Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of:
(a) Only carbon monoxide
(b) Carbon monoxide in traces and carbon dioxide
(c) Only carbon dioxide
(d) Coal [NCERT Examplar]
Answer:
(b) Carbon monoxide in traces and carbon dioxide
Explanation: Only 0.03% of atmospheric air contatins carbon in the form of carbon dioxide. The natural concentration of carbon monoxide in the air is around 0.2 parts per million (ppm). It is produced by the incomplete combustion of carbon due to a limited supply of oxygen. It is a pollutant which is formed when hydrocarbons such as petrol and diesel are burnt. Carbon monoxide (CO) is short-lived and gets oxidised into carbon dioxide (CO2).
Related Theory
Carbon also occurs in the form of minerals such as carbonates, fossil fuels and other organic compounds.
Question 2.
A molecule of ammonia (NH3) has:
(a) Only single bonds
(b) Only double bonds
(c) Only triple bonds
(d) Two double bonds and one single bond
Answer:
Question 3.
Buckminster fullerene is an allotropic form of:
(a) Phosphorus
(b) Sulphur
(c) Carbon
(d) Tin
Answer:
(c) Carbon
Explanation: Buckminsterfullerene is an allotrope of carbon with 60 carbon atoms, which are arranged in the shape of a football. Since this also looks like the geodesic dome designed by the US architect Buckminster Fuller, the molecule was named fullerene.
Question 4.
Which of the following is the correct representation of electron dot structure of nitrogen molecule?

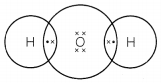
Question 5.
The correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is:

Answer:
![]()
Explanation: In a water molecule, the center oxygen atom contains two lone pairs of electrons and forms two single covalent bonds with two hydrogen atoms.
Oxygen (O) has 6 valence electrons and hydrogen (H) has 1.
All the 8 electrons must be arranged in pairs so that oxygen completes the octet structure (8 electrons in its valence cell). Each hydrogen atom has now 2 electrons in its valence shell.
Question 6.
Which of the following does not belong to the same homologous series?
(a) CH4
(b) C2H2
(c) C3H8
(d) C4H8
Answer:
(d) C4H8
Explanation: Methane (CH4) is the first member of the homologous series of alkanes. Successive members of the same homologous series differ by -CH2 unit.
Second member is ethane (C2H2) and the third member is propane (C3H8). The fourth member should be butane (C4H10).
Hence, C4H8 does not belong to the homologous series of alkanes.
CH4, C2H6, C3H3 belong to the same series that is of alkane and differ by -CH2 unit but C4H8 does not belong to alkanes.
Question 7.
![]()
In the above-given reaction, alkaline KMn04 acts as:
(a) Reducing agent
(b) Oxidising agent
(c) Catalyst
(d) Dehydrating agent
Answer:
Question 8.
In which of the following compounds is -OH the fi.ånctionoL group?
(a) Butanone
(b) Butanot
(c) Butanoic
(d) Butanat
Answer:
Question 9.
Structural the formula of ethyne is:
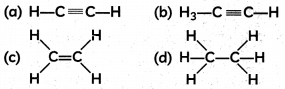
Answer:
Question 10.
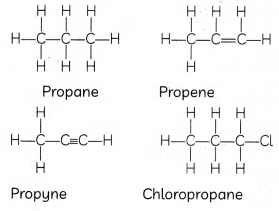
Identify the unsaturated compounds from the following:
(I) Propane
(II) Propene
(III) Propyne
(IV)Chloropropane
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (II) and (IV)
(c) (III) and (IV)
(d) (II) and (ill)
Answer:
(d) (II) and (III)
Explanation: Alkene and alkyne are unsaturated hydrocarbons as they have double and triple covalent bonds between carbon atoms. Alkanes such as propane are saturated hydrocarbons.
Propane and chloropropane are saturated hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds.
Related Theory:
A hydrocarbon in which two carbon atoms are connected by a ‘double bond’ or a ‘triple bond’ is called an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Question 11.
Chlorine reacts with saturated hydrocarbons at room temperature in the:
(a) absence of sunlight
(b) presence of sunlight
(c) presence of water
(d) presence of hydrochloric acid
Answer:
Question 12.
In the soap micelles
(A) The ionic end of soap ¡s on the surface of the cluster, white the carbon chain is in the interior of the cLuster.
(B) The ionic end of soap is in the interior of the cluster and the carbon chain is out of the cluster.
