Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements Class 12 Important Questions
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements Class 12 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Why is the froth flotation method selected for the concentration of sulphide ores? (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
Because the method is based on preferential wetting properties with the frothing agent and water, and the sulphide particles of ore stick to the oil droplets and rise in the form of froth.
Question 2.
What is meant by the term ‘pyrometallurgy’? (All India 2009)
Answer:
The process of extraction of metal by heating the metal oxide with a suitable reducing agent is called pyrometallurgy.
Question 3.
Differentiate between a mineral and an ore. (All India 2011)
Answer:
Mineral: The naturally occuring chemical substances in form of which the metals occur in the earth along with impurities are called minerals.
Ore: The mineral from which metal can be extracted conveniently and economically is called an ore.
Thus, all ores are minerals but all minerals are not oies.
Question 4.
What type of ores can be concentrated by magnetic separation method? (All India 2011)
Answer:
Magnetic separation method is used when either the ore or the impurities associated with it are magnetic in nature.
Example: Chromite (FeO.Cr2O3) -A an ore of chromium
Magnetite (Fe3O4) → an ore of iron.
Question 5.
Why is it that only sulphide ores are concentrated by ‘froth floatation process’? (All India 2011)
Answer:
As sulphide ores are wetted with pine oil and their particles come up along with froth, while their gangue (impurities) particles are wetted with water so such particles settle down.
Question 6.
What is the role of graphite in the electrometallurgy of aluminium? (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Graphite acts as an anode in the electro metallurgy of aluminium.
Question 7.
How is copper extracted from a low grade ore of it? (All India 2012)
Answer:
Copper is extracted by hydrometallurgy from low grade ores. It is leached out using add or bacteria.
Question 8.
What is the role of collectors in Froth Floatation process? (All India 2012)
Answer:
Collectors e.g. pine oils, fatty acids etc. enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles.
Question 9.
What is the role of depressants in the froth floatation process of dressing of ores? (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Depressants are used to prevent certain type of particles from forming the froth with the bubbles.
Example : In case of an ore containing ZnS and PbS, the depressant used is NaCN. It selectively prevents ZnS from coming to the froth but allows PbS to come with the froth.
Question 10.
Name the methods used for refining of following metals :
(i) Nickel
(ii) Titanium (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(i) Nickel: Mond process
(ii) Titanium: Van Arkel method
Question 11.
What types of metals are usually purified by the method of zone refining? Give an example. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
This method is very useful for producing metals of very high purity Example : germanium, gallium etc.
Question 12.
Which method is employed for extracting copper from low grade ores and scraps? (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
Hydrometallurgy; Copper is extracted from low grade ores and scrap.
Question 13.
What is the basic principle of zone refining of metals? (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
Principle of Zone refining : This method is based on the principle that “the impurities are more soluble in the melt state than in the solid state of the metal.”
Question 14.
Although thermodynamically feasible, in practice, magnesium metal is not used for reduction of Alumina in the metallurgy of aluminium. Why? (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
Below the temperature 1665K, the point of intersection of Al2O3 and MgO curves in Ellingham diagram, Mg can reduce Al2O3. However, Mg is a much costlier metal than A1 and hence the process will not be economical.
Question 15.
Name the method used for the refining of Nickel metal. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Mond process is used for refining of nickel metal.
Question 16.
What is the composition of ‘Copper matte’? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Copper matte chiefly consists of Cuprous Sulphide (Cu2S) and some uncharged Ferrous Sulphide (FeS).
Question 17.
Name the method used for refining of copper metal. (All India 2013)
Answer:
Electrolytic refining of copper metal.
Question 18.
Name the methods used for the vapour phase refining of impure titanium and nickel metals. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Mond process is used for refining of nickel and Van-Arkel method is used for refining of titanium.
Question 19.
State the principle of the method of zone refining of metals. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Zone refining: It is based on the principle that the impurities are more soluble in molten state than in the solid state of the metal.
Question 20.
Write the chemical reaction which takes place in Mond’s process for refining of nickel. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Mond process for refining of nickel :
Question 21.
Which reducing agent is employed to get copper from the leached low grade copper ore? (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Hydrogen /Iron
Question 22.
What is the role of zinc metal in the extraction of silver? (All India 2014)
Answer:
Zinc acts as a reducing agent which reduces complex of silver into silver
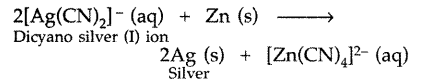
Question 23.
Name the method that is used for refining of nickel. (All India 2014)
Answer:
Mond’s process is used for refining of nickel.
Question 24.
Name the method used for refining of copper metal. (All India 2014)
Answer:
Electrolytic refining is used for refining of copper metal.
Question 25.
What is the function of SiO2 in the metallurgy of copper? (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
During roasting, copper pyrites are converted into a mixture of FeO and Cu2O.
2CuFeS2 + O2 \(\stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow}\) Cu2S + 2FeS + SO2
Copper pyrites
2CU2S + 3O2 → 2CU2O + 2SO2
2FeS + 3O2 → 2FeO + 2SO2
To remove basic FeO, an acidic flux silica is added during smelting. Now FeO combines with SiO2 (silica) to form ferrous silicate (FeSiO3) slag which floats over molten matte.
Question 26.
What role is played by CO2 in getting pure alumina (A1l2O3) in the extraction of aluminium? (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
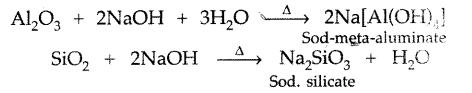
Role of CO2 in extraction of Al2O3 : During leaching the precipitated aluminium hydroxide is neutralised by CO2 to produce hydrated alumina which on heating gives pure alumina
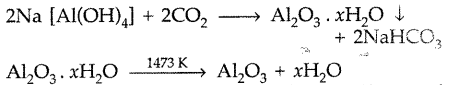
Question 27.
