clause, which wildcard symbol represents any sequence of none, one or more characters? (All India 2014c)
Answer:
The % wildcard symbol is used in LIKE clause to represent any sequence of none, one or more characters.
Question 3.
Write the UPDATE statement in MySQL to increase commission by 100.00 in the “Commission” column in the ‘EMP’ table. (All India 2014C)
Answer:
UPDATE Emp
SET Commission = Commission +100;
Question 4.
Rewrite the following SQL statement after correcting the error(s). Underline the corrections made. (All India 2014C)
INSERT IN STUDENT(RNO, MARKS) VALUEC5, 78.5);
Answer:
INSERT INTO STUDENT (RNO, MARKS) VALUES (5, 78.5);
Question 5.
What happens when auto-commit is set on? (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
When AUTOCOMMIT is set on then we do not need to start a transaction explicity using a BEGIN command but every statement is treated as an independent transaction and will COMMIT automatically immediate after its completion.
Question 6.
Table ‘CLUB’ has 4 rows and 3 columns. Table ‘MEMBER’ has 2 rows and 5 columns. What will be the cardinality of the Cartesian product of them? (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
The cardinality of the cartesian product of Table ‘CLUB’ and Table ‘MEMBER’ = 8.
Question 7.
Distinguish between ALTER TABLE and UPDATE commands of MySQL. (All India 2014)
Answer:
ALTER TABLE command is a DDL (Data Definition Language) statement which is used to modify the table structure. On the other hand UPDATE command is a DML (Data Manipulation Language) statement which is used to modify the data stored in a table.
Question 8.
Mention two categories in which MySQL commands are broadly classified. (All India 2014)
Answer:
Two categories of Mysql commands are:
- DDL (Data Definition Language)
- DML (Data Manipulation Language)
Question 9.
Give two characteristics of Primary Key. (All India 2014)
Answer:
Two characteristics of Primary Key are:
- All the values in the Primary Key field are unique.
- Does not allow NULL values.
Question 10.
Write two examples of DBMS software. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Two examples of DBMS Software are:
- MySQL
- Oracle
Question 11.
Write SQL command to create a SAVEPOINT called All (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Create Table CLASS (Rollno INTEGER, Name VARCHAR(20)); INSERT INTO CLASS(10, ‘CS’); SAVEPOINT Al;
Question 12.
Define a foreign key with reference to RDBMS. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Foreign Key It is primary key of another table. It’s used to join two tables. Name of the foreign key and the primary key may or may not be same but their data type has to be same.
Question 13.
Write the command to display the list of existing databases. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
The command to display list of existing databases are as follows:
Show databases;
Question 14.
Mr. William wants to remove all the rows from INVENTORY table to release the storage space, but he does not want to remove the structure of the table. What MySQL statement should be used? (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
The command to delete all rows from the Inventory table without deleting the structure of the table will be as follows:
DELETE FROM INVENTORY;
Question 15.
Write MySQL command to open an existing database. (All India 2012)
Answer:
The command to open an existing database is as follows:
USE database_name;
Question 16.
Give one difference between COMMIT and ROLLBACK commands used in MySQL. (HOTS; Delhi 2012; All India 2012)
Answer:
The COMMIT command is used to save the changes made during the execution of a transaction permanentely on the disk. After executing the COMMIT command, we cannot undo or cancel the changes made thereupon. Whereas the ROLLBACK command is used to undo the changes made during the execution of a transaction.
Question 17.
Write MySQL command, which will be used to open an already existing database “LIBRARY”. (All India 2012, Delhi 2011)
Answer:
The SQL command to open an already existing database LIBRARY will be as follows:
USE LIBRARY;
Question 18.
Differentiate between alternate key and candidate key (All India2011)
Answer:
The attribute or a combination of attributes that have unique values for each record known as candidate key whereas a candidate key that is not the primary key is known as an alternate key.
Question 19.
In MySQL Reena and Zebi are getting the following output of SELECT statement on a table EMPLOYEE (HOTS; Delhi2011c)
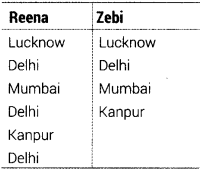
Which keyword has Zebi used with a select statement to get the above output?
