Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science with Solutions Set 7 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Set 7 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours.
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question numbers 1-12 are multiple choice questions of one mark each.
- Question numbers 13-18 are of 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 50 words each.
- Question numbers 19-23 are of 4 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 100 words each.
- Question numbers 24-26 are passage, cartoon, and map-based questions. Answer accordingly.
- Question numbers 27-30 are of 6 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 170 words.
Section – A (12 Marks)
Question 1.
Select one of the reasons how One-party dominance in India was different than in other countries. [1]
(a) In India, one-party dominance happened through democratic processes.
(b) In India, one-party dominance happened through military measures.
(c) In India, one-party dominance happened by compromising democracy.
(d) In India, one-party dominance happened by constitutional act.
Answer:
(a) In India, one-party dominance happened through democratic processes.
Question 2.
Which of the following statements is/are true? [1]
(i) The cold war affected the relationship between India and Pakistan.
(ii) The goal of India’s foreign policy was the preservation of territorial integrity.
(iii) India’s relationship with its neighbours was strained since time immemorial.
(iv) The treaty of Peace and Friendship in 1971 was the result of India’s closeness to USA.
Codes:
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer:
(b) (i) and (ii)
Question 3.
Dalai Lama was a__________. [1]
(a) Tibetan spiritual leader
(b) Tibetan political leader
(c) Tibetan tribal leader
(d) Tibetan educationist
Answer:
(a) Tibetan spiritual leader
Question 4.
Choose the correct sections of the society of which the Janata Party became the platform. [1]
(a) Middle class from North India
(b) Upper class
(c) SCs and STs
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Middle class from North India
![]()
Directions for Q.Nos. 5 and 6
In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read these statements and choose one correct answer from the given options.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Question 5.
Assertion(A) : WSF stands for World Social Forum. [1]
Reason(R): It is an organisation that opposes the negative impacts of globalisation in society.
Answer:
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Question 6.
Assertion(A): The rise of a uniform culture is not a global culture. [1]
Reason(R) : It is imposition of Western culture on the entire world.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 7.
The state of Emergency was declared on___________. [1]
(a) 25 June, 1975
(b) 25 June, 1970
(c) 12 July, 1975
(d) 19 August, 1976
Answer:
(a) 25 June, 1975
Question 8.
Which of the following statements about South Asia are true? [1]
(i) All countries in South Asia do not follow democracy.
(ii) There are ethnic and resource sharing conflicts in the region.
(iii) South Asia is diverse yet in a single geopolitical space.
(iv) China is a part of South Asia.
Codes:
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer:
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Question 9.
Name the personality who prepared the ‘Sarvodaya Plan’. [1]
(a) Jai Prakash Narayan
(b) Acharya Narendra Dev
(c) Ram Manohar Lohiya
(d) Kanshi Ram
Answer:
(a) Jai Prakash Narayan
Question 10.
Arrange the following in chronological order: [1]
(i) Nepal became a democratic republic
(ii) Indus Waters Treaty
(iii) India and Pakistan conducted nuclear tests
(iv) Establishment of SAARC
Codes:
(a) (ii), (iv), (iii), (i)
(b) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(c) (i), (iii),(ii), (iv)
(d) (iii), (i),(ii), (iv)
Answer:
(a) (ii), (iv), (iii), (i)
Question 11.
Name the person under whose leadership the Second Five-Year Plan was drafted. [1]
(a) K. N. Raj
(b) P. C. Mahalanobis
(c) M. Visvesvaraya
(d) D.R.Gadgil
Answer:
(b) P. C. Mahalanobis
![]()
Question 12.
Choose the odd one out of the following: [1]
(a) The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) was framed in 1994.
(b) It provides that the parties should act to protect the climate system.
(c) It should be “on the basis of equity and in accordance with their common but differentiated responsibilities and respective capabilities.”
(d) The parties to the Convention agreed that the largest share of historical and current global emissions of greenhouse gases has originated in developed countries.
Answer:
(a) The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) was framed in 1994.
Section – B (12 Marks)
Question 13.
Highlight the meaning of ‘Shock Therapy’. [2]
Answer:
‘Shock Therapy’ refers to a sudden and drastic change that no one has the time to understand or grasp. In the context of the USSR, it referred to the dramatic shift from the ideology of Socialism with Communism to Liberal Democracy.
Question 14.
What is ‘surplus majority coalition’? [2]
Answer:
The previous coalitions i.e., before 2014 were led by one of the national parties, the NDA III coalition was not only steered by a national party, i.e., BJP it was also dominated by BJP with an absolute majority of its own in the Lok Sabha. It was also called a ‘surplus majority coalition’.
Question 15.
While throwing so light on Decade 1960s, explain why the decade 1960s is known as dangerous decade. [2]
Answer:
This is because in Indian politics many challenges and unresolved problems like poverty, inequality, communal and regional division etc. could lead to failure of democratic projects or disintegration of country in this decade.
Question 16.
Highlight some of the reasons for which India suffered food crisis during 1965-1967. [2]
Answer:
India suffered a food crisis during 1965-1967 due to a plethora of reasons:
1. India fought two significant wars during this period that led to the economic crisis in the country and put the burden on its food.
2. During this decade the situation of drought and famine became common that led to an acute shortage of food.
Question 17.
Name the core leaders of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM). [2]
Answer:
The core leaders of the NAM were Jawaharlal Nehru from India, Nkrumah from Ghana, Nasser from Egypt, Sukarno from Indonesia, and Tito from Yugoslavia.
![]()
Question 18.
Evaluate any one feature of the ideology of Swatantra Party. [2]
Answer:
One of the main features of the ideology of the Swatantra Party was : Less involvement of the government in controlling the economy of the State and the principle that prosperity can come only through individual freedom.
Section – C (20 Marks)
Question 19.
“In spite of the decline of Congress dominance, the Congress party continues to influence politics in the country.” Do you agree with the given statement? Give reasons to prove your answer. [4]
Answer:
The Congress Party is the oldest party in India and has been successful in influencing the politics in the country.
1. They have successfully ruled for 10 years from 2004 to 2014 under the United Progressive Alliance. Since then they have been in opposition.
2. The Congress has a strong base in the country and has been still a major political force in several states.
3. The ideologies of the Congress has still have support for the wide sections of the society.
Question 20.
What do you mean by the Earth Summit?.How far did the summit prove useful? [4]
Answer:
The growing focus on environmental issues within the arena of global politics was firmly consolidated at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development held at Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, in June 1992. This was named as the ‘Earth Summit’ in which 170 states, NGOs and MNCs participated in this summit.
Usefulness of Summit:
1. The Rio Summit produced conventions dealing with climate change, biodiversity, forestry and advocated a list of development practices called ‘Agenda 21’.
2. There were some significant differences and difficulties which were left unsolved. There was an agreement on combining economic growth with ecological responsibility and this approach came to be known as ‘sustainable development’.
Question 21.
Explain the border disputes between India and China. [4]
Answer:
There was a boundary dispute between India and China that came into the picture during the late 1950s. India felt that the boundary dispute was resolved during the colonial times. But the Chinese did not felt that.
1. There was dispute about the western and eastern ends of the border between the two nations. China started claiming two areas of the India territories.
2. China claimed the area of Aksai Chin in the Ladakh region of India which is now a Union territory at present.
3. The other region claimed by the Chinese was the area of Arunachal Pradesh which was then known as the NEFA (National Eastern Frontier Agency).
Question 22.
Give some real-life examples of the impact of globalisation on our lives? [4]
Answer:
As consumer in today’s world, some of us are having a wide choice of goods and services before us. The latest model of digital comers, mobile phone and television made by the leading manufacturers of the world are within our reach. In early years Ambassador and Fiat were the only cars on Indians reads. But every new season, new models of automobiles can be seen on Indian roads. Today, Indians are buying car produced by nearly all the top companies in the world. A similar explosion of brands can be seen for many other goods from shirts to television to processed fruit juice.
Question 23.
What do you understand by traditional security and cooperation? [4]
Answer:
In traditional security, there is a recognition that cooperation in limiting violence is possible. These limits relate both to the ends and the means of war. It is now an almost universally-accepted view that countries should only go to war for the right reasons, primarily self-defence or to protect other people from genocide. War must also be limited in terms of the means that are used. Armies must avoid killing or hurting noncombatants as well as unarmed and surrendering combatants. They should not be excessively violent. Force must in any case be used only after all the alternatives have failed. Traditional views of security do not rule out other forms of cooperation as well. The most important of these are disarmament, arms control, and confidence building. Disarmament requires all states to give up certain kinds of weapons.
![]()
Section – D (12 Marks)
Question 24.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow: [4]
Jaya Prakash Narayan (JP) was the first leader in post-independence India who took a principle stand against corruption and fought against it with the help of youth, particularly in two states: Gujarat and Bihar. He advocated the office of Lokpal against corruption. He believed in Communitarian Socialism as per which the Indian society has three key layers, viz., ‘community, region and rashtra’- all combining together as an example of true federation.
(i) Which of the following two states were the main centres in JP’s fight against corruption?
(a) Bihar and Gujarat
(b) Bihar and Bengal
(c) Gujarat and Uttar Pradesh
(d) Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu
Answer:
(a) Bihar and Guj
(ii) JP fought against corruption with the help of the________.
(a) Youth
(b) Media
(c) Congress
(d) Dalits
Answer:
(a) Youth
(iii) What is Total Revolution according to JP?
(a) Transformation of individual, society and state.
(b) War against Capitalist powers of the world.
(c) Revolution to bring about communism in society.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Transformation of individual, society and state.
(iv) JP advocated an office of the_______to fight against corruption.
(a) Lokpal
(b) Lokdal
(c) Parties
(d) Villages
Answer:
(a) Lokpal
Question 25.
In the given political outline map of South Asia, four countries have been marked as (A), (B), (C) and (D). Identify these countries on the basis of information given below and write their correct names in your answer book along with the respective serial number of the information used and the concerned alphabet given in the map as per the following format. [4]
(i) The country which is a peaceful Himalayan nation.
(ii) The country which came into existence in 1971.
(iii) The country which has fought war against India on several occasions.
(iv) The country which has free visa entry with India.
| Sr. no. of the Information used | Concerned alphabet | Name of the State |
| (i) | ||
| (ii) | ||
| (iii) | ||
| (iv) |
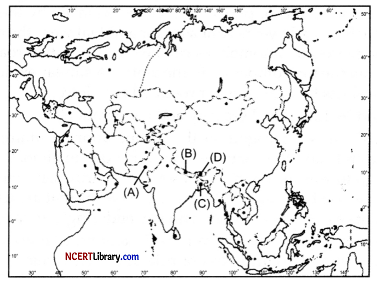
Answer:
| Sr. no. of the Information used | Concerned alphabet | Name of the State |
| (i) | D | Bhutan |
| (ii) | C | Bangladesh |
| (iii) | B | Pakistan |
| (iv) | A | Nepal |
Question 26.
Study the given Cartoon and answer the questions that follow: [4]

(i) Which of the following leaders are shown in the cartoon?
(a) Rajendra Prasad, Sardar Patel and Zakir Hussain
(b) Morarji Desai, G.B. Pant and H.N. Kunzru
(c) Jawaharlal Nehru, G.B. Pant and Zakir Hussain
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru, Rajendra Prasad and Morarji Desai
Answer:
(c) Jawaharlal Nehru, G.B. Pant and Zakir Hussain
(ii)_______sacrificed his life after 56 days of indefinite fast for demanding a separate Andhra province.
(a) Alluri Sitarama Raju
(b) Potti Sriramulu
(c) Subramaniya Siva
(d) A.K. Gopalan
Answer:
(b) Potti Sriramulu
(iii) Which of the following states was the first to be reorganised on the linguistic basis?
(a) Karnataka
(b) Tamil Nadu
(c) Maharashtra
(d) Andhra Pradesh
Answer:
(d) Andhra Pradesh
(iv) The State Reorganisation Commission was appointed in the year________.
(a) 1950
(b) 1953
(c) 1956
(d) 1958
Answer:
(b) 1953
![]()
Section – E (24 Marks)
Question 27.
Mention the six principal organs of the United Nations and describe the functions of any two of them.
OR
Describe the composition of the UN Security Council. What is the major difference in the privileges given to its permanent and non-permanent members? [6]
Answer:
There are six organs of the U.N.
1. General Assembly
2. Security Council
3. The Economic and Social Council
4. International Court of Justice
5. Trusteeship Council
6. The Secretariat.
Functions of General Assembly are:
1. The General Assembly may attract the attention of the Security Council towards a situation disturbing international peace and security.
2. The non-permanent members of the Security Council and all members of the Trusteeship Council and those of the Economic and Social Council are all elected by the General Assembly.
The main functions of Security Council are:
1. It maintains international peace and security in accordance with the principles and purposes of the UN.
2. It investigates any dispute or situation which might lead to international friction.
3. It recommends methods to adjust such disputes among the nations.
4. It can take military action against an aggressor.
5. It recommends the admission of new members to the UNSC.
OR
Composition of the UN Security Council: The Security Council is an important organ of the United Nations Organisation (UNO). It consists of five permanent members (China, United States of America, United Kingdom, Russia and France) and ten non-permanent members who are elected for a period of two years. The selection of the permanent members was on the basis of their powerful position immediately after the Second World War and because they constituted the victors in the war.
The difference in the privileges given to the permanent and non-permanent members:
1. The UN Charter gave the permanent members a privileged position to bring about stability in the world. The main privileges enjoyed by the permanent members are: Permanency and Veto power.
2. The non-permanent members are elected only for two years at a time and cannot be re-elected immediately after completing two years. They are elected in a manner so that they represent all continents of the world.
3. The non-permanent members do not have the veto power. When decisions are taken by Security Council, voting is done.
4. All members have one vote. But the permanent members can vote in a negative manner so that even if all other permanent and non-permanent members vote for a particular decision, any permanent member’s negative vote can stall the decision. This negative vote is the veto.
Question 28.
How the relationship between the India and China has evolved from the 1950s to the present times?
OR
Name all the members of the ASEAN. What purpose is served by the body? [6]
Answer:
The relationship between the India and China has passed through several phases from the 1950s to the present times:
1. During the Nehru period various cooperative treaties had been signed. Hindi-Chini Bhai- Bhai slogan became very popular.
2. The two nations faced a confrontation in the year 1962 on the issue of territorial disputes in Arunachal Pradesh and Aksai Chin in Ladakh.
3. The diplomatic relationship between the two nations revived in the year 1976 that was downgraded after the war.
4. They started a negotiation process in the year 1981 for the resolution of the border disputes that further strengthened by the visit of former Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi to China in 1988.
5. The relationship between the two nations has been improved after the end of the Cold war period. Both nations understood their economic and strategic importance and wanted to cooperate in the development of each other.
6. They have adhered to the rules and regulations of the international institutions like the World Trade Organisation (WTO), BRICS gave a nice platform for their relationship also. Although in the Modi Administration the Doklam stand off of Indo-China disturbed the relations but the economic cooperation is still between them.
OR
ASEAN is composed of 10 member nations at present. Initially, it was founded by the five-member nations Philippines, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia and Thailand in 1967. Subsequently, countries like Brunei, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam and Myanmar also became its members.
Some of the important functions of the ASEAN body are:
1. It sought economic integration of the South East Asian nations along with the maintenance of the sovereignty of the member nations.
2. It sought to bring the political integration of its members and establish a platform for efficient dialogue for the South East Asian nations.
3. The cultural exchange among the member nations is also an important motive of the organisation.
4. The matters of security and peace are crucial for the organisation.
5. The member nations have adopted the feature of rule of law and the principles of the United Nations Charter for its functioning.
![]()
Question 29.
Analyse any three positive and three negative features each of the Soviet system in the Soviet Union.
OR
Discuss three reasons why did the Soviet Union, the second most powerful country in the world disintegrate? [6]
Answer:
The three positive features of the Soviet system were:
1. The Soviet economy was more developed than the rest of the world except for the US. It had a complex communications network, vast energy resources, machinery production, and a transport system that connected its remotest areas.
2. A minimum standard of living for all citizens was ensured by the Soviet state, and the government subsidised basic necessities including health, education, childcare and other welfare schemes.
