Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions Set 6 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Set 6 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 70
General Instructions:
- Question paper is divided into 4 sections A, B, C & D
- In section A question number 1 to 17 are MCQ-type questions.
- In section B question number 18-23 are SA-type questions (80-100 words). Question 18 & 19 are Source based questions.
- In section C question number 24 to 28 are Long Answer based questions (120-150 words).
- In section D question number 29 & 30 are Map based questions having 5 sub parts.
Section – A (17 Marks)
Question 1.
Which of the following is correct matched? [1]
| Ports | Types of cargo handled |
| a. Oil port | Warships and repair workshops |
| b. Naval Port | Processing and shipping of oil |
| c. Port of Call | Commercial ports |
| d. Packet Station | Ferry port |
Ans.
| d. Packet Station | Ferry port |
Question 2.
In which year among the following, General Agreement for Tariffs and Trade was transformed into the World Trade Organization? [1]
(a) 1st January 1990
(b) 1st January 1985
(c) 1st January 1995
(d) 2nd January 1995
Ans.
(c) 1st January 1995
Question 3.
Arrange the following activities in a logical sequence. [1]
(i) Do a simple processing of the collected plants and parts.
(ii) Gatherers collect valuable plants or various parts of plants.
(iii) Sell the products in the market.
(iv) Do sorting of collected items.
Choose the correct option:
(a) (iv), (ii), (i), (iii)
(b) (i), (iv), (iii), (ii)
(c) (ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
(d) (ii), (iv), (i), (iii)
Ans.
(d) (ii), (iv), (i), (iii)
![]()
Question 4.
When developing countries lag behind developed countries in providing ICT access and benefits to their citizens, it is known as _______. [1]
(a) technological lag
(b) developmental divide
(c) progress lacuna
(d) digital divide
Ans.
(d) digital divide
Question 5.
Which among the following is not major factor of population flow from rural to urban areas? [1]
(a) Higher demand of labour in urban areas.
(b) Low job opportunities in rural areas.
(c) Unbalanced pattern of development between urban and rural areas.
(d) Higher education in urban areas.
Ans.
(d) Higher education in urban areas
Question 6.
In which type of societies is the physical environment looked upon as ‘Mother Nature’? [1]
(a) Traditional societies
(b) Primitive societies
(c) Developing societies
(d) Rural societies
Ans.
(b) Primitive societies
Question 7.
Which of the following columns is not matched correctly? [1]
| Pollution | Pollutants Involved |
| a. Air | Oxides of Sulphur |
| b. Land | Nitrates and Nitrites |
| c. Water | Sulphates and Sulphides |
| d. Noiseÿ | Noise above tolerance levels |
Ans.
| b. Land | Nitrates and Nitrites |
Question 8.
Which of the following states has a very high percentage of rural population? [1]
(a) Bihar and Sikkim
(b) Goa and Maharashtra
(c) Karnataka and Kerala
(d) Tamil Nadu and Andhra
Ans.
(a) Bihar and Sikkim
Question 9.
The urban transport system in Kolkata and Delhi is revolutionised by: [1]
(a) Metro Rail
(b) National Highways
(c) District Road
(d) CNG Buses
Ans.
(a) Metro Rail
Question 10.
Which of the following is NOT true about Marmagao Port? [1]
(a) It is an artificial harbour in Goa.
(b) Construction of Konkan railway has considerably extended the hinterland of this port.
(c) Karnataka, Goa, Southern Maharashtra constitute its hinterland.
(d) It gained significance after its remodelling in 1961 to handle iron-ore exports to Japan.
Ans.
(a) It is an artificial harbour in Goa.
Question 11.
What is the full form of SFDA? [1]
(a) Small Farmers Development Area
(b) Small Farmers Development Administration
(c) Small Farmers Development Authority
(d) Small Farmers Development Agency
Ans.
(d) Small Farmers Development Agency
Question 12.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct option from them: [1]
I. The use of transport and communication depends upon our need to move things from place of their availability to the place of their use.
II. Human beings use various methods to move goods, commodities, ideas from one place to another.
Options:
(a) Only statement I is correct
(b) Both I and II are correct
(c) Only II is correct
(d) Both are incorrect
Ans.
(b) Both I and II are correct
![]()
Question 13.
Assertion (A): Human beings do not depend on nature as they have introduced technology.
Reason (R): There is direct dependence of human beings on nature for resources which sustain them. [1]
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Ans.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question 14.
Assertion (A): Noise pollution refers to the state of unbearable and uncomfortable to human beings which is caused by noise from different sources.
Reason (R): This matter has become a serious concern only in recent years due to a variety of technological innovations. [1]
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Ans.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Read the passage carefully and answer any three of the following questions:
In ancient times, transporting goods over long distances was risky, hence trade was restricted to local markets. People then spent most of their resources on basic necessities- food and clothes. Only the rich people bought jeweler, costly dresses and this resulted in trade of luxury items. The Silk Route is an early example of long-distance trade connecting Rome to China- along the 6,000 km route.
The traders transported Chinese silk, Roman wool and precious metals and many other high-value commodities from intermediate points in India, Persia and Central Asia. After the disintegration of the Roman Empire, European commerce grew during twelfth and thirteenth century with the development of ocean-going warships trade between Europe and Asia grew and the Americas were discovered.
Fifteenth-century onwards, the European colonialism began and along with trade of exotic commodities, a new form of trade emerged which was called slave trade. The Portuguese, Dutch, Spaniards, and British captured African natives and forcefully transported them to the newly discovered Americas for their labour in the plantations.
Slave trade was a lucrative business for more than two hundred years till it was abolished in Denmark in 1792, Great Britain in 1807 and United States in 1808.
Question 15.
In early times the biggest challenge for international trade was _______. [1]
(a) Safety for long travel
(b) Local consumption of commodities
(c) Money in the hand of few people
(d) All of the above
Ans.
(a) Safety for long travel
Question 16.
Which of the present-day country does not fall on old silk route? [1]
(a) Iran
(b) India
(c) Greece
(d) Ethiopia
Ans.
(d) Ethiopia
Question 17.
The demand for trade slave was very high in _______. [1]
(a) Africa
(b) Europe
(c) South Asia
(d) Latin America
Ans.
(b) Europe
Section – B (18 Marks)
Question 18.
Read the passage carefully and answer the following questions:
The population growth or population change refers to the change in number of inhabitants of a territory during a specific period of time. This change may be positive as well as negative. It can be expressed either in terms of absolute numbers or in terms of percentage. Population change in an area is an important indicator of economic development, social upliftment and historical and cultural background of the region.
(i) Define population growth.
Answer:
The population growth or population change refers to the change in number of inhabitants of a territory during a specific period of time.
(ii) Give one characteristic of population change.
Answer:
This change may be positive as well as negative.
(iii) What is the importance of population growth?
Answer:
Population change in an area is an important indicator of economic development, social upliftment and historical and cultural background of the region.
Question 19.
Study the picture given below and answer the following questions:
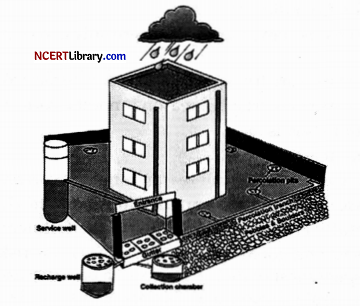
(i) Identify the conservational method depicted in the diagram.
Answer:
Rainwater Harvesting.
(ii) What do the cloud and water droplets represent in the diagram?
Answer:
It represents rainfall, which is being collected and stored for future use.
(iii) Describe the method depicted in the diagram.
Answer:
Rainwater harvesting is a method to collect and store rainwater for various uses. It is a low-cost and eco-friendly technique for preserving every precious drop of water by guiding the rainwater to bore well, pits, and wells.
Question 20.
In what ways, developed network of transportation and communication help international trade?
OR
Write three points on how can international trade be detrimental for countries.
Answer:
1. Developed transportation and communication network takes lesser time and makes the international trade feasible.
2. Better transportation network reduces the cost.
3. Transport and communication network open the new areas and markets for the countries to invest.
OR
International trade can prove to be detrimental to nations in the following ways:
1. It leads to dependence of less developed countries on other more developed countries.
2. Resource get used faster than they can be replenished because composition to trade more, i.e., production rise up.
3. Global trade also results in uneven development level in countries. Critics believe it creates situation where rich countries go richer and poor countries go poorer.
![]()
Question 21.
What do you mean by urban agglomeration?
Answer:
An urban agglomeration may consist of any one of the following three combinations:
1. A town and its adjoining urban outgrowths.
2. Two or more contiguous towns with or without their outgrowths.
3. A city and one or more adjoining towns form a contiguous spread with their outgrowths.
Question 22.
Describe how international trade has changed over the years in India?
OR
Give two important characteristics of India’s marine ports. Name any two states which have two major ports.
Answer:
Indian international trade has changed over the years are as follows:
1. Agriculture and related items have lost their market share, whereas petroleum and crude products and other commodities have gained market dominance.
2. Over the years 2009-10 to 2010-11 and 2015-16 to 2016-17, the proportions of ore minerals and manufactured products have remained constant.
3. Traditional agricultural goods, such as coffee, cashew, and so on, are seeing a decrease in exports. In contrast, floricultural products, fresh fruits, marine products, and sugar, among other things, have experienced an increase.
OR
1. India’s 95% of trading by volume is done through maritime transport it stands of 70% by value.
2. India has a total of 12 major ports. These are India’s import and export entry points. These act as collecting points for goods destined for export as well as those destined for distribution in India.
3. Kolkata and Haldia are the two major ports in West Bengal. Chennai and Tuticorin are the two largest ports in Tamil Nadu.
Question 23.
Describe any three advantages of community participation under Common Property Resources.
Answer:
Three advantages of community participation under Common Property Resources are as follows:
1. Large-scale practice of sustainability in agriculture and allied sectors.
2. Encouragement to cottage and small-scale industries.
3. Growth and development of rural economy.
Section – C (25 Marks)
Question 24.
Discuss Industries based on Inputs or Raw Materials.
Answer:
On the basis of the raw materials used, the industries are classified into these following categories:
Agro-based Industries: These industries uses the raw material obtained from agricultural products, like agro processing industries. Major Agro-processing industries are food processing, sugar, pickles, fruit juices, beverages (tea, coffee and cocoa), spices and oils fats and textiles (cotton, jute, and silk), rubber, etc.
Mineral-based Industries: These industries use minerals as raw material. Some industries use ferrous metallic minerals which contain ferrous (iron), such as iron and steel industries, while others use non-ferrous metallic minerals, such as aluminum, copper and jeweller industries.
Chemical-based Industries: Such industries use natural chemical minerals, e.g. mineral oil (petroleum) is used in petrochemical industry. Salts, sulphur and potash industries also use natural minerals. Chemical industries are also based on raw materials obtained from wood and coal. Synthetic fiber plastic, etc., industries are other examples of chemical-based industries.
Forest-based Raw Material using Industries: The forests provide many major and minor products which are used as raw material. Timber for furniture industry, wood, bamboo and grass for paper industry, lac for cosmetic industries come from forests.
Animal-based Industries: This industry takes its raw material from animals. Leather for leather industry and wool for woolen textiles are obtained from animals. Besides, ivory is also obtained from elephant’s tusks.
Question 25.
Explain any three aims of Human Geography.
OR
What do you mean by Dualism in Geography?
Answer:
Human Geography aims at studying the human and natural resources of a region, so that these resources can be used for the progress and welfare of the people. It also looks into the effects of the environment on human groups. Human Geography aims to study the interactive relationship between man, environment and economic activities.
It examines human civilisation and how they evolved their society, culture, politics, economy, etc., within the context of their environment. It performs the study of human race; their development, growth and density of population of the various part of the world, their demographic attributes and migration pattern and physical and cultural difference between human groups.
OR
The focus of Geography is on the study of nature and human beings. Geography is subjected to dualism and the wide-ranging debates started whether geography as a discipline should be law-making (nomothetic) or descriptive (idiographic). There is a wide-ranged debate whether geography should be studied with a regional or systematic approach.
This is called dualism. It means whether geographical phenomena should be interpreted theoretically or through a historic institutional approach. There does exist a dichotomy between physical and human geography.
Question 26.
“Human progress is not directly proportional to the size of a territory or per capita income.” Give instances to back up your assertion.
OR
What is the definition of human development? Examine the four pillars of development.
Answer:
“Human progress is not directly proportional to the size of a territory or per capita income.” The following instances illustrate this assertion:
Human progress is not purely composite indicator of economic. Economic factors do not provide idea of human capital formation (education, training, health condition), gender equality and condition of human rights. Many minor countries and areas have progressed significantly in comparison to larger countries.
Gross national product and per capita income are commonly used to measure economic growth and productivity. Certain comparatively impoverished nations have been ranked higher than many other countries in terms of the human development index. Poverty is reflected in a low standard of living. Hundreds of thousands of people are malnourished, deprived, illiterate, and have a low degree of human development. It is irrespective of the size of the territory.
Within India, Kerala performs much better that Punjab and Gujarat in human development index, despite having a lower per capita income. Despite having lower GDP, Bhutan, Sri Lanka perform better in human development index as compared to India according to the HDI report 2021.
OR
Human development is described as the sort of progress that broadens people’s choices and enhances their lives.
Equity, sustainability, productivity, and empowerment are four ideas in human development. These ideas are known as pillars of human development and are based on human development.
Equity: It refers to a person’s access to equal chances. There is no discrimination on the basis of gender, colour, income, or caste for the available opportunities. A good life is feasible if resources are made available based on the fact that all individuals are equal.
Sustainability: It refers to the availability of possibilities in a constant manner. Human growth is feasible when a country’s present and future generations are given opportunities. It must be ensured that equal access to a resource should be available to the next generation.
Productivity: Human labour productivity, often known as productivity in the context of human work, refers to human development productivity. A country should invest in its productive workforce by improving healthcare, education, and training opportunities. People who are healthy and educated can contribute more to the progress of a country than those who are unhealthy and uneducated.
Empowerment: It refers to the ability to make decisions. The power and capacity to make a decision can be enhanced through freedom and capabilities. Through excellent administration and people-centered policies, the government may increase empowerment.
Question 27.
Write the distribution of Iron Ore in India.
Answer:
India is endowed with fairly abundant resources of iron ore. It has the largest reserve of iron ore in Asia.
1. The two main types of ore found in our country are hematite and magnetite.
2. The total production of iron ore in Indian was around 200 million metric tons in the year 2020.
3. About 95 percent of total reserves of iron ore is located in the States of Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Karnataka, Goa, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
4. In Odisha, iron ore occurs in a series of hill ranges in Sundergarh, Mayurbhanj and Jhar.
5. Similarly hill ranges of Jharkhand have some of the oldest iron ore mines and most of the iron and steel plants are located around them. Other iron ore mines are Noamundi and Guaare located in Poorbi and Pashchimi Singhbhum districts. This belt further extends to Durg, Dantewara and Bailadila. Dalli, and Rajhara in Durg are the important mines of iron ore in the country.
6. In Karnataka, iron ore deposits occur in Sandur-Hospet area of Ballari district, Baba Budan hills and Kudremukh in Chikkamagaluru district and parts of Shivamogga, Chitradurga and Tumakuru districts.
7. The districts of Chandrapur, Bhandara and Ratnagiri in Maharashtra, Karimnagar and Warangal district of Telangana, Kurnool, Cuddapah and Anantapur districts of Andhra Pradesh, Salem and Nilgiris districts of Tamil Nadu are other iron mining regions. Goa has also emerged as an important producer of iron ore.
Question 28.
“Indian ports continued to flourish after independence, despite the setback inflicted by partition.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer:
India has a long history of seaport-based international trade. Following the arrival of European traders and the British colonial rule in of India, these ports became global trade hubs. Local markets were linked to regional markets, regional markets to national markets, and national markets to international markets through seaports. This procedure was carried on until the country gained independence.