Answer:
Zebi has used DISTINCT clause with the SELECT command.
Question 20.
Write MySQL command, which will open an already existing database “CONTACTS (Delhi 2011c)
Answer:
The SQL command to open an already existing database CONTACTS will be as follows:
Use CONTACTS;
Question 21.
Write SQL command used to display the structure of a table. (Delhi 2011c)
Answer:
The command to display the structure of a table is as follows:
DESCRIBE table_name; or DESC table_name;
Question 22.
Mr. lames created a table CLIENT with 2 rows and 4 columns. He added 2 more rows to it and deleted one column. What is the Cardinality and Degree of the Table CLIENT?
Answer:
Cardinality = 4
Degree = 3
Cardinality are the number of rows and degree is number of the columns in a table.
2 Marks Questions
Question 23.
(i) If you have not executed the COMMIT command, executing which command will reverse all updates made during the current work session in MySQL?
(ii) What effect does SET AUTOCOMMIT have in transactions? (All India 2014C)
Answer:
(i) ROLLBACK command can only be used to undo transactions.
(ii) Autocommit simply means that each statement in its own transaction which commits immediately. When autocommit is set ON, the SET IMLICITTRANSACTION sets the connection to implicit transaction mode. When set OFF, it returns the connection to autocommit transaction mode.
Question 24.
A table FUN FOOD has 13 rows and 17 columns. What is the cardinality and degree of the table? (All India 2014)
Answer:
Cardinality of FUN FOOD = 13
Degree of FUN FOOD = 17
Question 25.
What happens when “ROLLBACK” command is issued in a transaction process? (All India 2014)
Answer:
When a ROLLBACK command is issued in a transaction process then all the progress made by a transaction process upto that point will be lost i.e. all the changes made by that transaction process are undone.
Question 26.
Gopi Krishna is using a table EMPLOYEE. It has the following columns:
Code, Name, Salary, Dept code He wants to display maximum salary Departmentwise.
He wrote the following command:
SELECT Dept code, Max(Salary) FROM EMPLOYEE:
But he did not get desired result.
Rewrite the above query with necessary change to help him get the desired output. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
SELECT Deptcode, Max(Salary) FROM EMPLOYEE GROUP BY Deptcode;
Question 27.
What is the use of COMMIT statement in SQL? How is it different from ROLLBACK statement? (Delhi 2013C)
Answer:
The use of the COMMIT statement in MySQL is to end your current transaction and make all changes permanent performed in the transaction. ROLLBACK statement roll back the present transaction, which means canceling a transaction’s changes.
Question 28.
Name two categories into which SQL commands may be categorized. Also, give one example of SQL commands in each category. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
The two categories of SQL commands are as follow:
(i) DDL DDL stands for Data Definition Language. The DDL commands are used to Create, Modify or Destroy the structure of the database objects,
E.g., CREATE TABLE, ALTER TABLE are of this category.
(ii) DML DML stands for Data Manipulation Language. The DML commands are used to insert, display, delete or change data in tables,
E.g.,
SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, etc., commands are of this category.
Question 29.
The Mname Column of a table Members is given below

Based on information, find the output of the following queries
(i) SELECT Mname FROM Members WHERE Mname ' “%\v"; (ii) SELECT Mname FROM Members WHERE Mname LIKE "%e%"; (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
The output of given commands will be as follows
(i) Hirav, Rajeev
(ii) Sheetal, Rajeev.
Question 30.
What is the purpose of ALTER TABLE command in MySQL? How it is different from UPDATE commands? (All India 2011)
Answer:
The ALTER TABLE command is used to change the structure of an existing table. It can be used to add a new column, to change the size or type of a column or to remove a column from a table. But update commands cannot effect the table structure.
Question 31.
The Doc_name column of a table HOSPITAL is given below (All India 2011)

Based on information, find the output of the following queries
(i) SELECT Doc_name FROM HOSPITAL WHERE Doc_name LIKE ‘%v’;. (ii) SELECT Doc_name FROM HOSPITAL WHERE Doc_name LIKE
Answer:
The output of given commands will be as follows:
(i) Sanjeev
(ii) Deepak, Sanjeev.
