Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science with Solutions Set 6 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Set 6 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours.
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question numbers 1-12 are multiple choice questions of one mark each.
- Question numbers 13-18 are of 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 50 words each.
- Question numbers 19-23 are of 4 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 100 words each.
- Question numbers 24-26 are passage, cartoon and map-based questions. Answer accordingly.
- Question numbers 27-30 are of 6 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 170 words.
Section – A (12 Marks)
Question 1.
A review of the implementation of the agreements at the Earth Summit in Rio was undertaken by India in __________. [1]
(a) 1997
(b) 1987
(c) 1990
(d) 1980
Answer:
(a) 1997
Question 2.
Globalisation affects what we eat, drink, think and watch. This is called __________ globalisation. [1]
(a) economic
(b) political
(c) cultural
(d) ideological
Answer:
(c) cultural
Question 3.
__________ security is about the protection of people more than the protection of states. [1]
(a) Government
(b) Traditional
(c) Non-traditional
(d) Human
Answer:
(d) Human
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following personalities is credited to provide the first blueprint of economic planning in India? [1]
(a) M. Visvesvaraya
(b) Subhash Chandra Bose
(c) Dadabhai Naoroji
(d) Acharya Narendra Dev
Answer:
(a) M. Visvesvaraya
Directions for Q.Nos. 5 and 6
In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read these statements and choose one correct answer from the given options.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Question 5.
Assertion (A): The Awami League was the most popular party in East Pakistan that led to the start of the freedom movement in the region.
Reason (R): Awami League fought for the rights of Bengali Muslims. [1]
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Sri Lanka has the highest per capita Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in South Asia even during the time of the civil war.
Reason (R): It has soundly managed its economic resources. [1]
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and Ris the correct explanation of A
Question 7.
Which of the following was not the provision of Punjab Accord? [1]
(a) Tribunal for solving border dispute between Punjab and Haryana
(b) Tribunal for deciding the water dispute of Ravi- Beas river
(c) Withdrawn of AFSPA
(d) Resuming of trade between Punjab and Pakistan
Answer:
(d) Resuming of trade between Punjab and Pakistan
Question 8.
Which of the following statements about the 1971 general elections are true? [1]
(i) These elections were held in January 1971.
(ii) The Congress had an alliance with Swantatra Party.
(iii) All the major opposition parties formed an electoral alliance against the Congress Party.
(iv) Indira Gandhi gave the famous slogan: ‘Garibi Hatao’.
Codes:
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer:
(b) (iii) and (iv)
Question 9.
The ‘People’s Plan’ of 1945 was prepared by which of the following? [1]
(a) M. N. Roy
(b) C. Rajagopalachari
(c) John Baptista
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru
Answer:
(a) M. N. Roy
Question 10.
Arrange the following in the chronological order of their establishment: [1]
(i) ILO
(ii) WHO
(iii) UNESCO
(iv) UNICEF
(a) (ii), (iii), (i), (iv)
(b) (iii), (iv), (i), (ii)
(c) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(d) (i), (iii), (iv), (ii)
Answer:
(d) (i), (iii), (iv), (ii)
Question 11.
The majority of the population in the region of Kashmir is of __________. [1]
(a) Hindus
(b) Muslims
(c) Sikhs
(d) Buddhists
Ans.
(b) Muslims
Question 12.
Find the odd one out in the context of the Congress ‘Syndicate’: [1]
(a) S. Nijalingappa of Karnataka
(b) Lai Bahadur Shastri of Uttar Pradesh
(c) K. Kamaraj of Tamil Nadu
(d) Atulya Ghosh of West Bengal
Answer:
(b) Lai Bahadur Shastri of Uttar Pradesh
![]()
Section – B (12 Marks)
Question 13.
Discuss some of the limitations of the land reforms in India. [2]
Answer:
Some of the limitations of land reforms in India are:
1. The government has imposed ceiling on the maximum amount of land that can be held by an individual. However, this law was not efficiently implemented on ground.
2. The tenants were provided security against the eviction however this provision was also not implemented on ground.
Question 14.
Identify one similarity and one difference between the crisis in Punjab and Assam during the 1980s. [2]
Answer:
Both in Punjab and Assam crisis, the common factor was responding to regional aspirations as well as finding solution through democratic negotiations. The uncommon aspect in both of these was that in the Punjab crisis the focus was on the demand of political autonomy for the region whereas in the Assam crisis the movement was against outsiders i.e., immigrants from Bangladesh.
Question 15.
Explain the meaning of garage sale in the context of shock therapy. [2]
Answer:
As a result of the shift to capitalism, many state-owned industries were sold to private ownership and this led to virtual disappearance of entire industries as the industries were sold at throw-away prices. This was termed as the ‘Garage Sale’.
Question 16.
“Jammu and Kashmir comprises of some social and political regions.” Support the statement with any two examples from any two regions. [2]
Answer:
1. Jammu and Kashmir comprises three major social and political regions—Jammu, Kashmir and Ladakh.
2. Jammu region comprises of foothills and plains inhabited by an equal ratio of Hindus, Muslims and Sikhs and speakers of various languages.
3. Kashmir region is the Kashmir valley, the people here are Kashmiri speaking and mostly Muslim with a small population of Kashmiri Hindus.
Question 17.
What do you know about Demolitions in Turkman Gate area, Delhi. [2]
Answer:
Emergency witnessed large-scale displacement of people living in Delhi’s poorer localities. The ‘jhuggi jhopris’ were forcibly relocated in the then barren areas across the river Yamuna. One such affected area was the colonies in Turkman gate. The ‘jhuggis’ of the area were demolished.
Question 18.
What was the major foundation of the foreign relations of India which is laid even in the Directive Principles of State Policy? [2]
Answer:
The ideology of the Indian government on the issue of foreign policy was:
1. India said to give respect to the sovereignty of all the nations.
2. India showed its commitment towards maintaining peace in international relations for ensuring its security as well as the other nations security.
Section – C (20 Marks)
Question 19.
Evaluate any three consequences of the emergency imposed in 1975. [4]
Answer:
The three consequences of the emergency imposed in 1975:
Effects on civil liberties of citizens: The government made large-scale arrests under preventive detention. Arrested people could not challenge the arrest and the government claim edit unnecessary to inform the accused of the ground on which they were detained.
Impact on relationship with Parliament and Judiciary: The Parliament brought in many changes in the Constitution declaring that the election of PM, President and Vice-President could not be challenged in the court. The 42nd amendment was also passed to bring in a series of changes in the Constitution. It was proved that the government could take away citizen’s right to life and liberty by overruling courts during an emergency.
Functioning of mass media: It affected the functioning of mass media also, as well since press censorship took place, Freedom of press and newspapers was taken away, and they had to take prior approval before publishing any news.
Question 20.
“Welfare State is getting replaced by market.” Analyse the reason for this change. [4]
Answer:
“The Welfare State is a society in which an assured minimum standard living and opportunity becomes the possession of every citizen.” The Welfare State is a system wherein government agrees to underwrite main levels of employment, income, education, medical aid, social security, housing for all its citizens. Welfare state is being replaced by increasing trend of globalisation.
1. Globalisation results in erosion of state capacity.
2. Concept of state sovereignty is getting affected.
3. It withdraws many welfare functions from the government.
Question 21.
Suggest any two steps to be taken by the government to check pollution and save environment. [4]
Answer:
The government can take following steps to check pollution and save environment:
1. Afforestation: More plantation drive should be organised by the government to lessen the greenhouse effect.
2. Auto fuel policy: Government should take strict policies for the implementation of cleaner and safer auto fuel along with banning polluting vehicles.
3. Should frame policies to reduce pollution created by industries.
4. Must encourage the citizens for the use of renewable energy.
Question 22.
Explain how global poverty is a source of insecurity? [4]
Answer:
Global poverty refers to low economic growth, low national income and low standard of living of developing or least developed countries. It is a source of insecurity.
The reasons are:
1. Half the world’s population growth occurs in just six countries-India, China, Pakistan, Nigeria, Bangladesh and Indonesia, considered developing countries and even in poorest countries population is expected to triple in next 50 years.
2. Globally, this disparity contributes to the gap between the Northern and Southern countries of the world.
3. Poverty in the South has also led large migration to seek a better economic opportunities in the North.
4. All these created international political friction as international law and norms make a distinction between migrants and refugees as they do not get ready to accept migrants.
Question 23.
Highlight any five steps as decided by the member states in 2005, to make the United Nations more relevant in the changing context. [4]
Answer:
The following steps were proposed by the member states in 2005 to make the UN more relevant in the changing scenario:
1. Peacebuilding commission to be created.
2. UN to accept its responsibility in case of failure of National Government to save their citizens from atrocities.
3. Creation of Human Rights Council.
4. To condemn terrorism in all its forms and manifestations.
5. To create Democracy fund.
6. Agreement regarding dissolving the Trusteeship Council.
![]()
Section – D (12 Marks)
Question 24.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow: [4]
The 1967 election was a landmark election. The results jolted the Congress at both the national and state levels. Many contemporary political observers described the election results as a ‘political earthquake’. The Congress did manage to get a majority in the Lok Sabha, but with its lowest tally of seats and share of votes since 1952. Half of the ministers of Indira Gandhi’s Cabinet were defeated. The political stalwarts who lost in their constituencies included Kamaraj in Tamil Nadu, S.K. Patil in Maharashtra, Atulya Ghosh in West Bengal and K. B. Sahayin Bihar.
(i) 1967 election results are called as __________.
(a) Political earthquake
(b) Start of coalition politics
(c) End of congress rule
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Political earthquake
(ii) Congress managed a victory in 1967 elections, its seat tally was __________.
(a) Highest ever
(b) Lowest ever
(c) Same as earlier
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Lowest ever
(iii) Which of the following statements about the 1967 elections is true?
(a) Congress won all seats.
(b) One-fourth of the ministers of Indira Gandhi’s Cabinet were defeated.
(c) There was no change in the stature of Congress.
(d) Various opposition parties came together to form anti-Congress front.
Answer:
(d) Various opposition parties came together to form anti-Congress front
(iv) Pick the ODD one out.
(a) Kamaraj – Tamil Nadu
(b) S.K. Patil – Maharashtra
(c) Atulya Ghosh – West Bengal
(d) K. B. Sahay – Karnataka
Answer:
(d) K. B. Sahay – Karnataka
Question 25.
In the given political outline map of India, four states have been marked as (A), (B), (C) and (D). Identify these states on the basis of information given below and write their correct names in your answer book along with the respective serial number of the information used and the concerned alphabet given in the map as per the following format. [4]
(i) The state from which Haryana was carved out.
(ii) The state which was created in 1963.
(iii) The state from which Jharkhand was carved out.
(iv) The state which was formed by separating Telugu-speaking areas from Madras (now Tamil Nadu)
| Sr. no. of the Information used | Concerned alphabet | Name of the State |
| (i) | ||
| (ii) | ||
| (iii) | ||
| (iv) |
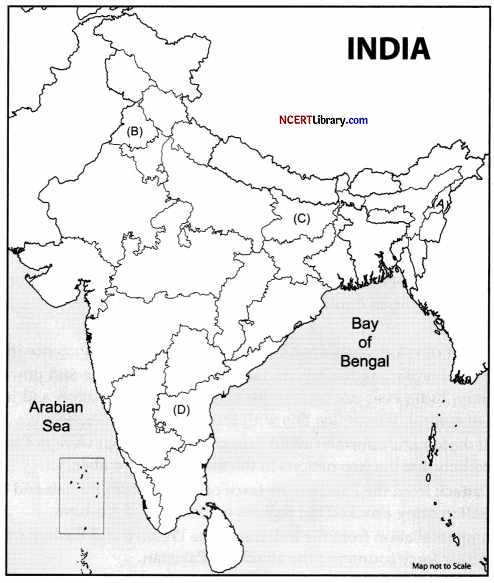
Answer:
| Sr. no. of the Information used | Concerned alphabet | Name of the State |
| (i) | B | Punjab |
| (ii) | A | Nagaland |
| (iii) | C | Bihar |
| (iv) | D | Andhra Pradesh |
Question 26.
Study the given Cartoon and answer the questions that follow: [4]

(i) Whom among the following is shown as the lion in the cartoon?
(a) Sri Lankan leaders
(b) Tamil militants
(c) Indian Peace Keeping Forces
(d) Sinhala hardliners
Answer:
(d) Sinhala hardliners
(ii) Name the person who is balancing the lion and the tiger in the given cartoon.
(a) Gotabaya Rajapaksa
(b) Mahinda Rajapaksa
(c) Ranil Wickremesinghe
(d) Ranasinghe Premadasa
Answer:
(b) Mahinda Rajapaksa
(iii) Since __________ LTTE has been fighting an armed struggle in Sri Lanka.
(a) 1980
(b) 1983
(c) 1999
(d) 1948
Answer:
(b) 1983
(iv) Which of the following statements about LTTE is NOT correct?
(a) It controls the northeastern part of Sri Lanka.
(b) It is a military organization.
(c) Its movement is non-violent and peaceful.
(d) It wants a separate country for the Sri Lankan Tamils.
Answer:
(c) Its movement is non-violent and peaceful.
![]()
Section – E (24 Marks)
Question 27.
Does India’s foreign policy reflect her desire to be an important regional power? Argue your case with the Bangladesh war of 1971 as an example.
OR
Analyse any two major developments after 1980 that led to a cycle of violence in Punjab.
Answer:
India is one of the most important nations in Asia. It is also very huge and powerful as compared to its neighbours. However, India does not undermine the status of any nation and interferes only when the situation goes out of control. We can see this with the example of Bangladesh.
1. India made all diplomatic efforts to avoid full scale war but that were not successful and ultimately the war started between the two nations in the month of December.
2. There was an attack from the Pakistan air force on the lands of Punjab and Rajasthan. On the other hand, the Pakistan army attacked the regions of Jammu and Kashmir.
3. There was strong retaliation from the Indians on the Western and Eastern front of the border. Indian army, navy and air force countered the attacks of Pakistan.
4. The Indian army also received support from the local population due to which it was able to make the Pakistan army surrender within ten days.
5. There were 90,000 Pakistani soldiers who surrendered to the Indian army. East Pakistan was declared independent and it became the Bangladesh.
OR
1. In 1980, the Akali Government was dismissed in Punjab and it launched a movement on the issue of distribution of waters between Punjab and its neighbouring states.
2. A section of religious leaders raised the question of an autonomous Sikh identity and the more extreme elements started advocating secession from India, raising slogans for the formation of “Khalistan”. When the leadership shifted from the moderate Akali Dal to the extremist militant groups, the movement took the form of an armed insurgency.
The militants set up their headquarters inside the Holy Shrine, i.e., the Golden Temple at Amritsar, turning it into an armed fortress. In order to control this situation, in June, 1984, the Government of India carried out the ‘Operation Blue Star’, a code name for an army action where it successfully flushed out the militants. But the conducted army operation also damaged the structure of the shrine and hurt many Sikh sentiments, leading to a cycle of violence in Punjab.
Question 28.
Describe the main features of the Soviet system.
OR
Examine the role of Gorbachev to reform the Soviet system.
Answer:
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) came into being after the socialist revolution in Russia in 1917. This was the biggest event in human history to abolish the institution of private property and establish equality in the society.
Features of the Soviet system:
1. The Soviet system was based on the ideals of socialism as opposed to capitalism and the need for an egalitarian society.
2. Primacy was given to the state and the institution of the party. The only party allowed to exist was the Communist Party.
3. Economy was planned and controlled by the state.
4. It had a complex communications network.
5. It had a domestic consumer industry that produced everything from pins to cars.
6. The Soviet state ensured a maximum standard of living for all its citizens, subsidised basic necessities including health, education, childcare and other welfare schemes.
7. No unemployment existed.
8. Land and productive assets were owned and controlled by the Soviet state.
OR
Mikhail Gorbachev, after becoming the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union in 1985, initiated some reforms in the Soviet system.
1. Gorbachev decided to normalise relations with the West to democratise and reform the Soviet Union.
2. Gorbachev introduced economic and political reform policies of perestroika (restructuring) and glasnost (openness).
3. He stopped the arms race with the US.
4. He withdrew Soviet troops from Afghanistan and Eastern Europe.
5. He also helped in the unification of Germany.
Effects of the Reforms on the USSR:
1. Gorbachev promised to reform the economy- catch up with the West- yet Soviet Union collapsed.
2. The Communist Party members felt that their power and privileges were eroding.
3. His reforms gave rise to nationalism and the desire for sovereignty within various republics including (Russia and the Baltic Republics- Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania).
4. Even the ordinary people felt alienated from the Central Asians and from each other. They felt that they were paying too high a price to stay within the Soviet Union.
Question 29.
Describe any three important events that led to the split in the Congress Party in 1969.
OR
Analyse any four factors that led the Congress Party to a spectacular win in 1971 elections.
Answer:
Three causes of the split in the congress party in 1969:
Differences with the syndicate: After the 1967 elections, PM Indira Gandhi had to deal with the syndicate, a group of powerful and influential leaders within the congress, who had played major role in her election as the leader of the party. These leaders expected her to follow their advice. However, Indira Gandhi gradually attempted to strengthen her position and carefully sidelined the Syndicate.
Their rivalry came in the open in 1969 over the presidential elections following President Zakir Hussain’s death and also differences over the reforms introduced by Indira Gandhi.
Presidential Elections 1969: Following President Zakir Hussain’s death, the post of the president of India fell vacant in 1969. Despite Mrs. Gandhi’s reservations, the ‘Syndicate’ nominated her long-time opponent, N. Sanjeeva Reddy as the official Congress candidate. Mrs. Gandhi retaliated by encouraging Vice-president V. V. Giri to file his nomination as an independent candidate.
The defeat of N. Sanjeeva Reddy formalised the split in the party into Congress (organisation) and the other was led by Indira Gandhi as Congress (Requisitionists).
Reforms by Indira Gandhi: Revolutionary steps taken by Indira Gandhi were not welcomed by the Congress leaders. She had launched a series of initiatives like public distribution of food grains, land reforms, nationalisation of fourteen private banks, abolition of the ‘privy purse’ or the special privileges given to former princess.
Her policies were opposed by Morarji Desai and older leaders, too, had serious reservations about this left programme.
OR
The new Congress had something that its big opponents lacked—it had an issue, an agenda and a positive slogan. The Grand Alliance did not have a coherent political programme. Indira Gandhi said that the opposition alliance had only one common programme: Indira Hatao (Remove Indira). In contrast to this, she put forward a positive programme captured in the famous slogan: Garibi Hatao (Remove Poverty).
She focused on the growth of the public sector, imposition of ceiling on rural land holdings and urban property, removal of disparities in income and opportunity.
Abolition of princely privileges. Through Garibi Hatao, Indira Gandhi tried to generate a support base among the disadvantaged, especially among the landless labourers—Dalits and Adivasis, minorities, women and the unemployed youth. The slogan of Garibi Hatao and the programmes that followed it were part of Indira Gandhi’s political strategy of building an independent nationwide political support base.
Indira Gandhi had managed to gain positive image of her personality and took initiatives for the benefit of the country.
Question 30.
How the relationship between the India and China has evolved from the 1950s to the present times?
OR
Name all the members of the ASEAN. What purpose is served by the body?
Answer:
The relationship between the India and China has passed through several phases from the 1950s to the present times:
During the Nehru period various cooperative treaties had been signed. The slogan ‘Hindi-Chini Bhai-Bhai’ became very popular. The two nations faced a confrontation in the year 1962 on the issue of territorial disputes in Arunachal Pradesh and Aksai Chin in Ladakh. The diplomatic relationship between the two nations revived in the year 1976 that were downgraded after the war.
They started a negotiation process in the year 1981 for the resolution of the border disputes that further strengthened by the visit of former Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi to China in 1988. The relationship between the two nations have improved after the end of the Cold war period. Both the nations have understood their economic and strategic importance and wanted to cooperate in the development of each other.
They have adhered to the rules and regulations of the international institutions like the World Trade Organization (WTO), BRICS which gave a platform to improve their relationship. Although in the Modi Administration, the Doklam standoff of Indo-China disturbed the relations but the economic cooperation still pessists.
OR
ASEAN is composed of ten member nations at present. Initially, it was founded by five member nations Philippines, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia and Thailand in 1967. Subsequently, countries like Brunei, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam and Myanmar became its members.
Some of the important functions of the ASEAN body are:
1. It sought economic integration of the South East Asian nations along with the maintenance of the sovereignty of the member nations.
2. It sought to bring the political integration of its members and establish a platform for efficient dialogue for the South East Asian nations.
3. The cultural exchange among the member nations is also an important motive of the organization.
4. The matters of security and peace are crucial for the organization.
5. The member nations have adopted the feature of rule of law and the principles of the United Nations Charter for its functioning.
![]()