Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Beams of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of box through the holes C and D respectively, as shown in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
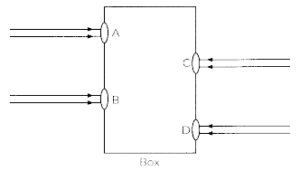
(a) A rectangular glass slab
(b) A convex lens
(c) A concave less
(d) A prism
Answer:
Question 2.
A beam of light is incident through the holes on side A and emerges out of the holes on the other face of the box as shown in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
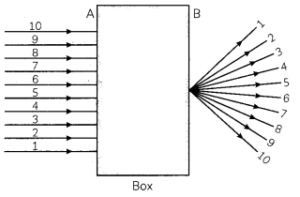
(a) Concave lens
(b) Rectangular, glass slab
(c) Prism
(d) Convex lens
Answer:
(d) Convex lens
Explanation: In the given diagram, parallel rays converge at a point and emerge from face B. So, there will be a convex lens inside the box.
Question 3.
When an object is kept within the focus of a concave mirror, an enlarged image is formed behind the mirror. This image is:
(a) real
(b) inverted
(c) virtual and inverted
(d) virtual and erect
Answer:
Question 4.
A full length image of a distant tall building can definitely be seen by using:
(a) a concave mirror
(b) a convex mirror
(c) a plane mirror
(d) both concave as well as plane mirror
Answer:
Question 5.
Your school laboratory has one large window. To find the focal length of a concave mirror using one of the walls as screen, the experiment may be performed:
(a) on the same wall as the window.
(b) on the wall adjacent to the window.
(c) on the wall opposite to the window.
(d) only on the table as per laboratory arrangement.
Answer:
(d) only on the table as per laboratory arrangement.
Question 6.
The path of a ray of light coming from air passing through a rectangular glass slab is traced by four students shown as A, B, C and D in the figure. Which one of them is correct?
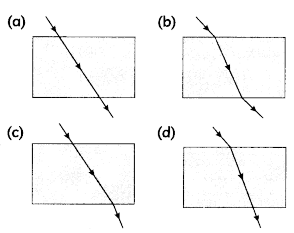
Answer:
Question 7.
In order to determine the focal length of a concave mirror by obtaining the Image of a distant object on screen, the position of the screen should be:
(a) parallel to the pLane of concave mirror
(b) perpendicular to the plane of concave mirror
(c) IncLined at an angle 600 to the plane of mirror
(d) in any direction with respect to the plane of concave mirror [Dikshaj
Answer:
(a) parallel to the plane of concave mirror
Explanation: AD the refLected light rays converge and pass through the focus (F) of a concave mirror. Since the focus of a concave mirror is in front of the mirror, the screen has to be placed parallel in front of the mirror.
Question 8.
A student carries out the experiment of tracing the path of a ray of Light through a rectangular glass slab for two different values of angLe of incidence ∠i = 300 and ∠i = 45° In the two coses the student is likely to observe the set of vaLues of angle of refraction and angLe of emergence as
(a) ∠r =30, ∠e = 20° and ∠r = 45’, ∠e = 28°
(b) ∠r =30°. ∠e = 30° and ∠r=45°, ∠e= 450
(c) ∠r =200, ∠e = 30° and ∠r = 28°, ∠e=45°
(d) ∠r =20°, ∠e = 20° and ∠r = 28°, ∠e = 28°
Answer:
(c) ∠r=20° ∠e=30° and ∠r= 28 ∠e=45°
Related Theory:
The angle of refraction must be less than the angle of incidence. White angle of emergence is equal to angle of incidence.
for ∠i = 300. ∠r = 20° and ∠e = 30
for ∠i = 450e ∠r = 28° and ∠e = 45°
Question 9.
If you focus a distant object of the shape using a concave mirror, the Image obtained must be of the shape
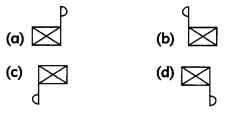
Answer:
Question 10.
In which of the following diagrams has the protractor (D) been correctly placed to measure the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence?
