Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
If the key in the arrangement as shown below is taken out (the circuit is made open) and magnetic field lines are drawn over the horizontal plane ABCD, the lines are:
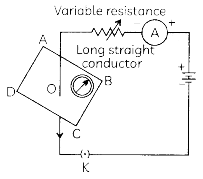
(a) Concentric circles
(b) Elliptical in shape
(c) Straight lines parallel to each other
(d) Concentric circles near the point O but of elliptical shapes as we go away from it
Answer:
(c) Straight lines parallel to each other
Explanation: If the circuit connection breaks by taking the key out, then no current will flow through the wire and no magnetic field will exist due to the conductor.
Therefore, at the point O, there will be only Earth’s magnetic field and they are straight lines parallel to each other.
Question 2.
A current-carrying conductor is held in exactly vertical direction. In order to produce a clockwise magnetic field around the conductor, the current should passed in the conductor:
(a) from top towards bottom
(b) from left towards right
(c) from bottom towards top
(d) from right towards left
Answer:
Question 3.
A circular loop placed in a plane perpendicular to the plane of paper carries a current when the key is on. The current as seen from points A and B (in the plane of paper and on the axis of the coil) is anticlockwise and clockwise respectively. The magnetic field lines point from B to A. The N-pole of the resultant magnet is on the face close to:
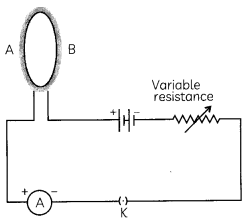
(a) A
(b) B
(c) A if the current is small and B if the current is large
(d) B if the current is small and A if the current is large
Answer:
Question 4.
A uniform magnetic field exists in the plane of paper pointing from left to right as shown in the figure. In the field, an electron and a proton move as shown. The electron and the proton experience:
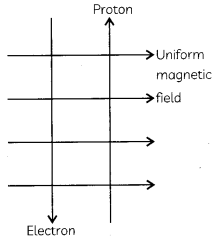
(a) forces both pointing into the plane of paper
(b) forces both pointing out of the plane of paper
(c) forces pointing into the plane of paper and out of the plane of paper, respectively
(d) forces pointing opposite and along the direction of the uniform magnetic field respectively
Answer:
(a) forces both pointing into the plane of paper
Explanation: Apply Fleming’s left hand rule and considering that the flow of current in the direction of the movement of proton and in the direction opposite to the flow of electrons. So, the current due to both electron and proton will be in the same direction because of which, the forces acting on both will be in the same direction. By Fleming’s Left hand rule, the direction of force is pointing into the plane of paper.
Question 5.
For a current in a long straight solenoid N and S-poles are created at the two ends. Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is:
(a) The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines, which indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid
(b) The strong magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can be used to magnetize a piece of magnetic material Like soft iron, when placed inside the coil
(c) The pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet
(d) The N and S-poles exchange position when the direction of current through the solenoid is reversed.
Answer:
Question 6.
An electron moves with a speed v along positive direction of the x-axis. If a magnetic field B acts along the positive y-direction, then the force on the electron will act along:
(a) x-axis
(b) y-axis
(c) -ve z-direction
(d) +ve z-direction [Diksha]
Answer:
(c) -ve z-direction
Explanation: As electron is moving in positive x-direction, then, according to Maxwell’s right-hand thumb rule, the current is moving in negative x-direction and the magnetic field acts on positive y-direction.
Thus, the thumb will be in negative z-direction, which is the direction of force.
Question 7.
Which of the following is not attracted by a magnet:
(a) Steel
(b) Cobalt
(c) Brass
(d) Nickel
Answer:
Question 8.
The magnetic field lines:
(a) intersect at right angles to one another
(b) interest at an angle 45° to each another
(c) do not cross one another
(d) cross at an angle of 60° to one another
Answer:
(c) do not cross one another
Explanation: The magnetic field lines do not cross one another because the resultant force at any point on the north pole can only be in one direction. This is impossible if the Lines intersect
Related Theory
If two magnetic field lines are found to cross each their, it means that at the point of intersection, the compass needle would point towards two directions. which is not possible.
Question 9.
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid carrying current is
(a) uneven
(b) zero
(c) same at aLL points
(d) different at aU Points
Answer:
(c) same at all points
Explanation: The magnetic field lines inside a long straight solenoid carrying current is in the form of parallel straight tines which indicates that the magnetic field is some at oIL points inside the solenoid.
Question 10.
To convert an AC generator into DC generator:
(a) Split ring type commutator must be used
(b) SLIp rings and brushes must be used
(c) A stronger magnetic fieLd has to be used
(d) A rectangular wire Loop has to be used
Answer:
Question 11.
The most important safety method used for protecting home appliances from short-circuiting or overloading is:
(a) Earthing
(b) Use of fuse
(c) Use of stabiLizers
(d) Use of electric meter
Answer:
Question 12.
Which of the given statements are incorrect regarding magnetic field Unes?
(I) The direction of magnetic field at a point is taken to be the direction In which the south pole of a magnetic compass needle points.
(II) Magnetic field Lines are closed curves.
(III) If magnetic field Lines are parallel and equidistant, they represent zero-field strength.
(IV)Relative strength of magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (III)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(c) Both (I) and (III)
Explanation: The direction of magnetic field at a point is taken to be the direction in which the north pole of a magnetic compass needle points. If magnetic field lines are parallel and equidistant, they represent uniform field strength.
Question 13.
The north pole of a long bar magnet was pushed slowly into a short solenoid connected to a galvanometer. The magnet was held stationary for a few seconds with the north pole in the middle of the solenoid and then withdrawn rapidly.
Select the correct observations:
(I) The maximum deflection of the galvanometer will be observed when the magnet was moving out of the solenoid.
(II) The maximum deflection of the galvanometer will be observed when the magnet was moving slowly into of the solenoid.
(III) The minimum deflection of the galvanometer will be observed when the magnet was at rest inside the solenoid.
(IV) The minimum deflection of the galvanometer will be observed when the magnet was moving towards the solenoid.
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(a) Both (I) and (III)
Explanation: The maximum deflection of the galvanometer will be observed when the magnet was moving out of the solenoid as maximum current is induced in the coil due to the relative motion between the solenoid coil and the magnet. Whereas, the minimum deflection of the galvanometer will be observed when the magnet was at rest inside the solenoid as no current is induced in the coil.
Question 14.
A student places some iron fillings around a magnet. The iron fillings arrange themselves as shown in image below.

Four points labelled A, B, C and D have been marked in the figure.
Select the correct statement regarding the strength of magnetic field at these points:
(I) The magnetic field will be strongest at A.
(II) The magnetic field will be strongest at B.
(III) The magnetic field will be weakest at C.
(IV)The magnetic field will be weakest at D.
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 15.
The figure below shows an electric generator.
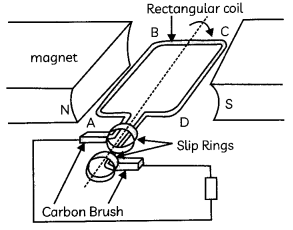
The coil ABCD is rotated and the direction of induced current is noted initially and when coil completes half cycle of the rotation.
Select the row containing correct direction of induced current in the coil ABCD.
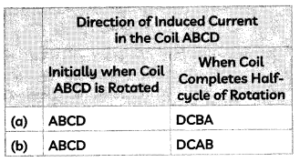

Answer:
(a) Initially when coil ABCD is rotated ABCD; when coil complete is half cycle of rotation DCBA
Explanation: Length AB of the coil ABCD is moving upwards and the magnetic field acts from left to right. Hence, according to Fleming’s right-hand rule, the direction of induced current will be from A to B. And the direction of induced current in the length CD will be from C to D. The direction of current in the coil is ABCD. After half a rotation, length AB starts moving down whereas length CD starts moving upward. The direction of the induced current in the coil gets reversed as DCBA.
Question 16.
Study the graphs (A) and (B) shown below and select the row containing incorrect information from the table.
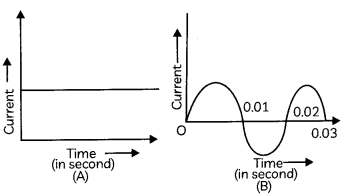
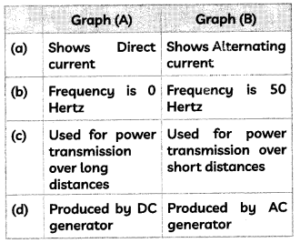
Answer:
Question 17.
The magnetic field lines inside a current-carrying solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines which indicate that:
(a) The magnetic field is zero inside the solenoid.
(b) The field is uniform inside the solenoid.
(d) The field is non-uniform inside the solenoid.
(d) The field is very strong inside the solenoid.
Answer:
(b) The field is uniform inside the solenoid.
Explanation: The magnetic field lines inside a current-carrying solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines which indicate that the field is uniform inside the solenoid.
Question 18.
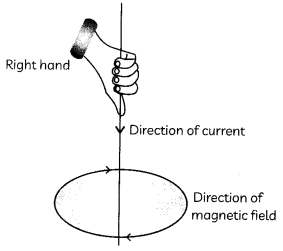
A current-carrying conductor is held in the vertical direction. In order to produce a clockwise magnetic field around the conductor, the current should be passed in the conductor:
(a) From top to bottom
(b) From left to right
(c) From bottom to top
(d) From right to left
Answer:
(a) From top to bottom
Explanation: By applying right-hand thumb rule, we note that in order to produce a clockwise magnetic field around the conductor, the current should be passed from top to bottom in the conductor as shown:
Question 19.
An induced emf is produced when a magnet is moved into a coil. The magnitude of induced emf does not depend on:
(a) The number of turns of the coil
(b) The speed with which the magnet is moved
(c) The strength of the magnet
(d) The resistivity of the wire of the coil
Answer:
Question 20.
Imagine that a negative charge is moving towards a person. The direction of magnetic field lines will be in:
(a) Clockwise direction
(b) Anticlockwise direction
(c) Vertically upward direction
(d) Vertically downward direction
Answer:
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Science Chapter 13
For the following questions, two statements are given one labeled Assertion (A) and the other labeled Reason (R). Select the correct Answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c), and (d) as given below.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is flase, but R is true.
Question 21.
Assertion (A): The energy of charged particle moving in a uniform magnetic field does not change.
Reason (R): Work done by magnetic field on the charge is zero.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 22.
Assertion (A): The compass placed near the current-carrying wire remains stationary.
Reason (R): The current flowing through a wire gives rise to a magnetic field.
Answer:
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Explanation: The compass when placed near the current-carrying wire gets deflected because the current flowing through the wire gives rise to a magnetic field.
Question 23.
Assertion (A): The direction of force acting on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field gets reversed on reversing the direction of current flowing through the conductor.
Reason (R): Magnitude of force is highest when direction of current is parallel to direction of magnetic field.
Question 24.
Assertion (A): Current can be induced in a coil by changing the magnetic field around it.
Reason (R): A galvanometer connected to a coil can deflect either to the left or right of the zero marks.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion. Explanation: Voltage and hence current is induced in a coil due to a changing magnetic field and this process is known as electromagnetic induction.
A galvanometer is a device that detects the presence of current by deflecting the needle to one side of the zero mark, but this does not explain the current induced in the coil.