Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics with Solutions Set 1 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics Set 1 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours.
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains 34 questions.
- Marks are indicated against each question.
- Answers should be brief and to the point.
- Answers to the questions carrying 3 marks may be from 50 to 75 words.
- Answers to the questions carrying 4 marks may be about 150 words.
- Answers to the questions carrying 6 marks may be about 200 words.
Section – A (Macro Economics)
Question 1.
Read the following statements carefully: [1]
Statement 1: The consumption curve is an upward-sloping straight-line curve due to the direct relationship between income and consumption and the assumption of constant Marginal Propensity to Consume.
Statement 2: Aggregate Demand curve and Consumption curve are parallel to each other.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
(a) Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false
(b) Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false
Answer:
(c) Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
Explanation: The consumption curve slopes upward i.e., it shows the positive or direct relation between income and consumption. When MPC is constant then the consumption curve will be straight or linear. AD curve and consumption curve are parallel to each other because of autonomous investment.
Question 2.
‘Owing to the Russia-Ukraine crisis, the world is experiencing rising crude prices due to supply-side issues.’
Identify the most likely impact on the Balance of Payment situation of the Indian economy from the following: [1]
(a) Production of cars in India will rise.
(b) Production and sale of cycles in India will rise.
(c) Inflow of US Dollars in India will rise.
(d) Outflow of US Dollars from India will rise.
Answer:
(d) Outflow of US Dollars from India will rise.
Explanation: India imports a huge quantity of crude oil and makes payment in US Dollars. Increase in price of crude will increase the outflow of US Dollars from India.
Question 3.
_____ is an institution that accept deposits for lending purposes. (Fill up the blank with correct alternative) [1]
(a) Commercial Banks
(b) Life Insurance Corporation
(c) Reserve Bank of India
(d) Government of India
Answer:
(a) Commercial Banks
Explanation: Commercial banks perform both functions i.e. acceptance of deposits from people and advancing loans. A commercial bank is a type of financial institution that accepts public deposits and grants borrowers loans for profit-making investments and consumption. RBI and Government are not in direct contact with people for accepting deposits and advancing loans. LIC only accepts deposits from people but do not provide loans to people.
![]()
Question 4.
Read the following statements carefully: [1]
Statement 1: Export of financial services by India will be recorded on credit side of current account.
Statement 2: Foreign Direct Investments in India will be recorded on credit side of capital account.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative:
(a) Statement1 is true and statement 2 is false
(b) Statement1 is false and statement 2 is true
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false
Answer:
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true
Explanation: Export of Services is a part of Current account of BOP. FDI in India is a capital transaction and a part of Capital Account of BOP. Exports and Investment in India leads to Inflow of foreign exchange. So, these will be recorded on the credit side.
Question 5.
Read the following statements carefully: [1]
Statement 1: Net investment is a stock concept.
Statement 2: Capital is a flow concept.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative from the following:
(a) Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false
(b) Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false
Answer:
(d) Both statements1 and 2 are false
Explanation: Net Investment is a flow concept because it is measured over a period of time. Capital is a stock concept because it is measured at a point of time.
OR
Read the following figure carefully and choose the correct pair from the alternatives given below: [1]
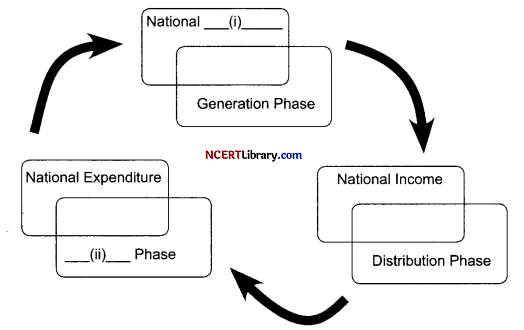
Alternatives:
(a) Output, Production
(b) Value added, Production
(c) Output, Disposition
(d) Wealth, Development
Answer:
(c) Output, Disposition
Explanation:
• 3 Phases of Circular Flow of Income
• 1st phase- Generation Phase- National output is generated by taking services of factors of production.
• 2nd phase- Distribution Phase- National output or national income is distributed among factors of production for rendering their services.
• 3rd phase- Disposition Phase- National income is spent or disposed and again, reaches in the hands of producers.
Question 6.
If in an economy, the value of investment multiplier is 4 and Autonomous Consumption is ₹30 crore, the relevant consumption function would be: [1]
(a) C = 30 + 0.75 Y
(b) C = (-)30 + 0.25 Y
(c) C = 30 – 0.75 Y
(d) C = 30 – 0.25 Y
Answer:
(a) C = 30 + 0.75 Y
Explanation:
Investment Multiplier (K) = 4
Autonomous Consumption (C) = 30 crore
\(\begin{aligned}
K &=\frac{1}{1-M P C} \\
4 &=\frac{1}{1-M P C}
\end{aligned}\)
4 – 4MPC = 1
4MPC = 3
MPC = 3/4 = 0.75
MPC = 0.75
Consumption function:
C = AC + MPC (Y)
C = 30 + 0.75 Y
OR
If increase in National Income is equal to increase in consumption, identity the value of Marginal Propensity to Save:
(a) Equal to unity
(b) Greater than one
(c) Less than one
(d) Equal to zero
Answer:
(d) Equal to zero
Explanation:
Increase in National Income = Increase in consumption
Or ΔY = ΔC
We Know that ΔY = ΔC + ΔS
ΔY – ΔC = ΔS
ΔY – ΔY = ΔS (Because here, ΔY = ΔC )
0 = ΔS
Now, \(\begin{aligned}
\mathrm{MPS} &=\frac{\Delta \mathrm{S}}{\Delta \mathrm{Y}} \\
&=\frac{0}{\Delta \mathrm{Y}}
\end{aligned}\)
= 0
Question 7.
Money supply in India may increase if, _____ [1]
1. Reserve Bank of India(RBI) injects more money in circulation.
2. The commercial banks expand their credit operation.
3. Tax rates are reduced by the Central Government
4. Reserve Bank of India increases the Bank Rate.
Alternatives:
(a) 1, 2, and 3 are correct
(b) 2, 3, and 4 are correct
(c) 1, 3, and 4 are correct
(d) 1, 2, and 4 are correct
Answer:
(a) 1, 2, and 3 are correct
Explanation: Printing of notes, Expansion of Credit and reduction in tax rate leads to increase in money supply. Increase in Bank rate soaks the excess money supply from the circulation.
![]()
Question 8.
Suppose, following data is presented, for an imaginary economy: (all figures in ₹ ‘000 crore) [1]
| Year | Visible Exports | Visible Imports |
| 2010 | 280 | 240 |
| 2020 | 580 | 460 |
Identify, which of the statement about the period 2010 to 2020 is correct?
(a) Improvement in balance of trade
(b) Increase in trade deficit
(c) Improvement in balance in invisibles items
(d) Deterioration of balance of trade
Answer:
(a) Improvement in balance of trade
Explanation:
In 2010,
BOT = Visible Exports – Visible Imports
= 280 – 240
= 40
In 2020,
BOT = Visible Exports – Visible Imports
= 580 – 460
= 120
In 10 years, BOT has improved from 40 to 120.
OR
The following information is given for an imaginary country:
| Current Account | Amount (in ₹ ‘000 crore) |
| Visible Exports | 100 |
| Visible Imports | 150 |
| Invisible Exports | 70 |
| Invisible Imports | 30 |
| Net current transfer balance | 15 |
Balance on current account will be _____ of ₹ _____ thousand crore.
(a) deficit, 10
(b) surplus, 5
(c) deficit, 5
(d) surplus, 10
Answer:
(b) surplus, 5
Explanation:
Balance of Trade = Visible Exports – Visible Imports
=100 – 150
= -50
Balance of Invisibles = Invisible Exports – Invisible Imports
= 70 – 30
= 40
Net current transfer balance = 15
Balance on Current Account = Balance of Trade + Balance of Invisibles + Net current transfer balance
=-50 + 40 + 15
= 5 (Surplus)
Question 9.
Read the following statement – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below: [1]
Assertion (A): Ex-post Investments represent planned Investments; whereas ex-ante Investments represent actual level of investments.
Reason (R): At equilibrium level, Ex-ante Savings and Ex-ante Investments are always equal.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Explanation: Ex- post Investments are actual Investments and Ex- ante Investments are planned Investments. Ex- ante Savings and Ex- ante Investments are always equal at Equilibrium level of Income.
Question 10.
Read the following Statement-Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below: [1]
Assertion (A): Saving curve makes a negative intercept on the vertical axis at zero level of income.
Reason (R): Saving function refers to the functional relationship between saving and income.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Explanation:
At zero level of income, savings are negative to the extent of autonomous consumption. Saving function shows the relation between saving and income. Savings are negative due to positive autonomous consumption.
Question 11.
Suppose in a hypothetical economy there are only two Firms A and B, Firm A sold goods for ₹ 2,000 to Firm B and purchased goods for ₹ 1,000. Firm B exported goods for ₹ 2,500 and had domestic sales of ₹ 1,500. Calculate Net Domestic Product at market price, if consumption of fixed capital is ₹ 200. [3]
Answer:
| Firm A | Firm B |
| Value of Production = Sales to Firm B = 2000
Intermediate Consumption = Purchases from Firm |
Value of Production = Exports + Domestic Sales = 2500 + 1500 = 4000
Intermediate consumption = Purchases from Firm |
Explanation:
GDPMp = GDPMp (firm A) + GDPMp (firm B)
= 1000 + 2000
= 3000
NDPMp = GDPMp – Consumption of fixed Capital
= 3000 – 200
= ₹ 2800
![]()
Question 12.
Explain, how exchange rate is determined under a free market exchange rate system. [3]
OR
Distinguish between autonomous and accommodating transactions in Balance of Payments Accounts. [3]
Answer:
Determination of Exchange Rate under Free Market Exchange Rate System:
1. Exchange rate will be determined at the point where quantity demanded and quantity supplied of foreign exchange is equal. This is the Equilibrium rate of exchange.
2. If Quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied of foreign currency, its price will rise. Rise in price will lead to fall in Quantity demanded and increase in quantity supplied. It will continue till equilibrium is established again.
3. If Quantity demanded is less than Quantity supplied of foreign currency, its price will fall. Fall in price will lead to rise in Quantity demanded and fall in quantity supplied. It will continue till equilibrium is established again.
OR
| Basis of Difference | Autonomous Transactions of BOP | Accommodating Transactions of BOP |
| 1. Meaning | Those international transactions which are undertaken by a country with economic motive. | Those international transactions which are undertaken deliberately to bring equality in BOP. |
| 2. Undertaken by whom | These are undertaken by the private sector. | These are undertaken by the apex monetary authority of a country. |
| 3. Example | Reliance Trend Store opened in Canada | Purchase of Gold by RBI in international Market. |
Question 13.
If an economy plans to increase its income by ₹ 2,000 crore and the Marginal Propensity to Consume is 75%. Estimate the increase in investment required to achieve the targeted increase in income. [4]
Answer:
Given: Increase in Income = ΔY = 2000 crore
MPC =75% = 0.75
To Find: Increase in Investment = ΔI=?
Investment Multiplier
\(\begin{aligned}
&=k=\frac{1}{1-\mathrm{MPC}} \\
&=\frac{1}{1-0.75} \\
&=\frac{1}{0.25}
\end{aligned}\)
=4
Now,
\(\begin{aligned}
k &=\frac{\Delta \mathrm{Y}}{\Delta \mathrm{I}} \\
4 &=\frac{2000}{\Delta \mathrm{I}} \\
\Delta \mathrm{I} &=\frac{2000}{4}
\end{aligned}\)
ΔI = ₹ 500 crore
Question 14.
As per the following news published in The Economic Times on 26th December 2021: ‘Reserve Bank of India has sold government securities worth? 8,710 crore in the secondary market, over the last four weeks, to drain out excessive liquidity’. Identify the likely cause and the consequences behind, this type of action plan of the Reserve Bank. [4]
Answer:
This action of RBI is Open Market Operations (OMO). OMO refers to purchasing and selling Government securities in the open market by RBI.
Likely Cause: RBI has sold securities to soak excess liquidity from the economy. Therefore, the most likely cause is to check on inflation.
Consequences: Selling securities in the market will reduce the money in circulation which will further lead to fall in lending capacity of Commercial banks. It will cause fall in consumption and investment demand or fall in AD. Fall in AD will lead to fall in price level in the economy.
Question 15.
Read the following text carefully, discuss briefly the relevant function of the Central Bank, indicated: [4]
Recently, Reserve Bank ofIndia (RBI) conducted a statutory inspection for supervisory evaluation against a Commercial Bank. The commercial bank was imposed with stringent penalties, owing to deficiencies in regulatory compliances. As per the Central Bank, the inspection revealed non-compliances vis-a-vis different directions issued by RBI, on the following fronts:
i. ATM Card frauds
ii. Ensuring integrity and quality of data
iii. Loans to small borrowers
OR
‘Reserve Ratio and Credit Creation are inversely related.’ Do you agree with the given statement? Justify your answer with a suitable numerical example.
Answer:
The text given discusses the ‘Banker’s Bank’ function of Central Bank.
i. RBI acts as a supervisor/regulator for the entire banking system.
ii. Every Commercial bank is required to follow directions issued by central bank. For e.g. granting loans to small borrowers, maintaining CRR and SLR as specified by central bank, maintenance of proper accounts, KYC norms etc.
iii. If any Commercial bank is involved in non-compliance of directions issued by central bank, then central bank takes strict action against that bank. For e.g. cancellation of license, monetary penalties etc.
OR
Yes, I agree with the statement, “Reserve Ratio and Credit Creation are inversely related”.
| Deposits | Loans | LRR = 20 % | |
| Round 1 | 100 | 80 | 20 |
| Round 2 | 80 | 64 | 16 |
| Round 3 . . . . |
64 . . . . |
51.20 . . . . |
12.80 . . . . |
| Total | 500 | 100 | 100 |
\(\begin{aligned}
\text { Money Multiplier } &=\frac{1}{\text { Legal Reserve Ratio }} \\
&=\frac{1}{20} \times 100
\end{aligned}\)
= 5 times
Credit Creation = Initial Deposits x Money Multiplier
= 100 x 5 = ₹ 500
LRR ↓→ Money Multiplier ↑→ Credit Creation ↑
Question 16.
(a) Define Gross Domestic Product (GDP) deflator and discuss its importance.
(b) State and discuss any two precautions to be considered while estimating national income by Expenditure Method. [6]
Answer:
(a) GDP Deflator: It is a price index which is used to eliminate the effect of price fluctuations in the economy
\(\text { GDP Deflator }=\frac{\text { Nominal GDP }}{\text { Real GDP }} \times 100\)
Importance of GDP Deflator:
1. It is a price index which deflates the Nominal GDP to Real GDP.
2. It helps in comparison of economic growth of a country between two different periods of time.
(b) Precautions while estimating National Income by Expenditure Method:
1. Expenditure on purchase of final goods is taken into account. Expenditure on Intermediate goods is not taken into account so as to avoid the problem of double counting. It is because expenditure on final goods includes expenditure on intermediate goods.
2. Expenditure on purchase of share, debentures and bonds are not taken into account because it represents only transfer of ownership from one person to another. It does not lead the production of any good or service in the economy.
![]()
Question 17.
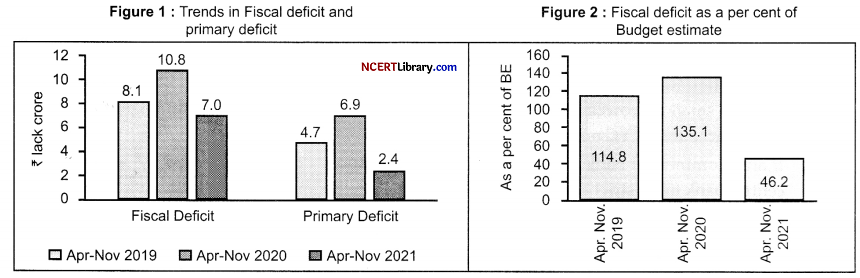
(a) Compare the trends depicted in the figures given below:
(b) Elaborate the objective of ‘allocation of resources’ in the Government budget. [6]
OR
(a) Distinguish between revenue receipts and capital receipts of the government, with suitable examples.
(b) Distinguish between direct and indirect taxes, with suitable examples. [6]
Answer:
(a) Comparison of Trends:
1. Fiscal Deficit in 2020 increased to 10.8 lakh crore from 8 lakh crore in 2019. But in 2021, it went down to 7 lakh crore. In one year, it decreased by 3.8 lakh crore, which is a big achievement.
2. Primary Deficit in 2020 increased to 6.9 lakh crore from 4.7 lakh crore in 2019. In 2021, it went down to 2.4 lakh crore. In one year, it decreased by 4.5 lakh crore, which is also a big achievement.
3. Fiscal Deficit in 2020 increased to 135.1% of budget expenditure from 114. 8% in 2019. In 2021, it is 46.2% of budget expenditure.
(b) Allocation of Resources:
1. Objective of private sector is to maximise profits while objective of public sector is to maximise social welfare. Budget tries to maintain the balance between different objectives of all sections.
2. Private Sector allocates its resources where it finds profitable like liquor, cigarettes etc. But under budgetary policy, Government imposes heavy taxes on these socially undesirable goods so as to discourage their consumption.
3. Public Sector allocates its resources where it finds socially desirable like water supply, sanitation etc. So, no taxes are imposed or even subsidies are given as to encourage their consumption.
OR
(a)
| Basis of difference | Revenue Receipts | Capital Receipts |
| 1. Meaning | Those receipts of Government which
|
Those receipts of Government which
|
| 2. Nature | These are recurring in nature. | These are non-recurring in nature. |
| 3. Examples | Tax and Non-tax Receipts (Fees, fines, Escheat, Income from PSUs) etc. | Borrowings, Disinvestment, Recovery of Loans etc |
(b)
| Basis of Difference | Direct Taxes | Indirect Taxes |
| 1. Meaning | Those tax which are paid by those on whom the taxes are imposed i.e., Burden of tax cannot be shifted onto another person. | Those taxes whose initial burden is on one person but he shifts the burden partially or wholly on another person. |
| 2. Imposition | These are imposed on Income, wealth and profits of Individuals and corporate sector. | These are imposed on goods and services consumed by household sector. |
| 3. Examples | Income Tax, Wealth Tax, Gift Tax, Corporate, Profit Tax etc. | GST |
Section-B (Indian Economic Development)
Question 18.
Identify, which of the following indicates the adverse impact of British rule in India. [1]
(a) Introduction of communication networks in India.
(b) Change in composition of India’s foreign trade.
(c) Introduction of modern administrative system in India.
(d) Introduction of railways in India.
Answer:
(b) Change in composition of India’s foreign trade.
Explanation: Introduction of Railways, communication network and effective administrative system are positive impacts of British rule in India.
Question 19.
_____ committee was set up for the development and promotion of small scale industries in India. [1]
(a) Karve
(b) Tapas Majumdar
(c) Mahalanobis
(d) TRYSEM
Answer:
(a) Karve
Explanation: Karve committee was set up for the development and promotion of small scale industries in India in 1955. Karve committee was named after economist D. G. Karve.
OR
First Industrial Policy Resolution of Independent India was announced in the year _____. (Fill in the blank with correct alternative) [1]
(a) 1947
(b) 1948
(c) 1951
(d) 1956
Answer:
(b) 1948
Explanation: First Industrial Policy resolution of Independent India was announced in 1948. First Industrial Policy was implemented in 1956.
![]()
Question 20.
_____and _____ are the reasons for the slowdown of the Pakistan economy since independence. [1]
I. political instability.
II. over-dependence on remittances from abroad.
III. stable performance of agriculture sector.
IV. growth of service sector
Alternatives:
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) III and IV
(d) I and IV
Answer:
(a) I and II
Explanation: Political Instability and over-dependence on remittances from abroad are the major reasons for slowdown of Pakistan economy.
OR
‘GLF’ with respect to the People’s Republic of China referred to as _____. (Choose the correct alternative). [1]
(a) Giant Leap Forward
(b) Great Lead Forum
(c) Great Leap Forward
(d) Giant Lead Forum
Answer:
(c) Great Leap Forward
Explanation: Great Leap forward was a campaign started by China in 1958 for speeding up the process of Industrialisation.
Question 21.
Identify which of the following is a source of non-institutional credit in the rural areas of India. [1]
(a) NABARD
(b) Regional Rural Banks
(c) Money Lenders
(d) Commercial Banks
Answer:
(c) Money Lenders
Explanation: NABARD, RRBs and Commercial banks are source of institutional credit in the rural areas of India.
Question 22.
From the set of the events given in Column-I and corresponding facts given in Column-II, choose the correct pair of statement: [1]
| Column-I | Column-II |
| I. Dual Pricing | 1. Economic Reforms of 1991 |
| II. Setting up of Special Economic Zones in China | 2. To attract foreign Direct Investment |
| III. Commune System | 3. Backyard based Industrial production units |
| IV. Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution | 4. Collective Farming |
Choose the correct alternative:
(a) I – 1
(b) II – 2
(c) III – 3
(d) IV- 4
Answer:
(b) II – 2
Explanation: SEZs were set up in China so as to attract foreign investment because various amenities and benefits were provided to investors like tax holiday.
![]()
Question 23.