Question 32.
A table “TRAINS” in a database has degree 3 and cardinality 8. What is the number of rows and columns in it? (Delhi 2011; All India 2011)
Answer:
There will be 8 rows and 3 columns.
Question 33.
Sarthak, a student of class XI created a table “CLASS”. Grade is one of the column of this table. To find the details of students whose Grades have not been entered, he wrote the following MySQL query, which did not give the desired result
SELECT * FROM CLASS WHERE GRADE = "NULL”
Help Sarthak to run the query by removing the errors from the query and write the correct query. (Delhi 2011; All India 2011)
Answer:
The correct query is
SELECT * FROM CLASS. WHERE GRADE IS NULL;
Question 34.
Anurag, a student of class XI created a table “PLAYER SCORE”. Current score is one of the column of this table. To find the details of players whose current score is more than 100, he wrote the following MySQL query, which did not give the desired result
SELECT * FROM PLAYER_SCORE WHERE Current_score>“100”;
Help Anurag to run the query by removing the errors from the query and write the correct query. ‘
Answer:
As score is a numeric data type, so double quotes are not allowed.
SELECT * FROM PLAYER_SC0RE WHERE Current_Score > 100;
Question 35.
Differentiate between COMMIT and SAVEPOINT.
Answer:
| S.No. | Commit | Save Point |
| 1. | Ends the current transaction | Define the breakpoints for the transaction |
| 2. | No rollback after the commit | Partial rollback is allowed up to the save point |
Question 36.
Amit, a salesman in an Outlet, created a table TRANSACTIONS an Amount is one of the column of this Table. To find the details of customer whose transaction amount is more than 800, he wrote the following MySQL query, which did not give the desired result:
SELECT * FROM TRANSACTIONS WHERE Amount > “800”;
Help Amit to run the query by removing the errors from the query and write the correct query.
Answer:
Correct query is
SELECT * FROM TRANSACTIONS WHERE Amount > 800;
Question 37.
Anushka, a salesman in an Outlet, created a table, CUSTOMERS. PhoneNumber is one of the column of this table, which is character type. To find the details of customers whose PhoneNumber is 259624, she wrote the following MySQL query, which did not give the desired result:
SELECT * FROM CUSTOMERS WHERE PhoneNumber = 259624;
Help Anushka to run the query by removing the errors from the query and write the correct query.
Answer:
As PhoneNumber is character type so it must be enclosed in single quotes So, correct query is
SELECT * FROM CUSTOMERS WHERE PhoneNumber = ‘259624’;
Question 38.
Natasha, a salesgirl in an outlet, created table SUPPLIERS. PhoneNumber is one of the column of this table, which is numeric type. To find the details of customers whose number is 345941, she wrote the following MySQL query, which did not give the desired result:
SELECT * FROM SUPPLIERS WHERE PhoneNumber = “345941”;
Answer:
As PhoneNumber is numeric type so it should not be enclosed in double quotes. The correct query is
SELECT * FROM SUPPLIERS WHERE PhoneNumber = 345941;
Question 39.
Shammi, a student of class XII created a table FRIENDS. Pincode is one of the column of this table, which is character type. To find the details of friend whose pin code number is 262122, he wrote the following MySQL query, which did not give desired result:
SELECT * FROM FRIENDS WHERE PinCode = 262122;
Help Shammi to run the query by removing the errors from the query and write the correct query.
Answer:
The correct query is
SELECT * FROM FRIENDS WHERE PinCode = ‘262122’;
4 Marks Questions
Question 40.
In a database BANK, there are two tables with a sample data given below
TABLE EMPLOYEE
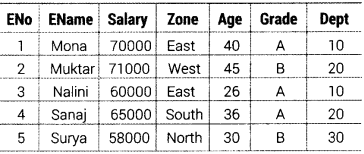
TABLE DEPARTMENT
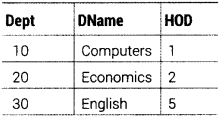
Note:
– EName refers to Employee Name
– DName refers to Department Name
– Dept refers to Department Code
– HOD refers to Employee number (ENO) of the Head of the Department
Write SQL queries for the following:
(i) To display ENo, EName, Salary and corresponding DName of all the employees whose age is between 25 and 35 (both values inclusive).