(C) Both the ionic end and carbon chain are in the interior of the cluster.
(D) Both the ionic end and carbon chain are on the exterior of the cluster.
Answer:
(a) The ionic end of soap ¡s on the surface of the cluster, while the carbon chain is in the interior of the cluster.
ExpLanation: The soap molecule has a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail. When soap is mixed into the water, the soap molecules arrange themselves into tiny clusters called ‘micelles’. The hydrophilic parts of the soap (water-Loving) molecules point outwards, forming the outer surface of the micelle. The hydrophobic part (oil-loving) group together and point towards the inner side. Micelles can trap fats in the center and help to get rid of oil and dirt.
Question 13.
The structura[formuta of benzene is:
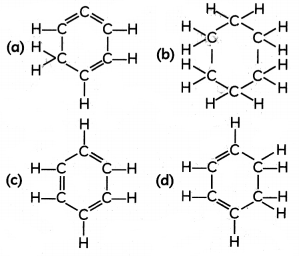
Question 14.
Ethanol reacts with sodium and forms two products. These are:
(a) Sodium ethanoate and hydrogen
(b) Sodium ethanoate and oxygen
(c) Sodium ethoxide and hydrogen
(d) Sodium ethoxide and oxygen
Answer:
(c) Sodium ethoxide and hydrogen
Explanation: Ethanol (C2H5OH) reacts with sodium to form sodium ethoxide (C2H5ONO) along with the Liberation of hydrogen gas.
2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2
Question 15.
The correct structural formula of butanoic acid is;
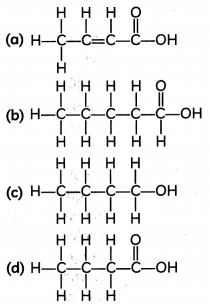
Answer:
Question 16.
Mineral acids are stronger acids than carboxylic acids because:
(I) Mineral acids are completely ionized.
(II) Carboxylic acids are completely ionized.
(III) Mineral acids are partially ionized.
(IV) Carboxylic acids are partially ionized.
(a) (I) and (IV)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (I) and (II)
(d) (III) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 17.
Which of the following is not a straight-chain hydrocarbon?
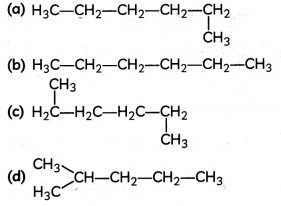
Answer:
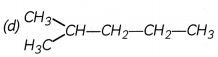
Explanation: In structures (1), (2), and (3), all the carbon atoms are attached by covalent bonds in a continuous straight chain.
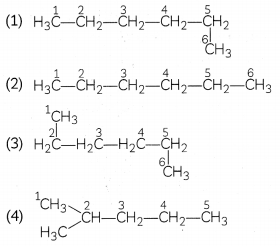
In structure (4), the -CH 3 group is attached to the second carbon atom of the chain forming a branch. Hence, a compound in structure (iv) is a branched-chain hydrocarbon.
Related Theory
A branch-chain hydrocarbon contains some side chains which are bonded with the parent carbon chain.
Question 18.
Which among the following are unsaturated hydrocarbons?
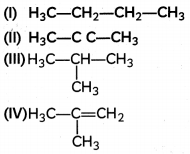
(a) (I) and (III)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (II) and (IV)
(d) (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(c) (II) and (IV)
Explanation: Unsaturated hydrocarbons are organic compounds that consist of a double or a triple bond between two adjacent carbon atoms. The hydrocarbons having at least one double bond between two adjacent carbon atoms are called alkenes, whereas the hydro¬carbons which contain a carbon-carbon triple bond are referred to as alkynes. Both (II) and (IV) structures have double or triple carbon-carbon bonds respectively.
Question 19.
The name of the compound, CH3—CH2— CHO is:
(a) Propanol
(b) Propanone
(c) Ethanol
(d) Ethanal
Answer:
Question 20.
Which of the following represents saponification reaction?
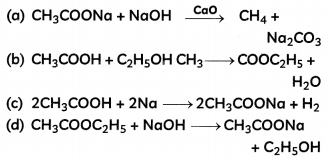
Answer:
Question 21.
