Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
A student traces the path of a ray of light through a glass prism for different angles of incidence. He analyses each diagram and draws the following conclusion:
(I) On entering prism, the Lightray bends towards its base.
(II) light ray suffers refraction at the point of incidence and point of emergence while passing through the prism.
(III) Emergent ray bends at a certain angle to the direction of the incident ray.
(IV) White emerging from the prism, the Lightray bends towards the vertex of the prism.
Out of the above inferences, the correct ones are:
(a) (I), (II) and (III)
(b) (I), (III) and (IV)
(c) (II), (III) and (IV)
(d) (I) and (IV)
Answer:
(a) (I), (II) and (III)
Related Theory:
In a prism, the ray of light from air into glass bends towards the normal. The ray of light from glass to air bends away from the normal. In both cases, when a ray of light passes through a prism, it bends towards the base of the prism.
Question 2.
A clear sky appears blue, because:
(a) blue light gets absorbed in the atmosphere
(b) ultraviolet radiations are absorbed in the atmosphere
(c) violet and blue lights get scattered more than the lights of all other colours by the atmosphere
(d) lights of all other colours are scattered more than the violet and blue colour lights by the atmosphere
Answer:
Question 3.
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of light of different colours of white light in the air?
(a) Red light moves the fastest.
(b) Blue light moves faster than green light.
(c) All the colours of the white light travel at the same speed.
(d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of red and violet light.
Answer:
Question 4.
In the following diagram, the correctly marked angles are:
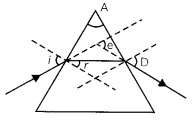
(a) All
(b) Only ∠i, and ∠A
(c) ∠i, ∠r and ∠A
(d) ∠i, ∠A and ∠D
Answer:
Question 5.
The bluish colour of water in deep sea is due to:
(a) the presence of algae and other plants found in water
(b) reflection of the sky in water
(c) scattering of light
(d) absorption of light by the sea
Answer:
(c) scattering of light
Explanation: The bluish colour of water in deep sea is due to scattering of light. The fine particles in water scatter mainly blue light having shortest wavelength.
Related Theory
Water appears blue because when white light from the Sun falls on the water molecules, only blue light is reflected and scattered and reaches our eyes.
The absorption of light by a molecule depends on the wavelength and the size of the molecule. A molecule absorbs light of a wavelength either equal to or greater than the order of the size of the object.
Since red, orange and yellow have longer wavelengths, they are absorbed by the water molecules, whereas blue, having a shorter wavelength, is scattered.
Question 6.
During the experiment, to trace the path of ray of light through the glass prism, students reported the following observations:
(I) The ray of light from air to glass at the first refracting surface bends away from the normal after refraction.
(II) At the second refracting surface, light rays entered from air to glass.
(III) Lightray suffers two refractions on passing through a prism and in each refraction it bends towards the base of the prism.
(IV) Lightray suffers two refractions on passing through a prism. In first refraction, it bends away from the normal while in the second refraction it bends towards the normaL
The correct observation is/are:
(a) (I) and (II) only
(b) (III) only
(c) (II) and (IV) only
(d) (I) and (IV) only
Answer:
Question 7.
In an experiment to trace the path of a ray of light through a triangular glass prism, a student would observe that the emergent ray
(a) is parallel to the incident ray.
(b) is along the same direction of incident ray.
(c) gets deviated and bends towards the thinner part of the prism.
(d) gets deviated and bends towards the thicker part (base) of the prism.
Answer:
Question 8.
In the following ray diagram the correctly marked angle are:
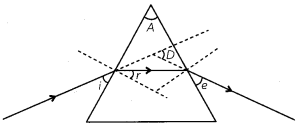
(a) ∠i, and ∠e
(b) ∠A and ∠D
(c) ∠i, ∠e and ∠D
(d) ∠r, ∠A and ∠D
Answer:
(d) ∠r, ∠A and ∠D
Question 9.