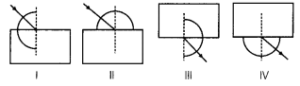
a) I, III
(b) I, IV
(c) II, III
(d) II, IV
Answer:
(a) I, III
Explanation: The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the normal at the point of incidence. The angle of emergence is the angLe between the emergent ray and the normal at the point of emergence.
Moreover, the protractor should always be placed in such a way that its base is always along the normal of the incident ray or the emergent ray.
Question 11.
An optical device has been given to a student and he determines its focal Length by focusing the image of the sun on a screen placed 24 cm from the device on the same side as the sun. Select the correct statement about the device.
(a) Convex mirror of Focal Length 12 cm
(b) Convex Lens of focal Length 24 cm
(c) Concave mirror of focal length 24 cm
(d) Convex tens of Focal Length 12 cm
Answer:
Question 12.
A student is performing the experiment of determining the Focal Length of a given concave mirror by focussing a distant tree on a screen. Which one of the following kinds of images he is likely to obtain on the screen?
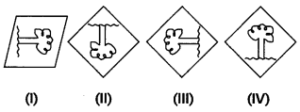
(a) (I)
(c) (III)
(b) (II)
(d) (IV)
Answer:
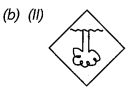
Explanation: A concave mirror forms a real and inverted image of a distant object, such as tree, at its focus.
Question 13.
A student has focussed on the screen a distant building using a convex lens. If he has selected a blue coloured building as object, select from the following options the one which gives the correct characteristics of the image formed on the screen.
(a) Virtual, erect, diminished and green shade
(b) Real, inverted, diminished and in violet shade
(c) Real, inverted, diminished and in blue shade
(d) Virtual, inverted, diminished and in blue shade
Answer:
(c) Real, inverted, diminished and in blue shade
Explanation: As the student has focussed a distant blue coloured building on the screen using a convex lens, a real inverted and diminished image is formed at the principal focus of the convex lens.
As object is quite far, a diminished image will be formed at the principal focus.
The colour of image will be same as colour of the object because no change in colour takes place during refraction.
Question 14.
Study the following four experimental setups by four students A, B, C and D showing the incident ray to trace the path of a ray of light through a glass slab. Which of these will get the best result?
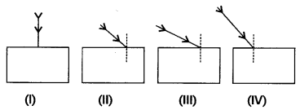
(a) (I)
(b) (II)
(c) (III)
(d) (IV)
Answer:
Question 15.
The focal length of the concave mirror in the following experimental set-up is:
Answer:
(d) 6.6 cm
Explanation: The least count of optical bench \(\frac{1}{5}\)cm = 0.2 cm
Position of the concave mirror = 12.8 cm
Position of the screen = 6.2 cm
Focal length of the concave mirror = distance of the screen from the pole of the concave mirror = 12.8 – 6.2 cm = 6.6 cm
Question 16.
Three students A, B and C focussed a distant building on a screen with the help of a concave mirror. To determine focal length of the concave mirror they measured the distances as given below:
Student A: From mirror to the screen
Student B: From building to the screen
Student C: From building to the mirror
Who measured the focal length correctly:
(a) Only A
(b) Only B
(c) A and B
(d) B and C
Answer:
(a) Only A
Explanation: A concave mirror forms a distinct image of a distant object at its focus. As student ‘A’ measures the distance between mirror to the screen to find the focal length, he measured the focal length correctly.
Question 17.
A student has traced the path of a ray of light through a glass slab as follows. If you are asked to label 1, 2, 3 and 4, the correct sequencing of labelling Zi, Ze, Zr and lateral displacement respectively is
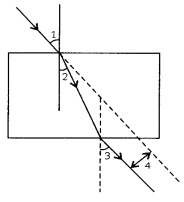
(a) 2,1, 3, 4
(b) 1, 2, 3, 4
(c) 1, 3, 2, 4
(d) 1, 3, 4, 2
Answer:
(c) 1, 3, 2, 4
Related Theory
Angle of emergence (e): The angle of the light coming out of a medium.
Lateral displacement: The perpendicular distance between the incident ray and the emergent ray.
Question 18.
A student determines the focal length of a device X by focusing the image of a distant object on a screen placed 20 cm from the device on the same side as the object.
The device X is
(a) Concave lens of focal length 10 cm
(b) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm
(c) Concave mirror of focal length 10 cm
(d) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm
Answer:
Question 19.
A student obtained a sharp image of a candle flame placed at the distant end of the laboratory table on a screen using a concave mirror to determine its focal length. The teacher suggested him to focus a distant building about 1 km far from the laboratory, for getting more correct value of the focal length. In order to focus the distant building on the same screen the student should slightly move the:
(a) mirror away from the screen
(b) screen away from the mirror
(c) screen towards the mirror
(d) screen towards the building
Answer:
(c) screen towards the mirror
Question 20.
A student obtains a sharp image of the distant window (W) of the school laboratory on the screen (S) using the given concave mirror (M) to determine its focal length. Which of the following distances should he measure to get the focal length of the mirror?
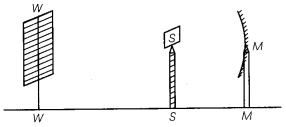
(a) MW
(b) MS
(c) SW
(d) MW – MS
Answer:
Question 21.
The image formed by a plane mirror is:
(a) virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged
(b) virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object
(c) real, at the surface of the mirror and enlarged
(d) real, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object
Answer:
(b) Virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object
Question 22.
When object moves closer to convex lens, the image formed will be
(a) away from the lens on the other side of lens.
(b) towards the lens.
(c) away from the lens on the same side of an object.
(d) first towards and then away from the lens.
Answer:
Question 23.
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in figure?
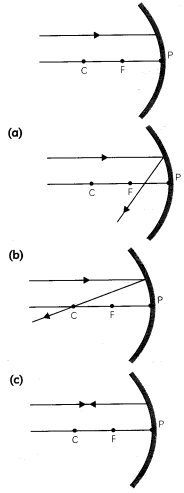
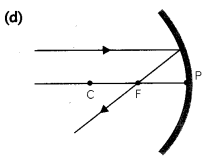
Answer:

Explanation: Ray of light parallel to the principal axis towards the mirror after reflection from the mirror will pass through the focus.
Question 24.
The refractive index of four substances P, Q, R and S are 1.50, 1.36, 1.77 and 1.31 respectively. The speed of light is the maximum in the substance:
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
Question 25.
Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens?
(a) Water
(b) Glass
(c) Plastic
(d) Clay
Answer:
(d) Clay
Explanation: Clay is opaque and does not let light to pass through it.
Question 26.
A small bulb is placed at the focal point of a converging lens. When the bulb is switched on, the lens produces:
(a) a convergent beam of light
(b) a divergent beam of light
(c) a parallel beam of light
(d) a patch of coloured light
Answer:
(c) A parallel beam of light
Explanation: When an object is placed at the focus of a convex lens, the convex lens convert the diverging rays of light coming from the object into a parallel beam of light rays which form an image at infinity.
Question 27.
In torches, search lights and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed:
(a) between the pole and the focus of the reflector
(b) very near to the focus of the reflector
(c) between the focus and centre of curvature of the reflector
(d) at the centre of curvature of the reflector
Answer:
Question 28.
You are given water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene. In which of these media, a ray of light incident obliquely at some angle would bend the most? (Refractive index of water = 1.33, Mustard oil = 1.46, Glycerine = 1.473, Kerosene = 1.44)
(a) Kerosene
(b) Water
(c) Mustard oil
(d) Glycerine
Answer:
(d) Glycerine
Explanation: Out of the given four materials, the refractive index of glycerine is highest. So, greatest deviation of incident light ray is observed in case of glycerine.
Related Theory
A substance having higher refractive index is optically denser than another substance having lower refractive index. We can conclude, the higher the refractive index of a substance, more it will change the direction of a beam of light passing through it.
Question 29.
A student obtained a sharp inverted image of a distant tree on the screen placed behind a convex lens. He then removed the screen and tried to look through the lens in the direction of the object. He would now observe:
(a) a blurred image on the wall of the laboratory
(b) an erect image of the tree on the lens
(c) no image as the screen has been removed
(d) an inverted image of the tree at the focus of the lens
Answer:
Question 30.
Magnification produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles:
(a) is less than one
(b) is more than one
(c) is equal to one
(d) can be more than or less than one depending upon the position of the object in front of it.
Answer:
(a) is less than one
Explanation: Convex mirror is used as a rear view mirror in vehicles. It forms virtual, erect and diminished images of the objects.
As magnification is defined as the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object, hence, magnification produced by a rearview
Question 31.
You are provided four convex lenses of focal length 10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm. Which out of the four lenses will converge light the most and the least?
Select the row containing the correct answer and reason:
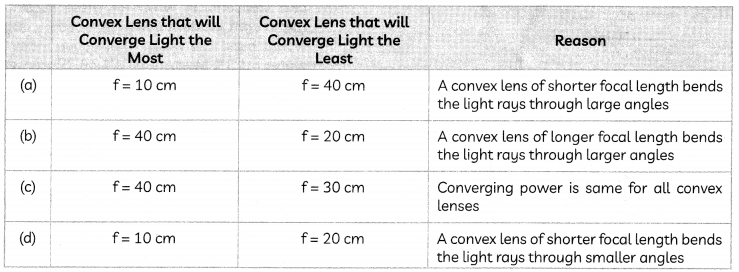
Answer:
Question 32.
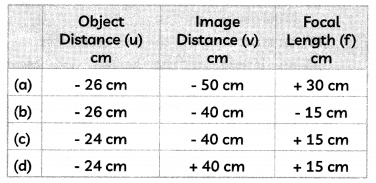
A student-focussed the image of a candle flame on a white screen using a convex lens. He noted down the position of the candle screen and the lens as under
Position of candle = 26.0 cm
Position of convex lens = 50.0 cm
Position of the screen = 90.0 cm
Students noted down the values of object distance (u), image distance (v) and also calculated the focal length (f) of the convex lens used.
Select the row containing the correct values as per the sign convention:
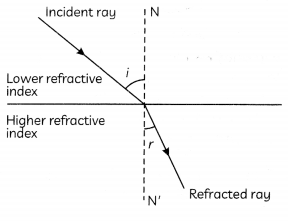
Question 33.
Select the correct statements from the statements given below regarding refraction of light when light is incident from a medium A having refractive index 1.85 on a glass slab having refractive index 1.50.
(I) Light will bend towards the normal in the glass slab.
(II) Emergent ray will be parallel to the refracted ray.
(III) Speed of light will be more in glass slab as compared to medium A.
(IV) Angle of refraction will be more than angle of incidence.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (II) and (IV)
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Explanation: As light is incident from the medium A having higher refractive index than glass, speed of light will be less in medium A as compared to glass. When light traveLs from a denser to a rarer medium, it bends away from the normal. Therefore, angle of refraction will be greater than the angle of incidence.
Question 34.
Four statements are written below which are the general rules for drawing ray diagrams in case of lenses. Select the incorrect statements:
(I) A ray of light from the object, parallel to the principal axis, after refraction from a concave lens, passes through the principal focus on the other side of the lens.
(II) A ray of light appearing to meet at the principal focus of a convex lens, after refraction, will emerge parallel to the principal axis.
(III) A ray of light passing through a principal focus, after refraction from a convex lens, will emerge parallel to the principal axis.
(IV) A ray of light passing through the optical centre of a lens will emerge without any deviation.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 35.
Given below are statements regarding sign conventions for reflection by spherical mirrors. Select the correct statements.
(I) All distances parallel to the principal axis are measured from the pole of the mirror.
(II) All the distances measured to the left of the origin (along – x-axis) are taken as positive while those measured to the right of the origin (along + x-axis) are taken as negative.
(III) Distances measured perpendicular to and above the principal axis (along + y-axis) are taken as positive.
(IV) Distances measured perpendicular to and above the principal axis (along +y-axis) are taken as negative.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (III)
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 36.
Refractive indices of turpentine oil, sapphire, water and crown glass are 1.47, 1.77, 1.33 and 1.52 respectively. In which of these media will a ray of light incident obliquely at the same angle from air would bend the least?
(a) Turpentine oil
(b) Sapphire
(c) Water
(d) Crown glass
Answer:
(c) Water
Explanation: The speed of light in a medium is inversely proportional to the refractive index of the medium. And the amount of bending is also inversely proportional to the refractive index of the medium. As the refractive index of water is the least out of the given media, it is optically rarer as compared to the other media. So, light will bend the least in water.
Question 37.
Kaashvi performed an activity using a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm. She placed the object 30 cm in front of the mirror. Where is the image likely to be formed?
(a) At 10 cm behind the mirror
(b) At 10 cm in front of the mirror
(c) At 60 cm in front of the mirror
(d) At 60 cm behind the mirror
Answer:
Question 38.
The angle between the incident and reflected rays is 90° as shown below:
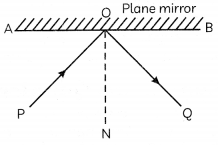
If the plane mirror is rotated by 10° about O in the anti-clockwise direction, then the angle between the incident and reflected rays will be:
(a) 55°
(b) 90°
(c) 100°
(d) 110°
Answer;
Question 39.
Two lenses, a convex lens of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens of focal length 25 cm, are held close to each other. The focal length of the combination of the lenses is:
(a) + 45 cm
(b) – 5 cm
(c) – 45 cm
(d) + 100 cm
Answer:
(d) + 100 cm
Explanation: The power of combination of two lenses is P = P1 + P2, where P1 is the power of convex lens of focaL length 20 cm and P2 is power of concave lens of focal length 25 cm.
As Power (in Dioptre) = P = \(\frac{1}{f(\text { inm })}\)
Therefore, \(\frac{1}{f_{1}}+\frac{1}{f_{2}}=+\frac{100}{20}-\frac{100}{25}\) = +1
Thus, focal length of combination = +100 cm
Question 40.
Magnification produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles:
(a) is less than one
(b) is more than one
(c) is equal to one
(d) can be more than or less than one depending upon the position of the object in front of it.
Answer:
(a) is Less than one
Explanation: Convex mirror is used as a rear view mirror in vehicles. It forms virtual, erect and diminished images of the objects.
As magnification is defined as the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object, hence, magnification produced by a rear view mirror, fitted in vehicles is less than one.
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Science Chapter 10
For the following questions, two statements are given one labelled Assertion (A) and the Other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answers to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question 41.
Assertion (A): A convex mirror is used as a rearview/driver’s mirror.
Reasoning (R): Convex mirrors have a wider field of view as they are curved outwards. They also give an erect, although diminished image. [Diksha]
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not correct explanation of the assertion. Explanation: Since the image formed is highly diminished in convex mirror, we can see the full image of far away objects, which is otherwise not possible in concave and plane mirrors.
Question 42.
Assertion (A): The word AMBULANCE on the hospital vans is written in the form of its mirror image as AMBULANCE in inverted form.
Reason (R): The image formed in a plane mirror is same size of the object.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not correct explanation of the assertion.
Explanation: The word AMBULANCE is written backwards (inverted) as when it is seen through a mirror in the vehicles ahead the drivers see it as AMBULANCE without inversion and give way to it on priority.
Question 43.
Assertion (A): Light travels faster in glass than in air.
Reason (R): Glass is denser than air.
Answer:
Question 44.
Assertion (A): A convex lens has a real focus.
Reason (R): All light rays pass through the focus of a convex lens after refraction.
Answer:
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
Explanation: A convex lens has a real focus as all the light rays parallel to the principal axis actuaLly pass through the focus of the convex lens after refraction. However, rays which are not parallel to the principal axis do not pass through the focus of the convex lens.
Question 45.
Assertion (A): A ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror is reflected back along the same path.
Reason (R): The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie on the same plane.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not correct explanation of the assertion. Explanation: A ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror is reflected back along the same path because the rays are incident normally on the mirror. Therefore, angle of incidence = 0° and so, angle of reflection is also 0°. The law of reflection, namely, angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection is being followed here.
Question 46.
Assertion (A): The power of a concave lens is negative.
Reason (R): A concave lens has a virtual focus.
Answer: