Metals and Non-metals Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following properties is generally not shown by metals?
(a) Electrical conduction
(b) Sonorous in nature
(c) Dullness
(d) Ductility
Answer:
(c) Dullness
Explanation: Metals generally do not show dullness. Metals such as gold and silver are usuaLly shiny rather than dull.
Related Theory:
Conduction: Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity as they have free electrons. Silver and copper are the best conductors of heat, whereas lead and mercury are poor conductors of heat. Sonorous: Metals that produces a sound on striking a hard surface.
Metallic lustre: Metal, in its pure state, has a shining surface. This property is known as metallic lustre. Ductility: The ability of metals to be drawn into thin wires. Cold is the most ductile metal.
Question 2.
The solution of one of the following compounds will not conduct electricity. This compound is:
(a) NaCl
(b) CCl4
(c) MgCl2
(d) CaCl2
Answer:
Question 3.
Which one of the following metals does not react with cold as well as hot water?
(a) Na
(b) Ca
(c) Mg
(d) Fe
Answer:
Question 4.
An aluminium strip is kept immersed in freshly prepared ferrous sulphate solution taken in a test tube, the change observed is that:
(a) Green solution slowly turns colourless
(b) Lower end of test tube becomes slightly warm
(c) A colourless gas with the smell of burning sulphur is observed
(d) Light green solution changes to blue
Answer:
Question 5.
Which of the following oxide(s) of iron would be obtained on the prolonged reaction of iron with steam?
(a) FeO
(b) Fe2O3
(c) Fe3O4
(d) Fe2O3 and Fe3O4
Answer:
(c) Fe3O4
Question 6.
What happens when calcium is treated with water?
(I) It does not react with water.
(II) It reacts violently with water.
(III) It reacts Less violently with water.
(IV) Bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of calcium.
(a) (I) and (IV)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (I) and (II)
(d) (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) (III) and (IV)
Explanation: When calcium is treated with water, it reacts vigorously with water and to produce a cloudy white precipitate of calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas is released as bubbles.

‘Related Theory
Sometimes hydrogen bubbles get stuck to the surface of calcium metaL making it tight arid thus calcium starts floating. Reaction of calcium with water is exothermic but the heat produced in this reaction is not sufficient so that hydrogen can catch
Question 7.
Which of the foLLowing are not ionic compounds?
(I) KCl
(II) HCl
(III) CCl4
(IV) NaCl
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (III) and (IV)
(d) (I) and (III)
Answer:
Question 8.
Generally, non-metals are not Lustrous. Which of the following non-metals is lustrous?
(a) Sulphur
(b) Oxygen
(c) Nitrogen
(d) Iodine
Answer:
(d) Iodine
Explanation: Iodine is a non-metal with a lustrous appearance and exists in solid state.
Related Theory
Graphite is another non-metaL that is shiny and Lustrous.
Question 9.
2 mt each of conc. HCL, HNO3, and a mixture of conc. HCL and conc. HNO3 in the ratio of 3:1 were taken in test tubes labelled as A, B and C. A small piece of metal was put in each test tube. No change occurred in test tubes A and B but the metaL got dissolved in test tube C. The metal could be:
(a) Al
(b) Au
(c) Cu
(d) Pt
Question 10.
An element A is soft and can be cut with a knife. This is very reactive to air and cannot be kept ¡n open air. It reacts vigorously with water. Identify the element from the following:
(a) Mg
(b) Na
(c) P
(d) Co
Answer:
(b) Na
Explanation: Na (sodium) possesses all the above properties. It is too soft and can be cut with a knife. It is also very reactive and reacts with oxygen or moisture present in air and produces sodium hydroxide, which is a highly exothermic reaction producing a lot of heat. It also reacts with water and burns due to the vigorous formation of hydrogen gas. That is why sodium is stored in kerosene oil to prevent any reaction.
Question 11.
Which among the following statements is incorrect for magnesium metal?
(a) It burns in oxygen with a dazzling white flame.
(b) It reacts with cold water to form magnesium oxide and evolves hydrogen gas.
(c) It reacts with hot water to form magnesium hydroxide and evolves hydrogen gas.
(d) It reacts with steam to form magnesium hydroxide and evoLves hydrogen gas.
Answer:
Question 12.
The electronic configurations of three elements X, Y and Z are X – 2, 8; Y – 2, 8, 7 and Z – 2, 8, 2. Which of the following ¡s correct?
(a) X is a metal
(b) Y is a metaL
(c) Z ¡s a non-metal
(d) Y is a non-metaL and Z is a metaL
Question 13.
In the given reaction,
Al2O3 + NaOH → X + H2O.
What is element X?
(a) NaAlO2
(b) Na3Al
(c) Na2O3
(d) NaAl2O3 [Diksha]
Question 14.