However, India suffered a significant setback when the country’s division resulted in the loss of Karachi and Chittagong ports. Karachi port served Pakistan, whereas Chittagong port served East Pakistan (now Bangladesh). Many additional ports were built to compensate for the loss. For example, on the river Hugli, Kandala in the west and Diamond Harbour in the east near Kolkata.
India was able to rebound from this setback and continue to expand its ports. These Indian ports now handle a substantial volume of local as well as international trade. In most Indian ports, modem infrastructure amenities are present. Many private enterprises have been asked to participate in the modernisation of the country’s ports.
Indian ports’ cargo handling capacity has grown from 20 million tonnes in 1951 to over 586 million tonnes in 2008-09. There are now 12 major ports and 200 smaller or intermediate ports operating in India. Major ports handle a bigger portion of overall traffic.
![]()
Section – D (10 Marks)
Question 29.
On the given political map of the world, the following seven features are shown. Identify any five of these features and write their correct names on the lines marked near each feature.
A. Identify the country with most population in the Asian continent.
B. Identify the region is famous for its copper belt in Africa.
C. One of the important country where commercial livestock rearing is practices.
D. Countries that has the highest sex ratio in the world?
E. The country which has highest Human Development Report in 2020.
F. Which one of the following is a thickly populated region in Japan?
G. Identify the country that use Gross National Happiness.
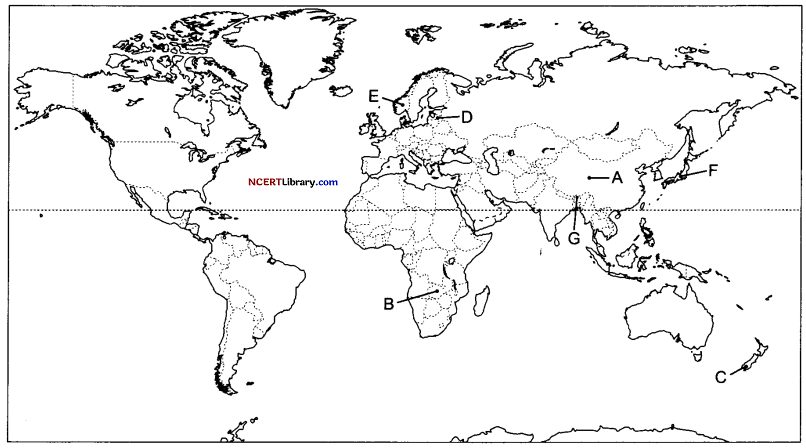
Answer:
A. China
B. Katanga Zambia
C. New Zealand
D. Latvia
E. Norway
F. Kobe—Osaka
G. Bhutan
Question 30.
On the given political map of India, locate and label any five of the following with appropriate symbols:
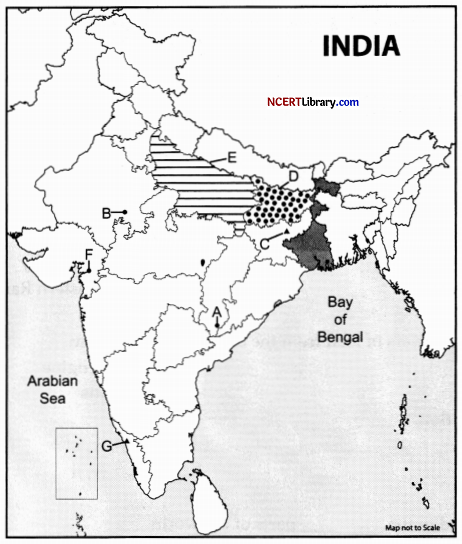
A. Iron mine in Chhattishgarh.
B. Nuclear power plant in Rajasthan.
C. Coal mine in Jharkand.
D. Identify states that has the lowest female literacy rate.
E. Identify the state that has highest density of population.
F. Identify the mining town in Gujarat.
G. Identify the important transport city in Kerala.
Answer:
A. Bailadila
B. Rawatbhata
C. Bokaro
D. Bihar
E. Uttar Pradesh
F. Ankleshwar
G. Kozhikode