(ii) To display DName and corresponding EName from the tables DEPARTMENT and EMPLOYEE, (Hint’ HOD of the DEPARTMENT table should be matched with ENo of the EMPLOYEE table for getting the desired result).
(iii) To display EName, Salary, Zone and Income Tax
(Note Income Tax to be calculated as 30% of salary) of all the employees with appropriate column headings. (HOTS; Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(i) SELECT e.ENo,e.EName,e.Salary,d.DName FROM EMPLOYEE e, DEPARTMENT d WHERE e.Dept = d.Dept AND e.Age BETWEEN 25 AND 35; (ii) SELECT e.EName,d.DName FROM EMPLOYEE e, DEPARTMENT d WHERE e.ENO = d.HOD; (iii) SELECT EName, Zone, Salary x 0.3 “Income Tax” FROM EMPLOYEE;
Question 41.
TABLE ITEM
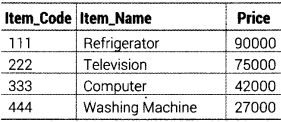
TABLE BRAND
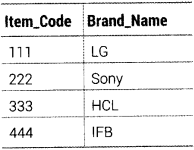
Write MySQL queries for the following
(i) To display ltem_Code, ltem_Name and corresponding Brand_Name of those items, whose Price is between 20000 and 40000 (both values included).
(ii) To display ltem_Code, Price and Brand_Name of the item which has ltem_Name as “Computer”.
(iii) To increase the prices of all the items by 10%.
Answer:
(i) SELECT i. Item_Code,i. Item_Name, b.Brand_Name FROM ITEM i, BRAND b WHERE i .Item_Code = b.Item_code AND i.Price BETWEEN 20000 AND 40000; (ii) SELECT i.Item_Code, Price, b.Brand_Name FROM ITEM i, BRAND b WHERE i. Item_Code = b. Item_Code AND i. Item_Name = ‘Computer’; (iii) UPDATE ITEM SET Price = Price + (Price*0.1);
Question 42.
TABLE ITEM
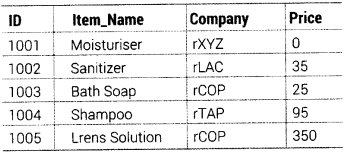
TABLE CUSTOMER
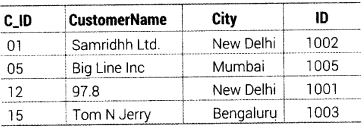
Write MySQL queries for the following:
(i) To display the details of Item, whose Price is in the range of 40 and 95 (both values included).
(ii) To display CustomerName, City from table CUSTOMER and ItemName and Price from table ITEM, with their corresponding matching ID.
(iii) To increase the prices of all the Items by 50%. (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
(i) SELECT * FROM ITEM WHERE Price BETWEEN 40 AND 95; (ii) SELECT CUSTOMER. CustomerName, CUSTOMER.City, ITEM.Item_Name, ITEM.Price FROM ITEM, CUSTOMER WHERE ITEM.ID = CUSTOMER.ID; (iii) UPDATE ITEM SET Price = Price + Price * 0.50;
Question 43.
Create table CUSTOMER as per following Table Instance Chart
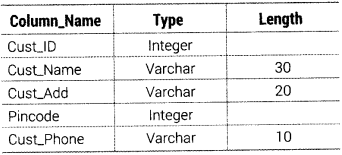
Answer:
The SQL command to create a table as per given structure is as follows:
CREATE TABLE CUSTOMER (Cust ID INTEGER, Cust_Name VARCHAR(30), Cust_Add VARCHAR(20), Pincode INTEGER, Cust_Phone VARCHARC10));
Question 44.
