Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science with Solutions Set 2 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Set 2 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours.
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question numbers 1-12 are multiple choice questions of one mark each.
- Question numbers 13-18 are of 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 50 words each.
- Question numbers 19-23 are of 4 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 100 words each.
- Question numbers 24-26 are passage, cartoon and map-based questions. Answer accordingly.
- Question numbers 27-30 are of 6 marks each. Answers to these questions should not exceed 170 words.
Section – A (12 Marks)
Question 1.
The part of Kashmir occupied by Pakistan is addressed by her as_______. [1]
(a) Azad Pakistan
(b) Siachen
(c) Gilgit
(d) Mini Kashmir
Answer:
(a) Azad Pakistan
Question 2.
Name the article of the Constitution under which Jammu and Kashmir were accorded special status. [1]
(a) Article 370
(b) Article 375
(c) Article 380
(d) Article 368
Answer:
(a) Article 370
Question 3.
Select one of the most appropriate statements about ‘Global Commons. [1]
(a) The earth’s atmosphere, Antarctica, ocean floor and outer space are considered part of the global commons.
(b) The global commons are outside the sovereign jurisdiction.
(c) The question of managing the global commons reflected the North-South divide.
(d) The countries of the North are more concerned about the protection of the global commons than the countries of the South.
Answer:
(a) The earth’s atmosphere, Antarctica, ocean floor and outer space are considered part of the global commons.
Question 4.
The vision of the Bombay Plan of 1944 was that of________. [1]
Choose the economy of which the Bombay Plan of 1944 was the vision.
(a) Planned Economy
(b) Unplanned Economy
(c) Capitalistic Economy
(d) Deregulated Economy
Answer:
(a) Planned Economy
![]()
Directions for Q.Nos. 5 and 6
In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read these statements and choose one correct answer from the given options.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Question 5.
Assertion (A): Security relates only to extremely dangerous threats. [1]
Reason (R): Threats that could so endanger core values that those values would be damaged beyond repair if we did not do something to deal with the situation.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Globalisation helps in increasing the wealth of rich people. [1]
Reason (R): Globalisation opens up ample of opportunities for foreign investors.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 7.
Name the year when Japan became a member of the OECD. [1]
(a) 1965
(b) 1999
(c) 1964
(d) 1980
Answer:
(c) 1964
Question 8.
Which of the following statements about EU are true? [1]
(i) It is a highly influential regional organization.
(ii) It has a currency of its own.
(iii) It is the world’s biggest economy with a GDP of more than $17 trillion in 2016.
(iv) It can challenge the power of the US in trade, diplomacy and military areas.
Codes:
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Answer:
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Question 9.
Name the personality who introduced the LPG model of development in India. [1]
(a) Rajiv Gandhi
(b) V.P. Singh
(c) Dr Manmohan Singh
(d) Dr Pranav Mukherjee
Answer:
(c) Dr Manmohan Singh
Question 10.
Arrange the following in chronological order: [1]
(i) Kargil War between India and Pakistan
(ii) Pakistan got independence
(iii) Afghanistan joined SAARC
(iv) Indo-Sri Lanka Accord
Codes:
(a) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(b) (iii), (ii), (i), (iv)
(c) (ii), (iv),(i), (iii)
(d) (ii), (i),(iii), (iv)
Answer:
(c) (ii), (iv),(i), (iii)
Question 11.
Why did India send troops to Maldives in 1988? [1]
(a) To stop an ethnic conflict.
(b) To stop the insurgency.
(c) To end the Sri Lankan Civil War between Sri Lankan Tamil Militant groups- the LTTE and the Sri Lankan Military.
(d) To crush a student’s mass movement.
Answer:
(b) To stop the insurgency.
![]()
Question 12.
Find the odd one out in the context of the UN Secretaries-General: [1]
(a) Kofi A. Annan: created the Global Fund to fight AIDS.
(b) Ban Ki-moon: focused on the Millennium Development Goals.
(c) Boutros Boutros-Ghali: worked for the independence of Namibia.
(d) U Thant: worked for resolving the Cuban Missile Crisis.
Answer:
(c) Boutros Boutros-Ghali: worked for the independence of Namibia.
Section – B (12 Marks)
Question 13.
Name the two blocs in which the world got divided after the World War II. [2]
Answer:
The world got divided into two blocs aftermath of world war II. One bloc was led by the US that came to be known as the Capitalist bloc and the other was led by the USSR that came to be known as the Communist bloc.
Question 14.
Highlight any two consequences of ‘Shock Therapy’. [2]
Answer:
1. Every country had to make a total change from a socialist economy to a capitalist economy.
2. Each of these countries had to adopt private ownership as a dominant pattern of ownership of property.
Question 15.
Why is violence between two communities considered as a threat to democracy? [2]
Answer:
Violence between two communities disrupts the functioning of the government, delays decision making and destabilises the routine of democracy affecting the religious freedom of individual.
Question 16.
How the definition of development can vary for different sections? [2]
Answer:
People have different development goals, because people come from different backgrounds. Different people have different dreams and aspirations. Ex. Adivasis, farmers, industrialist have different goal even for single piece of land.
Question 17.
Highlight the most important outcomes of the Rio Summit. [2]
Answer:
Outcomes of Rio Summit:
1. The Rio Summit produced conventions dealing with climate change, biodiversity, forestry, etc.
2. It recommended a list of developmental practices called ‘Agenda 21
3. There was consensus on sustainable development.
Question 18.
How is oil continued to be the most important resource in the global strategy? Explain with an example. [2]
Answer:
Oil is the most important resource. In its uneven distribution and non-availability to some nations, there has always been a struggle over it. The First and the Second Gulf War are the prime examples of this struggle.
![]()
Section – C (20 Marks)
Question 19.
‘The question of indigenous people brings the issue of environment, resources and politics together’. Justify the statement. [4]
Answer:
Indigenous people today live more in conformity with their particular social, economic, and cultural customs and traditions than the country of which they now form a part.
1. They appeal to governments to come to terms with the continuing existence of indigenous nations as enduring communities with an identity of their own. 30 crore indigenous population spread across the world.
2. Irrespective of their geographical location, they are strikingly similar with respect to their land and variety of life systems supported by it.
3. The loss of land is the most obvious threat to their survival as they depend for their subsistence primarily on the cultivation of land.
4. They enjoy constitutional protection in political representation.
5. They are displaced by various developmental projects.
Question 20.
Was the Emergency necessary to protect Indian democracy from internal agitation? Give arguments to support your answer. [4]
Answer:
No, the emergency was not the only solution to protect Indian democracy because, Indian democracy shows unity in diversity. Each and every citizen of Indian has right to express their view against the government in meaningful way, without violation of law. Ex. J.R Narayan called peaceful agitation in Bihar and Gujarat. If agitation turns into armed rebellion then bring emergency clauses into action on certain ares and not on the whole country. In 1975, whole country faced the emergency clauses because of anti-government agitation in north Indian state but these agitation were peaceful not armed rebellion.
Question 21.
What are the reasons behind the rise of international terrorism? [4]
Answer:
The reasons behind the rise of international terrorism are as follows:
1. Islamic Fundamentalism: Orthodoxy, religious fundamentalism and the narrow-mindedness which preaches antagonistic feelings among different communities is responsible for the growth of International terrorism.
2. US Hegemony: US policy of interference and its intentions of spreading hegemony across the world has been vehemently opposed by the people of Iran, Iraq, Cuba, Palestine, etc. and the same is also responsible for the spread of terrorism across the globe.
3. Failure of UN and other International Bodies: The UNO has remained merely a debating forum under the influence of major world powers and the opinions and wishes of developing countries have been largely ignored. The same is responsible for the growth of international terrorism.
4. Uneven growth of economy: Some part of the world is overdeveloped, whereas major part of the world have remained underdeveloped and people in these countries are facing the problems of rampant unemployment, illiteracy, hunger, poverty, etc. Suffering of people in these countries is also responsible for the growth of international terrorism.
Question 22.
What was ‘Operation Blue Star’? Why did it hurt the sentiments of the Sikh Community? [4]
Answer:
1. ‘Operation Blue Star’ ‘was a code name for army action in the Golden Temple, Amritsar carried out by Government of India under the prime ministership of Indira Gandhi.
2. In this operation, the government could successfully flush out the militants, but it damaged the historic temple and deeply hurt the sentiments of the Sikhs.
3. Sikhs across the world and in India assume this military operation as an attack on their religious faith.
4. This sentiment further gave the energy to extremist groups.
![]()
Question 23.
Explain the economic relationship between India and China since the 1990s. [4]
Answer:
The economic engagement between both nations has increased significantly since the 1990s.
1. Since the year 1999 the trade between the two nations is growing at the rate of 30 per cent. Several border posts for trade have been opened between the two nations.
2. The magnitude of trade has increased from $338 million in 1992 to $84 billion in 2017. These numbers spoke for themselves about the magnitude of trade between the two Nations.
Section – D (12 Marks)
Question 24.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow: [4]
In recent years there has been the demand to reform the UN. Two basic kinds of reforms face the UN: reform of the organization’s structures and processes; and a review of the issues that fall within the jurisdiction of the organization. The biggest discussion has been on the functioning of the Security Council. Related to this has been the demand for an increase in the UN Security Council’s permanent and non-permanent membership so that the realities of contemporary world politics are better reflected in the structure of the organization. On 1 January 1997, Kofi Annan started a process to see how to reform the UN.
(i) Which is not TRUE about the proposed reforms in the UN?
(a) The structures and processes of the UN need to be reformed.
(b) What all issues of UN come under the gambit of the UN.
(c) Almost all agree that the UN requires certain reforms.
(d) The UN should be replaced by some other international body.
Answer:
(d) The UN should be replaced by some other international body.
(ii) The major demand for reform has been around the_______.
(a) General Assembly
(b) Security Council
(c) Trusteeship Council
(d) Secretariat
Answer:
(b) Security Council
(iii) Which of the following statements is NOT correct about the Security Council?
(a) There is a need to increase the Security Council members.
(b) Members need to increase to reflect the changing dynamics of the world.
(c) The Security Council is one of the main organs of the UN.
(d) There is a demand to scrap the Security Council.
Answer:
(d) There is a demand to scrap the Security Council.
(iv) Kofi Annan launched a process in_______to see how to bring about reforms in the UN.
(a) January 1997
(b) January 1998
(c) February 1997
(d) March 1998
Answer:
(a) January 1997
![]()
Question 25.
In the given outline map of South Asia, four countries have been marked as (A), (B), (C) and (D). Identify them on the basis of the information given below and write their correct names in your answer book with their respective serial number of the information used and the alphabet concerned as per the following format: [4]
(i) The country has experienced civilian as well as military rule both.
(ii) Democracy was restored in this country in 2006.
(iii) This country is still a monarchy.
(iv) This country is a part of India’s ‘Look East Policy via Myanmar.’
| Sr. no. of the Information used | Alphabet Concerned | Name of the Country |
| (i) | ||
| (ii) | ||
| (iii) | ||
| (iv) |
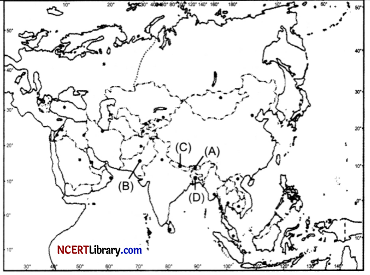
Ans.
| Sr. no. of the Information used | Alphabet Concerned | Name of the Country |
| (i) | B | Pakistan |
| (ii) | C | Nepal |
| (iii) | A | Bhutan |
| (iv) | D | Bangladesh |
Question 26.
Study the given Cartoon and answer the questions that follow: [4]

(i) Which of the following Princely States refused to join India after Independence?
(a) Gwalior
(b) Mysore
(c) Hyderabad
(d) Baroda
Answer:
(c) Hyderabad
(ii) Who among the following played a decisive role in the integration of Princely States with the Indian Union?
(a) Jawaharlal Nehru
(b) V.P. Menon
(c) Lord Mountbatten
(d) H.N.Kunzru
Answer:
(b) V.P. Menon
(iii)_______was called the ‘Iron Man of India’.
(a) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
(b) Mahatma Gandhi
(c) Vallabhbhai Patel
(d) Ram Manohar Lohia
Answer:
(c) Vallabhbhai Patel
(iv) Name the document signed between the Indian government and the native rulers.
(a) Instrument of Accession
(b) Standstill Agreement
(c) Instrument of Union
(d) Instrument of Merger
Answer:
(a) Instrument of Accession
Section – E (24 Marks)
Question 27.
Give an analysis of the events that took place in Tibet. How it affected the relationship between India and China? [6]
OR
Analyse the events that took place during the India-Pakistan war of 1965 and the aftermath of the war.
Answer:
The region of Tibet plateau was claimed by the China from time to time. After the establishment of the communist government; China made efforts to take over the control of Tibet.
1. In the year 1950, China became successful in gaining over the control over Tibet. However, there was large section of the Tibetan population who resisted this takeover by the China.
2. In the early years India made efforts to persuade China to recognise the autonomy of the Tibet, but China was not willing to accept this.
3. In the Panchsheel Accord of 1954 India and China decided to respect each other’s territorial integrity. India also accepted the claim of the China over the lands of Tibet.
4. In the year 1956, the Chinese premier Zhou Enlai visited India. He was also accompanied by the spiritual guru of Tibet Dalai Lama. Dalai Lama informed Nehru about the worsening situation of Tibet, but Nehru could not do anything as he has recognized the autonomy of China over Tibet.
5. In the year 1958, there was armed uprising in Tibet against the occupation of the Chinese. This occupation was suppressed by China. In 1959, the situation became worse and Dalai Lama had to seek asylum from India and he was granted that asylum. This led to the strain in the relationship between the China and India.
OR
India and Pakistan came in direct conflict in the year 1965. Some of the events that took place during the war are:
1. The Pakistan launched an offensive in the area of Rann of Kutch in Gujarat in April 1965.
2. Subsequently, the Pakistan also launched a major offensive in the region of Jammu and Kashmir in the months of August and September. The Pakistani government was hoping a support from the locals but it did not took place.
3. Lai Bahadur Shastri made a smart choice of releasing the pressure from Kashmir. He sent the Indian troops to the Punjab front. Here many fierce battles took place and ultimately Indian troops were successful in reaching the Lahore border.
4. The hostilities between the two nations came to an end after the intervention of the United Nations.
5. In January 1966. The Indian premier Lai Bahadur Shastri and Pakistan’s General Ayub Khan signed the Tashkent agreement which was brokered by the Soviet Union.
![]()
Question 28.
Why was the year 1967 considered as landmark year in India’s political and electoral history? [6]
OR
Analyse any three factors which were responsible for Indira Gandhi’s achieving a thumping majority in 1971 Lok Sabha elections.
Answer:
The fourth general election held in 1967 was the first election to be held without Nehru. Congress was a dominant party before 1967, but the scenario was likely change after 1967’s election. Several non-Congress parties joined together to bring Congress down. They realized that their disintegration kept Congress in power. So, they joined to form a big alliance called Samyukt Vidhayak Dal.
Congress still managed to win in the Lok Sabha election, but with the poorest performance ever. Congress lost in many states. Influential leaders of Congress lost their position. Many Congress leaders left the party in order to join the other party. Local politics gained momentum. In Tamil Nadu, a non-Congress party won on its own for the first time. 1967 elections showcased a new element which never came into light. Defection and coalition played an important role and new elements were in the scene of electoral politics.
The opposition parties got together and formed anti-congress fronts in some states. This strategy was given the name of non-Congress by Ram Manohar Lohia. He argued that Congress rule was undemocratic and opposed the interests of ordinary people. Therefore, the non-Congress parties were necessary for reclaiming democracy for the people.
OR
Indira Gandhiji had adopted a very bold strategy. She converted simple power struggle into an ideological struggle. She launched a series of initiatives to give the government policy a Left orientation. She got Congress Working Committee to adopt a Ten Point Programme in May 1967. This program included social control of banks, nationalization of General Insurance, a ceiling on urban property and income, public distribution of food grains, land reforms and provision of house sites to the rural poor.
While the ‘Syndicate’ leaders formally approved this Left-wing program, they had serious reservations about the same. She also announced several big and popular policy measures like the nationalization of fourteen leading private banks and the abolition of the ‘privy purse’ or the special privileges given to former princes. Morarji Desai was the Deputy Prime Minister and Finance Minister.
She put forward a positive program captured in the famous slogan: Garibi Hatao (Remove Poverty). She focused on the growth of the public sector imposition of ceiling on rural land holdings and urban property, removal of disparities in income and opportunity, and abolition of princely privileges. Through Garibi Hatao, Indira Gandhi tried to generate a support base among the disadvantaged, especially among the landless labourers, Dalits, Adivasis, minorities, women and the unemployed youth.
The slogan of Garibi Hatao and the program that followed it were a part of Indira Gandhi’s political strategy of building an independent nationwide political support base.
Question 29.
Write a note on the 16th Lok Sabha election held in 2014.
OR
‘Coalition Governments proved to be a boon for democracy in India.’ Support this statement with any two suitable arguments. [6]
Answer:
In India the 16th Lok Sabha Elections of April – May 2014 were conducted in 9 stages.
