Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions Set 5 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Set 5 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 70
General Instructions:
- Question paper is divided into 4 sections A, B, C & D
- In section A question number 1 to 17 are MCQ-type questions.
- In section B question number 18-23 are SA-type questions (80-100 words). Question 18 & 19 are Source based questions.
- In section C question number 24 to 28 are Long Answer based questions (120-150 words).
- In section D question number 29 & 30 are Map based questions having 5 sub-parts.
Section – A (17 Marks)
Question 1.
Assured and speedy transportation, along with efficient communication, promote_______. [1]
(a) cooperation and unity among scattered people
(b) unity among scattered people in urban areas
(c) cooperation among scattered people in rural areas
(d) socialisation among scattered people
Answer:
(a) cooperation and unity among scattered people
Question 2.
Basis of International Trade can be categorized into: [1]
(a) Difference in national resources, National boundary, Stage of economic development
(b) Difference in national resources, Population factors, National boundary
(c) National boundary, Population factors, Stage of economic development
(d) Difference in national resources, Population factors, Stage of economic development
Answer:
(d) Difference in national resources, Population factors, Stage of economic development
Question 3.
Intensive subsistence agriculture is largely found in_______regions of monsoon Asia. [1]
(a) sparsely populated
(b) thinly populated
(c) densely populated
(d) unevenly populated
Answer:
(c) densely populated
![]()
Question 4.
Arrange the steps followed in ‘slash and bum agriculture’. [1]
(i) The farmers move to a new patch of land and clear it by slashing and burning.
(ii) Vegetation is cut, cleared and set on fire.
(iii)Ashes add to soil fertility and the cleared patch of land is cultivated.
(iv)After harvesting the crop for a few years, the field is abandoned.
Choose the correct option:
(a) (iii), (i), (iv), (ii)
(b) (ii), (iv), (iii), (i)
(c) (ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
(d) (ii), (i), (iv), (iii)
Answer:
(c) (ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
Question 5.
Which of the following is not an approach in human geography? [1]
(a) Exploration and description
(b) Areal differentiation
(c) Spatial organisation
(d) Quantitative revolution
Answer:
(d) Quantitative revolution
Question 6.
Which of the following is a person who works for at least 183 days (or six months) in a year? [1]
(a) Cultivator
(b) Agricultural labourer
(c) Marginal worker
(d) Main worker
Answer:
(d) Main worker
Question 7.
Which one of the following is not a type of wasteland? [1]
(a) Gullies
(b) Barren rocky areas
(c) Marshy areas
(d) Oceans
Answer:
(d) Oceans
Question 8.
Which one of the following pairs is not matched correctly regarding land degradation? [1]
| Activities | Agents of degradation |
| (a) Glaciers | Natural Agent |
| (b) Industrial Wastelands | Human Agents |
| (c) Land with scrub | Both natural and human Agents |
| (d) Degraded forests | Natural Agents |
Answer:
| (d) Degraded forests | Natural Agents |
Question 9.
Which one of the following is not included in Bharatmala, which is a proposed umbrella scheme for the development of roads and highways? [1]
(a) State Roads
(b) Backward areas, religious and tourist places
(c) Longest road of the world
(d) District headquarter connectivity
Answer:
(c) Longest road of the world
Question 10.
Which of the following is correctly matched? [1]
| Port | Location |
| (a) Kandla port | Gulf of Kuchchh |
| (b) Jawarharlal Nehru port | Goa |
| (c) Marmagao Port | Karnataka |
| (d) Ennore | Kerala |
Answer:
| (a) Kandla port | Gulf of Kuchchh |
Question 11.
Which objective of watershed management given below is correct?
I. To create a balance among natural elements as well as in society.
II. To enable the villagers to conserve water for various uses such as drinking, irrigation, fisheries and afforestation. [1]
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) Both I and II
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Both I and II
Question 12.
Which one of the following is a source of noise pollution at harbour? [1]
(a) Loading and unloading activities being carried at harbour
(b) Noise of aircraft etc., passing over harbour
(c) Heavy traffic at harbour
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
![]()
Question 13.
Assertion (A): The beginning of human geography did not start with the interaction of environment and human beings.
Reason (R): The concerns of human geography have a long temporal though the approaches to articulate them have changed over time. [1]
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Answer:
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question 14.
Assertion (A): Water transport is the cheapest means of transport.
Reason (R): It is a fuel efficient and eco-friendly mode of transport. [1]
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Read the following case study and answer questions no 15 to 17.
Read the passage and answer any three of the questions that follow:
Communication
Human beings have used different methods of long-distance communication of which the telegraph and the telephone were important. The telegraph was instrumental in the colonization of the American West. During early and mid-twentieth century, the American Telegraph and Telephone Company (AT & T) enjoyed a monopoly over USA’s telephone industry. In fact, the telephone became a critical factor in the urbanization of America Firms centralized their functioning at city headquarters and located their branch offices in smaller towns.
Even today, the telephone is the most commonly used mode. In developing countries, the use of cell phones, made possible by satellites, is important for rural connectivity. Today, there is a phenomenal pace of development. The first major breakthrough is the use of optic fiber cables (OFC). Faced with mounting competition, telephone companies all over the world soon upgraded their copper cable systems to include optic fiber cables. These allow large quantities data transmitted rapidly, and securely and virtually error-free. With digitization of information in the 1990s, telecommunication slowly merged with computers to form integrated networks termed as Internet.
Question 15.
During which century did the American Telegraph and Telephone Company (AT & T) enjoy a monopoly over USA’s telephone industry? [1]
(a) During the mid-nineteenth century
(b) During the early and mid-twentieth century
(c) During the early nineteenth century
(d) During the late twentieth century
Answer:
(b) During the early and mid-twentieth century
Question 16.
Which scientific technology has tremendously improved rural connectivity in developing countries? [1]
(a) Telephone
(b) Telegraph and telephone
(c) The use of cell phones, made possible by satellites
(d) The use of Speed post and telegraph
Answer:
(c) The use of cell phones, made possible by satellites
Question 17.
What is the major breakthrough and up gradation adopted in the telephone companies across the world? [1]
(a) Underground cabling
(b) Change to copper cable systems
(c) A blend of copper cables and OFC
(d) The use of optic fiber cables (OFC)
Answer:
(d) The use of optic fiber cables (OFC)
Section – B (18 Marks)
Question 18.
Read the information given below and answer the following questions:. [3]
Case Study: A Role Model to Restore the Ecology and Safeguard. Human Health in Daurala Based on the universal law ‘Polluter pays’, effort to restore the ecology and safeguard the human health with people’s participation has taken place in Daurala near Meerut. These efforts are now bearing fruits after a span of three years when Meerut-based NGO had developed a model for ecological restoration. The meeting of the Daurala Industries officials, NGOs, Government officials and other stakeholders at Meerut has brought out results. The powerful logics, authentic studies and the pressure of people have brought a new lease of life to the twelve thousand residents of this village.
It was in the year 2003 that pitiable condition of Dauralaites drew the attention of the civil society. The groundwater of this village was contaminated with heavy metals. The reason was that the untreated wastewater of Daurala industries was leaching to the groundwater table. The NGO conducted a door-to-door survey of the health status of the residents and came out with a report. The organisation, the village community and people’s representatives sat together to find out sustainable solutions to the health problem.
The industrialists showed a keen interest towards checking the deteriorating ecology. The overhead water tank’s capacity in the village was enhanced and a 900m extra pipeline was laid to supply potable water to the community. The silted pond of the village was cleaned and recharged by desilting it. Large quantity of silt was removed paving way to large quantity of water so that it recharged the aquifers. Rainwater harvesting structures have been constructed at different places which has helped in diluting the contaminants of the groundwater after the monsoons. 1000 trees have also been planted which have improved the environment.
(i) What is main reason for contaminated groundwater in Daurala?
Answer:
Daurala’s groundwater contaminated due to untreated wastewater discharge from industries, which was leaching to the groundwater table.
(ii) How the water problem of Daurala’s community got sorted?
Answer:
Water problem of Daurala’s community get sorted by providing 900m extra pipeline to supply potable water to the community. The silted pond of the village was cleaned and recharged by desilting it.
(iii) What steps were taken to improve the condition of Daurala?
Answer:
1. Planted 1000 trees to improve the environment.
2. Rainwater harvesting structure have been constructed at different places.
3. Large quantity of silt was removed, that helped in recharging the aquifiers.
Question 19.
Study the picture given below answer the questions that follow:. [3]

(i) Identify the crop in the picture given above.
Answer:
Sugarcane
(ii) Name the state in north India where this crop is grown.
Answer:
Uttar Pradesh
(iii) Name two states in western India which produce this crop.
Answer:
Gujarat and Maharashtra
Question 20.
What is Cyberspace? Describe any two advantages of internet.
OR
Explain three functions of WTO.. [3]
Answer:
Cyberspace is the electronic digital world for communicating information over computer networks without physical movement of the sender and the receiver.
Advantages of internet are:
1. Cyberspace has expanded the contemporary economic and social space of humans through e-mail, e-commerce, e-leaming and e-govemance.
2. Internet, together with fax, television and radio, will be accessible to more and more people across different place.
OR
1. WTO is the only international organisation dealing with the global rules of trade between nations.
2. It sets the rules for the global trading system and resolves disputes between its member nations.
3. WTO also covers trade in services, such as telecommunication and banking, and others issues such as intellectual rights.
Question 21.
Explain with examples three economic factors influencing the population distribution in the world.. [3]
Answer:
Three economic factors that influence the population distribution in the world are:
1. Minerals: Areas with mineral deposits attract industries and generate employment. Skilled and semi-skilled workers move to these areas and make them densely populated. Example; Katanga Zambia copper belt in Africa.
2. Urbanisation: Cities offer better employment opportunities, educational and medical facilities, better means of transport and communication. The availability of civic amenities and attraction of urban life draws people to cities. It leads to rural urban migration. Example; Mega cities, metropolitan cities of the world.
3. Industrialisation: This provides job opportunities and attract large numbers of people. Provide different types of jobs to different categories of people, for example semi-skilled labour, and literate and illiterate people. Example; Kobe-Osaka region of Japan.
![]()
Question 22.
Explain the main features of rural settlements. [3]
Answer:
Features of rural settlements are:
1. Rural settlements are most closely and directly related to land.
2. Agriculture, animal husbandry, fishing and other primary activities dominate them.
3. These settlements are small in size, with a slow rate of growth and expansion.
Question 23.
“The Golden Quadrilateral is a milestone endeavor of the National Highway Development Project”. Elaborate.
OR
State the three main advantages of waterways. [3]
Answer:
The Golden Quadrilateral is one of the major projects taken up by the NHAI in country, under different phases. The Golden Quadrilateral comprises of a construction of 4/6 lane, high density traffic corridor, which is 5,846 km long, connecting India’s big four metropolises- Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata. With its construction, the time, distance and cost of movement among these megacities will be reduced considerably. Therefore, it is a milestone endeavour of the National Highway Development Project (NHDP).
OR
The three main advantages of waterways are as follows:
1. It is an important mode of transport for both, passengers as well as cargo traffic in India.
2. It is the cheapest means of transport and the most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky material.
3. It is a fuel-efficient and eco-friendly mode of transport.
Section – C (25 Marks)
Question 24.
Describe the main features and development of commercial grazing in different types of grasslands. [5]
Answer:
Commercial livestock rearing is more organized and capital-intensive. Commercial livestock ranching is essentially associated with western cultures and is practiced on permanent ranches. These ranches cover large areas and are divided into a number of parcels, which are fenced to regulate over-grazing. When the grass of one parcel is removed due to grazing, animals are moved to another parcel. The number of animals in a pasture is kept according to the carrying capacity of the pasture.
This is a specialized activity in which only one type of animal is reared Important animals include sheep, cattle, goats, and horses. Products such as meat, wool, hides and skin are processed and packed scientifically and exported to different world markets. The rearing of animals in ranching is organized on a scientific basis. The main emphasis is on breeding, genetic improvement, disease control, and healthcare of the animals. New Zealand, Australia, Argentina, Uruguay and United States of America are important countries where commercial livestock rearing is practiced.
Question 25.
Define ‘Human Geography’ in your own words. Mention any four fields of Human Geography.
OR
Support the statement “Nature is extremely important to develop technology”. [5]
Answer:
According to Ratzel, “Human Geography is the synthetic study of the relationship between human societies and earth’s surface”. Human geography defines the impact and behavior of people and their implications in the physical world It includes religion, language, and government of people that vary across the world It also discusses the standards of living and quality of life across the world It shows the inter-relationship between the physical environment and socio-cultural environment created by human beings through mutual interaction with each other. The different fields of human geography are as follows:
1. Social Geography: It is a field of human geography that is associated with social sciences and sociology. Its sub-fields are behavioral geography, the geography of social well-being, historical, medical geography, etc.
2. Urban Geography: It is a field of human geography associated with urban studies and planning.
3. Political Geography: It is a field of human geography associated with science. Its sub-fields are electoral geography, military geography, etc.
4. Population Geography: It is a field of human geography associated with demography.
OR
Technology is being developed by humans for ages and with every passing day, technology keeps getting more developed. But this development depends on nature and natural products including wood, plastic, rubber, paper, etc. Without these products, it is nearly impossible to bring about technological improvement. Technology indicates the level of cultural development of society. Human beings were able to develop technology after they developed a better understanding of natural laws. Humans will be able to bring out technological advancement only when they understand nature and natural laws.
Question 26.
Describe in brief the different trends of population growth in the world from an early period to the present day.
OR
Explain the three components of population change in the world Analyse the impacts of population change. [5]
Answer:
The trends in population growth are as follows:
- In the early periods of history, i.e., 8000 to 12000 years ago, the population grew at a slow rate. The population of the era was 8 million.
- The count of population in the first century was below 300 million.
- By 1600 AD, the world population increased to 0.5 billion, as expansion in trade and the industrial revolution increased settlements.
- World population touched 1 billion in 1830 due to advancement in the field of science and technology.
- In the next 100 years, i.e., in 1930, the population doubled to 2 billion due to improved medical, healthcare and sanitation facilities.
- In 1960, the population was 3 billion and in 1975, it was 4 billion. After that one billion was added in every 12 years.
- There is a great variation among regions in doubling their population.
OR
The three components of population change in the world are:
1. Crude Birth Rate: It is referred to as a number of live births in a year per thousand of the population. It leads to increase in population.
2. Crude Death Rate: It is referred to as a number of deaths in a particular year per thousand of the population in a particular region. It leads to decline in population.
3. Migration: It refers to the displacement of people from their place of origin to their place of destination. In-migration increases the population. Out-migration decreases the population.
Impacts of population change are as follows:
1. If the population change results in high population growth, then it puts pressure on the resources leading to their scarcity and other problems.
2. Population change resulting in the decline of the population shows that the available resources are not sufficient to sustain the population.
Question 27.
Mention and discuss the land-use categories as maintained in the Land Revenue records. [5]
Answer:
The land-use categories as maintained in the Land Revenue records are as follows:
1. Forests: It is important to note that area under actual forest cover is different from the area classified as forest. The latter is the area which the Government has identified and demarcated for forest growth. The land revenue records are consistent with the latter definition. Thus, there may be an increase in this category without any increase in the actual forest cover.
2. Barren and Wastelands: The lands which may be classified as a wasteland such as barren hilly terrains, desert lands, ravines, etc., normally cannot be brought under cultivation with the available technology.
3. Land put to Non-agricultural Uses: Land under settlements (rural and urban), infrastructure (roads, canals, etc.), industries, shops, etc., are included in this category. An expansion in secondary and tertiary activities would lead to an increase in this category of land use.
4. Area under Permanent Pastures and Grazing Lands: Most of this type of land is owned by the village ‘Panchayat’ or the Government. Only a small proportion of this land is privately owned The land owned by the village panchayat comes under ‘Common Property Resources.
5. Area under Miscellaneous Tree Crops and Groves (Not included in Net sown Area): The land under orchards and fruit trees included in this category. Much of this land is privately owned.
6. Culturable Wasteland: Any land which left fallow (uncultivated) for more than five years included in this category. It can be brought under cultivation after improving through reclamation practices.
7. Current Fallow: This is the land that is left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year. Following is a cultural practice adopted for giving rest to the land The land recoups the lost fertility through natural processes.
8. Fallow other than Current Fallow: This is also cultivable land that is left uncultivated for more than a year but less than five years. If the land is left uncultivated for more than five years, it would be categorized as a culturable wasteland.
9. Net Sown Area: The physical extent of land on which crops are sown and harvested is known as the net sown area.
Question 28.
How do the physical factors affect the population distribution in India? [5]
Answer:
The physical factors that affect the population distribution in India are:
1. Terrain and Topography: The Great Plains of North India supports higher population density and is home to the largest population concentration in India; land for agriculture, development of transport, industries and other economic activities being largely responsible; mountainous, plateau regions with steep slopes and adverse circumstances discourage population concentration.
2. Climate: Extreme, harsh climate discourages the concentration of population, like the cold climate of the Himalayas or the hot climate of the Thar desert; moderate climate is most favoured; rainfall also determines the population distribution.
3. Soil: An important factor for agricultural countries like India; fertile soil supports larger population, while infertile soil has low population concentration; The Great North Indian Plains, the Coastal Plains and the black soil regions of the Deccan Plateau of India are a few examples.
4. Availability of Water: Water is essential for population concentration; it is required for various purposes like irrigation, industries, transport, and domestic affairs; most of the population in India is concentrated in the river valleys.
5. Mineral Resources: These attract population as an economic resource; the Chhota Nagpur Plateau areas engulfing Jharkhand and Odisha is a major example.
Section – D (10 Marks)
Question 29.
On the given political map of the world, the following seven features are shown. Identify any five of these features and write their correct names on the lines marked near each feature. [5]
A. Busiest port of the world on the mouth of the Yangtze River in China
B. Busiest Airport of Asia
C. A canal that connects the Mediterranean Sea with the Red Sea.
D. An important Iron and steel center in Russia.
E. Nation that has emerged as the leading country of medical tourism in the world.
F. Western terminal of Trans-Canadian Railway.
G. Important industrial region in South Asia.
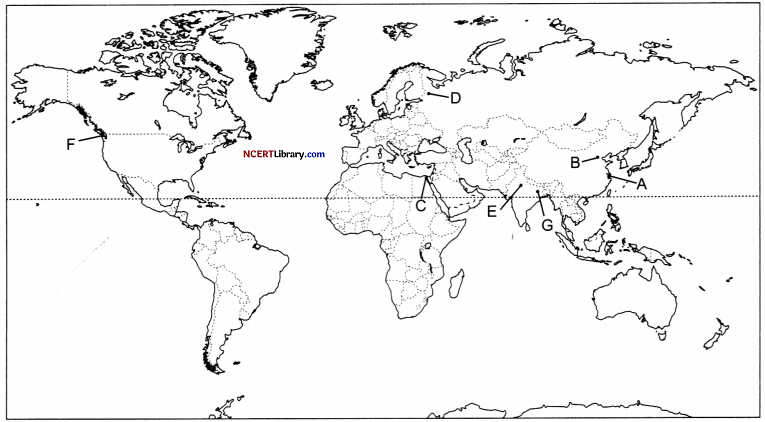
Answer:
A.Shanghai
B. Beijing
C. Suez Canal
D. St. Petersburg
E. India
F. Victoria (Canada)
G. Damodar Valley
![]()
Question 30.
On the given political map of India, locate and label any five of the following with appropriate symbols: [5]
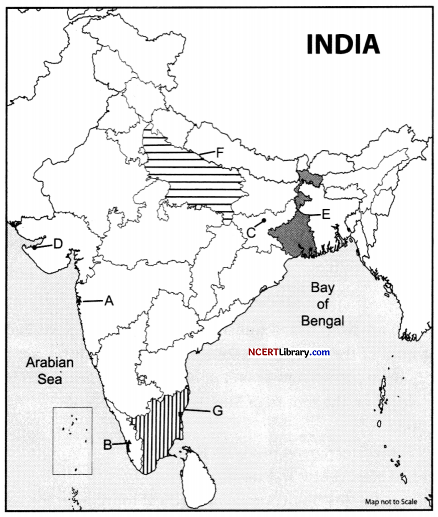
A. Identify the port that handel a large portion of India’s crude oil imports.
B. Natural harbor in the state of Kerala.
C. Coal mine in Jharkhand.
D. Oil refineries Gujarat.
E. The state which is the leading producer of jute in India.
F. The state which is the leading producer of wheat in India.
G. Identify the state has the highest proportion of urban population in India according to the 2011 Census.
Answer:
A. Jawaharlal Nehru port
B. Kochi port
C. Bokaro
D. Jamnagar
E. West Bengal
F. Uttar Pradesh
G. Tamil Nadu