Practising the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 History with Solutions Set 7 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 History Set 7 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours.
Max. Marks: 70
General Instructions:
- Question paper comprises five Sections – A, B, C, D and E. There are 34 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – Question 1 to 21 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Question no. 22 to 27 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60-80 words.
- Section C – Question no. 28 to 30 are Long Answer Type Questions, carrying 8 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 300-350 words.
- Section D – Question no. 31 to 33 are Source based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section E – Question no. 34 is Map based, carrying 5 marks that include the identification and location of significant test items. Attach the map with the answer book.
Section – A (21 Marks)
Question 1.
Identify the ruler with the following set of information: [1]
I. He was also known as the Piyadassi.
II. He adopted the path of peace after the Battle of Kalinga.
A. Ashoka
B. Bindusara
C. Chandragupta Maurya
D. Samudragupta
Answer:
A. Ashoka
Question 2.
The seals used to contain some sort of writing probably related to the. [1]
A. Name and title of owner
B. Purpose of the sent consignment
C. Invoice of the consignment
D. None of these
Answer:
A. Name and title of owner
Question 3.
Match the following and select the correct option: [1]
| List-I | List – II |
| 1. Megasthenes | a. Arthashastra |
| 2. Kautilya | b. Prayaga Prashasti |
| 3. Harishena | c. Malavikaagnimitra |
| 4. Kalidasa | d. Indika |
A. 1 – b, 2- c, 3 -d, 4- a
B. 1 – a, 2- d, 3 -c, 4- b
C. 1 – c, 2- b, 3 -d, 4- a
D. 1 – d, 2- a, 3 -b, 4- c
Answer:
D. 1 – d, 2- a, 3 -b, 4- c
Question 4.
Which of the following commodities was recovered in large numbers from the archaeological sites? [1]
A. Bricks
B. Bronze statues
C. Gold
D. None of these
Answer:
A. Bricks
![]()
Question 5.
Identify the given image from the following options: [1]

A. Bindusara
B. Chandragupta Maurya
C. Brihadratha
D. Kanishka
Answer:
B. Chandragupta Maurya
Question 6.
Who was the first Director of ASI? [1]
A. R.D Bannerjee
B. William Jones
C. Alexander Cunningham
D. Warren Hastings
Answer:
C. Alexander Cunningham
Question 7.
The Dargah of the famous Sufi saint Muinuddin Chishti is situated in which of the following cities? [1]
A. Delhi
B. Ajmer
C. Hyderabad
D. Agra
Answer:
B. Ajmer
Question 8.
Fill in the blank:
Ibn Battuta’s description about China is often compared with the description of_______. [1]
A. Marco Polo
B. Atanasius Nikitin
C. Bernier
D. Jean Baptise Travemier
Answer:
A. Marco Polo
Question 9.
The representatives of the Muslim orthodoxy were known as the. [1]
A. mamas
B. Sufis
C. Hadis
D. Tirthankar
Answer:
A. Ulamas
Question 10.
Given below are two statements, one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). [1]
Assertion (A): Ibn Batuta got the patronage of Muhammad Bin Tughlaq
Reason (R): Batuta spend all his life in India and did not left the nation and lead a settled life.
A. Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
B. Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
C. (A) is correct, but (R) is not correct.
D. (R) is correct, but (A) is not correct.
Answer:
D. (R) is correct, but (A) is not correct.
Question 11.
Complete the following with the correct options: [1]
Ain-i-Akbari: Abul Fazl:: Alamgir Nama:_______.
A. Mirza Muhammad Kazim
B. Mirza Ghalib
C. Mirza Ghulam Azad
D. Abul Fazl
Answer:
A. Mirza Muhammad Kazim
![]()
Question 12.
Which among the following is correctly matched? [1]
| List -1 | List – II |
| A. Daulatabad | Feroz Shah Tughlaq |
| B. Rihla | A1 Biruni |
| C. Kitab-ul Hind | Tavernier |
| D. Marco Polo | Italian |
Answer:
D. Marco Polo— Italian
Question 13.
Given below are two statements, one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). [1]
Assertion (A): India became independent but had to accept the partition of the nation.
Reason (R): There was widespread communal violence in the country.
A. Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
B. Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
C. (A) is correct, but (R) is not correct.
D. (R) is correct, but (A) is not correct.
Answer:
B. Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Question 14.
Consider the following statements and select the correct from the following options: [1]
Consider the following statements about the Quit India movement.
I. It was launched by Gandhiji.
II. Independent governments were formed in several parts of the nation.
III. Socialists did not participate in this movement.
Choose the correct statements.
A. I and III
B. III and II
C. I and II
D. I, II and III
Answer:
C. I and II
Question 15.
The epic of “Mahabharata” is written by which of the following personalities? [1]
A. Valmiki
B. Ved Vyasa
C. Tulsidas
D. Surdas
Answer:
B. VedVyasa
Question 16.
Which of the following activities were funded by Sultan Jehan Begum? [1]
A. Construction of museum
B. Construction of Guesthouse
C. Publication of volumes on Sanchi
D. All of the above
Answer:
D. All of the above
Question 17.
In 1857, the sepoys reached the Red Fort in Delhi and convinced_______to lead the mutiny. [1]
A. Nana Sahib
B. Kunwar Singh
C. Bahadur Shah
D. Peshwa Baji Rao II
Answer:
C. Bahadur Shah
Question 18.
Which of the bodies now preserves and controls the site of Sanchi Stupa? [1]
A. Archaeological Survey of India
B. Centre of Heritage
C. Ministry of Home Affairs
D. None of the above
Answer:
A. Archaeological Survey of India
![]()
Question 19.
Find out from the following pairs which one is NOT correctly matched: [1]
A. Sangama Dynasty: First Dynasty in Vijayanagara
B. Tuluva Dynasty: Krishna Deva Raya
C. Amara Nayaka System : Iqta System
D. Rama Raya: Battle of Rakshas Tangdi
Answer:
D. Rama Raya: Battle of Rakshas Tangdi
Question 20.
Ryotwari system was introduced by which of the following Viceroys? [1]
A. Lord Munro
B. Lord Hastings
C. Lord Wellesley
D. Lord Cornwallis
Answer:
A. Lord Munro
Question 21.
What was the stand of Gandhiji on the subject of separate electorates for depressed classes? [1]
A. He supported the separate electorates
B. He opposed the separate electorates
C. He remained quiet on this issue
D. None of these
Answer:
B. He opposed the separate electorates
Section – B (18 Marks)
Question 22.
Why sixth century BCE is considered to be a major turning point in ancient history? [3]
Answer:
The sixth century BCE proves a major turning point in ancient history due to the following reasons:
1. The establishment of major cities, the growing prevalence of the use of iron and the introduction of a formal coinage system are some of the features of the early sixth BCE.
2. The introduction of the two new religions Buddhism and Jainism also changed the social structure in society.
Question 23.
Mention the factors that accounted for the constant expansion of agriculture during the 16th and 17th centuries. [3]
Answer:
1. The abundance of land, available labour and the mobility of peasants were three factors that accounted for the constant expansion of agriculture.
2. Irrigation projects received state support as well.
3. Though agriculture was labour-intensive, peasants did use technologies that often harnessed cattle energy.
Question 24.
Visual images and literature as much as the writing of history have helped in keeping alive the memory of the revolt of 1857.” Assess this statement. [3]
Answer:
The writing of history, art and literature contributed remarkably to immortalising the sacred memory of the struggle of 1857.
1. The leaders of the revolt were presented as heroes, taking the country towards the battlefield they were depicted as heroes, inspiring the common masses to begin a struggle against the oppressive colonial power.
2. Many heroic poems were composed, narrating the bravery of Laxmi Bai, holding a sword one hand and the reins of the horse in the other, fighting for the independence of her motherland.
3. Thus, it becomes clear that visual representations produced various images of the revolt. We should understand that these images were not mere expressions of contemporary ideas and sentiments, but they also reflected contemporary sensibilities.
![]()
Question 25.
How did Mahatma Gandhi want to celebrate 26 January 1930? [3]
Answer:
Gandhiji suggested that the time of the meeting should be advertised in the traditional way, by the beating of drums. The celebrations would begin with the hoisting of the national flag. The rest of the day would be spent “in doing some constructive work, whether it is spinning, or service of ‘untouchables’, or reunion of Hindus and Mussalmans, or prohibition work, or even all these together, which is not impossible”. Participants would take a pledge affirming that it was “the inalienable right of the Indian people, as of any other people, to have freedom and to enjoy the fruits of their toil”, and that “if any government deprives a people of these rights and oppresses them, the people have a further right to alter it or abolish it.”
Question 26.
Give a brief life sketch of Al-Biruni.
OR
Why travellers who came to India did, sometimes took social inequalities for granted as a natural state of affairs? [3]
Answer:
1. Al-Biruni was born in 973 C.E., in Khwarizm in present-day Uzbekistan.
2. Khwarizm was an important centre of education.
3. Al-Biruni received the best available education over there and was well-versed in many languages including Syrian, Persian, Hebrew and Sanskrit.
4. Although he was not aware of the Greek language, he was completely familiar with the works of Plato and other Greek philosophers.
5. He read their works through their Arabic translations.
6. Mahmud of Ghazni attacked Khwarizm in 101 CE and took back many scholars and poets to his capital.
OR
1. Travellers, who came to India, sometimes took social inequalities like a caste system for granted because they did not consider it unique. For example, Al-Biruni had explained the caste system in India.
2. He did not consider it unique, as such social divisions were prevalent in ancient Persia.
3. He even accepted the Brahmanical description of the caste system.
4. But he did not accept the notion of pollution as social pollution was contrary to the laws of nature.
5. Actually, he tried to explain the caste system in comparison with its parallels in other societies.
6. But he also expressed that all humans are treated equally in Islam and they differ only in their observance piety.
Question 27.
How did the message about the revolt spread?
OR
Briefly discuss about the participation of taluqdars of Awadh in the Revolt of 1857. [3]
Answer:
The message of the revolt spread in the following ways:
1. It has been often noticed that the message of rebellion was carried by ordinary men and women and in places by religious men too.
2. From Meerut, there were reports that a fakir had appeared riding on an elephant and that the sepoys were visiting him frequently.
3. In Lucknow, after the annexation of Awadh, there were many religious leaders and self-styled prophets who preached the destruction of British rule.
4. Local leaders emerged, urging peasants, zamindars and tribals to revolt in some places.
5. Shah Mai mobilised the villagers of pargana Barout in Uttar Pradesh.
6. Gonoo, a tribal cultivator of Singhbhum in Chotanagpur, became a rebel leader of the Koltribals of the region.
OR
The annexation of Awadh displaced not just the Nawab, but it also dispossessed the taluqdars of the region. Before the coming of the British, the taluqdars maintained armed men, built forts, and enjoyed a degree of autonomy.
1. The countryside of Awadh was dotted with the estates and forts of the taluqdars who were now disarmed and their forts destroyed.
2. The first British revenue settlement, known as the Summary Settlement of 1856, was based on the assumption that the taluqdars were interlopers with no permanent stakes in land.
3. The Summary Settlement proceeded to remove the taluqdars, wherever possible.
4. The demand for revenue was doubled. It generated a sense of anger among the taluqdars.
5. The dispossession of the taluqdars meant the breakdown of an entire social order. The ties of loyalty and patronage that had bound the peasant to the taluqdar were disrupted.
Section – C (24 Marks)
Question 28.
Discuss the occupations of the four castes in ancient society.
OR
What kind of treatment was received by the untouchables like the Chandalas? [8]
Answer:
The occupations of the four castes i.e., Brahamanas, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas and Shudras were specified in ancient society:
1. The general duty of the Brahamanas was to teach and study Vedas. They used to perform the sacrifices and received gifts from the King.
2. The primary duty of the Kshatriyas was to engage in warfare, give justice to the common people. They used to get the sacrifice performed and make gifts to Brahamanas and other religious institutions.
3. Vaishyas were generally engaged in trading activities, agriculture and worked as pastoralists.
4. The occupation of the Shudras was to serve the people of the higher three vamas.
OR
The untouchables were ill-treated from the other sections of the society.
1. They were considered as a polluted caste and people did not dine with them.
2. These people used to inhabit the areas on the outskirts of the city and were not allowed to enter the main city during the night.
3. They had to use discarded utensils and wear clothes of the dead and ornaments made of iron.
4. They generally performed lower-level jobs like cremation of the corpses and sanitation work.
5. Some of their classes had to sound a clapper while moving on the streets to be aware of the other people as their shadow was also considered polluted.
![]()
Question 29.
Why do Alvars and Nayanars travel to different parts of the country? What did they use to do during their journey?
OR
Why Buddhism and Jainism were opposed by the Tamil saints? [8]
Answer:
The Alvars and Nayanars generally started their journey from Tamil Nadu and then started travelling all over the country.
1. During their journey, they used to sing hymns in Tamil in the devotion of Lord Vishnu and Shiva.
2. They also identified certain shrines as the abodes of their deities.
3. The places identified by the Alvars and Nayanars as abodes of their deities saw the construction of the temples frequently.
4. The constructed temples developed as the centres of pilgrimage.
5. The poet-saints also used to attract several followers towards them and their style of worship was adopted by many.
OR
There were several reasons due to which Buddhism and Jainism were opposed by Tamil saints. Some reasons are as follows:
1. The composition of the Nayanars suggested hostility between the Nayanars and Buddhism and Jainism.
2. This hostility was due to the competition among different religious groups for royal patronage.
3. The powerful rulers of the Chola dynasty generally supported the Bhakti and Brahmanical traditions.
4. The rulers used to grant lands and resources for the construction of the temples of Vishnu and Shiva.
5. The rulers also wanted to receive the support of these saints to claim that their origin was divine.
Question 30.
Discuss the special sets of demands that the linguistic minorities, religious minorities and the Dalits put forward in front of the Constituent Assembly.
OR
What was the contribution of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar in the formation of the Constitution of India? [8]
Answer:
There were separate demands from the Constituent Assembly from every section of the country.
1. The linguistic minorities wanted the protection of their mother tongue.
2. The religious minorities wanted the right to freely follow their religion without any interference in their faith.
3. The Dalit’s demanded an end to the discriminatory system of caste-based oppression.
4. The demands for social and cultural rights were raised in almost every section of the country.
5. There was a demand for equal political rights from every section such as the Universal Adult Franchise.
OR
The contribution of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar in the formation of the Constitution of India is comparable to none.
1. B.R. Ambedkar was a prominent lawyer and economist due to which he was the perfect match for the Constituent Assembly.
2. He was appointed the Law Minister of the country and served as the Chairman of the Drafting Committee of the Constitution.
3. His role was significant in safeguarding the rights of the Dalits and other minorities.
4. He analysed the Constitution of India on every adequate parameter of law so that it was free from anomalies.
5. He suggested a strong Central Government to maintain the national unity of the country.
Section – D (12 Marks)
Question 31.
Read the following source carefully and answer the questions that follow: [4]
There were several pre-existing traditions of thought, religious belief and practice, including the early Vedic tradition, known from the Rigveda, compiled between c.1500 and 1000 BCE. The Rigveda consists of hymns in praise of a variety of deities, especially Agni, Indra and Soma. Many of these hymns were chanted when sacrifices were performed, where people prayed for cattle, sons, good health, long life, etc. At first, sacrifices were performed collectively. Later (c. 1000 BCE-500 BCE onwards) some were performed by the heads of households for the wellbeing of the domestic unit. More elaborate sacrifices, such as the rajasuya and ashvamedha, were performed by chiefs and kings who depended on Brahmana priests to conduct the ritual.
(i) What is the significance of Rigveda?
Answer:
Rigveda is the oldest veda that consist of hymns written in the praise of a variety of deities. The major deities are Agni, Indra and Soma.
(ii) On what occasions the hymns were chanted?
Answer:
The major chanting of the hymns took place during the performance of the sacrifices in which the people prayed for cattle, sons, good health and long life.
(iii) What is meant by elaborate sacrifices?
Answer:
The sacrifices that were performed by the chiefs and kings had to be conducted under the supervision of the Brahmanas and were known as elaborate sacrifices. Some of examples of these types of sacrifices are rajasuya and Ashvamedha.
![]()
Question 32.
Read the following source carefully and answer the questions that follow: [4]
A Sprawling City
This is an excerpt from Domingo Paes’s description of Vijayanagara:
The size of this city I do not write here, because it cannot all be seen from any one spot, but I climbed a hill whence I could see a great part of it; I could not see it all because it lies between several ranges of hills. What I saw from thence seemed to me as large as Rome, and very beautiful to the sight; there are many groves of trees within it, in the gardens of the houses, and many conduits of water which flow into the midst of it, and in places there are lakes; and the king has close to his palace a palm-grove and other rich fruit-bearing trees.
(i) Which city is called a sprawling city?
Answer:
Vijayanagara.
(ii) How is the size of the city described here?
Answer:
The city is very big because it cannot be seen from any one spot, but Paes used to climb a hill to see a great part of it. Then also, he could not see it all because it lies between several ranges of hills.
(iii) How is the beauty of the city described in the extract?
Answer:
The city is very beautiful to the sight, there were many groves of trees within it. In the gardens of the houses conduits of water flow into the midst of it. In places, there were lakes and the king had a palm- grove and other rich fruit-bearing trees fat his place.
Question 33.
Read the following source carefully and answer the questions that follow: [4]
When the estates of the zamindars were auctioned for failure to make revenue payments, jotedars were often amongst the purchasers. The jotedars were the most powerful in North Bengal, although rich peasants and village headmen were emerging as commanding figure in the countryside in other parts of Bengal as well. In some places they were called haoladars, elsewhere they were known as gantidars or mandals. Their rise inevitably weakened zamindari authority.
(i) Why the estates of the zamindars were often auctioned?
Answer:
The estates of the zamindars were often auctioned as they failed to pay the revenue to the government. Due to this, the British officia organised the auction of the estates of the zamindars.
(ii) Whose rise weakened the authority of the zamindars?
Answer:
The rise of the different classes of the people, such as the jotedars who were rich peasants, village headmen, haoladars and mandals, weakened the authority and the powers of the zamindars. These people influence the politics in the villages.
(iii) How did the jotedars assert their control over the estates of the zamindars?
Answer:
The land put to auction by the government due to the default in the payments was purchased by the jotedars. This way, the control of the jotedars over the administration of the villages got stronger.
Section – E (5 Marks)
Question 34.
1. On the given political map of India, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols: [3]
I. Ajanta – A Major Buddhist Site
II. Lucknow – A Main Centre of the Revolt of 1857
III. Kabul – A Territory Under the Control of Mughals
OR
Puhar – An Important Town during Chola Period
2. On the same outline map, two places have been marked as ‘A’ and ‘B’, as the Centres of the National Movements. Identify them and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them.[2]
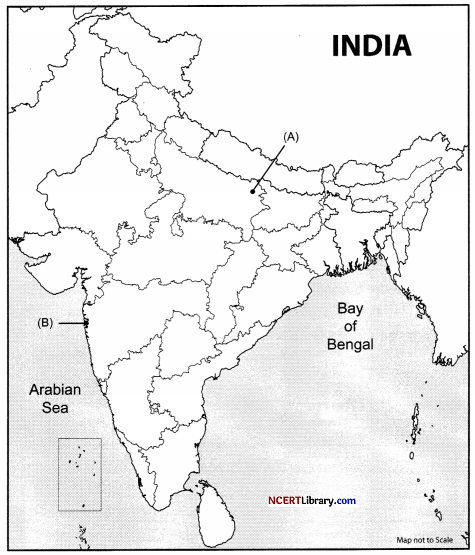
Answer:
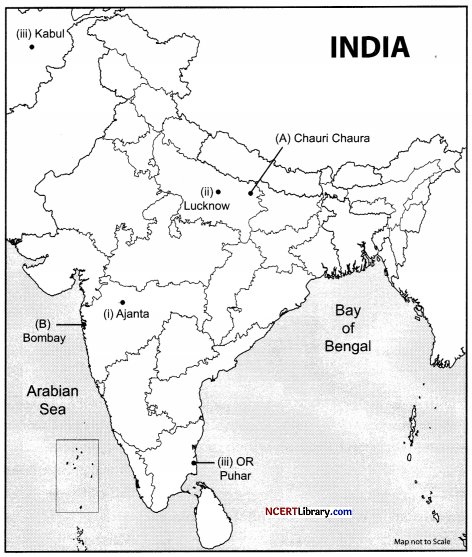
![]()