Create table STUDENT as per following Table Instance Chart
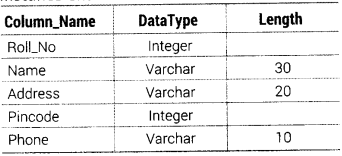
Answer:
The SQL command to create a table as per given structure is as follows:
CREATE TABLE STUDENT (RolI_No INTEGER, Name VARCHAR(30), Address VARCHAR(20), Pincode INTEGER, Phone VARCHAR!10));
Question 45.
Write an SQL query to create a table STUDENT with the following structure
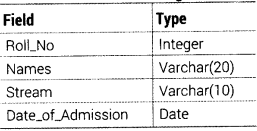
Answer:
The SQL command to create a table as per given structure is as follows:
CREATE TABLE STUDENT (Roll_Number INTEGER, Name VARCHAR(20), Stream VARCHAR(IO), Date_of_Admission Date);
Question 46.
Write an SQL query to create a table CUSTOMER with the following structure
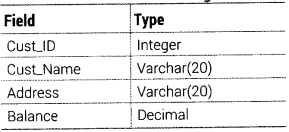
Answer:
The SQL command to create a table as per given structure is as follows:
CREATE TABLE CUSTOMER (Cust_ID INTEGER, Cust_Name VARCHAR(20), Address VARCHAR(20), Balance DECIMAL);
Question 47.
Write an SQL query to create a table TEACHER with the following structure
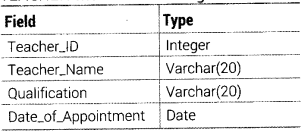
Answer:
The SQL command to create a table as per given structure is as follows:
CREATE TABLE TEACHER (Teacher_ID INTEGER, Teacher_Name VARCHAR(20), Qualification VARCHAR(20), Date_of_Appointment DATE);
Question 48.
Write an SQL query to create a table ITEM with the following structure
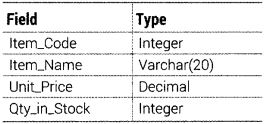
Answer:
The SQL command to create a table as per given structure is as follows:
CREATE TABLE ITEM (Item_Code INTEGER, Item_Name VARCHAR(20), Unit_Price DECIMAL, Qty_in_Stock INTEGER);
Question 49.
Write an SQL query to create a table ACCOUNTS with the following structure
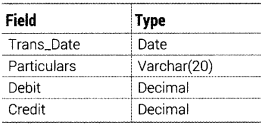
Answer:
The SQL command to create a table as per given structure is as follows:
CREATE TABLE ACCOUNTS (Trans_Date DATE, Particulars VARCHAR(20), Debit DECIMAL, Credit DECIMAL);
Question 50.
Write an SQL query to create a table LIBRARY with the following structure
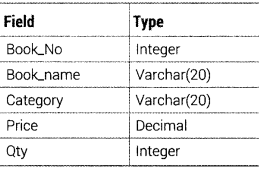
Answer:
The SQL command to create a table as per given structure is as follows:
CREATE TABLE LIBRARY (Book_No INTEGER, Book_name VARCHAR!20), Category VARCHAR(20), Price DECIMAL, Qty INTEGER);
Question 51.
Write an SQL query to create a table LAB with the following structure
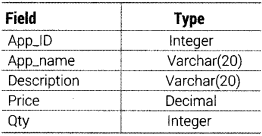
Answer:
The SQL command to create a table as per given structure is as follows:
CREATE TABLE LAB (App ID INTEGER, App_name VARCHAR (20), Description VARCHAR(20), Price DECIMAL, Qty INTEGER);
Question 52.
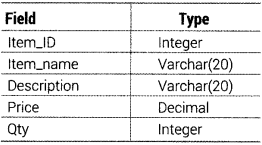
Write an SQL query to create a table SPORTS with the following structure
Answer:
The SQL command to create a table as per given structure is as follows:
CREATE TABLE SPORTS (Item_ID INTEGER, Item_name VARCHAR(20), Description VARCHAR(20), Price DECIMAL, Qty INTEGER);
We hope the Informatics Practices Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Database help you. If you have any query regarding Informatics Practices Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Database, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.