The main features of this election are as follows:
1. Enhancement in the Election Expenditure: The Central Government enhanced the Election expenditure limit in February 2014. Now a candidate for contesting the Lok Sabha seat can spend a maximum 70 Lacs Rupees whereas in the Legislative Assembly election a candidate can spend a maximum of 28 Lacs Rupees on his/her election.
2. Highest Percentage of Polling/Voting: In the 16th Lok Sabha election highest 66.38% vote-polling was recorded.
3. NOTA Button Used: In the 16th Lok Sabha election 60 Lacs voters used the Nota (None of the above) button.
4. Number of Voters: During the 16th Lok Sabha election, the number of total voters was 81 crores 40 Lacs by which nearly 55 crores voters cast their votes.
5. The Number of Political Parties: During the 16th Lok Sabha election the number of Political Parties was 1687 in which 6 National Parties were included.
6. Women Candidates were Elected: In the 16th Lok-Sabha elections maximum of 61 women were elected.
7. Shree Narendra Modi emerged as Prime Minister: In the 16th Lok Sabha Elections, Bhartiya Janata Party won 282 seats and whereas NDA Coalition got 334 Seats. And the leader of BJP and NDA Sh. Narendra Modi was administered the oath of Prime Ministership on 26 May 2014.
8. Formation of Council of Ministers: On 26 May 2014 Prime Minister Narendra Modi formed his Council of Ministers in which 23 Cabinet Ministers, 10 Independent Charge Ministers, and 12 State Ministers were included.
OR
The defeat of the Congress party marked the end of Congress’s dominance over the Indian Party system, thus, began an era of a multi-party system in which regional parties played a crucial role in forming ruling alliances. The nineties also saw the emergence of powerful parties and movements that represented the Dalits and backward castes in turn representing powerful regional assertion as well. There have been various coalition governments in the country, from 1977 till date. Coalition governments proved to be a boon because :
1. Ideological differences and controversies were weakened and the country enjoyed better decisions that were pragmatic.
2. They provided more alternatives for the people to choose from in the elections.
3. These governments established the importance of small and regional parties, they removed the dominance of two parties, and regional aspirations and demands came into the limelight.
4. These governments led to national unity as most of the parties got a chance to be partners in the policy formation.
5. Many disputed issues were put off due to the minimum common program.
Question 30.
Enlist any six consequences of the disintegration of the Soviet Union.
OR
Why are India’s relations with Russia considered an important aspect of India’s foreign policy? Explain. [6]
Answer:
A consequence of the disintegration of the Soviet Union:
1. End of Cold War confrontations. The ideological dispute over whether the socialist system would beat the capitalist system was not issue anymore.
2. End to arms race and possible new peace. But currently, Russian invasion in Ukraine destroyed that possibility.
3. Power relations changed in the world. Now one superpower would dominate and create a unipolar system, or different countries or groups of countries could become important players in international politics.
4. U.S. became the sole superpower. Capitalism became the dominant philosophy.
5. Emergence of many new countries.
6. The notion of liberal democracy emerged as the best way to organize political life.
7. The international system saw many new players emerge, each with its own identity, interests, and economic and political difficulties.
OR
India has maintained good relations with all the Post-Communist countries but it has the strongest relations with Russia which continue to date.
Following are some arguments to support the statement:
1. Indo-Russian relations are an important segment of India’s foreign policy. The relations between these two countries are embedded in a history of trust and common interests and are matched by popular perceptions. Famous Bollywood personalities are common names in Russia.
2. Both countries share a vision of multipolar world order. A multipolar world the co-existence of several powers in the international system, collective security, greater regionalism, negotiated settlements of international conflicts, an independent foreign policy for all countries, and decision-making through bodies like the UN.
3. From this relationship, India gets benefits on issues like Kashmir, energy supplies, sharing information on international terrorism, access to Central Asia, and balancing its relations with China. On the other hand, Russia stands to benefit from this relationship because India is the second largest arms market for Russia. The Indian military gets most of its hardware from Russia.
4. Russia is vital for India as it has repeatedly come to the assistance of India during its oil crises. India is trying to increase its energy imports from Russia and the republics of Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan.
5. Apart from this, Russia is important for India’s nuclear energy plants and assisted India’s space industry. For example, Russia provided the cryogenic rocket when India needed it. Due to the above reasons, Russia is considered an important aspect of India’s foreign policy.
![]()