Practising the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science with Solutions Set 3 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Set 3 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours.
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question numbers 1-12 are multiple choice questions of one mark each.
- Question numbers 13-18 are of 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 50 words each.
- Question numbers 19-23 are of 4 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 100 words each.
- Question numbers 24-26 are passage, cartoon and map-based questions. Answer accordingly.
- Question numbers 27-30 are of 6 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 170 words.
Section – A (12 Marks)
Question 1.
What was the immediate outcome of the reforms introduced by Mikhail Gorbachev? [1]
(a) Rapid development of the USSR.
(b) Independence movement across various East European countries, which were part of the USSR.
(c) USSR becomes the most developed part of the world.
(d) People of the USSR were elated with the much await reforms.
Answer:
(b) Independence movement across various East European countries, which were part of the USSR.
Question 2.
Name the personality who is known as the ‘Father of Green Revolution in India’. [1]
(a) Dr M.S. Swaminathan
(b) Dr Norman Borlaugh
(c) Dr. William Gande
(d) Dr. Verghese Kurien
Answer:
(a) Dr M.S. Swaminathan
Question 3.
Which of the following statements is/are true? [1]
(i) The foundation of steel plants, large dams and oil refineries was laid in the first two five-year plans of India.
(ii) The role of the private sector was highly regulated under these two plans.
Codes:
(a) Only (i)
(b) Only (ii)
(c) Both (i) and (ii)
(d) Neither (i) nor (ii)
Answer:
(c) Both (i) and (ii)
Question 4.
Choose the correct option that has significantly contributed to the process of ‘Globalisation’. [1]
(a) Fear of war
(b) Security threats
(c) Advancement of technology
(d) Achievements of the United Nations
Answer:
(c) Advancement of technology
![]()
Directions for Q.Nos. 5 and 6
In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read these statements and choose one correct answer from the given options.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Question 5.
Assertion (A): India adopted a democratic approach to the question of diversity. [1]
Reason (R): In a democracy, different culture sheets can be represented.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 6.
Assertion (A): As the colonies became free from the late 1940s onwards, their security concerns were often similar to that of the European powers. [1]
Reason (R): Some of the newly-independent countries, like the European powers, became members of the Cold War alliances.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 7.
Who was the ruler of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir after the independence? [1]
(a) Maharaja Hari Singh
(b) Maharaja Nihal Singh
(c) Maharaja Sonal Singh
(d) Maharaja Man Singh
Answer:
(a) Maharaja Hari Singh
Question 8.
Which of the following statements about the forest movements of the South are true? [1]
(i) Mexico, Chile, Brazil, Malaysia, Indonesia, Continental Africa and India are included in these movements.
(ii) Diversity is not an important trait of contemporary movements.
(iii) Forest clearing in the Third World continues at an alarming rate.
(iv) The destruction of the world’s last remaining grand forests has actually decreased in the last decade.
Codes:
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer:
(d) (i) and (iii)
Question 9.
Name the person who led the struggle against the dominance of West Pakistan. [1]
(a) Sheikh Mujib-ur Rahman
(b) Khaleda Zia
(c) SajeebWazed
(d) Sheikh Kamal
Answer:
(a) Sheikh Mujib-ur Rahman
Question 10.
Arrange the following in the chronological order of their establishment: [1]
(i) The World Trade Organisation
(ii) Amnesty International
(iii) League of Nations
(iv) World Bank
(a) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
(c) (iii), (iv), (ii), (i)
(d) (iv), (iii), (ii), (i)
Answer:
(c) (iii), (iv), (ii), (i)
Question 11.
_______visit to China in 1988 is seen as an important step in taking the relationship forward after the Indo-China war of 1962. [1]
(a) PV Narasimha Rao’s
(b) Rajiv Gandhi’s
(c) VP Singh’s
(d) Manmohan Singh’s
Answer:
(b) Rajiv Gandhi’s
![]()
Question 12.
Pick the odd one out in the context of Nepal. [1]
(a) 1990 – king accepted the new democratic constitution
(b) 2002 – king abolished parliament
(c) 2006 – there was a pro-democratic movement
(d) 2008 – monarchy is restored
Answer:
(d) 2008 – monarchy is restored
Section – B (12 Marks)
Question 13.
What is a mixed economy? [2]
Answer:A mixed economy is a model which incorporates the ideas of capitalism as well as socialism. In this model, both the private sector and public sector work for the development of the country.
Question 14.
What were Jaya Prakash’s views about ‘India’s Communitarian Socialism’? [2]
Answer:
His principle of Communitarian Socialism views India as society of communities encompassing three key layers, viz., community, region and “Rashtra” all combining together as an example of a true federation.
Question 15.
Highlight any one major distinction between the Soviet economy and the capitalist economy. [2]
Answer:
1. The Soviet economy was planned and controlled by the state only.
2. But the capitalist economy was enjoyed by the people or group of people as well as by the state.
Question 16.
How did the US perceived India’s decision of leading the Non-Aligned movement? [2]
Answer:
The US did not seem happy about the India’s policy of NAM as it wanted India to join the capitalist bloc. On the other hand, it was also worried about the proximity between India and Soviets in the 1950s.
Question 17.
What is the moderate view of economic globalisation? [2]
Answer:
The moderates feel that globalisation can be intelligently managed so that its fruits get distributed to all sections of society. One do not need to be judgemental about the process of globalisation as positive or negative
Question 18.
What are the cultural consequences of globalisation? [2]
Answer:
Globalisation affects our habits like food, clothing, thinking, etc. It affects how things are perceived in society, and most importantly it leads to cultural homogenisation.
Section – C (20 Marks)
Question 19.
Highlight some important features and functions of the European Union. [4]
Answer:
The features and functions of the European Union are:
1. The EU has its flag and the national anthem.
2. Most of the nations of the EU use a common currency as the medium of exchange.
3. The body has involvement in the formulation of the foreign policy and security policy of the European nations.
4. Its area of work is spread to political, economic, military and diplomatic matters.
5. Its main functions are to promote peace establish a unified economic and monetary system, promote inclusion and combat discrimination.
6. It further works to break down barriers to trade and borders and so on.
![]()
Question 20.
What is meant by alliance building as a component of traditional security policy? What are its advantages? [4]
Answer:
Alliance building is the fourth element of traditional security policy. An association or an alliance is a partnership of states which coordinate with each other to deter and defend against military attack.
Advantages of alliance building as a component or traditional security policy are:
1. Most alliances are made in written treaties and are based on a fairly clear identification that makes the threat.
2. Alliances are formed based on national interests and can change when national interests change.
3. Countries form alliances to increase their effective power relative to another country or alliance.
Question 21.
State the problem of Goa? [4]
Answer:
1. Goa was a colony of the Portuguese. Portuguese refused to withdraw from the territories of Goa, Daman and Diu.
2. Portuguese suppressed the people of Goa during their rule. The people of Goa were denied of their civil rights.
3. There was a strong popular movement within Goa for freedom. In December 1961 the Government of India sent the army which liberated these territories. Goa, Diu and Daman became Union Territory.
4. In January 1967, the Central Government held a special ‘opinion poll’ in Goa, the majority voted in favour of remaining outside of Maharashtra.
5. In 1987, Goa became a State of the Indian Union.
Question 22.
What reasons did the Government give for declaring a National Emergency in 1975? [4]
Answer:
Some of the reasons given by the government are:
1. There was a situation of internal disturbance in the country which undermined the security of the state.
2. The election of Indira Gandhi was declared void by the Allahabad High Court in the Raj Narain case.
3. The government imposed an emergency by Presidential order issued by President Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed. They said that this period will be used for the restoration of law and order and the welfare of the poor people.
Question 23.
Mention some of the recent agreements between India and Pakistan. Can we be sure that the two countries are well on their way to a friendly relationship? [4]
Answer:
1. The two countries have agreed to undertake confidence-building measures to reduce the risk of war.
2. Bus diplomacy initiative by India has led to opening of number of bus routes between the two countries.
3. Social activists and prominent personalities have collaborated to create an atmosphere of friendship among the people of both countries.
4. Leaders have met at summits to understand each other better and to find solutions.
Section – D (12 Marks)
Question 24.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow: [4]
No region exists in a vacuum. It is influenced by outside powers and events no matter how much it may try to insulate itself from non-regional powers. China and the US remain key players in South Asian politics. Sino-Indian relations have improved significantly in the last ten years, but China’s strategic partnership with Pakistan remains a major irritant. The demands of development and globalisation have brought the two Asian giants closer, and their economic ties have multiplied rapidly since 1991.
American involvement in South Asia has rapidly increased after the Cold War. The US has had good relations with both India and Pakistan since the end of the Cold War and increasingly works as a moderator in India-Pakistan relations. Economic reforms and liberal economic policies in both countries have greatly increased the depth of American participation in the region. The large South Asian diasporas in the US and the huge size of the population and markets of the region also give America an added stake in the future of regional security and peace.
(i) Which of these nations have a great influence in South Asian politics?
(a) China
(b) The USA
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) South Africa
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(ii) Which of the following is a threat for India?
(a) Proximity between Pakistan and China
(b) Proximity between the USA and Pakistan
(c) Proximity between Sri Lanka and Pakistan
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Proximity between Pakistan and China
(iii) What kind of relationship has the US had with India and Pakistan since the end of the Cold War?
(a) The US unilaterally supports Pakistan
(b) The US unilaterally supports India
(c) The US has good relations with both nations
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) The US has good relations with both nations
(iv) Why South Asian nations can be good partners for the USA?
(a) Economic reforms in the South Asian nations
(b) Liberalisation of the economy
(c) Large South Asian diaspora in the USA
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
![]()
Question 25.
In the given outline political map of India, four states have been marked as A, B, C and D. Identify these states on the basis of the information given below and write their correct names in your answer book along with respective serial number of the information used and the concerned alphabets in the map as per the following format. [4]
(i) The Princely State which resisted its merger with the Union of India.
(ii) The state which was carved out of Punjab in 1966.
(iii) The state was created in December 1952.
(iv) The 22nd State of the Indian Union.
| Sr. no. of the Information used | Concerned alphabet | Name of the State |
| (i) | ||
| (ii) | ||
| (iii) | ||
| (iv) |
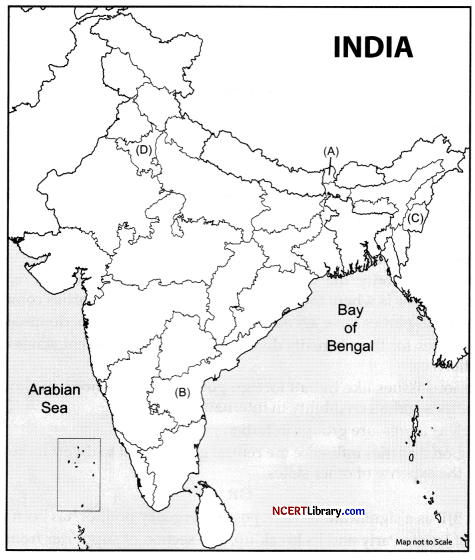
Answer:
| Sr. no. of the Information used | Concerned alphabet | Name of the State |
| (i) | C | Manipur |
| (ii) | D | Haryana |
| (iii) | B | Andhra Pradesh |
| (iv) | A | Sikkim |
Question 26.
Study the given Cartoon and answer the questions that follow: [4]

(i) To which of the following years does the given cartoon refer?
(a) 1963
(b) 1965
(c) 1967
(d) 1969
Answer:
(c) 1967
(ii) Name the person for whom the expression ‘Aya Ram, Gaya Ram’ was made.
(a) Ram Lai
(b) Gaya Lai
(c) Ram Singh
(d) Gaya Ram
Answer:
(b) Gaya Lai
(iii) To which of the following political parties did the above-mentioned person originally belong?
(a) Congress
(b) United Front
(c) Bharatiya Kranti Dal
(d) Lok Dal
Answer:
(a) Congress
(iv) After the 1967 general election, the breakaway Congress MLAs played a significant role in installing
non- Congress governments in_______.
(a) Haryana
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Madhya Pradesh
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Section – E (24 Marks)
Question 27.
“The regional parties have started playing an important role in Indian politics.” Comment.
OR
Trace the emergence of the BJP as a significant force in post-Emergency politics. [6]
Answer:
India as a democracy has a multi-party system which means there are several political parties competing for power. Apart from the primary parties, each state has their own local political parties that rule and compete in its region.
Regional parties play the following roles in Indian politics :
1. In absence of a clear majority, the largest party has to join hands with a regional party in order to form a government. This is where the importance of the regional parties comes into play.
2. Most of the regional parties have agendas furthering certain cultures dominant within that state.
3. The regional parties for their benefit divide the people of different states on the line of language, culture, traditions etc.
4. Sometimes serious issues like India’s foreign policy influenced and compromised by regional parties. This affects India’s credibility in international politics.
5. They also work as a pressure group in Indian politics.
6. Sometimes regional parties influence the central government to divert more annual budget funds to their states at the expense of other states.
OR
The emergence of the BJP as a significant force in post-Emergency politics has been described below:
1. After the failure of the Janata Party and its break-up, one section of supporters from Jana Sangh formed the Bharatiya Janata Party in 1980.
2. The BJP adopted a broader political platform than that of the Jana Sangh to gain support from more sections of people. It embraced ‘Gandhian Socialism’ as its ideology. However, it could not get much success in the elections held in 1980 and 1984.
3. After 1986, the party began to emphasise the Hindu nationalist elements in its ideology. The party pursued the politics of ‘Hindutva’ and adopted the strategy of mobilising the Hindus. For example, the BJP criticised the action of the government as an unnecessary concession and ‘appeasement policy of the minority community, in the 1985 Shah Bano case and the orders of the Supreme Court.
4. At the same time, the Ayodhya issue was made by the BJP as its major electoral and political plank. The BJP, in order to generate public support, took out the Rathyatra from Somnath in Gujarat to Ayodhya in UP.
5. As a result of above events, the BJP was able to consolidate its position in the often elections of 1989, 1991, 1996, 1999 and at last gained complete majority in the Lok Sabha elections of 2014 and 2019.
![]()
Question 28.
How Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru shaped the foreign policy of India?
OR
Does India’s foreign policy reflect her desire to be an important regional power? Argue your case with the Bangladesh war of 1971 as an example. [6]
Answer:
Pandit Jawahar Lai Nehru was the first Prime Minister of India and apart from this he was also the first foreign minister of India:
1. There were three major objectives of his foreign policy. His first objective was to preserve the sovereignty of India.
2. The second objective of Nehru was to ensure the territorial integrity of India and the third was to bring rapid economic development in India. These three visions guided his foreign policies.
3. For achieving these policies Nehru choose the path of Non-Alignment. He did not join any of the capitalist and communist blocs.
4. Nehru wanted to pursue his vision of a peaceful world and wanted to remain away from the cold war rivalries of the US and USSR.
5. In his policy of Non-Alignment Nehru received support from several other nations who have been sufferers of the imperial policies of the West. Some of the nations were Ghana, Egypt and Yugoslavia.
OR
India is one of the most important nations in Asia. It is also very big and powerful as compared to its neighbours. However, India does not undermine the status of any nation and interferes only when the situation is out of control. This can be understood by the example of Bangladesh.
1. India made all diplomatic efforts to avoid full scale war but they were not successful and ultimately the war started between the two nations in the month of December.
2. There was an attack from the Pakistan air force on the lands of Punjab and Rajasthan. On the other hand the Pakistan army attacked the regions of Jammu and Kashmir.
3. There was strong retaliation from the Indians on the Western and Eastern front of the border. Indians made use of the army, navy and air force to counter the attacks of Pakistan.
4. The Indian army also received support from the local population due to which it was able to make the Pakistan army surrender within ten days.
5. There was 90,000 Pakistani soldiers who surrendered to the Indian army. East Pakistan was declared independent and it was declared as Bangladesh.
Question 29.
Mention some important steps taken for the restoration of the dominance of the Congress Party after the split in 1969.
OR
Analyse any four factors that led the Congress Party to a spectacular win in the 1971 elections. [6]
Answer:
The factors responsible for the restoration of the Congress Party after its split in 1969:
1. Abolition of privy purse: The Government of India tried to bring a Constitutional Amendment in 1970 to abolish the privy purse.
2. Garibi Hatao after splitting, the new Congress had some positive agenda. Indira Gandhi said that the opposition alliance had only one common programme i.e., Indira Hatao. In contrast to this, she put forward a positive programme captured in the famous slogan: Garibi Hatao.
3. Indira Gandhi launched a series of initiatives to give the government policy a left orientation. She got the Congress Working Committee to adopt a Ten Point Programme. This programme included social control of banks, nationalisation of general insurance, a ceiling on urban property and income, public distribution of food grains, land reforms and provision of house sites to the rural poor.
4. 1971’s war, the crisis in East Pakistan and the Indo-Pak War led to the establishment of Bangladesh. Indira Gandhi’s statesmanship was admired. She was seen not only a protector but also a strong nationalist leader.
OR
1. The new Congress had something that its big opponents lacked—it had an issue, an agenda and a positive slogan. The Grand Alliance did not have a coherent political programme. Indira Gandhi said that the opposition alliance had only one common program: Indira Hatao (Remove Indira). In contrast to this, she put forward a positive programme captured in the famous slogan: Garibi Hatao (Remove Poverty).
2. She focused on the growth of the public sector, the imposition of ceiling on rural land holdings and urban property, and the removal of disparities in income and opportunity.
3. Besides the abolition of princely privileges, through Garibi Hatao’s slogan, Indira Gandhi tried to generate a support base among the disadvantaged, especially among landless labourers Dalits and Adivasis, minorities, women and unemployed youth. The slogan of Garibi Hatao and the programmes that followed it were part of Indira Gandhi’s political strategy of building an independent nationwide political support base.
4. Indira Gandhi had managed to gain a positive image of her personality dedicated to working for the benefit of the country.
Question 30.
Highlight any three positive and three negative features each of the Soviet system in the Soviet Union.
OR
Analyse the factors responsible for the disintegration of the USSR with special reference to Perestroika and Glasnost. [6]
Answer:
The three positive features of the Soviet system were :
1. The Soviet economy was more developed than the rest of the world except for the US. It had a complex communications network, vast energy resources, machinery production, and a transport system that connected its remotest areas.
2. A minimum standard of living for all citizens was ensured by the Soviet state, and the government subsidised basic necessities including health, education, childcare and other welfare schemes.
3. State ownership was given more importance. Land and productive assets were owned and controlled by the Soviet state.
The three negative features of the Soviet system were:
1. The Soviet system was very bureaucratic and authoritarian in nature. It turned the life of the people into disorder. Authoritarianism meant the absence of democracy and freedom of speech, which angered the people.
2. The Soviet economy witnessed economic stagnation for a long time which led to market failure when demand failed to meet supply in the market for consumer goods.
3. State Treasury had spent a huge fortune on building and maintaining nuclear arsenals and in developing its satellite states in East Europe and within the Soviet system. It turned into a large economic burden for the Soviet system.
OR
The declaration on the disintegration of the USSR was a surprise for the whole world.
1. The internal weaknesses of Soviet political and economic institutions, which failed to meet the aspirations of the people, were responsible for the collapse of the system.
2. The most important factor for the fall of the Soviet Union was a lack of proper leadership.
3. There was no clear-cut line between the party and the government as there was one political party which was wielding power.
4. Economic stagnation for many years led to severe consumer shortages and a large section of Soviet society began to doubt and question the system.
5. The Soviet economy used much of its resources in maintaining a nuclear and military arsenal and the developing of its satellite states in Eastern Europe.
6. Mikhail Gorbachev’s policies of ‘Perestroika (restructuring) and glasnost (openness)’ proved to be disastrous for the economic health of the USSR.
7. Anti-communist forces of the Soviet Union had the support of the USA and Western European countries.
8. Gorbachev due to his liberal policies did not try to uproot these forces. No effort was ever made to create a socialist human being and a socialist culture. The old Soviet Union was thus dead and buried.
![]()