A person cannot see distinctly the objects kept beyond 2 m. This defect can be corrected by using a lens of power:
(a) + 0.5 D
(b) – 0.5 D
(c) + 0.2 D
(d) – 0.2 D
Answer:
Question 10.
A student sitting on the last bench can read the letters written on the blackboard but is not able to read the letters written in his textbook. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) The near point of his eyes has receded away.
(b) The near point of his eyes has come closer to him.
(c) The far point of his eyes has come closer to him.
(d) The far point of his eyes has receded away.
Answer:
(a) The near point of his eyes has receded away.
Explanation: The student can see the object which is far from him but can’t see nearby objects. It means that the near point of his eyes has receded away. This condition is known as hypermetropia or farsightedness.
Question 11.
When light rays enter the eye, most of the refraction occurs at the:
(a) crystalline lens
(b) the outer surface of the cornea
(c) iris
(d) pupil
Answer:
(b) the outer surface of the cornea
Explanation: Light enters the eye through a thin membrane called the cornea. It causes most of the bending of incident light rays, i.e. refraction, to make them converge which in turn causes image formation on the retina.
Question 12.
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye muscles:
(a) are relaxed and the lens becomes thinner
(b) contract and the lens becomes thicker
(c) are relaxed and the lens becomes thicker
(d) contract and the lens becomes thinner
Answer:
Question 13.
Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) A person with myopia can see distant objects clearly.
(b) A person with hypermetropia can see nearby objects clearly.
(c) A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly.
(d) A person with hypermetropia cannot see distant objects clearly.
Answer:
(c) A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly.
Explanation: Myopia is also termed as short-sightedness. A person suffering from myopia can see nearby objects clearly but not the distant objects. Whereas hypermetropia is termed as long-sightedness. A person suffering from hypermetropia can see distant objects clearly but not the nearby objects.
Question 14.
Person suffering from cataract has:
(a) elongated eyeball
(b) excessive curvature of eye lens
(c) weakened ciliary muscles
(d) opaque eye Lens
Answer:
Question 15.
When we enter a dark room coming from outside, immediately the things inside the room do not appear clear to our eyes. This is because:
(a) pupils do not open at all in the dark.
(b) pupils take time to adjust.
(c) light travels slower in a dark room.
(d) pupils open very quickly in the dark.
Answer:
Question 16.
The phenomena of light responsible for the working of the human eye is:
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) power of accommodation
(d) persistence of vision
Answer:
Question 17.
The sky appears dark to passengers flying at very high altitudes mainly because:
(a) Scattering of light is not enough at such heights.
(b) There is no atmosphere at great heights.
(c) The size of molecules is smaller than the wavelength of visible light.
(d) The light gets scattered towards the earth.
Answer:
(a) Scattering of light is not enough at such heights.
Explanation: At higher altihide either the atmospheric medium is very rare or there are no particles present/ no atmosphere, thus the scattering of light taking place is not enough at such heights or no scattering of sunlight takes place. Hence, the sky appears dark to the passengers flying at very high altitude.
Question 18.
Given below are some common observations related to optics. Select the row containing incorrect observations and its reason.
| Observation | Reason |
| (a) Colour of water in deep sea | Scattering of light |
| (b) Apparent position of stars | Atmospheric refraction |
| (c) Fishes appear higher than their actual depth | Diffraction of light |
| (d) Spectrum seen on soap bubbles | Dispersion of light |
Answer:
(c) Observation: Fishes appear higher than their actual depth, Reason: Diffraction of light
Explanation: Fishes appear higher than their actual depth due to the refraction of light as light travels from water, an optically denser medium, to air, a rarer medium. Diffraction of light refers to the phenomena of bending of light around corners.
Question 19.
The defective eye of a person has near point 0.5 m and far point 75 cm. The table below lists the type of corrective lens and its power required for reading purposes and for seeing distant objects.
Select the row containing the correct information:
| For reading purpose | For seeing distant objects |
| (a) Concave lens of power – 0.5 D | Convex lens of power + 0.75 D |
| (b) Convex lens of power +0.5 D | A concave lens of power – 0.75 D |
| (c) Convex Lens of power + 0.5 D | Concave Lens of power-1.33 D |
| (d) Convex Lens of power + 2.0 D | Concave Lens of power -1.33 D |
Answer:
Question 20.
