Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics with Solutions Set 7 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics Set 7 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours.
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains 34 questions.
- Marks are indicated against each question.
- Answers should be brief and to the point.
- Answers to the questions carrying 3 marks may be from 50 to 75 words.
- Answers to the questions carrying 4 marks may be about 150 words.
- Answers to the questions carrying 6 marks may be about 200 words.
Section-A (Macro Economics)
Question 1.
Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: MPC can never be positive, neither zero nor negative.
Statement 2: MPC falls with the increase in income.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
(a) Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false.
(b) Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true.
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
Answer:
(b) Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true.
Explanation: The value of MPS can never be negative. It varies between 0 and 1.
Question 2.
If an Indian buys UK car Company, it enters _______of Balance of Payments as a _______item.
(a) current account transactions, debit
(b) capital account transactions, debit
(c) current account transactions, credit
(d) capital account transactions, credit
Answer:
(b) capital account transactions, debit
Explanation: As foreign exchange is flowing out of India. So, it enters Capital Account transactions as a debit item.
Question 3.
Which of the following is not helpful in controlling money supply?
(a) Free market policy
(b) Bank rate
(c) CRR
(d) Change in margin requirements
Answer:
(a) Free market policy
Explanation: A free market is one where voluntary exchange and the laws of supply and demand provide the sole basis for the economic system, without government intervention
Question 4.
Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: If US $ exchanges for ₹70, instead of ₹60 earlier, the domestic currency shows depreciation.
Statement 2: Depreciation of domestic currency encourages imports.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative:
(a) Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false.
(b) Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true.
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
Answer:
(a) Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false.
Explanation: Currency depreciation is a fall in the value of a currency in terms of its exchange rate versus other currencies. When the domestic currency depreciates, it discourages imports by making imported goods more expensive.
![]()
Question 5.
Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: Real Flow is also called as Physical Flow.
Statement 2: Money Flow is also known as Nominal Flow.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative:
(a) Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false.
(b) Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true.
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
Answer:
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
Explanation: In real flow, actual movement of goods and services between households and firms is seen. So, it is also termed as physical flow. When money is used as a medium of exchange while the transactions take place. This flow is called money flow and it is also known as nominal flow.
OR
On the basis of below chart answer the following question:

Choose the correct alternative to be filled in blank.
(a) NFIA
(b) NIT (Net Indirect Tax)
(c) Depreciation
(d) Net Export
Answer:
(b) NIT (Net Indirect Tax)
Explanation:
GDPFC = GDPMP – NIT
GDPMP = GDPFC + NIT
Question 6.
As a result of increase in investment by crores, national income rises by ₹240 crores. What will be the value of K?
(a) 4
(b) 5
(c) 6
(d) 7
Answer:
(a) 4
Explanation: Here,
ΔI = ₹60 crores
ΔY = ₹240 crores
K = \(\frac{\Delta Y}{\Delta I}=\frac{240}{60}\) = ₹ 4 Crores
OR
If APS is 0.6, how much will be APC?
(a) 0.4
(b) 0.5
(c) 0.6
(d) 0.7
Answer:
(a) 0.4
Explanation: Here,
APS + APC =1
0.6 + APC =1
APC =1 – 0.6
= 0.4
Question 7.
To soak the liquidity from the market_____________.
Choose the correct alternative:
1. Government securities should be purchased
2. Government securities should be sold
3. Repo rate should be decreased
4. CRR should be increased
Alternatives:
(a) 1 and 4 are correct
(b) 2 and 4 are correct
(c) 1 and 3 are correct
(d) 2 and 3 are correct
Answer:
(b) 2 and 4 are correct
Explanation: To control inflation government securities should be sold and CRR should be decreased as inflation lowers the real work of money.
Question 8.
| Items | 2020-21 (₹ crore) |
| Export | 125 |
| Imports | 165 |
| Non-factor Services | 22 |
| Income | 8 |
| Transfer | 14 |
On the basis of the above mentioned information answer the following question:
The value of goods and services balance will be:
(a)₹ 4 crore
(c) (-)₹ 18 crore
(b) (-) ₹ 10 crore
(d) ₹ 18 crore
Answer:
(c) (-) ₹ 18 crore
Explanation:
Goods and services balance = Trade balance + Balance on account of non-factor services
Trade balance = Exports- Imports
= 125- 165
= ₹(- 40) crore
Non-factor services = 22
Goods and services balance = – 40 + 22 = ₹(- 18) crore
OR
Suppose, following data is presented, for an imaginary economy: (all figures in ₹ ‘000 crore)
| Year | Invisible Items (Export) | Invisible Items (Import) |
| 2020 | 300 | 350 |
| 2021 | 600 | 550 |
Identify, which of the statement about the period 2020 to 2021 is correct?
(a) Increase in balance of trade
(b) Decrease in trade deficit
(c) Improvement in balance in invisible items
(d) Deterioration of balance of trade
Answer:
(a) Increase in balance of trade
Explanation: According to the data balance of trade was Less in 2020 in comparision with 2021.
![]()
Question 9.
Read the following statement -Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion (A): Dis-savings comes when there is no income.
Reasoif (R): Break-even point indicates a point where consumption becomes equal to income or consumption curve cuts the income curve.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
Explanation: Workers who are willing to work for the market rate or slightly less but are unable to do so because of circumstances beyond their control are said to be experiencing involuntary unemployment. These elements could be a lack of overall demand, rigidities in the labour market, implicit wage bargaining, and efficiency wage theory.
Question 10.
Read the following statement -Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion (A): Only involuntary unemployment is considered while estimating the total unemployment in an economy.
Reason (R): Somehow involuntary unemployment is the most dangerous situation in the country which suggest that country may go to depression.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Explanation: Workers who are willing to work for the market rate or slightly less but are unable to do so because of circumstances beyond their control are said to be experiencing involuntary unemployment. These elements could be a lack of overall demand, rigidities in the labour market, implicit wage bargaining, and efficiency wage theory.
Question 11.
Calculate the aggregate value of depreciation.
| S. No. | Particulars | Amount (₹ in crores) |
| (i) | GDPmp | 1,000 |
| (ii) | Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA) | 90 |
| (iii) | Net Indirect Taxes (Value of Indirect Taxes – Subsidies) | 140 |
| (iv) | National Income (NNPFC) | 840 |
GDPMp = NNPFC + Depreciation- NFIA + NIT
1000 = 840 + Depreciation- 90 + 140
1000 = Depreciation + 980 -90
= Depreciation + 890
Depreciation = ₹ 110 crore
Question 12.
Explain the difference between Fixed Exchange Rate and Flexible Exchange Rate.
OR
Explain from where supply of foreign exchange comes in the country.
Answer:
Difference between Fixed Exchange Rate and Flexible Exchange Rate:
| Basis | Fixed Exchange Rate | Flexible Exchange Rate |
| Determination | It is the rate which is officially fixed in terms of gold or any other currency by the government. | It is determined by forces of demand and supply of foreign exchange. |
| Control of Government | There is complete control of government as only it has the power to change it. | There is no intervention of government and it fluctuates freely according to the market conditions. |
| Stability | It generally remains stable and only a small variation is possible. | It keeps on changing. |
OR
Sources of supply of foreign exchange:
1. Export of goods and services to foreign countries.
2. Investment in bonds and equity shares by foreign nations in the domestic country or purchase of assets by the foreigners.
3. Receiving gifts from the rest of the world.
4. Inward movement of foreign currencies due to currency dealers and speculators.
![]()
Question 13.
Assume that an economy is in equilibrium. Calculate the Investment Expenditure from the following:
National Income = ₹ 800
Marginal Propensity to Save = 0.3
Autonomous Consumption = ₹ 100
Answer:
Given, Y = 800
MPS = 0.3
i.e.,MPC =1 – MPS =1 – 0.3 = 0.7
C = 100
We know that at equilibrium,
Y = C + 1
C =ab + by
= 100 + 0.7y
By putting at values of Y and C
800 = 100 + 0.7 (800) + 1
800 = 100 + 560 +1
I = 800- 660 = ₹ 140
Thus, the investment expenditure is ₹ 140.
Question 14.
An economy is operating at under-employment level of income. What is meant by the given statement? Discuss one fiscal measure and one monetary measure to tackle the situation.
Answer:
An economy is said to be operating at under employment equilibrium level, if the planned aggregate expenditure falls short of available output in the economy, corresponding to the full employment level.
It results into excess of output available over the anticipated aggregate demand at full employment level. To tackle such a situation the aggregate demand has to be increased up to the level that stocks can be cleared.
Following measures may be taken for the same:
1. Decrease in taxes: The government under its fiscal policy may decrease the rate of taxes (both direct and indirect taxes). This will ensure greater purchasing power in the hands of general public. This will help to increase aggregate demand and remove the deflationary gap.
2. Increase in money supply: Central bank through its expansionary monetary policy can increase the money supply in the economy. Central Bank can use tools like bank rate, cash reserve ratio, repo and reverse repo rates etc. to ensure greater money in the hands of general public which would in turn increase the aggregate demand in the economy and be helpful in reducing/removing the deflationary gap.
Question 15.
Explain the function “Lender of Last Resort” and “Custodian of Foreign Exchange Reserve” of Central Bank.
OR
Read the following statements correctly answer the following questions accordingly.
“If CRR is scrapped as a legal requirement, the whole economy could crash, the NPAs could further deteriorate the situation and the whole banking system can be considered as the system of frauds and no matter what the advance of loans and saving deposit could never be matched. This type of situation may cradle the economy and make short of money supply, which could lead to recession”.
(1) What is CRR?
(2) What happens when RBI decreases CRR?
(3) What is NPA?
Answer:
Lender of Last Resort: The Central Bank is the only institution which issue currency when commercial banks need more funds. When commercial banks have exhausted all resources to supplement their funds at times of liquidity crisis then Central Bank saves banks from possible failure by providing them financial accommodation and guarantees solvency.
Custodian of foreign Exchange Reserves: The Central Bank is the custodian of the country’s stock of gold and international currencies. All receipts and payments in foreign exchange rate are made by the Central Bank. Through this function, the Central Bank maintains the rate of exchange and manages exchanges control as well.
OR
(1) CRR is the ratio of which commercial banks needs to keep cash with RBI out of their total deposits.
(2) If RBI decreases CRR in that case the money supply in economy will increase and it will lead to availability of more credit in the economy.
(3) Non Performing Assets. It is a classification used by financial institutions for loans or advances that are in default or in arrears.
![]()
Question 16.
Calculate National Income by:
(a) Income Method and
(b) Output Method.
| S. No. | Particulars | Amount (in ₹ crores) |
| (i) | Value of output of primary sector | 10,000 |
| (ii) | Value of output of other sectors | 4,000 |
| (iii) | Raw materials purchased by primary sector | 5,000 |
| (iv) | Raw materials purchased by other sector | 3,000 |
| (v) | Factor income received from the rest of the world | 100 |
| (vi) | Factor income paid to the rest of the world | 150 |
| (vii) | Depreciation | 550 |
| (viii) | Indirect taxes | 1,000 |
| (ix) | Subsidies | 200 |
| (x) | Mixed income from self employed | 2,000 |
| (xi) | Compensation of employees | 1,700 |
| (xii) | Rent | 400 |
| (xiii) | Interest | 300 |
| (xiv) | Profit | 250 |
Answer:
(a) National Income by Income Method:
= Factor income received from the rest of the world- factor income paid to the rest of the world + mixed income of self-employed + compensation of employees + rent + interest + profit
= 100 – 150 + 2000 + 1700 + 400 + 300 + 250
= 100 + 2000 + 1700 + 400 + 300 + 250 – 150
= ₹ 4,600 crores
(b) National Income by Output Method:
= Value of Output of primary sector + Value of Output of the other sectors- Raw materials purchased by the primary sector- Raw material purchased by other sectors- depreciation- (Indirect Taxes Subsidies) + (Factor income from rest of the world- factor income to rest of the world).
= 10,000 + 4,000 – 5,000- 3,000 – 550- (1,000- 200) + (100 – 150)
= 14,000 – 8,550- 800- 50
= 14,000 – 9,400
= ₹ 4,600 crores
![]()
Question 17.
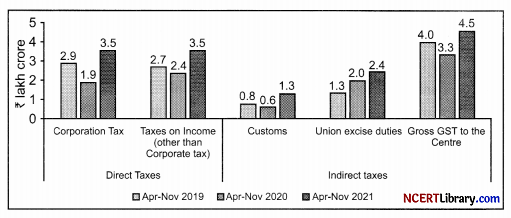
Trends in major direct and indirect taxes during April-November period
Source: CGA Monthly Accounts
On the basis of above mentioned figure :
(a) Compare the chart with respect to direct taxes and indirect taxes.
(b) Briefly explaining what do you mean by Corporation tax and Customs duty.
OR
Explain the difference between Balance of Trade and Balance of Payments.
Answer:
(a) Direct taxes are those taxes, the final burden of which falls on the person who is liable to pay to the government whereas Indirect taxes are those taxes, the final burden of which does not fall on the person who is liable to pay to the government.
In the given chart, the corporation tax and taxes on income considered as corporate taxes in 2019 and 2020 were 2.9 and 1.9 respectively and which states the decline in the taxes due to Covid-19 situation and again in respect to 2021 it was 3.5, a drastic increase in the collection.
In the given chart, it is clearly seen that in terms of Indirect taxes, much of the income is been generated through GST. It is clear that GST is one of the basic factoral reform for India as it has more collection compared to Customs and Excise duties.
(b) Corporation tax: The corporation tax is the tax on the income of the companies both domestic and foreign companies operating in India. It is a type of direct tax as the liability to pay the tax and actual burden of the tax lie on the same person.
Customs Duty: When the goods are transported across international borders ,the tax is imposed on goods. That tax is called as Custom Duty. The government levies this tax to raise its revenues and to regulate the movement of goods.
OR
| Basis | Balance of Trade | Balance of Payment |
| Meaning | It refers to the difference between exports and imports of visible items. | It is an accounting statement that provides a systematic record of all economic transactions, between residents of a country and rest of the world in a given period of time. |
| Components | BOT includes only visible items. | BOP includes visible items, invisible items, unilateral transfers and capital transfers. |
| Capital transactions | It does not record any transaction of capital nature. | It records all transactions of capital nature. |
| Scope | It is a narrower concept as it is only a part of BOP account. | It is a wider concept and it includes BOT. |
| Settlement | Unfavourable BOT can be met out of favourable BOP. | Unfavourable BOP cannot be met out of favourable BOT. |
Section-B (Indian Economic Development)
Question 18.
Which of the following statements is not true about the Indian Economy during the British rule?
(a) Slow growth of agricultural and industrial sector.
(b) The area of operation of public sector was very limited.
(c) Drain of India’s wealth despite export surplus.
(d) During the colonial period, the service sector accounted for the largest share of workforce.
Answer:
(d) During the colonial period, the service sector accounted for the largest share of workforce.
Explanation: During the colonial period, the service sector accounted for only 10 and 15-20 percent. The agriculture sector accounted for the largest share.
![]()
Question 19.
India had an economy before the advent of the British rule.
(a) dependent
(b) industrial
(c) independent
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) independent
Explanation: India had an independent economy before the advent of the British rule. Though agriculture was the main source of livelihood for most people, yet, the country’s economy was characterised by various kinds of manufacturing activities.
OR
__________is not a notable economist who estimated India’s per capita income during the colonial period. (Fill in the blank with correct alternative)
(a) Findlay Shirras
(b) Romesh Chunder Dutt
(c) William Digby
(d) Dadabhai Naoroji
Answer:
(c) Romesh Chunder Dutt
Explanation: Findlay Shirras, William Digby and Dadabai Naoroji were the economists who estimated India’s per capita income during the colonial period. Romesh Chunder Dutt, who was a contemporary of Dadabai Naoroji and Justice Ranade was not among them.
Question 20.
Under Import Substitution Policy, protection from the imports took two forms __________ and __________.
(a) tariffs, quotas
(b) import duty, custom duty
(c) excise duty, escheat
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) tariffs, quotas
Explanation: Tariffs are the taxes levied on imports and Quotas are the quantity restrictions hold by government on imports.
OR
Industrial Policy Resolution (IPR) 1956 formed the basis of the___________ Five Year Plan.
(a) first
(b) fouth
(c) second
(d) third
Answer:
(c) second
Explanation: The IPR 1956 was formed to build the basic for a socialist pattern of society.
Question 21.
Identify the apex institute for rural financing in India.
(a) SIDBI
(b) IDBI
(c) NABARD
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) NABARD
Explanation: NABARD is responsible for the development of the small industries, cottage industries, etc. It was established on 12th July 1982.
![]()
Question 22.
From the set of the events given in column-I and corresponding facts given in column-II, choose the correct pair of statement:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| I. | Subsidy | A | Seeds that give large proportion of output. |
| II. | HYV seeds | B | Monetary assistance given by the government from production activities. |
| C | Adoption of new technology. |
(a) I-A, II-B
(b) I-B, II-A
(c) I-QII-A
(d) I-B, II-C
Answer:
(b) I-B, II-A
Question 23.
Read the following statements carefully:
Statement 1: Indian economy under British rule was completely agrarian.
Statement 2: India was made market for British manufactured products.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative:
(a) Statement1 is true and statement 2 is false.
(b) Statement1 is false and statement 2 is true.
(c) Both statements1 and 2 are true.
(d) Both statements1 and 2 are false.
Answer:
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
Explanation: Britishers followed the policy of Drain of Wealth, and they had two fold effect making India importer of Finished goods and exporter of Raw material.
Question 24.
Read the following statement given below and choose the correct alternative:
Statement 1: The reforms of 1991, neglected the agricultural sector.
Statement 2: Direct Tax consists of taxes on the income of individuals and profits of business enterprises.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative:
(a) Statement1 is true and statement 2 is false.
(b) Statement1 is false and statement 2 is true.
(c) Both statements1 and 2 are true.
(d) Both statements1 and 2 are false.
Answer:
(a) Both statements 1 and 2 are true
Explanation: Direct taxes impose on the income of individuals and profits of business enterprise and the reforms of 1991, it neglected the agriculture sector.
![]()
Question 25.
Use of biogas is the strategy for________.
(a) sustainable development
(b) sustainable recycling
(c) methane use
(d) self consumption
Answer:
(a) sustainable development
Explanation: Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present, without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
OR
Organic Farming is related to :
(a) maintaining fertility of soil
(b) use of chemical fertilizers
(c) decreasing fertility of soil
(d) using pesticides
Answer:
(a) maintaining fertility of soil
Explanation: It is a method of farming, in which crops are grown without the use of chemical fertilizers.
Question 26.
Read the following statement -Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion (A): The major policy initiatives i.e land reforms and green revolution helped India to become
self-sufficient in food grains production.
Reason (R): The proportion of people depending on agriculture did not decline as expected.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
Explanation: Dependency on agriculture did not decline as expected as the major policy initiatives were taken like land reforms and Green Revolution which helped to become self-sufficient.
Question 27.
Read the following statement -Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion (A): Government of India enacted the Right to Education Act in 2009.
Reason (R): To make education free and compulsory is the fundamental right of all children in the age group of 6-14 years.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Explanation: The Right to Education Act, 2009 was enacted by Government of India. Free and compulsory education was made for all children in the age of 6-14 years.
Question 28.

Interpret the above picture and analysis the causes of environmental degradation.
Answer:
According to this picture the causes of environmental degradation can be:
(1) Excessive exploitation of natural resources.
(2) Rapid rise of our population.
(3) Increasing deforestation.
(4) Toss of biodiversity.
(5) Mismanagement of renewable resources.
![]()
Question 29.
“Compared to urban women, more rural women are found working”. Explain.
OR
State some factors that leads to increase in the level of unemployment in India.
Answer:
The difference in participation rates is very high between urban and rural women. In urban areas, for every 100 urban females, only about 14 are engaged in some economic activities.
In rural areas, for every 100 rural women, about 26 of them participate in the employment market. Hence, where men are able to earn high incomes, families discourage female members from taking up jobs. Earnings of urban male workers are generally higher than rural males and so urban families do not want females to work.
Apart from this, many activities of the household in which urban women are engaged, are not recognised as productive work, while women working on farms in the rural areas are considered a part of the workforce if they are being paid wages in cash or in the form of food grains.
OR
Rapid Growth of Population: As the population increases, the ratio of workers to the total population also increases, thus with effect of increase in the labour force, unemployment increases.
Joint Family System: In joint family system, set up more and more number of households people surrounds, due to which many of the eldest members restrict other women or men to do jobs in the outer cities even after greater employment opportunities. It encourages disguised unemployment as there is a high tendency to survive on joint income without work.
Decay of cottage and small scale industries: As many of the cottage industries are on a decline due to the increase in materialism and changing competition from outer world, which results in the closure of such sick units and ultimately, the workers working in there are left unemployed. Over-
dependence on technology: In India, manpower is available in large quantities but the technology is taking over the manpower which has led to unemployment. This is because of less requirement of manual labour to accomplish tasks with greater dependence on machines and technology.
Question 30.
Compare and analyse the following information related to employment of the three neighbouring nations:
| Sectors | Share in Employment (%) (2014-15) | ||
| India | China | Pakistan | |
| Primary | 47 | 28.3 | 42.3 |
| Secondary | 22 | 29.3 | 22.6 |
| Tertiary | 31 | 42.4 | 35.1 |
| 100 | 100 | 100 | |
Answer:
Primary sector: In the year 2014, around 28 percent workforce in China was involved in agriculture, whereas the ratio of India was (47%) and Pakistan (42%) which says that percent of China in contribution to the primary sector involvement in GDP is less than India and Pakistan. Secondary and
Tertiary Sector: In China,more employee are engaged in manufacturing sector as compared to India and Pakistan, same as in Service sector , employment share of workers is more in China . So, it indicates that Chinese economy is money ahead as compared to India and Pakistan according to the given information.
Question 31.
(a) Name two indicators of Human Development Index (HDI).
‘Special Economic Zone (SEZ) increases foreign investment’. Explain.
Answer:
(a) Per capita income and life expectancy at birth.
(b) A Special Economic Zone (SEZ) is a geographical region that has economic laws different form a country’s typical economic laws. Usually, the goal is to increase foreign investment.
Special Economic Zones attract investors since they offer high quality infrastructure of facilities and support services. Besides allowing duty free import of capital goods and raw materials, attractive and other procedures are offered in such zones.
OR
How is China able to lead in all the human development indicators?
Answer:
China is able to lead in almost all the human development indicators because of the establishment of infrastructure in the areas of education and health, land reforms, long existence of decentralised planning and the existence of small enterprises which can be easily regulated. Even before the reforms, basic health services were provided in villages, and food was equitably distributed through the common system. Each reform was implemented on a small scale initially and then spread out on a larger scale. Laws and policies, such as the one-child norm, among other’s, were strictly enforced.
![]()
Question 32.
State whether the following statements are true/false, with valid arguments:
(a) Human Capital and Physical Capital are corollary to each other.
(b) Gender bias in India is a hindrance in the process of skill formation.
Answer:
(a) FALSE, Physical capital is tangible in nature and can be sold in the market, but Human capital is intangible in nature and cannot be sold in the market, as it considers skills which cannot be taken away from the owner.
(b) TRUE, as India needs gender equality. Many of the schemes provides gender equality and focus on women’s empowerment and social justice, which ultimately helps to eradicate the hindrance.
Question 33.
“The gains of Green Revolution were significant, but with its own set of limitation.” Comment.
Answer:
With the onset of Green Revolution in the country, food grain production received a big boost, both in terms of production and productivity. Moreover, Green Revolution led to a significant rise in gross area under cultivation. Owning to Green Revolution, there was a significant rise in crop productivity. The country achieved self-sufficiency in food grain production. But, there were certain limitations, as well.
The limitations are as follows:
1. Limited Crops: Revolutionary rise in output was confined mainly to the production of food grains. They are being limited afterwhile no similar rise in production of pulses and commercial crops.
2. Un-even Spread: Spread of Green Revolution was not uniform across all regions of the country. There is lack of biodiversity across the country.
3. Limited Farming Population: The bulk of farming population in India consists of small and marginal farmers. The gains of Green Revolution eluded these farmers. Green Revolution requires expensive inputs such as HYV seeds, fertilizers which were beyond the reach of small and marginal farmers.
4. Economic Divide: Despite aid by the government in terms of subsidised inputs, HYV technology remained beyond the reach of most of the marginal holders. Consequently, the gulf between rich and poor tended to swell over time.
OR
(a) “Ujjawala Yojana has been a game changer for rural India.” State any three conventional fuels being targeted under the Ujjawala Yojana.
(b) “Economists believe that India should spend at least 6% of its GDP on Education for achieving desired results.” Justify the statement with valid reason.
(c) List the names of the services which are being outsourced by companies in developed countries to India?
Answer:
(a) The three fuels being targeted under the Ujjawala Yojna which are proven to be a game changer for rural India are as follows :
(i) Coal, (ii) Oil resources, (iii) Fuel wood, (iv) Petroleum.
(b) In 1952, we were spending a meager 0.6% of India’s GDP on education which rose to only 4% in 2014. This has fallen well short of the 6% target proposed by the Education Commission in 1964. Moreover, throughout this period the increase in education expenditure has not been uniform and there has been irregular rise and fall.
This shows the apathy of the government towards investment in the education system. If the recommended 6% p.a. of the GDP would have been spent properly the present education system would have reached unforseen heights.
(c) Voice-based business processes (popularly known as BPO or call centres), record keeping, accountancy, banking services, music recording, film editing, etc.
![]()
Question 34.
Read the following text carefully and answer the given questions on the basis of the same and common understanding:
V.Kotwani Ltd. Company focuses on Crop Diversification as they feel that it is better option to focus on more and more increasing needs of present era. Crop diversification provides better conditions for food security and enables farmers to grow surplus products for sale at market and thus help to obtain increased income to meet other needs related to household well-being.
Crop diversification can enable farmers to gain access to national and international markets with new products, food and medicinal plants. Diversifying from the monoculture of traditional staples can have important nutritional benefits for farmers in developing countries and can support a country for becoming more self-reliant in terms of food production.
Diversification can also manage price risk, on the assumption that not all products will suffer low market prices at the same time and increase the profitability of the farming community.
(a) What is diversification in terms of agriculture?
(b) Explain the need and importance of it.
Answer:
(a) Diversification can be regarded as the reallocation of some of the farm’s productive resources, such as land, capital, farm equipment and labour to other products.
Diversification in agriculture includes two aspects one relates to change in cropping pattern to shift from subsistence farming commercial farming (by shifting from single cropping system to multi-cropping system) and the other relates to a shift of workforce from agriculture to other allied activities (livestock, poultry, fisheries, etc.)
(b) The need and importance of diversification of such activities in rural sector are:
- There is a greater risk in depending exclusively on farming for livelihood.
- It is essential and useful to provide productive sustainable livelihood options to rural people in India.
- In India, much of agricultural employment activities are concentrated in the Kharif season, whereas, in Rabi season it becomes quite difficult to find gainful employment.
- Diversification of agricultural activities is important because it helps to generate supplementary and gainful employment.
(i) It reduces the risk of agriculture sector.
(ii) It helps to provide ecological balance.
(iii) It provides sustainable livelihood options to farmer.