What is the role of NaOH in the metallurgy of aluminium? (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
The powdered bauxite ore is heated with cone. NaOH to remove impurities of Fe2O3, SiO, and TiO2. ‘
Question 28.
What are the collectors used in froth floatation process? Name a substance that can be used as such. (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
Collectors : Pine oils, fatty acids etc. enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles;
Question 29:
What is the role of CO2 in the extractive metallurgy of aluminium from its ore? (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
The solution of sodium meta-aluminate is neutralized by passing CO2 when hydrated alumina separates out while sodium silicate remains in the solution.
Question 30.
Name the chief ores of aluminium and zinc. (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
Aluminium ore → Bauxite
Zinc ore→ Zinc blende
Question 31.
Write the main reason for the stability of colloidal sols. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
The stability of the colloidal solution is because of solvation and the presence of charge on the dispersed phase particles.
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements Class 12 Important Questions Short Answer Type -I [SA-I]
Question 32.
Explain the role of
(i) Cryolite in the electrolytic reduction of alumina.
(ii) Carbon monoxide in the purification of nickel. (Delhi 2009)
Answer:
(i) The role of cryolite (Na3AlF6) is to lower the melting point of the mixture and bring conductivity.
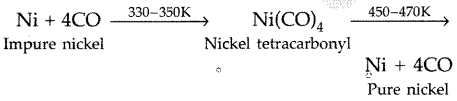
(ii) Nickel is heated in a stream of carbon monoxide forming a volatile complex, nickel tetracarbonyl which is further subjected to higher temperature so that it is decomposed to give pure nickel.

Question 33.
Describe the underlying principle of each of the following metal refining methods :
(i) Electrolytic refining of metals
(ii) Vapour phase refining of metals(All India 2009)
Answer:
(i) Electrolytic refining of metals: Here the impure metal is made to act as anode and a strip of the same metal in pure form is used as cathode. When they both are put in suitable electrolyte containing soluble salt of same metal, the more basic metal remains in the solution and the less basic ones go to the anode mud.
Example : In refining of Cu At anode : (oxidation)
Cu → Cu2+ + 2e–
Af cathode : (reduction)
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
(ii) Vapour phase refining of metals: In this method, the impure metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected elsewhere which is then decomposed by heating to a higher temperature to give pure metal. The requirements are
- the metal should form a volatile , compound with an available reagent.
- the volatile compound should be easily decomposable so that recovery is easy.
- Nickel, zirconium and titanium are refined using this method.
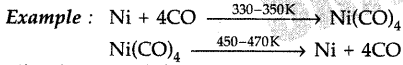
Question 34.
Describe the role of the following :
(i) NaCN in the extraction of silver from a silver ore.
(ii) Cryolite in the extraction of aluminium from pure alumina. (All India 2009)
Answer:
(i) NaCN acts as a leaching agent or oxidising agent, thus oxidises Ag to Ag+ which then combines with CN– ions to form respective soluble complex.
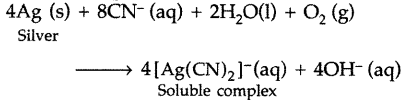
(ii) The role of cryolite (Na3AlF6) is to lower the melting point of the mixture and brings conductivity.
Question 35.
Describe the principle controlling each of the following processes :
(i) Vapour phase refining of titanium metal
(ii) Froth floatation method of concentration of a sulphide (All India 2011)
Answer:
Nickel is heated in a stream of carbon monoxide forming a volatile complex, nickel tetracarbonyl which is further subjected to higher temperature so that it is decomposed to give pure nickel.

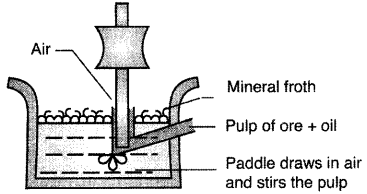
(ii) Froth floatation method : This method is used for removing gangue from sulphide ores. In this powdered ore is mixed with collectors (e.g. pine oils, fatty acids etc.) and froth stabilisers (e.g. cresols, aniline) which enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles and froth stabilisation respectively. As a result of which ore comes with froth and gangue remain in the solution.
Question 36.
Describe the principle controlling each of the following processes :
(i) Zone refining of metals
(ii) Electrolytic refining of metals (All India 2011)
Answer:
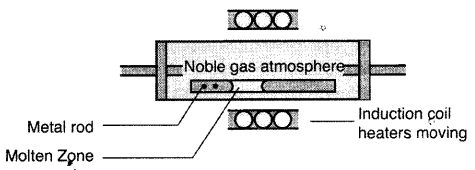
(i) Zone refining of metals: This method is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in the molten state of the metal (the melt) than in the solid state. In the process of zone refining, a circular mobile heater is fixed at one end of a rod of impure metal. As the heater moves, the molten zone of the mod also moves along with it. As a result, pure metal crystallizes out of the melt and the impurities pass to the adjacent molten zone. This process is repeated several times which leads to the segregation of impurities at one end of the rod. Then the end with impurities is cut off. Silicon, boron, gallium etc. can be purified by this process.
(ii) Electrolytic refining of metals : Here the impure metal is made to act as anode and a strip of the same metal in pure form is used as cathode. When they both are put in suitable electrolyte containing soluble salt of same metal, the more basic metal remains in the solution and the less basic ones go to the anode mud.
Example : In refining of Cu At anode : (oxidation)
Cu → Cu2+ + 2e–
Af cathode : (reduction)
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
Question 37.
Describe the principle controlling each of the following processes :
(i) Preparation of cast iron from pig iron.
(it) Preparation of pure alumina (Al2O3) from bauxite ore. (All India 2011)
Answer:
(i) Preparation of cast iron from pig iron : Cast iron is made by melting pig iron with scrap iron and coke using hot air blast. It has slightly lower carbon content (about 3%) and is extremely hard and brittle.
(ii) The bauxite ore is treated with sodium hydroxide solution. The impurities iron oxide and TiO2 are filtered out. Then the filterate containing sodium aluminate and sodium silicate is diluted with water to get ppt. of Al(OH)3.
The ppt. of Al(OH)3 is filtered, then dried and heated in the absence of air to get pure alumina
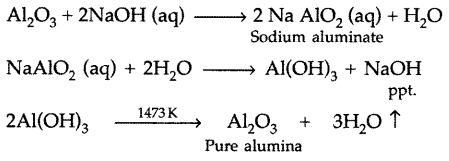
Question 38.
Describe the principle involved in each of the following processes :
(i) Mond process for refining of Nickel.
(ii) Column chromatography for purification of rare elements. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(i) Ability of nickel to form volatile compound which can decompose on further heating.
(ii) Different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an adsorbent.
Question 39.
Describe the following :
(i) The role of cryolite in electro metallurgy of aluminium.
(ii) The role of carbon monoxide in the refining of crude nickel. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(i) Cryolite works as a solvent, lowers the melting point of mixture of alumina in the extraction of aluminium and increases the conductivity of mixture.
(ii) In this process CO forms volatile complex on heating with Ni which decomposes to give pure nickle at high temperature.
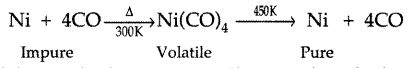
Question 40.
Which methods are usually employed for purifying the following metals :
(i) Nickel (ii) Germanium
Mention the principle behind each one of them. (All India 2012)
Answer:
(i) Nickel: Mond process. In this method, the metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected elsewhere. It is then decomposed to give pure metal.
(ii) Germanium: Zone refining. This method is based on the principle that “the impurities are more soluble in the molten than in the solid state of the metal.”
Question 41.
Explain the role of each of the following :
(i) NaCN in the extraction of silver
(ii) SiO2 in the extraction of copper (All India 2012)
Answer:
(i) Ag is leached with dil NaCN or KCN solution in the presence of air from which the metal is obtained by replacement.
4Ag + 8CN– + 2H2O + O2 → 4[Ag(CN)2]– + 4OH–
2[Ag(CN)2]– + Zn → [Zn(CN)4]-2 + 2Ag
(ii) SiO2 reacts with FeO to form fusible slag and can easily be removed.
FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3
Question 42.
Why is copper matte put in silica lined converter? (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Copper matte mainly contains Cu2S and FeS. When a hot air blast is blown through molten matte taken in a silica lined converter, FeS is oxidised to FeO. Silica (SiO2) present as lining acts as flux and combines with FeO to form slag.
2FeS + 3O2 → 2FeO + 2SO2
FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3 (slag).
Question 43.
What is the significance of leaching in the extraction of aluminium ? (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Leaching: Bauxite ore contains FeO, SiO2, TiO2 as impurities . The powdered ore is treated with a concentrated solution of NaOH at 473 – 523 K and 35 – 36 bar pressure when Al2O3 dissolves in alkali to form soluble complex while the impurities do not react and can be removed by filtration.
Question 44.
The extraction of gold by leaching with NaCN involves both oxidation and reduction. Justify giving chemical equations. (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
The extraction of gold involves leaching the metal with NaCN.
Oxidation : 4Au + 8NaCN + O2 + 2H2O → 4Na [AU(CN)2] + 4NaOH
In this reaction Au is oxidised to Au+ ions.
Reduction : 2Na [Au(CN)2] + Zn → Na2 [Zn(CN)4] + 2Au
In this reaction Au+ ions are reduced to Au.
Question 45.
(a) Which solution is used for the leaching of silver metal in the presence of air in the metallurgy of silver?
(b) Out of C and CO, which is a better reducing agent at the lower temperature range in the blast furnace to extract iron from the oxide ore? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) The 0.5% solution of sodium or potassium cyanide is used for the leaching of silver metal.
4Ag + 8NaCN + 2H2O + O2 → 4Na[Ag(CN)2] + 4NaOH Sod. dicyanoargentate (1)
(b) CO will be a better reducing agent at the lower temperature range in the blast furnace to extract iron from the oxide ore because in Ellingham diagram the CO2 line lies below Fe, FeO line. Hence CO reduces Fe2O3, Fe3O4, FeO etc.
FeO + CO \(\underrightarrow { 1123K } \) Fe + CO2
Question 46.
(a) Which of the following ores can be concentrated by froth floatation method and why?
Fe2O3, ZnS, Al2O3
(b) What is the role of silica (SiO2) in the metallurgy of Copper? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) Zns ore can be concentrated by froth floatation method because it is a sulphide ore.
(b) During roasting, copper pyrites are converted into a mixture of FeO and Cu2O.
2CuFeS2 + O2 \(\stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow}\) Cu2S + 2FeS + SO2
Copper pyrites
2CU2S + 3O2 → 2CU2O + 2SO2
2FeS + 3O2 → 2FeO + 2SO2
To remove basic FeO, an acidic flux silica is added during smelting. Now FeO combines with SiO2 (silica) to form ferrous silicate (FeSiO3) slag which floats over molten matte.
Question 47.
(a) Give an example of zone refining of metals. (b) What is the role of cryolite in the metallurgy of aluminium? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) Zone refining is based on the principal that the impurities are more soluble in the melt than in the solid state of the metal.
(b) The role of cryolite (Na3AIF6) is to lower the melting point of the mixture and brings conductivity.
Question 48.
(a) Name the method used for removing gangue from sulphide ores.
(b) How is wrought iron different from steel? (All India 2013)
Answer:
(a) Froth Floatation method is used for removing gangue from sulphide ores.
(b) Wrought iron is the purest form of commercial iron which contains about 0.2 – 0.5% carbon while steel contains about (0.5 – 1.5)% carbon.
Question 49.
Name the principal ore of aluminium. Explain the significance of leaching in the extraction of aluminium. (All India 2013)
Answer:
Bahxite (Al2O3,2H2O) is the principal ore of aluminium.
The significance of leaching in the extraction of aluminium is to prepare pure alumina from the bauxite ore in the following steps :
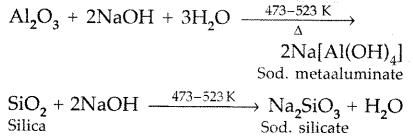
After filteration of impurities sod. meta aluminate is neutralized by passing CO2
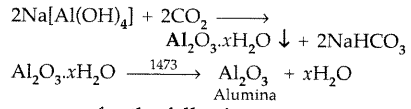
Question 50.
Give reasons for the following :
(a) Alumina is dissolved in cryolite for electrolysis instead of being electrolyzed directly.
(b) Zinc oxide can be reduced to metal by heating with carbon but Cr2O2 cannot be reduced by heating with carbon. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) Fused alumina is bad conductor of electricity, therefore cryolite is added to purified alumina which makes it a good conductor and reduces the melting point of the mixture.
(b) The standard free energy of formation (ΔfG°) of CO from C is lower at temperature above 1180 K while that of CO2 from C is lower at temperature above 1270 K than ΔfG° of ZnO. Thus above 1270 K, ZnO can be reduced to Zn by C.
Question 51.
Explain the role of the following :
(a) Iodine in the refining of titanium.
(b) NaCN in the extraction of silver from silver ore. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) The iodine is used in refining of titanium to form a volatile iodide which on decomposition at high temperature gives pure metal

(b) NaCN acts as a leaching agent or oxidising agent, thus oxidises Ag to Ag+ which then combines with CN– ions to form respective soluble complex.
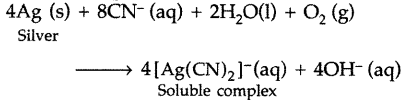
Question 52.
Outline the principles behind the refining of metals by the following methods :
(i) Zone refining method
(ii) Chromatographic method (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Zone refining of metals: This method is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in the molten state of the metal (the melt) than in the solid state. In the process of zone refining, a circular mobile heater is fixed at one end of a rod of impure metal. As the heater moves, the molten zone of the mod also moves along with it. As a result, pure metal crystallizes out of the melt and the impurities pass to the adjacent molten zone. This process is repeated several times which leads to the segregation of impurities at one end of the rod. Then the end with impurities is cut off. Silicon, boron, gallium etc. can be purified by this process.
(ii) Chromatographic method : It is based on the principle that different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on the adsorbent.
Question 53.
Write the principle behind the following methods of refining :
(i) Hydraulic washing
(ii) Vapour phase refining (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Hydraulic washing or Levigation : The process is based on the principle that lighter earthy particles are removed from heavier ore particles by washing with water (Difference in the gravities).
(ii) Vapour phase refining : In this method, the crude metal is freed from impurities by first converting it into a suitable volatile compound by heating with a specific reagent at a lower temperature and then decomposing the volatile compound at some higher temperature to give the pure metal.
Question 54.
Write the principles of the following methods :
(i) Froth floatation method
(ii) Electrolytic refining (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Froth floatation method : This method is used for removing gangue from sulphide ores. In this powdered ore is mixed with collectors (e.g. pine oils, fatty acids etc.) and froth stabilisers (e.g. cresols, aniline) which enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles and froth stabilisation respectively. As a result of which ore comes with froth and gangue remain in the solution.

(ii) Electrolytic refining of metals : Here the impure metal is made to act as anode and a strip of the same metal in pure form is used as cathode. When they both are put in suitable electrolyte containing soluble salt of same metal, the more basic metal remains in the solution and the less basic ones go to the anode mud.
Example : In refining of Cu At anode : (oxidation)
Cu → Cu2+ + 2e–
Af cathode : (reduction)
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
Question 55.
Describe the role of the following :
(i) SiO2 in the extraction of copper from copper matte
(ii) NaCN in froth floatation process (All India 2014)
Answer:
(i) During roasting copper pyrites are converted into a mixture of FeO and Cu2O.
2 CuFeS2 + O2 \(\stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow}\) Cu2S + 2 FeS + SO2
Copper pyrites
2 Cu2S + 3O2 \(\stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow}\) 2Cu2O + 2 SO2
2 FeS + 3O2 \(\stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow}\) FeO + 2 SO2
To remove FeO (basic), an acidic flux silica is added during smelting. FeO then combines with SiO2 to form ferrous silicate (FeSiO3) slag which floats over molten matte and hence can be easily removed
![]()
The silica is used to remove ferrous oxide and ferrous sulphide as slag.
(ii) NaCN is used as a depressant to separate PbS ore from ZnS in froth flotation process.
Question 56.
Write the principle behind the froth floatation process. What is the role of collectors in this process? (All India 2014)
Answer:
Froth floatation method : This method is used for removing gangue from sulphide ores. In this powdered ore is mixed with collectors (e.g. pine oils, fatty acids etc.) and froth stabilisers (e.g. cresols, aniline) which enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles and froth stabilisation respectively. As a result of which ore comes with froth and gangue remain in the solution.

Role : Collectors e.g. pine oils, fatty acids etc. enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles.
Question 57.
Define the following terms:
(i) Roasting (ii) Calcination (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Roasting: The process of heating strongly the concentrated sulphide ore in the presence of air is called roasting :
2ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2 ↑
Zinc blende
(ii) Calcination: The process of heating strongly the concentrated ore in the absence of air is called calcination :
ZnCO3 \(\stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow}\) ZnO + CO2 ↑
Calamine
Question 58.
Describe the principle involved in each of the following processes :
(i) Zone refining of metals
(ii) Vapour phase refining of metals (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Zone refining of metals : It is based on the principle that the impurities are more soluble in melt than in the solid state of the metal.
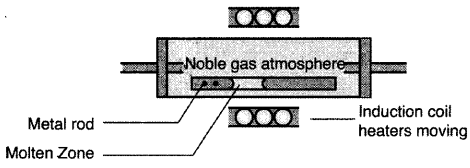
(ii) Vapour phase refining of metals : Flere the impure metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected elsewhere which is then decomposed by heating at a higher temperature to give pure metal. The requirements are
• the metal should form a volatile compound with an available reagent.
