Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions Set 3 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Set 3 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 70
General Instructions:
- Question paper is divided into 4 sections A, B, C & D
- In section A question number 1 to 17 are MCQ-type questions.
- In section B question number 18-23 are SA-type questions (80-100 words). Question 18 & 19 are Source based questions.
- In section C question number 24 to 28 are Long Answer based questions (120-150 words).
- In section D question number 29 & 30 are Map based questions having 5 sub-parts.
Section – A (17 Marks)
Question 1.
The colonial period provided an impetus to further explorations in order to inventory information. and to obtain. [1]
(a) explore new lands
(b) conduct geographical survey
(c) access the resources of the regions
(d) study human societies
Answer:
(c) access the resources of the regions
Question 2.
Which one of the following are the correct pair of Railway Zone and its headquarters? [1]
(a) Central-Mumbai CST
(b) Eastern-Bhubaneswar
(c) East Central-Kolkata
(d) East Coast-Hajipur
Answer:
(a) Central-Mumbai CST
Question 3.
What is the real wealth of a country? [1]
(a) Its climate
(b) people
(c) Its natural resources
(d) Its flora and fauna
Answer:
(b) people
Question 4.
The human development index measures_______. [1]
(a) technological and industrial developments
(b) attainments in human development
(c) poverty and resource distribution
(d) a shortfall in human development
Answer:
(b) attainments in human development
![]()
Question 5.
Arrange the following primary activities starting from the most primitive to the most modem. [1]
(i) Nomadic herding
(ii) Commercial livestock rearing
(iii)Domestication of animals
(iv)Hunting and gathering
Choose the correct option:
(a) (i), (iv), (iii), (ii)
(b) (iv), (iii), (i), (ii)
(c) (ii), (iv), (iii), (i)
(d) (iii), (i), (iv), (ii)
Answer:
(b) (iv), (iii), (i), (ii)
Question 6.
Which of the following pairs is matched correctly regarding iron ore centers and their correct location? [1]
| a. Duisburg | Germany |
| b. Appalachian region | United Kingdom |
| c. Creusot | Le Russia |
| d. Shanghai | Japan |
Answer:
| a. Duisburg | Germany |
Question 7.
Radio club of Bombay, Indian Broadcasting System, and All India Radio are examples of which of the following communication system? [1]
(a) Mass communication
(b) Personal communication
(c) Satellite communication
(d) Television communication
Answer:
(a) Mass communication
Question 8.
Which of the following columns is not matched correctly? [1]
| Short Form | Expanded Form |
| a. DD | Doordarshan |
| b. CNP | Common National Programmes |
| c. INSAT-IA | National Television Forum |
| d. AIR | All India Radio |
Answer:
| c. INSAT-IA | National Television Forum |
Question 9.
Which of the following statement(s) given below is/are correct? [1]
I. Water scarcity is the practice of using water efficiently to reduce unnecessary usage or wastage of water.
II. Water conservation is the practice of using water efficiently to reduce unnecessary usage or wastage of water.
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) Both I and II
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Only II
Question 10.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of minerals? [1]
(a) There is an inverse relationship in the quality and quantity of minerals.
(b) Minerals are unevenly distributed over space.
(c) All minerals are exhaustible over time.
(d) All minerals are inorganic in origin.
Answer:
(d) All minerals are inorganic in origin.
Question 11.
Which one of the following is not an objective of the Namami Gange Programme? [1]
(a) Developing sewerage treatment systems in towns
(b) Monitoring of industrial effluents
(c) The Ganga aarti
(d) Cleaning of the river surface
Answer:
(c) The Ganga aarti
![]()
Question 12.
Which of the following is not a conventional source of energy? [1]
(a) Coal
(b) Petroleum
(c) Geothermal energy
(d) Nuclear energy minerals
Answer:
(c) Geothermal energy
Question 13.
Assertion (A): Human beings interact with their physical environment with the help of technology.
Reason (R): Human beings were able to develop technology after they developed a better understanding of natural laws. [1]
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Answer:
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 14.
Assertion (A): The urban centres located near the trade route experience rapid development.
Reason (R): The location of a specific region is responsible for the development. [1]
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation: The site and situation of a location of a particular region specify its growth. The location of urban centres is decided in relation tp their function. For instance, the locational requirements of a vacation resort are different in comparison that of an industrial city. The use of contemporary technologies has helped to locate urban communities distant from the source of these minerals. The surroundings have a significant impact on the growth of cities. The urban centres that are near a major commerce route have undergone fast growth.
Read the following case study and answer questions no 15 to 17.
Read the passage carefully and answer any three of the following questions:
Winters in the town of Trondheim mean fierce winds and heavy snow. The skies are dark for months. Kari drives to work in the dark at 8 am. She has special tires for the winter and keeps the headlights of her powerful car switched on. Her office is artificially heated at a comfortable 23 degree Celsius. The campus of the university she works at is built under a huge glass dome. This dome keeps the snow out in winter and lets in the sunshine in the summer. The temperature is controlled carefully and there is adequate lighting.
Even though fresh vegetables and plants don’t grow in such harsh weather, Kari keeps an orchid on her desk and enjoys eating tropical fruits like bananas and kiwis. These are flown in from warmer areas regularly. With a click of the mouse, Kari can network with colleagues in New Delhi. She frequently takes a morning flight to London and returns in the evening in time to watch her favorite television serial. Though Kari is fifty-eight years old, she is fitter and looks younger than many thirty-year-olds in other parts of the world.
Question 15.
What type of climate has been described in Trondheim? [1]
(a) Moderate winter
(b) Continental climate
(c) Fierce winter
(d) Tropical climate
Answer:
(c) Fierce winter
Question 16.
What has made life possible in Trondheim? [1]
(a) The people are rich to afford such a lifestyle.
(b) The people like to live in Trondheim so are ready to bear all difficulties.
(c) The people are educated and hardworking.
(d) Technology has enabled people to overcome natural constraints.
Answer:
(d) Technology has enabled people to overcome natural constraints.
Question 17.
How does Kari being fifty-eight years old, look younger than many thirty-year-olds? [1]
(a) With the help of technology
(b) By using the products of nature in a healthy way
(c) By physical fitness
(d) Strong will
Answer:
(b) By using the products of nature in a healthy way
Section – B (18 Marks)
Question 18.
Read the passage carefully and answer the following questions: [3]
India’s urbanization is attributable primarily to the deregulation of its economy in the 1990s, which facilitated the growth of the private sector. Despite the fact that India’s urbanization is accelerating, just one-third of the country’s population lives in cities. According to the 2011 census, India has 53 cities with a population of one million or more, with that number expected to climb to 87 by 2031. Some of these metropolitan regions will grow into huge economic powerhouses, with GDPs exceeding nations like Israel, Portugal, and the United Arab Emirates.
After 1941, India’s four major metropolitan cities, Kolkata, Delhi, Mumbai and Chennai, saw significant expansion. The country’s economy grew as a result of the industrial revolution, and the creation of new technology raised people’s living standards in metropolitan regions. The public sector’s expansion led to the construction of public transportation, roads, water supply, power, and other urban infrastructure.
Some cities, such as Three Tier cities, are seeing population growth. Maharashtra was India’s most urbanized main state till 1991, falling behind Tamil Nadu in 2001 and third in 2011, with Kerala coming in second in terms of urban-to-total state population ratio. Although cities have a huge number of people in compact area, they offer enormous economies scale that provide employment, housing, and services, and they offer tremendous prospects for sustainable development.
It is critical to fully achieve Indian cities’ ecological, economic and social sustainability potential. However, inclusive planning offers inexpensive transportation, constant water supply, modem sewage treatment, and a competent, solid waste management system is the only way to harness and maintain rising urbanization.
(i) How many cities are having more than one million of the population in India?
Answer:
53
(ii) How did the economic growth of India grow after post-1941?
Answer:
After 1941, India’s four major metropolitan cities, Kolkata, Delhi, Mumbai, and Chennai, saw significant expansion. The country’s economy grew as a result of the industrial revolution, and the creation of new technology raised people’s living standards in metropolitan regions.
(iii) What is the impact of urbanisation in India?
Answer:
The public sector’s expansion led to the construction of public transportation, roads, water supply, power and other urban infrastructure. Although cities have a huge number of people in a compact area, they offer enormous economies of scale that provide employment, housing and services, and the other offer tremendous prospects for sustainable development.
![]()
Question 19.
Study the picture given below and answer the questions that follow: [3]

(i) Identify the crop in the picture given above.
Answer:
Rice.
(ii) Name the leading producer of this crop in India.
Answer:
West Bengal.
(iii) Name the states where the yield level of this crop is high.
Answer:
Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Haryana, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, West Bengal, and Kerala.
Question 20.
Why is Geography often called the ‘mother of all Sciences’? [3]
OR
Give examples of how both physical and human phenomena are described in metaphors using symbols from the human anatomy.
Answer:
Geography is an inter-disciplinary subject which links and has an influence on other scientific fields that include anthropology, biology, geology, chemistry, mathematics etc Geography explores new ideas, place and culture often related to human knowledge. Therefore, Geography is often called the Mother of all Sciences.
OR
There are various examples in the physical world, where human symbols and metaphors are used:
1. The ‘face’ of the earth
2. ‘Eye’ of the storm
3. ‘Mouth’ of the river
4. ‘Snout’ (nose) of the glacier
5. ‘Neck’ of the isthmus
6. ‘Profile’ of the soil.
Villages, towns, and regions have been described as organisms. German geographers describe a country as a ‘living organism’. Networks of roads, railways, and waterways have often been described as ‘arteries of circulation.
Question 21.
Whatissatellite communication? How has it brought revolutionary changes in the field of communication in the world? [3]
Answer:
Communication through satellites which emerged as a new area in communication technology is called satellite communication. Artificial satellites are successfully deployed in the earth’s orbit to connect even the remotest comers of the globe with limited onsite verification. These have rendered the unit cost and time of communication invariant in terms of distance. This means, it costs the same to communicate over 500 km as it does over 5,000 km via satellite.
Question 22.
Why is Agricultural Density important for India?
OR
What is the National Youth Policy of the Government of India? [3]
Answer:
Agricultural Density is important for India because:
1. India is the home to a large agricultural population.
2. It measures the number of farmers specifically on each unit of farmland.
3. It analyses land-use in agricultural countries more accurately.
OR
The National Youth Policy of the Government of India is:
1. NYP-2014 is to empower youth to achieve full potential and enable them to find its rightful place in the community of nations.
2. NYP-2014 replace NYP-2003 and cover the entire catering the need of all youth in the age group of 15-29 years, which constitutes 27.5% of the population.
3. Aims on youth and women empowerment with respect to effective participation in decision making and carrying the responsibility of an able leader.
![]()
Question 23.
What are the three types of railway tracks in India? [3]
Answer:
The three types of railway tracks found in India are as follows:
1. Broad Gauge: The distance between the rails in broad gauge is 1.676 meters. The total length of these lines is 38914.91 km.
2. Metre Gauge: The distance between the rails in metre gauge is one meter. The total length of such a gauge is 2402.25 km.
3. Narrow Gauge: The distance between the rails in narrow gauge is 0.61 or 0.76 meters. The total length of this type of railway track is 1604.12 km.
Section – C (25 Marks)
Question 24.
What is the ‘demographic cycle’? Describe three stages of Demographic Transition Theory. [5]
Answer:
The demographic cycle represents the changes in the population of a region as it moves from high births and high deaths to low births and low deaths as that region/society progress from rural, agrarian and illiterate to an urban, industrial and literate society. These changes occur in three stages that are collectively called Demographic Transition Theory.
The three stages are:
1. The First Stage: This stage is marked by high fertility and high mortality. The death rate is also high due to epidemics and variable food supply. Therefore, population growth is slow and life expectancy is low. People are mostly illiterate and engaged in agriculture, due to which large families are preferred (d) Level of technology is also low.
2. Second Stage: In this stage, the expansion of the population remains high because the death rate reduces due to the improvement in sanitation and health conditions but the fertility rate remains high. Though, at a later stage, it declines with time. The mortality rate also decreases. The net addition to a population in this stage is high.
3. Third Stage: In the last stage, both fertility and mortality rate declines considerably and the population either stabilizes or grows slowly. The family size is deliberately controlled as the population becomes urbanized and literate. There is high level of technical know-how at this stage. High technical knowledge contributes deliberately in controlling the family size.
Question 25.
Discuss the major trends of modem industrial activities, especially in the developed countries of the world.
OR
Explain why high-tech industries in many countries are being attracted to the peripheral areas of major metropolitan centers. [5]
Answer:
Some major trends of modem industrial activities especially in developed countries are:
1. Division of work: Workflow in the modem industry is divided into smaller tasks. These tasks are then assigned to individual workers, who work on it repeatedly. This way, the worker obtains specialization in that particular work. Division of work is also effective in producing more goods/products with less effort.
2. Mechanization: It refers to using modem gadgets to finish a task. High-tech computers, robotics, automation and control systems are being used without human aid to accomplish a task. Mechanization helps in boosting productivity and efficiency of the production work.
3. Technological innovation: Today, industries in developed countries are largely investing in research and development and finding new ways to improve quality, eliminate wastage and inefficiency, and combating pollution. Technological innovation helps an organization become operationally effective, responsive and improve outcomes.
OR
The following are the reasons to attract high-tech industries or technological parks to the peripheral areas of major metropolitan cities:
1. Especially light Industry which depends upon components finds it perfect to sell their output in nearby metropolitan areas.
2. Greater prospectives for future development because extensive land is available in peripheral areas.
3. Cost of land is generally less in peripheral areas.
4. Transport facilities are accessible through link and ring roads to the peripheral areas.
5. A pollution-free environment is an additional benefit in peripheral areas.
6. Cheap and abundant labor supply from neighboring residential areas.
![]()
Question 26.
Name the canal which has significantly shortened the distance between Europe and Asia Write the importance of this canal.
OR
Elaborate the development of communication that led to the development of human beings. [5]
Answer:
The Suez Canal has shortened the distance between Europe and Asia This canal was constructed in 1869 in Egypt between Port Said in the north and Port Suez in the south, linking the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea Its important features are:
1. It provides Europe a new gateway to the Indian Ocean and reduces direct sea route distance between Liverpool and Colombo as compared to the Cape of Good Hope route.
2. It is a sea-level canal without locks which is about 160 km long and 11 to 15 m deep.
3. About 100 ships travel daily and each ship takes 10-12 hours to cross this canal.
4. A railway follows the canal to Suez, and from Ismailia, there is a branch line to Cairo.
5. A navigable fresh-water canal from the Nile also joins the Suez Canal in Ismailia to supply fresh water to Port Said and Suez.
OR
Human beings have used different methods of long-distance communication of which the telegraph and the telephone were important.
1. The telegraph was instrumental in the colonization of the American West. During the early and mid-twentieth century, the American Telegraph and Telephone Company (AT&T) enjoyed a monopoly over U.S.A.’s telephone industry.
2. In fact, the telephone became an essential factor in the urbanization of western countries. Today there is a phenomenal pace of development. The first major breakthrough is the use of Optic Fiber Cables (OFC). These allow large quantities of data to be transmitted rapidly, securely, and are virtually error-free.
With the digitization of information in the 1990s, telecommunication slowly merged with computers to form integrated networks termed as Internet. Cyberspace will expand the contemporary economic and social space of humans through e-mail, e-commerce, e-leaming and e-governance. It is these modem communication systems, more than transportation, that has made the concept of the global village a reality.
Question 27.
Discuss any three issues that developing nations face regarding urban settlements. [5]
Answer:
Issues that developing nations face regarding urban settlements are as follows:
1. Economic Issues: In emerging nations, dwindling employment prospects in rural and smaller urban regions continually force the populace towards metropolitan areas. The massive migrant population creates a pool of unskilled and semi-skilled labor that is already overburdened in cities. This puts more strain on cities’ current infrastructure.
2. Social-cultural Issues: Cities in emerging nations are plagued by a variety of social issues. Inadequate financial resources prevent the development of appropriate social infrastructure from meeting the fundamental demands of the massive population. The existing educational and health services are still out of reach for the urban poor. Crime rates are exacerbated by lack of work and education. The sex ratio in these cities is distorted by male selective migration to urban regions.
3. Environmental Issues: In developing countries, the vast urban population not only consumes but also disposes of a considerable amount of water and various waste products.
Question 28.
“Increasing population is the sole reason behind the rising environmental degradation on a global level.” Justify the statement by citing one example for each one of the four types of pollution. [5]
Answer:
High growth rate of the population at a global level has been the most important cause of increasing pressure on the environment and its resources, environmental degradation and pollution. Each type of pollution marks the increasing population as the major cause of its existence and increase.
1. Water Pollution: Increasing population implies to increase usage of ground and surface water source. Likewise, increase usage in agricultural and industrial production implies increasing use of chemicals, thereby increasing the toxic waste run-off.
2. Air Pollution: Increasing population pertains to increased use of automobile and increased production and toxic gaseous emissions from industries causing serious rise in air pollution and its consequent health hazards.
3. Land Pollution: Increasing population results in high demand of infrastructure through landfill, increased pressure on soil due to high demand for food, thus reducing its fertility, increased waste generation and reduced green cover, thus increasing air pollution.
4. Noise Pollution: Increasing population also signifies increased congestion, traffic, nuisance and noises from automobiles which increase noise pollution.
Section – D (10 Marks)
Question 29.
On the given political map of the world, the following seven features are shown. Identify any five of these features and write their correct names on the lines marked near each feature. [5]
A. An important industrial region of the USA.
B. An important industrial region of Russia.
C. An Inland port of the USA of river Mississippi.
D. A commercial port in Panama.
E. Country of the USA in which subsistence agriculture is practiced.
F. Identify the country where intensive subsistence agriculture is largely found in Asia.
G. Eastern Point of Australian Trans-Continental Railway.
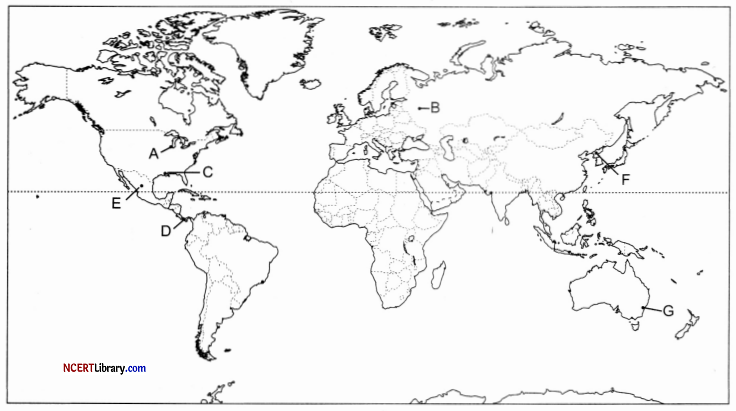
Answer:
A. Chicago
B. Moscow
C. New Orleans
D. Colon
E. Mexico
F. North Korea
G. Sydney
Question 30.
On the given political map of India, locate and label any five of the following with appropriate symbols: [5]
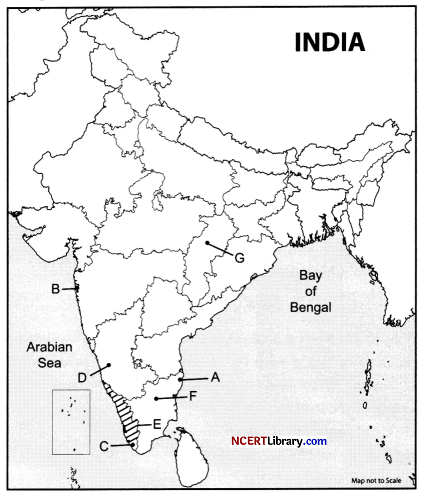
A. Headquarters of Southern Railway Zone in India.
B. Largest port in India.
C. India’s first satellite launching station.
D. Manganese mines of Karnataka.
E. Identify the state which has vast surface water resources in the lagoons and lakes.
F. The reason in southern India where tea is cultivated.
G. Bauxite mines of Chhattisgarh.
Answer:
A. Chennai
B. Mumbai port
C. The Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station (TERLS) (Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre) Thiruvananthapuram.
D. Shimoga
E. Kerala
F. Nilgiris
G. Bilaspur
![]()