A student takes about 4 mL of distilled water in four test tubes marked P, Q, R, and S. He then dissolves in each test tube an equal amount of one salt in one test tube, namely sodium sulfate in P, potassium sulfate in Q, calcium sulfate in R and magnesium sulfate in S. After that he adds an equal amount of soap solution in each test tube. On shaking each of these test tubes well, he observes a good amount of lather (foam) in the test tubes marked:
(a) P and Q
(b) Q and R
(c) P, Q and S
(d)P, Rand S
Answer:
Question 22.
Consider the following oils:
(I) Mobil oil
(II) Castor oil
(III) Turpentine oil
(IV) Kerosene
(V) Mustard oil
(VI) Coconut oil
Which of these can be used for the preparation of soap?
(a) I, II, III, VI
(b) M, V, VI
(c) II, III, V, VI
(d) II, III, VI
Answer:
(b) II, V, VI (Mustard oil, castor oil, coconut oil)
Related Theory
Oil in soaps used to moisturizes the skin and creates creamy lather.
Question 23.
A student is testing water to know which is best for cleansing purposes with soaps. He would find that the cleansing action of soaps is best wben he uses water obtained from:
(a) rain
(b) tap
(c) hand pump
(d) pond
Answer:
Question 24.
You have four test tubes, A, B, C, and D containing sodium carbonate, sodium chloride, lime water and blue litmus solutions respectively. Out of these the material of which test tube/test tubes would be suitable for the correct test of acetic/ ethanoic acid?
(a) only A
(b) A and B
(c) B and C
(d) A and D
Answer:
Question 25.
A student took four test tubes P, Q, R, and S and filled about 8 mL of distilled water in each. After that he dissolved an equal amount of Na2SO4 in P, K2SO4 in Q, CaSO4 in R, and MgSO4 in S. On adding an equal amount of soap solution and shaking each test tube well, a good amount of lather will be obtained in the test tubes:
(a) P and Q
(b) P and R
(c) P, Q, and S
(d) Q, R, and S
Answer:
Question 26.
A student wants to prepare soap in the laboratory. Which of the following sets of materials he should use?
(a) Neem oil and NaCl
(b) Neem oil and Na2CO3
(c) Mustard oil and NaOH
(d) Mineral oil and NaOH
Answer:
Question 27.
You have neem oil in a beaker. In order to study saponification reaction, which of the following chemical substances would you add to this oil?
(a) 20% Ca(OH)2
(b) 20% NaOH
(c) 30% Mg(OH)2
(d) 10% Ca(OH)2
Answer:
(b) 20% NaOH
Explanation: Oil or fat when treated with sodium hydroxide solution, gets converted into sodium salt of fatty acid (soap) and glycerol.
fat + NaOH → glycerol + sodium salt of fatty acid
In options (a) and (d) the base used is Ca(OH)2 whereas in option (c), the base used is 30 % Mg(OH)2.
Therefore, the correct option is (b) as it uses 20% NaOH,
Question 28.
If you take some distilled water in a test- tube, add an equal amount of acetic acid to it, shake the test tube well and leave it undisturbed on the test tube stand, then after about 5 minutes, what would you observe?
(a) There is a Layer of water over the layer of acetic acid.
(b) A precipitate is settling at the bottom of the test tube.
(c) Bubbles of colorless gas are coming out of the test tube.
(d) There is a clear, colorless transparent solution in the test tube.
Answer:
(d) There is a dear, colorless transparent solution in the test tube.
Explanation: Acetic Acid is miscible in water and therefore when acetic acid is added to water it dissolves readily in water forming a homogeneous solution.
Question 29.
Soaps are formed by alkaline hydrolysis of:
(a) Inorganic salts
(b) Carboxylic acids
(c) Esters of long-chain fatty acids
(d) Esters of small chain fatty acids
Answer:
Question 30.
In the preparation of soap addition of sodium chloride causes:
(a) Complete saponification
(b) Complete hydrolysis
(c) Complete precipitation
(d) Complete neutralization
Answer:
(c) Complete precipitation
Related Theory
The soap is formed by the precipitation by the common salt (NaCl). When the salt is added in the aqueous solution then the reaction occurs and the soap is precipitate out from the solution. When the soap is added to the solution then the solubility of the soap became decreases and the soap precipitates out from the solution as a solid form of the soap.
Question 31.
A student is given equal amount of three samples of water with temporary hardness labeled as ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’. He keeps the three samples at different temperatures – A at room temperature, B at 50 °C and C at 95 °C. Which sample will give maximum amount of lather when 10 mL of soap solution is added to each sample and shaken for equal time?
(a) (A) only
(b) Both (A) & (B)
(c) Both (B) and (C)
(d) (C) only
Answer:
(d) C only.
Related Theory
Soap form lather with soft water and at 95° C the hardness of water gets reduced and soap lather in good amount.
Question 32.
Which one of the following compounds can show addition reaction?
(a) C3H8
(b) C4H8
(c) CH3Cl
(d) C2H5OH
Question 33.
An organic compound of molecular formula C2H4O2 gives brisk effervescence with sodium hydrogen carbonate. The name and formula of the organic compound are:
Select the correct option:

Answer:
(b) The organic compound is ethanoic acid and its formula is CH3COOH.
Explanation: Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogen carbonate to form sodium ethanoate, carbon dioxide gas, and water.
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O
Question 34.
Carbon compounds have:
(a) High boiling point but low melting point.
(b) High melting but low boiling point.
(c) Low melting and boiling point
(d) High melting and boiling point.
Answer:
Question 35.
The substance used for oxidation of ethanol and the compound formed on oxidation of ethanol is:
Select the correct option:
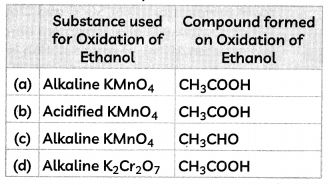
Answer:
Question 36.
The structure of a hydrocarbon is given below:
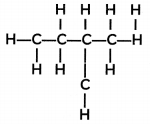
Study the structure above and select the correct statements:
(I) The molecular formula of the compound is C5H12
(II) The IUPAC name of the compound is 2-Methyl pentane
(III) It is an isomer of pentane
(IV) It has 14 single covalent bonds
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) (I), (II), and (III)
(d) (I), (III), and (IV)
Answer:
(b) Both (I) and (III)
Explanation: The structure is that of pentane, whose molecular formula is C5H12 and it shows isomerism. Structural isomers are compounds with identical molecular formula but different structures.
It has 16 single covalent bonds, – 4 single bonds between carbon atoms and 12 single bonds between C-H atoms.
Question 37.
Which of the following compounds do not contain the Carboxylic acid functional group?
(I) C2H5COOH
(II) C3H7OH
(III) CH3COOH
(IV) CH3CHO
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (III)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Explanation: The functional group carboxylic acid is represented by HCOOH or RCOOH, where R is the alkyl group.
Whereas, the functional group alcohol is represented by ROH and aldehyde by RCHO.
So, (II) is an alcohol, propanol and (IV) is an aLdehyde, ethanal.
Question 38.
The structural formula of propene is:

Answer:
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2
For the following questions, two statements are given one labeled Assertion (A) and the other labeled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is correct explanation of the assertion
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true
Question 39.
Assertion (A): Chemical bonds in organic compounds are covalent in nature.
Reason (R): Covalent bond is formed by the sharing of electrons in the bonding atoms. [Diksha]
Answer:
(a) (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the (A).
Question 40.
Assertion(A): Carbon has a strong tendency to either lose or gain electrons to attain noble gas configuration.
Reason (R): Carbon has four electrons in its outermost shell and has the tendency to share electrons with carbon or other elements.
Question 41.
Assertion (A): Carbon forms covalent compounds with other atoms.
Reason (R): Carbon can gain 4 electrons forming C4 anion.
Question 42.
Assertion (A): Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
Reason (R): Covalently bonded molecules have weak intermolecular forces.
Answer:
(a) (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the (A).
Question 43.
Assertion (A): The following belong to the same homologous series: C2H4, C3H6, C4H8.
Reason (R): Gradation in physical properties is seen with an increase in molecular mass in any homologous series.
Question 44.
Assertion (A): Esterification is a process in which a sweet-smelling substance is produced.
Reason (R), When esters react with sodium hydroxide an alcohol and sodium salt of carboxylic acid are obtained.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Explanation: Esterification is a process in which esters are formed by the reaction of an acid and alcohol.

Saponification is a process in which an ester is converted back to alcohol and sodium salt of carboxylic acid and it is used in the preparation of soap.
![]()
Question 45.
Assertion (A): Following are the members of a homologous series: CH3OH, CH3CH3OH, CH3CH2CH2OH
Reason (R): A series of compounds with the same functional group but differing by -CH2– unit is called a homologous series.