Globe Latitudes and Longitudes Class 6 Extra Questions Social Science Geography Chapter 2
NCERT Extra Questions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Globe Latitudes and Longitudes
Globe Latitudes and Longitudes Class 6 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Define a latitude.
Answer:
Angular distance from the equator on both sides (North and South) is called latitude. Latitudes are 180°-90° north of equator and 90° south of equator.
Question 2.
What are the latitudes of North and South Poles?
Answer:
The angular distance of the North Pole and South Pole from the equator is 90°. So, the latitude of the North Pole is 90°N and that of South Pole is 90°S.
Question 3.
What is the difference between the Parallels of Latitude and the Meridians of Longitude?
Answer:
The difference between the Parallels of Latitude and the Meridians of Longitude is given below:
| Parallels of Latitude |
Meridians of Longitude |
| 1. These are imaginary circles. They run parallel to the Equator in it’s North and South. | 1. These are imaginary semi-circles. They run from the North Pole to the South Pole. |
| 2. Their number is 180. | 2. Their number is 360. |
Question 4.
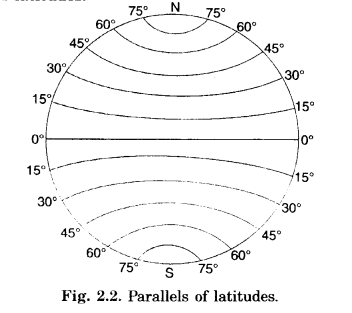
What are parallels of latitudes?
Answer:
Parallels of Latitudes. The equator is the line of 0° latitude. All the lines of latitudes are parallel to the equator. Hence they are called parallels of latitudes.
Globe Latitudes and Longitudes Class 6 Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What does the Earth look like? What is its shape?
Answer:
- The Earth looks like an orange. It bulges on the sides and is slightly flat on the top and at the bottom.
- Its true shape is geoid which means earth – like shape.
- A globe is the three dimensional model of the Earth.
Question 2.
What is a globe? What are its types?
Answer:
Globe is the three dimensional model representing the true shape of the Earth.
Globes are of various sizes and types:
- Big Size Globe. Can not be carried easily.
- Small Pocket Globe
- Balloon Like Globe. They can be inflated and are handy and carried with ease.
Question 3.
What is the use of Globes?
Answer:
- On globes, countries, continents and oceans are shown in their correct shape.
- Distance and directions are also shown correctly on the globe.
- The extent of relief features is correct.
Question 4.
What are longitudes?
Answer:
Longitudes:
- Angular distance from the Prime Meridian is termed as longitude.
- Lines joining the North Pole and the South Pole are called the lines of longitude.
- They are also called meridian because noon occurs at the same time at places located on a line of longitude.
Question 5.
Define local time.
Answer:
Local Time:
- Local time is calculated by the position of the Sun at noon of a given place.
- It bases on the local meridian passing through that place.
When the Sun is exactly overhead at that meridian, it is 12 noon. - The places lying North and South on the same meridian will have the same local time. On the otherhand the places lying East or West of that meridian have different local times.
Globe Latitudes and Longitudes Class 6 Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
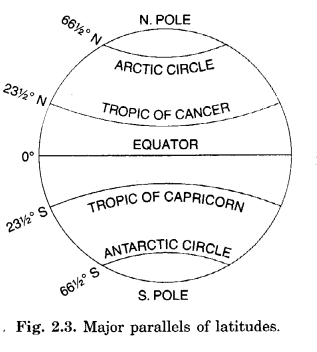
Describe important parallels of latitudes. Answer: Important Parallels.
Equator:
- Equator is the longest parallel running in the East-West direction.
- It is a great circle.
Tropic of Cancer:
It is the parallel of 23 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)° N in the Northern hemisphere.
Tropic of Capricorn:
It is the parallel of 23 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)° S in the Southern hemisphere.
Arctic Circle:
It lies at 66\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)° north of the equator.
Antarctic Circle:
It lies at 66 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)° south of the equator.
90° Parallel:
It is shown by a point.
Its length is zero.
North Pole:
It is at 90° north of equator.
South Pole:
It is at 90° south of equator.
Question 2.
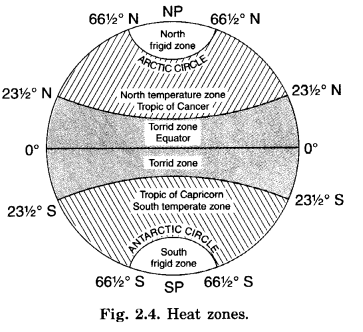
Describe major heat zones of the Earth.
Answer:
Heat Zones of the Earth.
1. Torrid Zone:
- Torrid means hot.
- This zone receives the maximum amount of heat throughout the year, because the rays of the Sun fall vertically on this zone.
- This zone is located between the Tropic of Cancer (23\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)° N) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)° S).
2. Temperate Zone:
- The temperate zones lie in both the hemispheres.
- North temperate zone lies in northern hemisphere between Tropic of Cancer and Arctic Circle.
- South temperate zone lies in the southern hemisphere between the Tropic of Capricorn and Antarctic Circle.
- These zones are neither too hot nor too cold.
3. Frigid Zone:
- Frigid means cold.
- Beyond the Arctic Circle and Antarctic Circle temperatures are very low and the climate is very cold.
- This is due to the extreme slanting of the Sun’s rays.
- The North Frigid Zone lies between the Arctic Circle (66\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)° N) and the North Pole in the Northern hemisphere.
- The South Frigid Zone lies between Antarctic Circle (66\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)°S) and the South Pole in the Southern hemisphere.
Question 3.
Explain major features of meridians.
Answer:
The following are the major features of meridians:
- Meridians are equal in length.
- The longitude running through the Greenwich pear London was first chosen as the Prime Meridian (Prime Meridian means chief or main meridian) having noon at the same time at all places on this line.
- It is the 0° longitude.
- It divides the earth into eastern and western hemispheres.
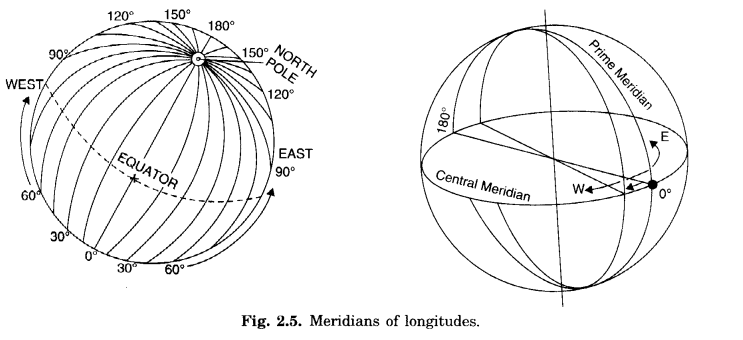
- They are semicircles.
- They are 360 in all -180 in the East and 180 in the West of Prime Meridian. 180°E and 180° W is one longitude.
Question 4.
How do longitudes help us in calculating time?
Answer:
Longitude and Time.
- Longitudes help us to calculate time.
- Time is measured by the movement of the Earth.
- The Earth moves on its axis from West to East. It is called rotation.
It takes 24 hours for the earth to complete one rotation:
- This means in 24 hours the Earth completes 360°.
- Hence, it takes about 4 minutes for crossing one degree of longitude (or it takes one hour in crossing 15 degrees of longitude)
- Accordingly, the Earth has been divided into 24 time zones of one hour each.
- This means each place has different time of Sunrise and Sunset.
- Places east of the Greenwich Meridian experience day or sunrise earlier than the places lying west of this Meridian. In other words time is ahead in the east than that in the west, at the rate of 4 minutes per degree of longitude.
Question 5.
What is Standard Time?
Answer:
Standard Time:
- Local time of a place is based on the longitude of that place. It means places situated on different meridians will have different local tidies.
- It creates much confusion and problem for people to function.
- To solve these problems every country fixes its central meridian, which is considered the standard meridian
- of that country.
The local time of this meridian is considered standard for the whole country. It is called standard time. - In India the longitude of 82\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)°E (82° 30° E) is treated as the standard meridian.
- The local time of this meridian is followed all over the country.
- This is known as Indian Standard Time (IST).
- Through an international agreement, the local time of all places is linked to the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Different places have different times.
Question 6.
Kabeer lives in a small town near Bhopal. He tells his friend Alok that they will not be able to sleep tonight. A day and night cricket match between India and England had started, at 2 p.m. in London. This means that the match would finish well after 1 a.m. in the night. The match according to Indian Standard Time (1ST) has started at 7.30 p.m.
Do you know what is the time difference between India and England?
Answer:
- Vindhyachal (Mirzapur Distt., U.P.) -India is located east of Greenwich at 82°30′ E. Its time is 5 hours and 30 minutes ahead of Greenwich (London) (The GMT).
- So it will be 5.30 p.m. in India when it is 12.00 noon at London.
- When the cricket match starts at London at 2 p.m. The time of match-start in India is 7.30 p.m.
- Kabeer will not be able to sleep that night because the match will be seen in India during the night.
Question 7.
Why do we have Standard Time?
Answer:
- Places located on a meridian of longitude have the same time. It is called local time.
- Time at a meridian of longitude differs from the time of another meridian of longitude by 4 minutes (either less by 4 minutes or more by 4 minutes).
- The local time of Dwarka (Gujarat) lags behind by 1 hour 45 minutes from that of Dibrugarh (Assam).
- A person going from west to east will have to advance his/her watch by 4 minutes after crossing a meridian. On the other hand, a person going from east to west will have his/her watch moved backwards by 4 minute at each meridian. This creates problem for him.
- To remove this problem the local time of a central meridian of the country is assumed standard for the whole country. It is called Standard Time.
- All the watches indicate the same time in all parts of the country.
- People do not have to move their watches advanced or backed.
- All the work is done according to this time.
- In India the local time of 82°30′ E is taken as standard for the whole country. It is called Indian Standard Time (IST).
Globe Latitudes and Longitudes Class 6 Extra Questions Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
What is a globe?
(a) Earth
(b) True model of the earth
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
True model of the earth
Question 2.
Which of the following are shown on the globe in their true size?
(a) Countries
(b) Continents
(d Oceans
(d) All of these
Answer:
All of these
Question 3.
What is called a needle fixed through the globe in a tilted manner?
(a) Orbit
(b) Axis
(c) Latitude
(d) Longitude
Answer:
Axis
Question 4.
What divides the earth into two equal parts. The northern hemisphere and the southern hemisphere?
(a) Tropic of Capricorn
(b) Tropic of Cancer
(c) Equator
(d) Arctic Circle
Answer:
Equator
Question 5.
Name one of the following parallels of latitudes as Tropic of Cancer.
(a) 0°
(b) 23° 30′ S
(c) 23° 30′ N
(d) 66° 30′ N
Answer:
23° 30′ N
Question 6.
Between which parallels of latitudes is the Torrid Zone situated?
(a) Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn
(b) Tropic of Cancer and Arctic Circle
(c) Tropic of Capricorn and Antarctic Circle
(d) None of these
Answer:
Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn
Question 7.
Which of the following zone is situated between 66°30′ S and poles?
(a) Torrid Zone
(b) Temperate Zone
(c) Frigid Zone
(d) All of these
Answer:
Frigid Zone
Question 8.
Which of the following is called the Prime Meridian?
(a) 23° 30′ N
(b) 23° 30′ S
(c) 82° 30′ E
(d) 0° longitude
Answer:
0° longitude
Question 9.
What divides the earth into the eastern and the western hemispheres?
(a) Equator
(b) Prime Meridian
(c) 82° 30′ E
(d) None of these
Answer:
Prime Meridian
Question 10.
In which ocean are Tonga Islands situated?
(a) Indian Ocean
(b) Atlantic Ocean
(c) Pacific Ocean
(d) None of these
Answer:
Pacific Ocean
Question 11.
On which parallel of latitude is Mauritius located?
(a) 10° N
(b) 20° S
(c) 23° 30′ S
(d) 0°
Answer:
20° S
12. Which place is located at the intersection of 26° N and 90° E?
(a) Dhubri
(b) Mauritius
(c) Tonga
(d) Meerut
Answer:
Dhubri
Question 13.
What time does earth take, rotating from one degree longitude to next longitude?
(a ) 4 minutes
(b) 15 minutes
(c) 10 minutes
(d) None of these
Answer:
4 minutes
Question 14.
What is the time difference between the time of Dwarka in Gujarat and time of Dibrugarh in Assam?
(a) 2 hours
(b) 1 hour and 30 minutes
(c) hour and 45 minutes
(d) 5 hours and 30 minutes
Answer:
hour and 45 minutes
Question 15.
The local time of 82Q30’ E longitude is taken as a standard throughout India. It is known as
(a) local time of India
(b) Indian Standard Time (IST)
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer:
Indian Standard Time (1ST)
Question 16.
The time of India is ahead of that of England by
(a) 2 hours
(b) 5 hours and 30 minutes
(c) 3 hours
(d) none of these
Answer:
5 hours and 30 minutes