Sandhya took three beakers A, B and C containing zinc sulphate, silver sulphate and iron(ll) sulphate solutions respectively. Copper pieces were added to each beaker. The solution will appear blue in the case of:
(a) Beaker A
(b) Beaker B
(c) Beaker C
(d) Beakers B and C [Diksha]
Answer:
(b) Beaker B
Explanation: The solution will appear blue in Beaker B. Let us see how.
When pieces of copper metal are kept immersed in silver sulphate solution for some time, the solution gradually becomes blue and a shiny greyish-white deposit of silver metal is formed on the copper strip.
In this reaction, copper metal is displacing silver from silver sulphate solution, forming copper sulphate and silver metal. The solution becomes blue due to the formation of copper sulphate. The reason behind this displacement reaction is that copper is more reactive than silver.
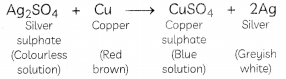
On the other hand, copper metal is less reactive than iron and zinc and hence cannot displace them from their respective salt solutions.
Question 15.
Arrange the following metal in the decreasing chemical activity series.
(I) Potassium
(II) Magnesium
(III) Gold
(IV) Iron
Correct options are:
(a) (I), (II), (III) and (IV)
(b) (I), (III), (IV) and (II)
(c) (I), (II), (IV) and (III)
(d) (I), (IV), (II) and (III)
Question 16.
Which metal can be displaced by copper from Its salt solution?
(I) Silver
(II) Magnesium
(III) iron
(IV) Iron
Correct options are:
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (I) and (III)
(c) (II) and (III)
(d) (I) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) (I) and (IV)
Silver and mercury are less reactive than copper and as copper will displace those metals from its salt solution which are less reactive than it, the correct option is (d).
Question 17.
Metals are refined by using different methods. Which of the following metals are refined by electrolytic refining?
(I) Au
(II) Cu
(III) Na
(IV) K
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (IV) and (III)
(c) (II) and (III)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(a) (I) and (II)
Explanation: Gold (Ag) and copper (Cu) obtained after extraction are in impure form. So, metals Au (gold) and Cu (copper) are refined by electrolytic refining. Other than gold and copper, electrolytic refining is used for metals such as Zn and Ag. Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) are extracted by electrolytic reduction. Metals obtained after electrolytic reduction are in pure form.
Related Theory
Alkali metals are very reactive, so they cannot be refined with the help of electrolytic refining process.
Question 18.
Galvanisation is a method of protecting iron from rusting by coating it with a thin layer of:
(a) Gallium
(b) Aluminium
(c) Zinc
(d) Silver
Answer:
(c) Zinc
Explanation: Zinc (Zn) metal is used to protect iron surface from rusting.
Related Theory
Galvanization is basically coating iron or steel with a layer of zinc to prevent it from rusting. Water pipes are also galvanized to prevent corrosion.
Question 19.
Stainless steel is a very useful material in our life, in stainless steel, iron is mixed with:
(a) Mi and Cr
(b) Cu and Cr
(c) Mi and Cu
(d) Cu and Au
Answer:
(a) Ni and Cr
Explanation: Stainless steel is an alloy of iron (74%), nickel (8%) and chromium (18%).
Related Theory
‘Alloying elements enhance the structure and properties such as durability, strength and toughness of the metal. It makes them corrosion-resistant.
Question 20.
If copper is kept in open air, it slowly loses its shining brown surface and gains a green coating. It is due to the formation of:
(a) CuSO4
(b) CuCO3
(c) CU(NO3)2
(d) CuO
Answer:
Question 21.
Which of the following metals are obtained by electrolysis of their chlorides in molten state?
(I) Na
(II) Ca
(III) Fe
(IV) Cu
(a) (I)and(IV)
(b) (III) and (IV)
(c) (I) and (III)
(d) (I) and (II)
Answer:
Question 22.
An electrolytic cell consists of:
(I) Positively charged cathode
(II) Negatively charged anode
(III) Positively charged anode
(IV) Negatively charged cathode
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (III) and (IV)
(c) (I) and (III)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) (III) and (IV)
Explanation: There is a positively charged anode and a negatively charged cathode in an electrolytic cell. Positively charged ions (cations) are deposited at the negatively charged cathode. Negatively charged ions (anions) are deposited at the positively charged anode.
Question 23.
During electrolytic refining of zinc, it gets:
(a) Deposited on cathode
(b) Deposited on anode
(c) Deposited on the cathode as well as anode
(d) Remains in the solution
Answer:
Question 24.
Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of a metal with a metal or non-metal. Which among the following alloys contains non-metal as one of its constituents?
(a) Brass
(b) Bronze
(c) Amalgam
(d) Steel
Answer:
(d) Steel
Explanation: SteeL contains non-metal as one of its constituents. Steel is an alloy made by combining iron and other elements, mainly carbon. Carbon gives strength to iron. It is used to make buildings, ships, automobiles, machines, and appliances.
Related Theory
- Brass – Copper and zinc
- Bronze – Copper and tin
- Amalgam – Mercury with other metal
- Steel – Iron with carbon
Question 25.
Which among the following alloys contains mercury as one of its constituents?
(a) Stainless steel
(b) Alnico
(c) Solder
(d) Zinc amalgam
Answer:
Question 26.
Which one of the following figures correctly describes the process of electrolytic refining?
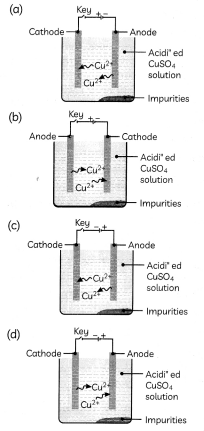
Answer:
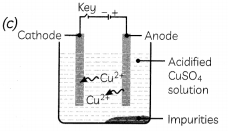
Explanation: In the electrolytic refining process, impure metal forms the anode, which is the positive electrode, whereas pure metal forms the cathode which is the negative electrode.
Figure (c) shows the process of electrolytic refining of copper metal. Copper from impure anode dissolves into the solution. Copper ions (Cu2+) from the solution are deposited on the cathode and impurities settle down below the anode as anode mud.
Question 27.
Select the incorrect statements):
(I) Solder is an alloy of lead and copper
(II) Solder is an alloy of lead and tin
(III) Melting point of solder is low
(IV) Melting point of solder is high
(a) Only (I)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) Both (II) and (IV)
(d) Both (I) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 28.
All ionic compounds:
(a) Have high melting point but low boiling point
(b) Are generally soluble in kerosene
(c) Are generally brittle
(d) Conduct electricity in solid-state
Answer:
Question 29.
The cations and anions present in aluminium oxide are:
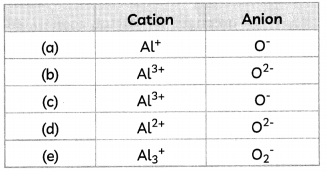
Answer:
(b) Cation: Al37; Anion: O2-
Explanation: Aluminium oxide or Al2O3 is formed by the transfer of electrons from aluminium atoms to oxygen atoms.
Aluminium (Atomic number = 13) has 3 valence electrons whereas oxygen (atomic number = 8) has 2 valence electrons.
So, each aluminium atom donates its 3 valence electrons to the oxygen atoms and forms cations [Al3+], whereas each oxygen atom gains two electrons and forms anions [O2-],
Question 30.
The metals which have very low melting points are:
(a) Gallium and caesium
(b) Gallium and sodium
(c) Caesium and potassium
(d) Sodium and potassium
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Science Chapter 3
For the following questions, two statements are given – one labelled Assertion (A) and other labeled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question 31.
Assertion (A): Alkali metals like sodium and potassium can be cut with a knife.
Reason (R): They have high densities.
Answer:
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
Explanation: Alkali metals like sodium and potassium are so soft that they can be cut with a knife as they have low densities.
Question 32.
Assertion (A): Magnesium is less reactive than sodium.
Reason (R): Sodium reacts more vigorously with oxygen than magnesium.
Question 33.
Assertion (A): In the following reaction between calcium and water, calcium starts floating.
Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
Reason (R): Calcium hydroxide is lighter than water.
Answer:
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
Explanation: In the reaction between calcium and water, calcium starts floating because the bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of calcium metal.
Question 34.
Assertion (A): Hydrogen gas is evolved when a metal reacts with nitric acid.
Reason (R): Nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent.
Question 35.
Assertion (A): The compound MgCl2 will not conduct electricity in solid-state.
Reason (R): Movement of ions in ionic compounds is not possible in solid-state.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are. true but (R) is not the correct explanation of the (A).
Explanation; The compound MgCl2 is an ionic compound as it is formed by transfer of electrons between magnesium and chlorine. It will not conduct electricity in solid state as the movement of ions in ionic compounds is not possible in a solid-state.
Question 36.
Assertion (A): The metals and alloys are good conductors of electricity.
Reason (R): Bronze Is an alloy of copper and tin and it is not a good conductor of electricity.
Answer:
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
Explanation: All the metals and alloys are not always good conductors of electricity like bronze is not a good conductor of electricity, its constituents are copper and tin. Copper is a good conductor whereas tin is not a good conductor of electricity. Alloy nichrome is a good conductor of electricity.
Related Theory
- Metals are good conductors of electricity because they.
- have a large number of free electrons.
- Possess small resistivity in the range of 10-8 W m to 10-6 W m. Whereas alloys have more resistivity.