• the volatile compound should be easily decomposable so that recovery is easy.
Example : Ni + 4CO \(\underrightarrow { 330-350K } \) Ni(CO)4
Ni(CO)4 4\(\underrightarrow { 450-470K } \) Ni + 4CO
Question 59.
Describe the underlying principle of each of the following processes :
(i) Recovery of silver from the solution obtained by leaching silver ore with a solution of NaCN.
(ii) Electrolytic refining of a crude metal. (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
(i) NaCN acts as a leaching agent or oxidising agent, thus oxidises Ag to Ag+ which then combines with CN– ions to form respective soluble complex
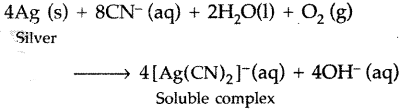
(ii) Electrolytic refining : Here the impure metal is made to act as anode and a strip of the same metal in pure form is used as cathode. When they both are put in suitable electrolyte containing soluble salt of same metal, the more basic metal remains in the solution and the less basic ones go to the anode mud.
Example : In refining of Cu At anode : (oxidation)
Cu → Cu2+ + 2e–
At cathode : (reduction)
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements Class 12 Important Questions Short Answer Type -II [SA-II]
Question 60.
Describe how the following changes are brought about:
(i) Pig iron into steel.
(ii) Zinc oxide into metallic zinc.
(iii) Impure titanium into pure titanium. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
(i) Pig iron into steel : For this Basic Oxygen Process (BOP) is used. The furnace is charged with molten pig iron and lime, and pure O2
is blown over the surface of the metal at a great speed through water-cooled retractable lances. The O2 penetrates through the metal and oxidises the impurities rapidly
2C + O2 → 2CO,
2Fe + O2 → 2FeO,
2FeO + Si → 2Fe + SiO2,
CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3 Slag
6CaO + P4O10 → 2Ca2 (P04)2 Slag
When all the impurities are removed, the required alloying elements (Cr, Ni, Mn etc) are added to produce steel of desirable properties.
(ii) Zinc oxide into metallic zinc : Above 1270 K, ΔG° for ZnO is higher than that of CO2 and CO from carbon therefore above 1270 K AG° for reduction of ZnO by carbon is negative and hence ZnO is easily reduced by coke. The ZnO is made into brickettes with coke and clay and heated above 673 K so that the reduction process goes to completion.
ZnO(s) + C(s) → Zn(s) + CO(g)
(iii) Impure titanium into pure titanium (By Van Arkel method) : The impure titanium is heated in an evacuated vessel with iodine at 870 K. The covalent volatile titanium tetraiodide thus formed is separated which is then decomposed by heating over a tungsten filament at 2075 K to give pure titanium.
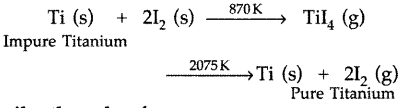
Question 61.
Describe the role of
(i) NaCN in the extraction of gold from gold ore.
(it) SiO2 in the extraction of copper from copper matte.
(iii) Iodine in the refining of zirconium. Write chemical equations for the involved reactions. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
(i) NaCN is used to leach the metal present in the ore by oxidising gold to Au+ which combines with CN– ions to form their respective soluble complexes.
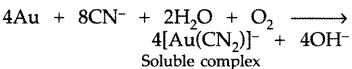
The metal is then recovered from this complex by using more electropositive reducing agent i.e. Zinc
2[AU(CN)2]– + Zn → 2Au + [Zn(CN)4]2-
(ii) During roasting copper pyrites are converted into a mixture of FeO and Cu2O.
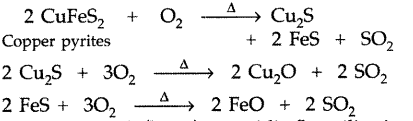
To remove FeO (basic), an acidic flux silica is added during smelting. FeO then combines with SiO2 to form ferrous silicate (FeSiO3) slag which floats over molten matte and hence can be easily removed

The silica is used to remove ferrous oxide and ferrous sulphide as slag.
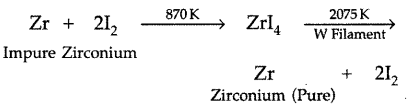
(iii) The iodine is used in refining of zirconium to form a volatile iodide which on decomposition at high temperature gives pure metal.
Question 62.
Describe the role of the following :
(i) NaCN in the extraction of silver from a silver ore
(ii) Iodine in the refining of titanium
(iii) Cryolite in the metallurgy of aluminium (All India 2010)
Answer:
(i) NaCN acts as a leaching agent or oxidising agent, thus oxidises Ag to Ag+ which then combines with CN– ions to form respective soluble complex.
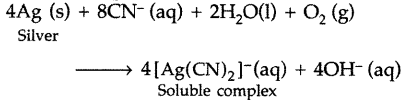
(ii) Impure titanium (Ti) is heated with iodine to form TiI4 in vapour phase, any impurity remains in solid form and can be removed easily. TiI4 on further heating decomposes to give Ti and I4.
(iii) The role of cryolite (Na4AlF6) is to lower the melting point of the mixture and brings conductivity.
Question 63.
Describe the principle involved in each of the following processes of metallurgy :
(i) Froth floatation method
(ii) Electrolytic refining of metals
(iii) Zone refining of metals (All India 2010)
Answer:
(i) Froth floatation method : This method is used for removing gangue from sulphide ores. In this powdered ore is mixed with collectors (e.g. pine oils, fatty acids etc.) and froth stabilisers (e.g. cresols, aniline) which enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles and froth stabilisation respectively. As a result of which ore comes with froth and gangue remain in the solution.

(ii) Electrolytic refining of metals: Here the impure metal is made to act as anode and a strip of the same metal in pure form is used as cathode. When they both are put in suitable electrolyte containing soluble salt of same metal, the more basic metal remains in the solution and the less basic ones go to the anode mud.
Example : In refining of Cu
At anode : (oxidation)
Cu → Cu2+ + 2e–
Af cathode : (reduction)
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
(iii) Zone refining of metals: This method is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in the molten state of the metal (the melt) than in the solid state. In the process of zone refining, a circular mobile heater is fixed at one end of a rod of impure metal. As the heater moves, the molten zone of the mod also moves along with it. As a result, pure metal crystallizes out of the melt and the impurities pass to the adjacent molten zone. This process is repeated several times which leads to the segregation of impurities at one end of the rod. The end with impurities is cut off. Silicon, boron, , gallium etc. can be purified by this process.
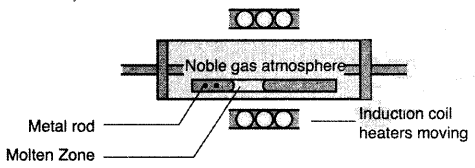
Question 64.
Explain the role of each of the following in the extraction of metals from their ores :
(i) CO in the extraction of nickel.
(ii) Zinc in the extraction of silver.
(iii) Silica in the extraction of copper. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
Nickel is heated in a stream of carbon monoxide forming a volatile complex, nickel tetracarbonyl which is further subjected to higher temperature so that it is decomposed to give pure nickel.

(ii) Zinc acts as a reducing agent which reduces complex of silver into silver
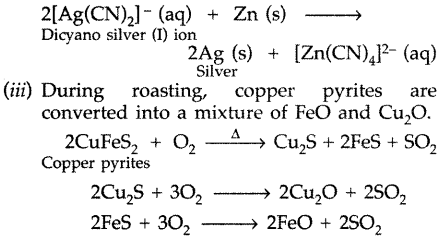
To remove basic FeO, an acidic flux silica is added during smelting. Now FeO combines with SiO2 (silica) to form ferrous silicate (FeSiO3) slag which floats over molten matte.
Question 65.
Outline the principles of refining of metals by the following methods :
(i) Zone refining
(ii) Vapour phase refining (All India 2013)
Answer:
(i) Zone refining of metals: This method is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in the molten state of the metal (the melt) than in the solid state. In the process of zone refining, a circular mobile heater is fixed at one end of a rod of impure metal. As the heater moves, the molten zone of the mod also moves along with it. As a result, pure metal crystallizes out of the melt and the impurities pass to the adjacent molten zone. This process is repeated several times which leads to the segregation of impurities at one end of the rod. The end with impurities is cut off. Silicon, boron, , gallium etc. can be purified by this process.

(ii) Vapour phase refining : Here the metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected elsewhere which then decomposed to give pure metal. The requirements are
- the metal should form a volatile compound with an available reagent.
- the volatile compound should be easily decomposable so that recovery is easy.
Example : Ni + 4CO \(\underrightarrow { 330-350K } \) Ni(CO)4
Ni(CO)4 \(\underrightarrow { 450-470K } \) Ni + 4CO
Question 66.
(a) Giving examples differentiate between calcination and roasting.
(b) What is the role of cryolite in the extraction of aluminium? (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
(a) Calcination : The process of heating strongly the concentrated ore in the absence of air is called calcination.
ZnCO2 \(\stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow}\) ZnO + CO2 ↑
Calamine
Roasting : The process of heating strongly the concentrated sulphide ore in the presence of air is called roasting.
2ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2 ↑
Zinc blende
(b) The role of cryolite (Na3AlF6) is to lower the melting point of the mixture and brings conductivity.
Question 67.
(i) Indicate the principle behind the method used for the refining of zinc.
(ii) What is the role of silica in the extraction of copper?
(iii) Which form of the iron is the purest form of commercial iron? (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(i) Zinc is refined by distillation method because zinc has low boiling point.
(ii) During roasting copper pyrites are converted into a mixture of FeO and CuzO.
2CuFeS2 + O2 \(\stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow}\) Cu2S + 2FeS + SO2
Copper pyrites
2 Cu2S + 3O2 \(\stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow}\) 2 Cu20 + 2 SO2
2 FeS + 3O2 \(\stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow}\) 2 FeO + 2 SO2
Silica acts as acidic flux in the extraction of copper to remove the iron oxide obtained during the process of roasting.
To remove FeO, silica is added during smelting. FeO then combines with SiO2 to form ferrous silicate (FeSiO3) slag which floats over molten matter and hence can be easily removed.
![]()
(iii) Wrought iron.
Question 68.
(i) Name the method of refining to obtain silicon of high purity.
(ii) What is the role of SiOz in the extraction of copper?
(iii) What is the role of depressants in froth floation process? (All India 2015)
Answer:
(i) Silicon of high purity can be obtained by zone refining.
(ii) SiO2 acts as acidic flux to remove the impurities of iron oxide.
(iii) Depressants prevent the formation of froth with air bubbles of other sulphide ore.
Question 69.
Outline the principles of refining of metals by the following methods :
(i) Distillation
(ii) Zone refining
(iii) Electrolysis (Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(i) Principle of Distillation : The impure metal is evaporated to obtain the pure metal as distillate. The metals having low boiling points (Bi, Hg, Cd etc.) readily change into vapours leaving behind impurities which further get collected in receivers and upon cooling, pure metal is obtained.
(ii) Depressants prevent the formation of froth with air bubbles of other sulphide ore.
(iii) Electrolytic refining : Here the impure metal is made to act as anode and a strip of the same metal in pure form is used as cathode. When they both are put in suitable electrolyte containing soluble salt of same metal, the more basic metal remains in the solution and the less basic ones go to the anode mud.
Example : In refining of Cu At anode : (oxidation)
Cu → Cu2+ + 2e–
At cathode : (reduction)
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
Question 70.
Write down the reactions taking place in different zones in the blast furnace during the extraction of iron. How is pig iron different from cast iron? (Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Reactions occur in blast furnace in the extraction of iron from iron oxide ores. The following oxidations occur in different zones of furnace :

Pig iron differs from cast iron with respect to the carbon contents. Pig iron has nearly 4% carbon content and cast iron has nearly 3% carbon content. Cast iron is hard and brittle whereas pig iron is soft.