3. State ownership was given more importance. Land and productive assets were owned and controlled by the Soviet state.
The three negative features of the Soviet system were:
1. The Soviet system was very bureaucratic and authoritarian in nature. It turned the life of the people into disorder. Authoritarianism meant the absence of democracy and freedom of speech which angered the people.
2. The Soviet economy witnessed economic stagnation for a long time which led to market failure when demand failed to meet supply in the market for consumer goods.
3. State Treasury had spent a huge fortune on building and maintaining nuclear arsenals and in developing its satellite states in East Europe and within the Soviet system. It turned into a large economic burden for the Soviet system.
OR
There were many factors that led to the collapse of the Soviet Union, including political policies, economic issues, defense spending, etc. The disintegration of the Soviet Union also marked the end of communism.
1. Internal weakness of Soviet political and economic institutions which failed to meet the aspirations of the people.
2. Economic stagnation for many years led to severe consumer shortages. ‘
3. The Soviet economy used much of its resources in maintaining a nuclear and military arsenal and the development of its satellite states in Eastern Europe and within the Soviet system.
4. Awareness among Soviet people about the economic advancement of the West. The reality of communism and its backwardness came as a political and psychological shock.
5. Stagnation in political and administrative fields.
6. The Communist Party that had ruled the Soviet Union for over 70 years was not accountable to the people.
7. Lack of openness and centralisation of authority.
8. Mikhail Gorbachev promised to reform economy, catch up with the West, and loosen the administrative system.
9. The rise of nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including Russia and the Baltic Republics.
10. During the Cold War many thought that nationalist unrest would be the strongest in the Central Asian republics given their ethnic and religious differences with the rest of the Soviet Union and their economic backwardness.
Question 30.
Analyse the areas of tension that arose on different occasions after independence. Which political aspirations were the causes of those tensions?
OR
“Jammu and Kashmir is one of the living examples of plural society and politics.” Support the statement with suitable arguments. [6]
Answer:
When the interest of one region or a state is asserted against the country as a whole or against another state then it can be called regionalism. Regionalism has remained perhaps the most potent force in Indian politics ever since independence.
1. Roots of regionalism are in India’s manifold diversity of languages, culture, ethnic groups, and religions and so on. For many centuries, India remained the land of many languages, culture and traditions.
2. First the issue of Jammu and Kashmir came up, which resulted as a political conflict between India and Pakistan due to political aspirations of that region after independence. Main demand was for a separate Kashmiri nation, merging with Pakistan and having greater autonomy for the state.
3. In some parts of the north-east, there was no consensus about being a part of India. First Nagaland and the Mizoram witnessed strong movements demanding separation from India territory.
4. Demands were mainly for political autonomy and secession from the Indian territory.
5. In the south, some groups from the Dravid movement briefly toyed with the idea of a separate country.
6. The movement focused on opposition to the Brahmins’ dominance, political and cultural domination of the North and against declaring Hindi the country’s official language.
7. From the late 1950s, people speaking the Punjabi language started agitating for a separate State for themselves. This demand was finally accepted and the States of Punjab and Haryana were created in 1966. Later, the States of Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand and Jharkhand were created. Thus, the challenge of diversity was met by redrawing the internal boundaries of the country.
OR
1. Jammu and Kashmir comprises of three major social and political regions-Jammu, Kashmir and Ladakh.
2. Jammu region comprises of foothills and plains inhabited by equal ratio of Hindus, Muslims, Sikhs and speakers of various languages.
3. Kashmir region is the Kashmir valley, where the people speak Kashmiri and, most of the population is Muslims with a small population of Kashmiri Hindus.
4. Ladakh region is mountainous with very little population equally divided between Buddhists and Muslims.
5. Jammu and Kashmir involves the issue of Kashmiri identity- Kashmiriyat and the aspirations of the people for political autonomy.
6. Politics in Jammu and Kashmir is made up of numerous strands-One group stands for a separate Kashmiri nation independent of both India and Pakistan. Another group wants Kashmir to merge with Pakistan.
7. A third group wants greater autonomy for Jammu and Kashmir within India.
8. The Ladakh region demands intra-state autonomy within Jammu.
![]()