Heredity and Evolution Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
In peas, a pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with a pure short plant (tt). The ratio of pure tall plants to pure short plants in F2 generation will be:
(a) 1: 3
(b) 3:1
(c) 1:1
(d) 2:1
Answer:
(c) 1:1
Explanation: The genotype ratio of F2 generation is: TT: Tt: tt = 1: 2: 1. Therefore, the ratio of TT and tt plants of F2 generation will be the same.
Question 2.
Two pink-colored flowers on crossing resulted in 1 red, 2 pink, and 1 white flower progeny. The nature of the cross will be:
(a) Double fertilization
(b) Self-pollination
(c) Cross-fertilization
(d) No fertilization
Answer:
(c) Cross-fertilization
Explanation: The nature of the cross will be cross fertilization, which is the transfer of pollen from one plant to the stigma of flower; borne on a different plant of the same species.
Related Theory:
- Self-pollination: Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower of the same plant.
- Cross-pollination: Transfer of pollen grains from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower.
- Double fertilization: This process occurs when one male nucleus fertilizes (fuses) with the egg cell to form a zygote cell and the other male nucleus fuses (fertilizes) with two polar nuclei to cause triple fusion. These two types of fertilization take place at the same time in the ovule of the plant.
Question 3.
In human males, all the chromosomes are paired perfectly except one. These unpaired chromosomes are:
(I) Large chromosome
(II) Small chromosome
(III) Y chromosome
(IV) X chromosome
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (III) and (II)
(c) (III) and (IV)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 4.
Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) For every hormone there is a gene.
(b) For every protein there is a gene.
(c) For production of every enzyme there is a gene.
(d) For every molecule of fat there is a gene.
Answer:
(d) For every molecule of fat there is a gene. Explanation: A section of DNA that provides information for one protein is called the gene for that protein. Hormones and enzymes are proteins, and the formation of any particular protein is controlled by a particular gene. Fat biosynthesis occurs through metabolic reaction. They are not related to genes.
Question 5.
Which one is a possible progeny in F2 generation of purebred tall plant with round seed and dwarf plant with wrinkled seeds?
(a) Tall plant with round seeds
(b) Tall plant with wrinkled seeds
(c) Dwarf plant with round seed
(d) All of the above
Question 6.
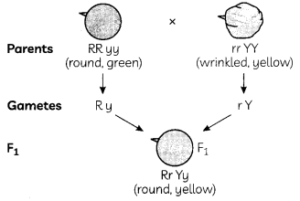
If a round, green-seeded pea plant (RR yy) is crossed with wrinkled, yellow seeded pea plant, (rr YY), the seeds production in the F1 generation are:
(a) Round and yellow
(b) Round and green
(c) Wrinkled and green
(d) Wrinkled and yellow
Answer:
(a) Round and yellow
Explanation: The cross between RR yy and rr YY seeds will obtain RrYy offspring which will exhibit round and yellow phenotype, as these traits are the dominant ones.
Question 7.
A zygote which has an X chromosome inherited from the father will develop into a:
(a) Boy
(b) Girl
(c) X chromosome does not determine the sex of a child
(d) Either boy or girl
Answer:
(b) Girl
Explanation: Humans follow XX- XY mechanism of sex determination i.e., women are XX while men are XY. All children will inherit an X chromosome from their mother regardless of whether they are boys or girls. Thus, the sex of the children will be determined by what they inherit from their father. A child who inherits an X chromosome from her father will be a girl and the one who inherits a Y chromosome from him will be a boy.
Question 8.
Select the incorrect statement:
(a) The frequency of certain genes in a population change over several generations resulting in evolution.
(b) The reduction in the weight of an organism due to starvation is genetically controlled.
(c) Low weight parents can have heavy weight progeny.
(d) Traits which are not inherited over generations do not cause evolution.
Answer:
Question 9.
Select the correct statement:
(a) The tendril of a pea plant and the phylloclade of Opuntia are homologous.
(b) The tendril of a pea plant and the phylloclade of Opuntia are analogous.
(c) The wings of birds and the limbs of lizards are analogous.
(d) The wings of bird and the wings of bats are homologous.
Answer:
Question 10.
If the fossil of an organism is found in the deeper layers of earth, then we can predict that:
(a) The extinction of the organism occurred recently.
(b) The extinction of the organism occurred thousands of years ago.
(c) The fossil position in the layers of Earth is not related to its time of extinction.
(d) The time of extinction cannot be deter¬mined.
Answer:
(b) The extinction of the organism occurred thousands of years ago.
Explanation: If we dig into the earth and start finding fossils, the fossils we find closer to the surface are more recent than the fossils we find in deeper layers.
Related Theory
Depth of each stratum signifies the relative age of fossils present in it. The deeper the stratum, the older the rock and the fossils present in it
Question 11.
A trait in an organism is influenced by:
(a) Paternal DNA only
(b) Maternal DNA only
(c) Both maternal and paternal DNA
(d) Neither paternal nor maternal DNA
Answer:
(c) Both maternal and paternal DNA
Explanation: DNA is contributed to an offspring by both the parents; hence, traits are influenced by both maternal and paternal DNA. During sexual reproduction, both mother and father pass their genes to their children, thus determining their traits; or characteristic features.
Question 12.
New species may be formed if:
(I) DNA undergoes significant changes in germ cells.
(II) The chromosome number changes in the gamete.
(III) There is no change in the genetic material.
(IV) Mating does not take place.
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (I) and (III)
(c) (II), (III) and (IV)
(d) (I), (II) and (III)
Answer:
Question 13.
which of the following statements is not true with respect to variation?
(a) All variations in a species have equal chances of survival.
(b) Change in genetic composition results in variation.
(c) Selection of variants by environmental factors forms the basis of evolutionary processes.
(d) Variation is minimum in asexual reproduction.
Answer:
Question 14.
According to the evolutionary theory, for¬mation of a new species is generally due to:
(a) Sudden creation by nature.
(b) Accumulation of variations over several generations.
(c) Clones formed during asexual reproduction.
(d) Movement of individuals from one habitat to another.
Answer:
Question 15.
The theory of the evolution of species by natural selection was given by:
(a) Mendel
(b) Darwin
(c) Morgan
(d) Lamarck
Answer:
Question 16.
Some dinosaurs had feathers although they could not fly but birds have feathers that help them to fly. In the context of evolution this means that:
(a) Reptiles have evolved from birds.
(b) There is no evolutionary connection between reptiles and birds.
(c) Feathers are homologous structures in both the organisms.
(d) Birds have evolved from reptiles.
Answer:
Question 17.
Select a set of homologous organs from the following:
(a) Wings of a bat and wings of a butterfly
(b) Wings of a pigeon and wings of a bat
(c) Wings of a butterfly and wings of a pigeon
(d) Forelimbs of a duck, forelimbs of a cow and forelimbs of a lizard
Answer:
(d) Forelimbs of a duck, forelimbs of a cow and forelimbs of a lizard
Explanation: Wings of a bat and wings of a butterfly (A), Wings of a pigeon and wings of a bat (B) and Wings of a butterfly and wings of a pigeon (C) are analogous organs as they all use wings for flying but the wings have different structures.
Bat wings consist of flaps of skin stretched between the bones of the fingers and arm, wings of pigeon consist of feathers extending all along the arm whereas butterfly wings are covered in scales.
On the other hand, Forelimbs of a duck, forelimbs of a cow and forelimbs of a lizard are homologous organs as they all have similar structures which have been modified to perform different functions.
Question 18.
Select the correct statements regarding monohybrid cross between a pure tall pea plant and pure short pea plant performed by Mendel:
(I) All plants of the F1 generation were tall.
(II) The tall plants in the F1 generation were exactly the same as the tall plants of the parent generation
(III) One-quarter of the F2 progeny of the F1 tall plants were short.
(IV) Both the tallness and shortness traits were inherited in the F1 plants
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) (I), (II) and (III)
(d) (I), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) (I), (III) and (IV)
Explanation: When a pure tall pea plant is crossed with a pure short plant, it was observed that all plants of the F1 generation were tall. But the tall plants in the F1 generation were not exactly the same as the tall plants of the parent generation. The genotype of the pure tall plant is TT, whereas the genotype of the tall plant in the F1 generation was Tt. The ratio of the tall and short plants in the F2 generation was 3:1. As 25 % of the pea plants in the F2 generation were tall, it means that both the shortness (t) and tallness (T) trait were inherited in the FI plants.
Question 19.
Which of the following are acquired traits?
(I) Attached or free earlobe
(II) Muscular body of a wrestler
(III) Body weight of starving animals
(IV) Brown and curly hair
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 20.
Consider the plants the pitcher plant, venus fly trap, poinsettia and cactus.
Select the row containing incorrect information regarding the leaves of these plants in terms of evolutionary relationships.
| (a) Leaves of these plants are homologous organs | The leaves are structurally similar but modified to perform different functions |
| (b) Leaves of these plants are analogous organs | The leaves are structurally dissimilar but perform similar functions |
| (c) Leaves of these plants are vestigial organs | Leaves are homologous to
similar leaves in other plants |
| (d) Leaves of these plants are neither homologous nor analogous | The leaves have no structural or functional similarity |
Answer:
Question 21.