Question 71.
Answer the following :
(i) What is the role of cryolite in the metallurgy of aluminium?
(ii) Difference between roasting and calcination.
(iii) What is meant by the term ‘chromatography’? (Comptt. All India 2015)
Answer:
(i) The role of cryolite (Na3AlF6) is to lower the melting point of the mixture and brings conductivity.
(ii)
| Roasting | Calcination |
| 1. The process of heating ore in presence of excess of air.
2. It is used for concentration of sulphide ores. e.g. 2ZnS + 302 \(\stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow}\) 2ZnO + 2S02 |
1. The process of heating ore in limited supply or absence of air.
2. It is used for the concentration of carbonate ores. e.g. ZnC03 \(\stackrel{\Delta}{\longrightarrow}\) ZnO + C02↑ |
(iii) The term chromatography was originally derived from the Greek word ‘chroma’ meaning colour and ‘graphy’ meaning writing because the method was first used for the separation of coloured substances into individual components. Chromatography is a widely used process for separation, purification, identification and characterization of the different components of a mixture which are differently adsorbed on a suitable adsorbent.
Question 72.
Write the reactions taking place in different zones of the blast furnace to obtain Iron. (Comptt. All India 2015)
Answer:
Extraction of iron from iron ore in different zones of blast furnace :
(i) Lower zone (zone of heat absorption) :
Temperature 1423 – 1673 K.
The CO2 formed near upper layers reacts with the coke which reduces it into CO.
CO2 (g) + C(s) → 2CO (g)
(ii) Middle zone (zone of slag formation) :
Temperature 1123 K.
Here limestone (CaCO3) decomposes into CaO and CO2. The CaO acts as a flux which combines with silica to form fusible calcium silicate slag.
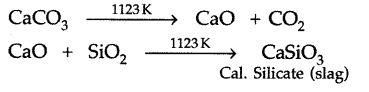
(iii) Upper zone (zone of reduction): Temperature 500 – 900 K.
Here ores are reduced to FeO by CuO.
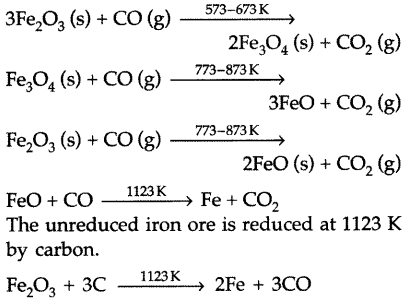
Question 73.
(i) Name the method of refining of metals such as Germanium.
(ii) In the extraction of Al, impure Al2O3 is dissolved in cone. NaOH to form sodium aluminate and leaving impurities behind. What is the name of this process?
(in) What is the role of coke in the extraction of » iron from its oxides? (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(i) Zone refining is used for refining of Germanium.
(ii) Leaching of Alumina or Bayer’s process.
(iii) Coke i.e., CO acts as a reducing agent in the extraction of iron from its oxides in the zone of reduction in blast fumance at 1123 K.
FeO + CO → Fe + CO2
Question 74.
(i) Name the method of refining of nickel.
(ii) What is the role of cryolite in the extraction of aluminium?
(iii) What is the role of limestone in the extraction of iron from its oxides? (All India 2016)
Answer:
(i) Mond’s Process.
(ii) The melting point of alumina is very high. It is dissolved in cryolite which lowers the melting point and brings conductivity.
(iii) Limestone decomposes in the blast fumance into CaO and CO2 where CaO acts as basic flux which combines with acidic impurities of the ore like silica i.e., SiO2 to form calcium silicate in the form of slag.
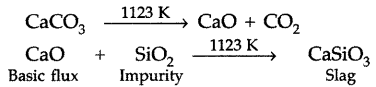
Question 75.
Describe the following :
(i) Role depressant in forth floatation process
(ii) Role of silica in the metallurgy of copper
(iii) Role of cryolite in the metallurgy of aluminium. (Comptt Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(i) To selectively prevent the formation of froth by one of the sulphide ore present in a mixture of sulphide ores.
(ii) To remove impurity FeO in the form of slag (FeSiO3)
FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3
(iii) Lowering down the melting point and increasing the conductivity.
Question 76.
Outline the principles of refining of metals by the following methods :
(i) Zone refining
(ii) Electrolytic refining
(iii) Vapour phase refining (Comptt. All India 2016)
Answer:
(i) Zone refining : Impurities are more soluble in the melt than element.
(ii) Electrolytic refining : More basic metal forms ions and are deposited on the cathode by passing electricity.
(iii) Vapour phase refining : Pure metal forms volatile compound with suitable reagent and the volatile compound is decomposed to give pure metal.
Question 77.
(a) Write the principle of method used for the refining of germanium.
(b) Out of PbS and PbCO3 (ores of lead), which one is concentrated by froth floatation process preferably?
(c) What is the significance of leaching in the extraction of aluminium? (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(a) For the refining of germanium, zone refining is used which is based on the principle that the impurities are more soluble in the melt then in the solid state of the metal.
(b) PbS (Lead sulphide) is concentrated by froth floatation process.
(c) The significance of leaching is to concentrate pure alumina from bauxite ore by digesting it with hot concentrated solution of NaOH to form sodium meta aluminate leaving behind impurities which then treated with CO2 and form hydrated alumina through precipitation.
Question 78.
Write the principles of the following methods:
(i) Vapour phase refining
(ii) Zone refining
(iii) Chromatography (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(i) Vapour phase refining of metals : Flere the impure metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected elsewhere which is then decomposed by heating at a higher temperature to give pure metal. The requirements are
- the metal should form a volatile compound with an available reagent.
- the volatile compound should be easily decomposable so that recovery is easy.
