Class 11 Geography Notes Chapter 2 The Origin and Evolution of the Earth
Many hypotheses were put forth by different philosophers and scientists regarding the origin of the earth.
One of the earlier and popular arguments was by German philosopher Immanuel Kant which was revised by mathematician Laplace in 1796. It is known as Nebular Hypothesis. According to this hypothesis the planets were formed out of a cloud of material associated with a youthful sun, which was slowly rotating.
In 1900, Chamberlain and Moulton considered that a wandering star approached the sun. As a result, a cigar-shaped extension of material was separated from the solar surface. As the passing star moved away, the material separated from the solar surface continued to revolve around the sun and it slowly condensed into planets. Later on, the arguments considered of a companion to the sun to have been coexisting. These arguments are called binary theories.
The most popular argument regarding the origin of the universe is the Big Bang Theory. It is also called expanding universe hypothesis. The Big Bang Theory considers the following stages in the development of the universe.
- In the beginning, all matter forming the universe existed in one place in the form of a“tiny ball” (singular atom) with an unimaginably small volume, infinite temperature and infinite density.
- At the Big Bang the “tiny ball” exploded violently. This led to a huge expansion. It is now generally accepted that the event of big bang took place 13.7 billion years before the present.
- Within 300,000 years from the Big Bang, temperature dropped to 4,500 K (Kelvin) and gave rise to atomic matter. The universe became transparent.
A galaxy contains a large number of stars. Galaxies spread over vast distances that are measured in thousands of light-years. The diameters of individual galaxies range from 80,000-150,000 light years.
Akash Ganga or the milky way, our galaxy started to form by accumulation of hydrogen gas in the form of a very large cloud called nebula. Eventually, growing nebula develops localised clumps of gas. These clumps continue to grow into even denser gaseous bodies, giving rise to formation of stars. The formation of stars is believed to have taken place some 5-6 billion years ago.
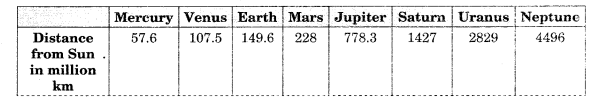
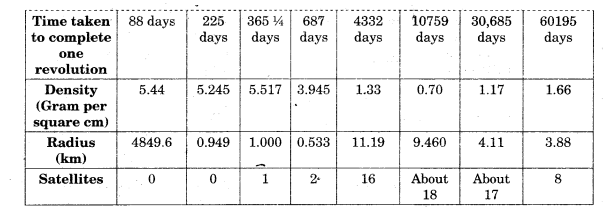
Our Solar system consists of eight planets. The nebula from which our Solar system is supposed to have been formed, started its collapse and core formation some time 5-5.6 billion years ago and the planets were formed about 4.6 billion years ago. Our solar system consists of the sun (the star), 8 planets, 63 moons, millions of smaller bodies like asteroids and comets and huge quantity of dust-grains and gases.
The Solar System:
The moon is the only natural satellite of the’ earth. It is now generally believed that the formation of moon, as a satellite of the earth, is an outcome of ‘giant impact’ or what is described as “the big splat”. A bbdy of the size of one to three times that of mars collided into the earth sometime shortly after the earth was formed. It blasted a large part of the earth into space. This portion of blasted material then continued to orbit the earth and eventually formed into the present moon about 4.44 billion years ago.
There are three stages in the evolution of the present atmosphere. The first stage is marked by the loss of primordial atmosphere. In the second stage, the hot interior of the earth contributed to the evolutipn of the atmosphere. Finally, the composition of the atmosphere was modified by the living world through the process of photosynthesis.
10. Sometime around 3,800 million years ago, life began to evolve. However, around 2,500-3,000 million years before the present, the process of photosynthesis got evolved. Life was f confined to the oceans for a long time.
Geological Time Scale:
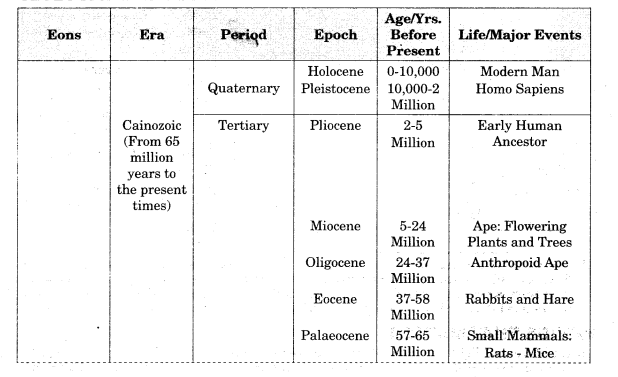
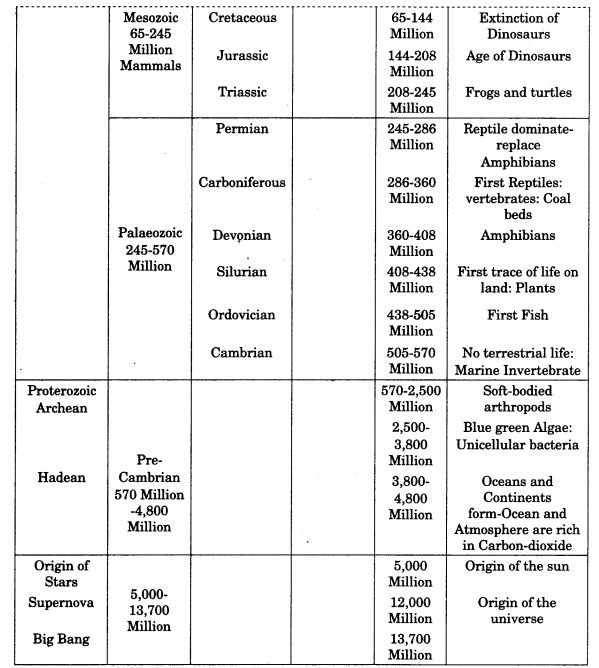
The record of life that existed on this planet in different periods is found in rocks in the form of fossils. The microscopic structures closely related to the present form of blue algae have been found in geologicad formations much older than some 3,000 million years. It can be assumed that life began to evolve sometime 3,800 million years ago.
Class 11 Geography Notes Chapter Important Terms:
- Light Year: A light year is equal to the number of kilometers traveled by light per second. It is a measure of distance and not of time. Light travels at a speed of 300,000 km/second. Therefore, the distances the light will travel in one year is taken to be as one light year.
- Planetesimals: The gas cloud starts getting condensed and the matter around the core develops into small- rounded objects. These small-rounded objects by the process of cohesion develop into what is called planetesimals.
- Universe: All matter, energy, heavenly bodies, and all that is there in space is as a group called the universe.
- Galaxy: Galaxy is a cluster of millions of stars and solar systems.
- Outer Planets: Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune and Pluto are called Outer Planets.
- Inner Planets: Mercury ,Venus, Earth and Mars are called Inner Planets.
- Big Bang Theory: The Big Bang Theory, also called as expand universe hypothesis. Edwin Hubble in 1920 provided the evidence that the universe is expanding. This theory is most universally accepted regarding origin of the earth.
- Binary theory: It is the principle of the origin of the earth given by Chamberlain and Moulton.
- Solar System: It consists of the sun, planets and their satellites and various other smaller heavenly bodies such as asteroids, comets and meteors.
- Nebular Hypothesis: It was a theory related to origin of the earth given by Immanuel Kant in 1755 and revised by Laplace in 1796.
- Nebula: Slow circular moving gaseous clouds are called nebula.
- The big splat: The origin of the moon as a satellite of the earth is the result of big collision which is called “the big splat”.
- Differentiation: The process through which the earth forming material got separated into different layers is called differentiation.
- Dwarf Planet: According to International Astronomical Union (IAU) on August 24,2006, a planet is a celestial body that
- orbits around the sun
- has sufficient mass so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape. The non-satellites bodies fulfilling these two rules are called dwarf planets. Pluto is now considered a dwarf planet. Ceres, Eris, Makemake, Haumea are some other dwarf planets.
- Jovian: Jovian means jupiter-like.
- Akash Ganga: Akash Ganga or milky way is the name of the galaxy to which our earth belongs.
- Expansion of Universe: Expansion of universe means increase in the distance between galaxies.