Study the organs and evolutionary relationship mentioned alongside. Select the row containing incorrect information.
| Organs Relationship | Evolutionary |
| (a) limbs of human being and frog | Homologous organs |
| (b) wings of bird and bat | Analogous organs |
| (c) Thorns and spines in plants | Analogous organs |
| (d) Tendril of pea plant and grape plant | Homologous organs |
Answer:
(d) Organs: Tendril of pea plant and grape plant; Evolutionary Relationship: Homologous organs
Explanation: Thorn is modification of stem and spine is modification of leaf. Tendrils in plant show similar function but they are different in origin. Pea plant has Leaf tendril whears. Grape plant has Stem tendril
Question 22.
which of the statements regarding evolution is correct?
(a) One species is always eliminated in order to give rise to a new species.
(b) The newly formed species are better than the old species.
(c) Evolution is the generation of diversity and the shaping of the diversity by environmental selection.
(d) More and more complex body designs have emerged over time as the older designs are ineffcient.
Answer:
Question 23.
which of the following cannot be an outcome of Mendel’s Experiment on crossing a tall pea plant with a short pea plant?
(a) 3 tall 1 short plant
(b) 4 tall plants and 1 medium height plant.
(c) 24 tall and 8 short plants
(d) 8 tall and 0 short plants
Answer:
Question 24.
Which of the following have a perfect pair of sex chromosomes?
(a) Only Girls
(b) Only Boys
(c) Both girls and boys
(d) It depends on many other factors
Answer:
(a) Only Girls
Explanation: Girls have a perfect paired 23rd chromosome, which is XX, whereas boys have a mismatched 23rd pair of chromosomes, which is XY.
Question 25.
Select the incorrect option.
Genetic drift is:
(a) A mechanism of evolution in which allele frequencies of a population remain constant over generations.
(b) It occurs in all populations of non-infinite size, but its effects are strongest in small populations.
(c) It may result in the loss of some alleles.
(d) It can have major effects when a population is sharply reduced in size by a natural disaster.
Answer:
Question 26.
Select the group which shares the maximum number of common characters:
(a) Two individuals of a species
(b) Two species of a genus
(c) Two genera of a family
(d) Two genera of two families
Answer:
Question 27.
Select the statements that describe the characteristics of genes:
(I) Genes are specific sequence of bases in a DNA molecule.
(II) A gene does not code for proteins.
(III) In individuals of a given species, a specific gene is located on a particular chromosome.
(IV) Each chromosome has only one gene.
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (I) and (III)
(c) (I) and (IV)
(d) (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) (I) and (III)
Explanation: Genes are units of heredity and are responsible for inheritance. Genes control the expression of a trait or a character in an organism. Genes are located on the chromosomes, which is present inside the nucleus of the cell in the crytoplasm.
Question 28.
The number of pair(s) of sex chromosomes in the zygote of humans is:
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
Answer:
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Science Chapter 9
For the following questions, two statements are given: one Labeled Assertion (A) and the other Labeled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question 29.
Assertion (A): The wing of an insect and wing of a bird are analogous organs
Reason (R): The organs which are quite different in fundamental structure and origin but perform the same function in different species are called analogous organs
Answer:
Question 30.
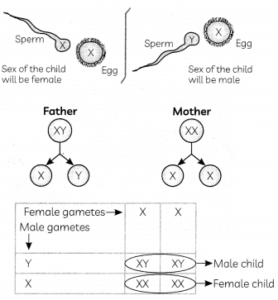
Assertion (A): The sex of a child in human beings will be determined by the type of chromosome he/ she inherits from the father.
Reason (R): A child who inherits ‘X‘ chromosome from his father would be a girl (XX), while a child who inherits a ‘Y‘ chromosome from the father would be a boy (XY).
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is correct explanation of the (A).
Explanation: Human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes. Out of which one pair is sex chromosomes and 22 pairs are autosomes. In men, sex chromosome pair is mismatched pair ‘XY‘, ‘X‘ is normal sized and Y is shorter than ‘X‘ chromosomes. Human females have ‘XX chromosomes. Males produce two types of sperms whereas females produce only one ovum having ‘X’ chromosomes. A child who inherits the ‘X’ chromosome from a father would be a girl ‘(XX)’.
While a child who inherits a Y chromosome from the father would be a boy (XY).
Question 31.
Assertion: A geneticist crossed a pea plant having violet flowers with a peaplant with white flowers, he got all violet flowers in first generation.
Reason: White colour gene is not passed on to next generation.
Answer:
Question 32.
Assertion (A): New combination of traits are observed in F2 offspring when tall plants with round seeds are crossed with short plants with wrinkled seeds.
Reason (R): Tallness and round seed are both dominant traits.
Answer: