Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following is not a physical change?
(a) Boiling of water to give water vapour.
(b) Melting of ice to give water.
(c) Dissolution of salt in water.
(d) Combustion of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG).
Answer:
(d) Combustion of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG).
Explanation: Since the combustion of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) produces new substances, a lot of heat is produced along with carbon dioxide and water vapour. It is also irreversible in nature. So it is a chemical change.
However, boiling of water to give water vapour, melting of ice to give water and dissolution of salt in water are physical changes, as here no new substance is formed, only the physical state of the substance changes.
A physical change does not produce a new substance although the initial and final substances appear different and it is reversible.
During a chemical change, the chemical composition of the substance changes and new substances with new properties are formed. Energy is either released or absorbed during a chemical change and it is irreversible.
Question 2.
Which of the following is (are) an endothermic process(es)?
(I) Dilution of sulphuric acid
(II) Sublimation of dry ice
(III) Condensation of water vapours
(IV) Evaporation of water
(a) (I) and (III)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Only (III)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 3.
Strong heating of ferrous sulphate leads to the formation of a brown solid and two gases. This reaction can be categorised as:
(a) displacement and redox.
(b) decomposition and redox.
(c) displacement and endothermic.
(d) decomposition and exothermic.
Answer:
(b) decomposition and redox reaction.
Explanation: When FeSO4 is heated strong, it decomposes to form a brown solid ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide.
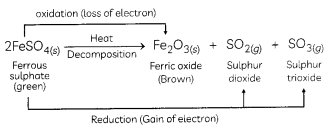
In this reaction, FeSO4 decomposes and forms new products so it is a decomposition reaction. Here FeSO4 is oxidised to Fe2O3 by loss of electrons. So this part of the reaction is oxidation reaction FeSO4 is also reduced to SO2 and SO3 by a gain of electrons.
Hence, the Heating of FeSO4 is both decomposition and Redox reaction.
Related Theory:
A reaction is called redox when both oxidation and reduction are taking place simultaneously.
The oxidation process involves:
- Gain of oxygen
- Loss of hydrogen
- Loss of electrons
Reduction process involves:
- Loss of oxygen,
- Gain of hydrogen
- Gain of electrons
The substance which loses electrons i.e. gets oxidised, acts as a reducing agent and the substance which gains electrons, i.e. it gets reduced and acts as an oxidising agent.
Question 4.
Which among the following is (are) double displacement reaction(s)?
(I) Pb + CuCl2 → PbCl2 + Cu
(II) Na2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4 + 2NaCl
(III) C + O2 → CO2
(IV) CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
(a) (I) and (IV)
(b) Only (II)
(c) (I) and (II)
(d) (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) only (II)
Explanation: A double displacement reaction involves the displacement of two ions of two different compounds that results in the formation of new compounds. Here, only in reaction (II), ions of both reactants are exchanged and two entirely different compounds are formed. For example.
Na2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4(s) (White ppt) + 2NaCl(aq)
In a double displacement reaction, exchange of ions takes place i.e., SO42- exchange place with Cl– ion. It is also called a precipitation reaction as BaSO4 is precipitated as insoluble salt in the solution.
Question 5.
Barium chloride on reacting with ammonium sulphate forms barium sulphate and ammonium chloride. Which of the following correctly represents the type of reaction involved?
(I) Displacement reaction
(II) Precipitation reaction
(III) Combination reaction
(IV) Double displacement reaction
(a) Only (I)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Only (IV)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 6.
When copper turnings are added to silver nitrate solution, a blue coloured solution is formed after some time. It is because copper:
(I) Displaces silver from the solution
(II) forms a blue coloured complex with AgNO3
(III) Is oxidized to Cu2+
(IV) ls reduced to Cu2+
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (I) and (III)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(c) (I) and (III)
Explanation: Copper is placed above silver in electrochemical series and thus reaction occurs
Cu + 2Ag+ → Cu2+ + 2Ag
Question 7.
One of the following does not happen during a chemical reaction. This is:
(a) Breaking of old bonds and formation of new bonds
(b) Formation of new substances with entirely different properties
(c) Atoms of one element change into those of another element to form new products
(d) A rearrangement of atoms takes place to form new products
Answer:
(c) atoms of one element change into those of another element to form new products. Explanation: It is not atoms but the bonds between these atoms break and form during chemical reactions. Atoms of elements can rearrange but cannot change into other elements.
Question 8.
You are given the solution of lead nitrate. In order to obtain a yellow precipitate, you should mix with it a solution of:
(a) potassium chloride
(b) potassium nitride
(c) potassium sulphide
(d) potassium iodide
Answer:
(d) potassium iodide
Explanation: Potassium iodide on reacting with lead nitrate gives yellow precipitate of Lead iodide.
2KI + Pb(NO3)2 → Pbl2 + 2KNO3
Question 9.
In which of the following chemical equations do the abbreviations represent the correct states of the reactants and products involved at reaction temperature?
(a) 2H2(l) + O2(l) → 2H2O(g)
(b) 2H2(g) + O2(l) → 2H2O(g)
(c) 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l)
(d) 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g)
Answer:
Question 10.
Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to granulated zinc taken in a test tube. The following observations are recorded. Point out the correct observation:
(a) The surface of metal becomes shiny.
(b) The reaction mixture turns milky.
(c) Odour of a pungent-smelling gas is recorded.
(d) A colourless and odourless gas is evolved. [Diksha]
Answer:
(d) A colourless and odourless gas is evolved. Explanation: The chemical reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid and granulated zinc is represented as follows:
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2↑
The product, zinc chloride, does not turn the reaction milky. Hydrogen gas evolved is colourless and odourless and released by the formation of bubbles. Hence, option (d) is correct.
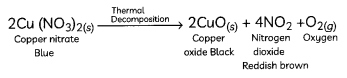
Question 11.
On heating, a blue coloured powder of copper (II) nitrate in a boiling tube, a black substance X, oxygen gas and a brown gas Y was formed. Select the option which identifies the products correctly:


Answer:
(c) X is Copper Oxide and Y is Nitrogen Dioxide Explanation: When blue coloured powder of copper (II) nitrate is heated, it decomposes to form black coloured substance which is copper oxide, oxygen gas and brown gas nitrogen dioxide.
The chemical equation for the reaction taking place is:
Question 12.
In the equation:
Cu + XHNO3 → CU(NO3)2 + yNO2 + 2H2O
The values of x and y are:
(a) 3 and 5
(b) 8 and 6
(c) 4 and 2
(c) 7 and 1
Answer:
(c) Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
Explanation: In order to find the values of x and y, we need to balance the chemical equation by equating the number of atoms of each element on both sides in the given equation.
Cu + XHNO3 → CU(NO3)2 + yNO2 + 2H2O

Equating the number of H atoms on both sides as per the law of conservation of mass, x = 4.
Putting this value in either the no. of atoms of N or O,
x = y + 2 means y = x – 2 = 4 – 2 = 2.
Therefore, x = 4 & y = 2 is the correct answer
Question 13.
In which of the following chemical equations, the abbreviations represent the correct states of the reactants and products involved at reaction temperature?
(a) AlCl3(aq) + 3NH4OH(aq) → Al(OH)3(s) + 3NH4Cl(aq)
(b) AlCl3(aq) + 3NH4OH(l) → Al(OH)3(aq) + 3NH4Cl(s)
(c) AlCl3(aq) + 3NH4OH(aq) → Al(OH)3(s) + 3NH4Cl(aq)
(d) AlCl3(aq) + 3NH4OH(aq) → Al(OH)3(aq) + 3NH4Cl(s)
Answer:
(a) AlCl3(aq) + 3NH4OH(aq) → Al(OH)3(s) + 3NH4CL(aq)
Explanation: When ammonium hydroxide solution is added to aluminium chloride solution, a white precipitate of aluminium hydroxide is formed alongwith ammonium chloride solution.
Question 14.
The reaction 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O is an example of:
(I) displacement reaction.
(II) double displacement reaction.
(III) neutralisation reaction.
(IV) combination reaction.
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (III) and (IV)
(d) (I) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 15.
Consider the following chemical equation:
X(aq) + sodium chloride(aq) → Y(white ppt) + Sodium nitrate(aq)

Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Science Chapter 1
For the following questions, two statements are given: one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question 16.
Assertion (A): Following is a balanced chemical equation for the action of steam on iron:
4Fe + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4 + 4H2
Reason (R): The law of conservation of mass holds good for a chemical equation.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Explanation: Iron (Fe) metal does not react with cold or hot water but it reacts with steam to form a metal oxide and hydrogen.
The law of conservation of mass holds good for a chemical reaction. The statement is true but it does not explain about the equation given in the Assertion.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): Magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling white flame.
Reason (R): Magnesium ribbon undergoes physical change on burning and melts.
Question 18.
Assertion (A): While equalizing the number of atoms to balance a chemical equation, we alter the formula of the compounds or elements involved in the reaction.
Reason (R): Chemical equation is balanced by making the number of atoms of each element equal on both sides of the arrow.
Answer:
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Explanation: A chemical equation is balanced by making the number of atoms of each element equal on both sides of the arrow without altering the formula of the compounds or elements involved in the reaction. It is balanced by putting coefficients in front of the compounds or elements.
Question 19.
Assertion (A): The reaction of calcium oxide with water to produce slaked lime releasing a large amount of heat is a combination reaction.
Reason (R): Double displacement reactions are the reactions in which there is an exchange of ions between the reactants.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Explanation: The reaction of calcium oxide with water to produce sLaked lime releasing a large amount of heat is a combination reaction as the two reactants combine to form a single product.
Whereas, in a double displacement reaction, there will be two reactants and two products which are formed by the exchange of ions between the reactants.
Question 20.
Assertion (A): The decomposition reaction of silver chloride into silver and chlorine is an exothermic process.
Reason (R): Reactions in which energy is absorbed are known as endothermic reactions.
Question 21.
Assertion (A): Zinc and lead displace copper from their compounds.
Reason (R): Zinc and lead are more reactive than copper.