Federalism Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option:
……………….. is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country.
(a) Dictatorship
(b) Unitary system
(c) Monarchy
(d) Federalism
Answer:
(d) Federalism
Question 2.
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option:
In a federal system, the central government…………..order the state government to do something.
(a) Can
(b) Cannot
(c) May
(d) Should
Answer:
Question 3.
Which subject does not come under the State List in India?
(a) Police
(b) Agriculture
(c) Banking
(d) Trade
Answer:
(c) Banking
Explanation: Banking comes under the Union List.
Question 4.
On which of the following subjects can both the Union as well as the State Governments make laws?
(a) Communications
(b) Defence
(c) Trade Unions
(d) Agriculture
Answer:
(c) Trade Unions
Explanation: Trade unions is a part of a concurrent list. On a concurrent list, both the state and central governments can make laws.
Question 5.
Based on the table below, answer the question that follows:
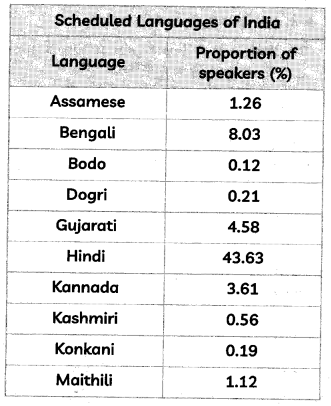
Which is the second most commonly spoken language according to the table?
(a) Hindi
(b) Bodo
(c) Gujarati
(d) Bengali
Answer:
(d) Bengali
Explanation:
Hindi: 43%
Bodo: 0.12%
Gujarati: 4.58%
Bengali: 8.03%
Question 6.
States such as Assam, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram enjoy special powers under certain provisions of the Constitution of India (Article 371), under which context do they get these provisions?
(a) Their historical circumstances
(b) Protection of land rights of indigenous people
(c) Special provisions for agriculture
(d) Preferential employment in government services.
Answer:
(c) Special provisions for agriculture.
Question 7.
On which basis were states like Nagaland, Uttarakhand and Jharkhand created?
(a) On the basis of history
(b) On the basis of culture and ethnicity
(c) On the basis of religion
(d) On the basis of administrative efficiency
Answer:
(b) On the basis of culture and ethnicity
Question 8.
There are some units of the Indian Union that enjoy very little power. These are called:
(a) Cities
(b) Towns
(c) Villages
(d) Union Territories
Answer:
Question 9.
What is true regarding sources of revenue in a federal system?
(a) States have no financial powers.
(b) States are dependent on revenue on the central government.
(c) Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified in the constitution to ensure its financial autonomy.
(d) The Centre has no financial autonomy.
Answer:
(c) Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified in the constitution to ensure its financial autonomy.
Question 10.
Consider the following statements regarding language policy of Indian federation:
(1) Hindi was identified as the official language.
(2) Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as scheduled languages.
(3) English can be used along with Hindi for official purposes.
Choose the combination that provides the correct statements) from the following :
(a) (1) and (3)
(b) (1) and (2)
(c) only (1)
(d) (1), (2) and (3)
Answer:
(d) (1), (2) and (3).
Question 11.
what type of distribution of powers does the Indian Constitution provide for?
(a) Single-fold
(b) Two-fold
(c) Three-fold
(d) Four-fold
Answer:
Question 12.
Who presides over the meetings of Municipal Corporations?
(a) District Magistrate
(b) Mayor
(c) Deputy Mayor
(d) Governor
Answer:
(b) Mayor
Explanation: The head of the municipal corporation is called mayor.
Related Theory
The Mayor is the first citizen of the city and is elected by the members of the municipal corporation for the period of 5 year.
Question 13.
How many languages are included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution?
(a) 20
(b) 21
(c) 22
(d) 24
Answer:
(c) 22
Explanation: These 22 languages are calLed ‘Scheduled Languages.’
Question 14.
Which of the following pair of subjects is incorrect?
(a) Police and agriculture
(b) Banking and currency
(c) Computer software and trade unions
(d) Marriage and adoption
Answer:
Question 15.
Which of the following group of countries are an example of coming together federation?
(a) India, USA, Belgium
(b) USA, Switzerland, Australia
(c) India, Belgium, Spain
(d) USA, Spain, Australia
Answer:
(b) USA, Switzerland, Australia
Question 16.
Study the given picture and identify which of the following options best signifies this cartoon?

(a) Sharing of responsibility between Centre and State
(b) Centre undermining the power of States
(c) States pleading from centre for more power
(d) Misuse of power by the States
Answer:
Question 17.
Which of the following pair of languages is NOT included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution?
(a) Pali and Tulu
(b) Bodo and Maithili
(c) Nepali and Oriya
(d) Sindhi and Urdu
Answer:
(a) Pali and Tulu
Question 18.
Which of the following pairs of subjects are NOT associated with the union list?
(a) Education and Marriage
(b) Communications and currency
(c) Foreign Affairs and Currency
(d) Banking and Defence
Answer:
(a) Education and Marriage
Question 19.
Which of following language is spoken by the majority of our population?
(a) English
(b) Hindi
(c) Bengali
(d) Punjabi
Answer:
(b) Hindi
Explanation: No one language is the mother tongue of the majority of our population. Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 41 per cent Indians which is less than the 50 per cent of our total population.
Question 20.
How is Panchayat Samiti formed?
(a) By a few gram panchayats when are grouped together.
(b) By most members of the zila parishad
(c) By all MPs and MLAs in the block
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) By a few gram panchayats when are grouped together.
Explanation: Panchayat Samiti is also called Block or Mandal. The members of this local body are elected by all the panchayat members in that area.
Related Theory
All the Panchayat Samiti or Mandats in a district together constitute the zila Parishad. Most members of the zila parishad are elected which includes the Lok Sabha and MLAs of that district and another official of other district-level bodies. Zila parishad chairperson is the political head of the zila Parishad.
Question 21.
Which of the following is an advantage of the local government in India?
(a) It has deepened the democracy in our country
(b) It has uprooted the democracy at local level in our country
(c) It has failed in conducting the regular elections of local bodies
(d) It has given more power to the local government when compared to the centre.
Answer:
(a) It has deepened the democracy in our country
Identify the following on basis of the hints given:
Question 22.
Identify the country:
(1) The country shifted from unitary to federal form of government.
(2) The country gave regional governments constitutional powers in 1993.
(3) The country reduced the powers of the central government through an amendment.
Answer:
Question 23.
Identify the type of Government:
(1) There are two or more levels/tiers of governments.
(2) The jurisdictions of the respective levels or tiers of government are specified in the constitution.
(3) No government is subordinate to another.
Answer:
Federal Government
Explanation: Federal governments establish two or more tiers of each government and each government has its own powers and jurisdiction as given by the constitution. All levels are equal to one another.
Question 24.
Identify the institution:
(1) It resolves disputes between the states and state and centre.
(2) It interprets the constitution.
(3) It acts like an umpire and decides neutrally.
Answer:
Courts or Judiciary
Explanation: The highest court or the Supreme Court acts as an umpire if disputes arise between different levels of government in the exercise Of their respective powers. It has powers to interpret the constitution.
Correct and Rewrite/ True-False
State whether the following statements are True or False. If false, correct the statement.
Question 25.
In a federal government, different tiers of government govern the same citizens, but each tier has its own jurisdiction in specific matters of legislation, taxation and administration.
Answer:
True
Question 26.
The exact balance of power between the central and the state government is the same in every federation.
Answer:
Question 27.
The Constitution of India clearly provided a twofold distribution of legislative powers between the Union Government and the State Governments.
Answer:
False
The Constitution clearly provided a threefold distribution of legislative powers between the Union Government and the State Governments.
Explanation: It lays down subjects in form of three lists.
Question 28.
According to the constitution, the use of English for official purposes was to stop in 1956.
Answer:
According to the constitution, the use of English for official purposes was to stop in 1965.
Question 29.
At least two-third of all positions are reserved for women at Local level.
Answer:
At least one-third of all positions are reserved for women at local level.
Fill in the blanks with suitable information:
Question 30.
A ……….. has two levels of government.
Answer:
Federation
Question 31.
Indian Union is based on the principles of
Answer:
Federalism
Question 32.
Banking is included in the……………. List.
Answer:
Question 33.
……….. makes laws on Concurrent list subjects.
Answer:
Both States and the central government
Question 34.
…………. runs the Union Territories
Answer:
Central government.
Question 35.
The subjects that do not fall in any of the three lists are called……………. subjects.
Answer:
Residuary
Explanation: Subjects Like computer software that came up after the constitution was made are called residuary subjects and the union or central government has the power to legislate on these subjects.
Question 36.
The ……………. declared India as a Union of States.
Answer:
Constitution
Explanation: Indian constitution declares India as a union of states. It is an example of holding together federation where a large country decides to divide its power between the constituent states and the national or central government. In this system, generally central government is more powerful than its constituent units.
Question 37.
In 1956, an act passed by the Government in Sri Lanka recognised the Sinhala Language as the language of the state and disregard the …………… language.
Answer:
Question 38.
India, Spain and Belgium are examples of the …………….. type of federations.
Answer:
Holding Together
Explanation: There are two types of federations:
(1) The first type is ‘Coming Together Federation’ where states come together to form a bigger unit by pooling sovereignty and retaining identities. USA, Australia and Switzerland are the examples of coming together federations.
(2) The second type is where a large country decides to divide its power between the constituent states and the central government. India, Spain and Belgium are examples of this kind of‘holding together’ federations.
Question 39.
Australia is an example of type of federation.
Answer:
Coming together
Explanation: When independent States come together on their own to form a bigger unit, so that by pooling sovereignty and retaining identity they can increase their security, the type of federation is called Coming Together Type of federation. Another example is USA.
Match the Columns Choose the correct pairs:
Question 40.
Match the following subjects from column A with the lists given in column B:
|
Column A (Subjects) |
Column B (Lists) |
| (a) Banking | (i) State List |
| (b) Police | (ii) Union List |
| (c) Computer software | (iii) Concurrent List |
| (d) Education | (iv) Residuary subject |
Answer:
|
Column A (Subjects) |
Column B (Lists) |
| (a) Banking | (ii) Union List |
| (b) Police | (i) State List |
| (c) Computer software | (iv) Residuary subject |
| (d) Education | (iii) Concurrent List |
Explanation: Union List includes the subjects of national importance such as banking, defence, foreign affairs and the union government has the right to make laws on these subjects.
State list includes the subjects of state and Local importance such as police, trade, agriculture etc. and state government can make laws on these subjects.
The concurrent list includes subjects like education, forest, trade union, marriage etc. and both central and state governments can make laws on these subjects but in case if their laws conflict with each other, then the central government Law will be implemented.
On residuary subjects, central government has the power to make laws.
Related Theory
The constitution clearly provides a three-fold distribution of legislative powers between the Union Government and the State Governments via union list (97 subjects), state list (66 subjects), concurrent list (47 subjects) and the subjects which are not included in these lists are known as ‘residuary subjects.
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Civics Chapter 2
In each of the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding statement of Reason (R). Select the correct answers to codes (a), (b), (c) or (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Question 41.
Assertion (A): Belgium shifted from a unitary to a federal form of government.
Reason (R): Federal Governments last longer.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Explanation: Federal governments are more stable, more participative and can handle ethnic conflicts and divisions better than unitary governments.
Question 42.
Assertion (A): Tamil leaders want Sri Lanka to become a federal system.
Reason (R): Federal systems establish a peaceful and stable environment in the country.
Answer:
Question 43.
Assertion (A): The fundamental provisions of the constitution cannot be unilaterally changed by one level of government in a federal government.
Reason (R): In a Federal government, each government has its own constitutionally laid down jurisdiction.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Explanation: In a Federal government, each government has its own constitutionally laid down jurisdiction. Each government takes care of certain subjects which have been specified by the constitution. Hence all decisions have to be taken only after discussions and consensus.
Question 44.
Assertion (A): Federations that are formed by ‘holding together’ do not give equal power to its constituent units.
Reason (R): States should be treated differently to help them develop.
Answer:
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
Explanation: In the ‘holding together’ federations, a large country divided power between its constituent units carefully to ensure peace. Hence the distribution is unequal.