A 55 year old near-sighted person wears spectacles with a power of – 2.5 D for distance viewing. His doctor prescribes a correction of + 2.0 D in the near-vision section of his bifocals. This is measured relative to the main part of the lens.
Select the correct statements:
(I) The focal length of the distance-viewing part of the lens is – 40 cm.
(II) The focal length of the near-vision part of the lens is + 50 cm.
(III) The focal length of the distance-viewing part of the lens is + 50 cm.
(IV) The focal length of the near-vision part of the lens is – 40 cm.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (I) and (IV)
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 21.
A beam of white light falling on a glass prism gets split up into seven colours marked 1 to 7 as shown in the diagram
Select the incorrect statements regarding the colours marked from 1 to 7:
(I) The colour at position marked 7 and 5 are similar to the colour of the blood and colour of gold metal respectively.
(II) The colour at position marked 1 and 3 are similar to the colour of the blood and colour of gold metal respectively.
(III) The colour at position marked 3 and 4 are similar to the colour of the sky and colour of leaves in plants respectively.
(IV) The colour at position marked 5 and 4 are similar to the colour of the sky and colour of leaves in plants respectively.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 22.
The defects of vision hypermetropia and myopia can be corrected by:
(a) Concave and a plano-convex lens
(b) Concave and convex lens
(c) Convex and concave lens
(d) Plano-concave lens for both defects.
Answer:
(c) Convex and concave lens
Explanation: Hypermetropia or far sightedness can be corrected by using convex lens of appropriate power and myopia by a concave lens of appropriate power.
Question 23.
The layer of atmosphere whose temperature is less than that of the hotter layer behaves as an optically
(a) denser medium
(b) rarer medium
(c) inactive medium
(d) either denser or rarer medium
Answer:
(a) denser medium
Explanation: The layer of atmosphere whose temperature is less than that of hotter layer is more denser as compared to the hotter layer of the atmosphere. So, when light travels from a cooler layer of atmosphere to a hotter Layer, it will bend away from the normal.
Question 24.
The sun appears white at noon as:
(a) Blue colour is scattered the most
(b) Red colour is scattered the most
(c) Light is least scattered
(d) All the colours of the white light are scattered away
Answer:
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Science Chapter 11
For the following questions, two statements are given-one tabled Assertion (A) and the other labeled Reason (R) select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below: ,
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is correct explanation of the (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not correct explanation of the (A).
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
Question 25.
Assertion (A): Sky appears in blue colour.
Reason (R): Blue colour in sunlight travelling through atmosphere undergoes maximum scattering.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the (A).
Explanation: The blue colour of the sky is due to the scattering of blue colour to the maximum extent by dust particles. The blue colour appears to be coming from the sky. Blue colour has the least wavelength. Hence, the correct option is (a).
Question 26.
Assertion (A): When white light passes through a glass prism, red colour has deviated the least.
Reason (R): Red colour has the minimum speed in the glass prism.
Answer:
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
Explanation: When white light passes through a glass prism, red colour deviates the least because red colour has maximum speed in the prism.
Question 27.
Assertion (A): When objects are observed through hot air, they appear to be moving slightly.
Reason (R): Hotter air is optically denser and the cooler air is optically rarer.
Answer:
Question 28.
Assertion (A): A rainbow is always formed in the sky after a rain shower and in the same direction as the sun.
Reason (R): Water droplets act as tiny prisms.
Answer:
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
Explanation: A rainbow is always formed in the sky in a direction opposite to that of the sun. The water droplets present in the sky act as tiny prisms, which refract and disperse sunlight, then reflect it internally and finally refract it again when it comes out of the raindrop.
Question 29.
Assertion (A): The sun’s disc appears to be flattened at sunrise and sunset.
Reason (R): The sun is near the horizon at sunrise and sunset and sunlight suffers atmospheric refraction.
Answer: