b vGeography Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 14 Human Settlements is part of Geography Class 12 Important Questions. Here we have given Geography Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 14 Human Settlements.
Geography Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 14 Human Settlements
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
How is the level of urbanisation measured in India? Delhi 2015
Answer:
The level of urbanisation is measured by the percentage of urban population to the total population.
Question 2.
What two factors mostly helped in the development of ancient towns in India? Delhi 2015
Answer:
The two factors that mostly helped in the development of ancient towns in India are:
- Religion
- Culture
Question 3.
Give any two examples of ancient towns of India. Delhi 2014
Answer:
Varanasi, Pataliputra/Patna, Mathura, Allahabad are examples of ancient towns of India.
Question 4.
Give an example of ancient historical towns from Bihar, AH India 2014
Answer:
Patna/Pataliputra, Nalanda, Kaushambi are the examples of ancient historical towns from Bihar.
Question 5.
Give any two examples of mining towns in India. Delhi 2013
Answer:
Jharia, Bokaro, Raniganj, Digboi etc are examples of mining towns in India.
Question 6.
Give the meaning of clustered rural settlement of India. Delhi 2013
Answer:
It is a rural settlement where a number of families live close proximity to each other. This living place is not surrounded by farms, barn or pastures.
Question 7.
Name any two metropolitan cities of Andhra Pradesh. Delhi 2012
Answer:
Hyderabad and Visakhapatnam are the metropolitan cities of Andhra Pradesh.
Question 8.
Give the meaning of human settlement. Delhi 2011
OR
What is the meaning of Human settlement? Delhi 2008
Answer:
Human settlement refers to the cluster or group of human houses. These houses may vary from a small hut to a large bungalow or any type or size.
Question 9.
Name the metropolitan city of Karnataka state as per 2001 census. All India 2011
Answer:
Bengaluru is the metropolitan city of Karnataka state as per 2001 census.
Question 10.
Which class of cities has the highest percentage of the urban population in India? Delhi 2010
Answer:
Class I cities has the highest percentage of the urban population in India.
Question 11.
Which class of cities has the largest number of towns and cities in India? All India 2010
Answer:
Class IV cities have the largest number of towns and cities in India.
Question 12.
Name the largest metropolitan city of Uttar Pradesh. Write its population according to the census, 2001. Delhi 2009
Answer:
Kanpur is the metropolitan city of Uttar Pradesh. According to census 2001, its population is 26.9 lakh.
Question 13.
Name the largest metropolitan city of Madhya Pradesh. What was its population according to the census, 2001? All India 2009
Answer:
The largest metropolitan city of Madhya Pradesh in Indore. According to census 2001, its population is 16.4 lakh.
Question 14.
What is the meaning of rural settlement? AH India 2008
Answer:
Rural settlements are basically related to land-based activities. Hamlets and villages are examples of rural settlements. They are scattered and smaller in size. The main activities of the dwellers are primary activities, especially agriculture.
3 Marks Questions
Question 15.
Many of the modern towns of India were developed during the period of British. Explain in brief. Delhi 2016
OR
How have modern towns developed in India? Explain. All Indio 2015
Answer:
The British and other Europeans have developed a number of towns in India. Starting their foothold on coastal locations, they first developed some trading ports such as Surat, Daman, Goa, Pondicherry (Puducherry), etc. The British later consolidated their hold around three principal nodes i.e. Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata. Towns based on modern industries also evolved after 1850.
For their domination, they established their administrative centres, hill towns as summer resorts and added administrative and military areas. Railways for their administrative purposes equipped India on way of modernity.
Question 16.
Differentiate between ‘hamleted’ and ‘Dispersed’ rural settlement of India. Delhi 2016
OR
Explain any three characteristics each of hamleted and dispersed rural settlement in India. Delhi 2013
OR
What are hamleted settlements? Mention any two areas of India where such settlement are found. Delhi 2013
Answer:
The difference between hamleted settlements and dispersed settlements are as follows:
| Hamleted Settlement | Dispersed Settlement |
| It is a fragmented physical unit of settlement. | It is isolated forms of huts or hamlets in remote jungles. |
| Units are locally called Panna, para, Palli, nagla, Dhani etc | Caused by extreme fragmentation of terrain and land resources. |
| Found in the middle and lower Ganga plain, Chhattisgarh and lower valleys of the Himalayas. | Found in the areas of Meghalaya, Uttaranchal, Himachal Pradesh and Kerala. |
Question 17.
What makes rural settlement different from urban settlement in India? Explain. Delhi 2015
OR
Differentiate between rural and urban settlements of India in three points. Delhi 2014
Answer:
The differences between rural and urban settlement are as follows:
| Basis | Rural Settlement | Urban Settlement |
|
Economic Activities |
The major economic activities in rural areas are agriculture and other primary activities. | The urban settlement is specialised in industries and services. |
| Dependency | They are dependent on natural resources mainly land for their income. | They provide various types of services like transport and communication, etc. |
| Agricultural and other products in rural areas support industries of an urban area. Rural areas provide raw material to the industries. | On return, cities provide manufactured goods to rural areas and also to the people of cities. | Inter-relationships |
| social life | Social bonds in rural areas are stronger and life is simple. | Social bonds in urban areas are formal and life is complex, fast and surrounded with |
Question 18.
Explain any three physical factors responsible for different types of rural settlements in India. Delhi 2015
Answer:
Physical factors which are responsible for different types of rural settlements in India are:
Water Supply Settlements need water, they often locate on wet point sites for this. For e.g. in Rajasthan, scarcity of water has forced people to live in compact villages for maximum utilisation of available water resources.
Climate People usually prefer areas which have favourable climatic conditions. Harsh climate like very hot and cold regions have less or no settlements there. For e.g. coastal plains have favourable climate thus, are densely populated regions.
Nature of Terrain Nature of terrain plays an important role in determining the shape and size of rural settlements.
For e.g., plain areas have compact and larger settlements with dense population, whereas mountainous areas have scattered and hamleted rural settlements. Meghalaya, Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh have such types of rural settlement.
Question 19.
What are metropolitan cities and megacities? Give two examples of each of metropolitan cities and mega cities from India. Delhi 2015
Answer:
Metropolitan Cities Cities that have population more than one million but less than 5 million are considered as a metropolitan or metro city. For e.g. Kanpur, Nagpur, Nasik, Madurai, Jaipur, etc.
Mega Cities Cities that have population more than 5 million are considered as ‘megacities’ or ‘megalopolis’. For e.g. Greater Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai, Bangaluru, Hyderabad, etc.
Question 20.
Explain any three characteristics of clustered rural settlement of India. Delhi 2015
OR
What type of rural settlements are generally found in the fertile alluvial plains of India? Mention any two features of such type of settlements. All India 2010
Answer:
Clustered or compacted settlements are generally found in the fertile alluvial plain.
The important features of these settlements are as follows:
- In this type of rural settlements, space between the houses are less or they have no space. The houses in this type of settlement are closely built up often they share walls of their houses.
- People live in a specific area of settlement. This living place can be surrounded by farms, barn or pastures. It compact settlements, many district settlement patterns can take place such as rectangular, linear, triangular, radial, etc.
- This type of settlements generally develops in riverine fertile plain as they are more concentrated with a population.
Question 21.
Explain any three features of semi-clustered rural settlements of India. All Indio 2015
OR
Mention any three characteristics of semi-clustered rural settlements of India. Delhi 2010
Answer:
The characteristics of semi-clustered settlements in India are as follows:
- Semi clustered settlements are developed by the concentration of houses in a special or restricted area of a dispersed settlement. These settlements can also be developed by the division of a large clustered settlements.
- Semi clustered settlement can also be developed when a particular group start to live far from the centre or main village. In this condition, the dominant community or land owning community captures the most important part in the main village and may force others to live away.
- In India, these types of settlements are mostly found in the plain of Gujarat and Rajasthan.
Question 22.
Give the meaning of ‘dispersed settlement’. Explain any two reasons for the development of such settlement in India. Delhi 2014
Answer:
In this type of settlements, space between the houses is more. There are some scattered houses in these settlements. In India, the dispersed settlements are found in the form of few huts in remote jungles, hills with farms or pastures. Reasons for the development of such settlements are:
- Due to the extremely fragmented nature of terrain settlements developed.
- Especially tribal people use to live in these isolated huts as their livelihood is fully dependent on nature.
Question 23.
What are ancient towns ? Give four examples of ancient towns of India. Delhi 2012
Answer:
Ancient towns of India have historical background of over 2000 years. These towns are emerged during the ancient period and were developed by the important ancient kings. Most of these were temple towns. Later, they had become the hub of religion and cultures. Varanasi, Prayag (Allahabad), Patliputra (Patna), Madurai, etc are some of the ancient towns that emerged in India during the ancient period.
Question 24.
Explain the evolution of towns in India in three points, AM India 2012
OR
Classify Indian towns on the basis of their evolution in three different periods. Name one town of each period. All Indio 2009
Answer:
The towns of India can be classified into the following groups on the basis of their evolution in different periods:
Ancient Towns These towns of India have historical background of over 2000 years. Varanasi, Prayag (Allahabad), Patliputra (Patna) Madurai, etc were developed by the ancient kings.
Medieval Towns These towns were developed during the medieval period of India by king and Sultans of India as their headquarter and making their administration strong, e.g. Delhi, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Lucknow, Agra etc.
Modem Towns These towns were developed by the Britishers and other Europeans in India like Surat, Daman and Goa, Kolkata, Mumbai, etc.
Later, after independence, some towns like Bhilai, Durgapur, Chandigarh, Gandhinagar were established.
Question 25.
Explain any three factors that determine the type of rural settlements in India. Delhi 2on
Answer:
Types of rural settlements in India are determined by the following factors:
Physical Factors It includes nature of the terrain, altitude from sea level, climate and availability of water.
Cultural and Ethnic Factors Among these factors, social structure, caste and religion are important in India.
Security Factors It includes protection from thefts and robbers.
Above factors make Indian, settlements different in the world. Rural settlements can be of few houses in India to thousands of houses. The form and structure of rural settlement are different in different parts of India.
Question 26.
Name any three factors that determine the clustered or compact rural settlement in India. All India 2011
Answer:
The three factors that determine the clustered or compact moral settlement in India are as follows:
Fertile Alluvial Plain It provides a plain surface where houses are easy to build. Plain can support more population. Fertile plain provides a more agricultural output which attracts more population to live and engage in agriculture. More concentration of population resulted in a compact or clustered rural settlements.
Water It is another reason that can cause people to live in a compact condition. Scarcity of water force people to live together and maximum utilise the available water, e.g. compact settlements of Rajasthan.
Security or Defence It is another reason that causes people to live in a compact settlement in more concentrated conditions, e.g. people of Bundelkhand region and Nagaland live in compact settlements to avoid robbery and theft.
Question 27.
Distinguish between clustered and dispersed rural settlements of India by stating three points of distinction of each. All India 2008
Answer:
Differences between clustered and dispersed rural settlements of India are as follows:
| Basis | Clustered Rural Settlements | Dispersed Rural Settlements |
|
Spacing between houses |
Space between the houses is less. They are closely built up. | Space between the houses is more. They are scattered in areas. |
| Areas | These settlements are usually seen in the Northern Plains of India. | These settlements can be seen in remote hilly and mountainous areas or within the forests. |
|
Settlement patterns |
In clustered settlements, different types of settlement patterns emerge like rectangular, linear, radial and circular. | In dispersed settlements, no pattern emerges because of the scattering of houses. Houses are scattered in the overall area of the settlement. |
Map-Based Questions
Question 28.
Study the map of India given below carefully and answer the questions that follow. Delhi 2012
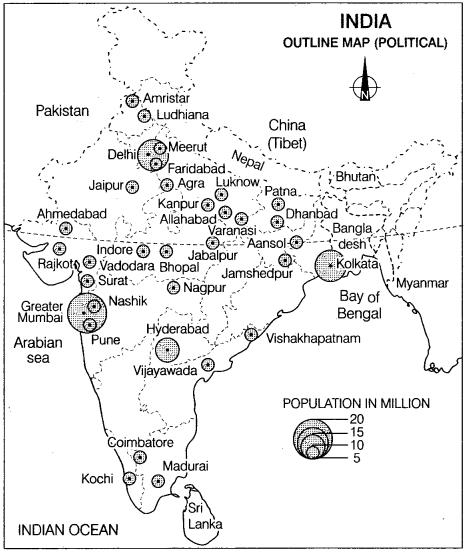
(i) Define the term metropolitan city.
(ii) Which state of India has the largest number of metropolitan cities? Name any two northern states of India which have no metropolitan city.
OR
(i) How many metropolitan cities are there in Maharashtra?
(ii) Which one of them is the largest metropolitan city?
(iii) Name the Easternmost metropolitan city of India as shown in the map.
OR
(i) Name the Northernmost, Southernmost and Westernmost metropolitan cities of the country and also name the states to which they belong.
Answer:
(i) Cities that have population more than one million but less than 5 million are considered as ‘metropolitan’ or ‘metro city’.
(ii) Uttar Pradesh has the largest number of metropolitan cities.
(iii) Jammu and Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh, are the Northern states of India which do not have any metropolitan city.
OR
Answer:
(i) There are four metropolitan cities in the state of Maharashtra.
(ii) Among the metropolitan cities of Maharashtra state. Greater Mumbai is the largest one.
(iii) It is a Kolkata metropolitan city.
| Metropolitan cities of India | States |
| Northernmost -Amritsar | Punjab |
| Southernmost – Madurai | Tamil Nadu |
| Westernmost – Rajkot | Gujarat |
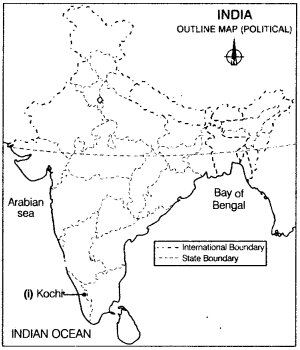
Question 29.
In the political outline map of India, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols.
(i) Which is the metropolitan city of Kerala? All Indio 2012
Answer:
(i) Kochi is the metropolitan city of Kerala state.
Data Based Questions
Question 30.
Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow.
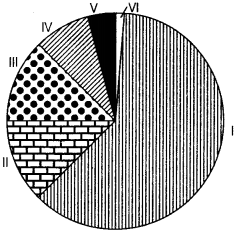
(i) Into how many classes are urban centres classified by the census of India?
(ii) Which class of urban centres has the largest urban population?
(iii) Which class of urban centres has the lowest urban population? Delhi 2008
OR
(i) Which class of cities has the highest percentage share in the total urban population?
(ii) Which class of cities has the second rank in the total population?
(iii) What is the population size of the second (II) class of cities? Delhi 2008
OR
(i) Find out percentage share of the urban population of class I cities from the diagrAnswer:
(ii) Which class of cities has the least percentage of total urban population?
(iii) What is the population size of class V cities? Delhi 2008
Answer:
(i) Census of India classifies urban centres into six classes.
(ii) The class I urban centres has the largest urban population.
(iii) Class IV urban centres have the lowest urban population.
OR
(i) Class I city has the highest percentage share in the total urban ‘ population.
(if) Class III city has the second rank in the total urban population.
(iii) The population size of the second (II) class of cities is from 50,000 – 99,999 persons.
OR
(i) The percentage share of the urban population of class I cities is 61.48%
(ii) Class VI of cities has the least percentage of the total urban population about 0.29%
(iii) The population size of class V cities is from 5000-9,999 persons.
Value Based Questions
Question 31.
“To earn livelihood people build houses and other structures and make their control over some areas and resources.” Identify the values given in the statement.
Answer:
Following value can be:
- Economic welfare
- Community relation
- Social structure
Question 32.
“Rural settlement are mainly smaller in size and sparsely spaced. The people of these settlements are mainly engaged in primary activity”. Identify the values which lead to the development of the rural settlement.
Answer:
Following values can lead to the development of rural settlement:
- Economic awareness
- Livelihood generation
- Family bonds
We hope the Geography Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 14 Human Settlements help you. If you have any query regarding Geography Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 14 Human Settlements, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.