Example : Ni + 4CO \(\underrightarrow { 330-350K } \) Ni(CO)4
Ni(CO)4 4\(\underrightarrow { 450-470K } \) Ni + 4CO
(ii) Zone refining of metals: This method is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in the molten state of the metal (the melt) than in the solid state. In the process of zone refining, a circular mobile heater is fixed at one end of a rod of impure metal. As the heater moves, the molten zone of the mod also moves along with it. As a result, pure metal crystallizes out of the melt and the impurities pass to the adjacent molten zone. This process is repeated several times which leads to the segregation of impurities at one end of the rod. The end with impurities is cut off. Silicon, boron, , gallium etc. can be purified by this process.

(iii) Chromatography. This is the method used for the separation and purification of elements. It can also be used for testing the purity of a compound. The principle behind the chromatography is that different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an adsorbent.
Question 79.
Write the principle of the following:
(a) Zone refining
(b) Froth floatation process
(c) Chromatography (All India 2016)
Answer:
(a) Zone refining of metals: This method is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in the molten state of the metal (the melt) than in the solid state. In the process of zone refining, a circular mobile heater is fixed at one end of a rod of impure metal. As the heater moves, the molten zone of the mod also moves along with it. As a result, pure metal crystallizes out of the melt and the impurities pass to the adjacent molten zone. This process is repeated several times which leads to the segregation of impurities at one end of the rod. The end with impurities is cut off. Silicon, boron, , gallium etc. can be purified by this process.

(b) Froth floatation process. This method is used for removing gangue from sulphide ores. In this powdered ore is mixed with collectors (e.g., pine oils, fatty acids, etc.) and froth stabilisers (e.g., cresols, aniline) which enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles and froth stabilisation respectively.
As a result of which ore comes with froth and gangue remains in the solution.
(c) Chromatography. This is the method used for the separation and purification of elements. It can also be used for testing the purity of a compound. The principle behind the chromatography is that different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an adsorbent.
Question 80.
(a) Write the principle of vapour phase refining.
(b) Write the role of dilute NaCN in the extraction of silver.
(c) What is the role of collectors in the froth
floatation process? Give an example of a collector. (All India 2016)
Answer:
(a) Principle of vapour phase refining. Here the metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected elsewhere which on strong heating is decomposed to give pure metal.
The requirements are
- the metal should form a volatile compound with an available reagent.
- the volatile compound should be easily decomposable so that recovery is easy.
(b) NaCN acts as a leaching agent or oxidising agent, thus oxidising Ag to Ag+ which then combine with CN– ions to form respective soluble complex.
(c) Collectors enhance non-wettability of mineral particles in the froth floatation process. For example, pine oil, fatty acids, xanthates.
Question 81.
(a) Write the principle involved in the ‘vapour phase refining’ of metals.
(b) Write the name of the metal refined by each of the following processes :
(i) Mond process (ii) van Arkel method
(c) What is the role of depressant in froth floatation process? (Comptt. Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(a) Principle of vapour phase refining. Here the metal is converted into its volatile compound and collected elsewhere which on strong heating is decomposed to give pure metal.
The requirements are
- the metal should form a volatile compound with an available reagent.
- the volatile compound should be easily decomposable so that recovery is easy.
(b) (i) Ni (ii) Ti/Zr
(c) Depressants prevent the formation of froth with air bubbles of other sulphide ores.
Question 82.
(a) What is the principle behind ‘zone refining’ of metals? Name an element which is refined by this method.
(b) Write the name of the metal refined by each of the following processes :
(i) Distillation
(ii) Liquation (Comptt. Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(a) Zone refining of metals: This method is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in the molten state of the metal (the melt) than in the solid state. In the process of zone refining, a circular mobile heater is fixed at one end of a rod of impure metal. As the heater moves, the molten zone of the mod also moves along with it. As a result, pure metal crystallizes out of the melt and the impurities pass to the adjacent molten zone. This process is repeated several times which leads to the segregation of impurities at one end of the rod. The end with impurities is cut off. Silicon, boron, , gallium etc. can be purified by this process.

Germanium can be refined by zone refining method.
(b) (i) Zinc can be refined by distillation.
(ii) Lead can be refined by liquation.
Question 83.
(a) Write the principle involved in the following :
(i) Zone refining of metals
(ii) Electrolytic refining
(b) Name the metal refined by each of the following processes:
(i) Mond process
(ii) van Arkel Method (Comptt. All India 2016)
Answer:
(a) Zone refining of metals: This method is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in the molten state of the metal (the melt) than in the solid state. In the process of zone refining, a circular mobile heater is fixed at one end of a rod of impure metal. As the heater moves, the molten zone of the mod also moves along with it. As a result, pure metal crystallizes out of the melt and the impurities pass to the adjacent molten zone. This process is repeated several times which leads to the segregation of impurities at one end of the rod. The end with impurities is cut off. Silicon, boron, , gallium etc. can be purified by this process.

(ii) Electrolytic refining : Here the impure metal is made to act as anode and a strip of the same metal in pure form is used as cathode. When they both are put in suitable electrolyte containing soluble salt of same metal, the more basic metal remains in the solution and the less basic ones go to the anode mud.
Example : In refining of Cu At anode : (oxidation)
Cu → Cu2+ + 2e–
At cathode : (reduction)
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
(b)
(i) Nickel
(ii) Titanium
Question 84.
(a) Write the principle of electrolytic refining.
(b) Why does copper obtained in the extraction from copper pyrites have a blistered appearance?
(c) What is the role of depressants in the froth floatation process? (All India 2016)
Answer:
(a) Electrolytic refining. Here the impure metal is made to act as anode and a strip of the pure metal is used as cathode. When they both are put in suitable electrolyte containing soluble salt of same metal and electricity is passed, metal ions from electrolyte are deposited at the cathode as pure metal and the impure metal from the anode is dissolved into the electrolyte in the form of ions. The impurities present in the impure metal gets collected below the anode as anode mud.
(b) Copper obtained from copper pyrites have a blistered appearance due to the evolution of SO2 and so it is called blister copper.
(c) To selectively prevent the formation of froth by one of the sulphide ore present in a mixture of sulphide ores.