Read the following statements carefully: [1]
Statement 1: On-the-job trainings help to bridge a gap between theoretical concepts and practical experiences.
Statement 2: On-the-job trainings update the employees, with the latest changes in their work field.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative:
(a) Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false
(b) Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false
Answer:
(c) Both Statements 1 and 2 are true.
Explanation: On the Job training make employees up to date with new changes and new technology and bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical knowledge.
Question 24.
Read the following statements carefully: [1]
Statement 1: Both India and Pakistan initiated their economic reforms without any external pressures.
Statement 2: Pakistan has successfully implemented the SEZ policy and reaped its benefits using the Export Promotion policy.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct alternative:
(a) Statement 1 is true and statement 2 is false
(b) Statement 1 is false and statement 2 is true
(c) Both statements 1 and 2 are true
(d) Both statements 1 and 2 are false
Answer:
(d) Both Statements 1 and 2 are false:
Explanation: Both countries initiated their economic reforms under pressures of World Bank and IMF. Progress of SEZ in Pakistan has been very little.
Question 25.
_____ is not a cause for environmental degradation. [1]
(a) Waste management
(b) Deforestation
(c) Global warming
(d) Guarding green cover
Answer:
(d) Guarding green cover
Explanation: Guarding of green cover helps in protection of environment.
OR
_____ is not the strategy for Sustainable Development. [1]
Choose the correct alternative
(a) Use of biogas
(b) Use of solar power
(c) Use of thermal power
(d) Use of hydel power
Answer:
(c) Use of Thermal Power
Explanation: Use of Bio-gas, solar power and hydel power help in sustainable development.
Question 26.
Read the following statement -Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below: [1]
Assertion (A): Unemployment and poverty are inseparable twins.
Reason(R): Unemployment is the root cause of all socioeconomic evils.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
Explanation: Unemployment causes poverty and poverty causes unemployment. Unemployment is one of the causes of socioeconomic evils.
Question 27.
Read the following statement -Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below: [1]
Assertion (A): In the late 1970s, China’s population growth rate had sharply declined.
Reason(R): China has witnessed an increase in the proportion of elderly people owing to stringent family planning programmes.
Alternatives:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Explanation: In the late 1970s, China’s population growth rate had sharply increased. China has seen an increase in proportion of elderly people due to one-child policy.
Question 28.
Interpret the given picture on account of current environmental challenges. [3]

Answer:
1. This picture talks about current environmental challenge i.e., Global Warming.
2. “We are running out of time” says that we are over exploiting our natural resources for the greed of increasing demands. In one way or the other, natural resources are getting depleted at a very fast rate. It can be seen as melting of glaciers, increase in temperature of earth etc. We are not preserving the environment for future generation.
3. “Act now before it is too late” warns us to take strict and timely actions so as to protect the environment otherwise we will have to face the consequences like rise in sea level, floods etc.
Question 29.
Defend or refute the following statement with valid explanation:
‘Disguised unemployment is a common form of unemployment in rural India’. [3]
OR
Critically evaluate the role of rural banking system in the process of rural development in India. [3]
Answer:
I defend the given statement that disguised unemployment is a common form of unemployment in rural India.
1. Disguised Unemployment refers to a situation when the number of workers employed is more than required. And it is quite common in rural areas.
2. In Rural Areas, the most common occupation is farming and most of the members of a family are engaged on the farms. They seem to work but their marginal productivity is zero.
3. If some of the members are removed from the farms, there will be no effect on production.
OR
Role of Banks in Rural Development in India:
1. Expansion of commercial banks and cooperative banks helped in mobilisation of idle savings of people in rural areas.
2. Provision of credit to rural people for farming and non-farming occupations encouraged them to become self-employed.
3. Increased employment opportunities have led to increase in income of people and their standard of living.
Question 30.
Compare and analyse the following information related to Imports and Exports of the three neighbouring nations: [4]
| Country | Exports from India (in ₹ crore) | Imports to India (in ₹ crore) | ||||
| 2004-05 | 2018-19 | Annual rate of growth (%) | 2004-05 | 2018-19 | Annual rate of growth (%) | |
| Pakistan | 2,341 | 14,426 | 3.7 | 427 | 3,476 | 5.1 |
| China | 25,232 | 1,17,289 | 2.6 | 31,892 | 4,92,079 | 10.3 |
Answer:
Comparison with Pakistan:
Exports have shown annual growth rate of 3.7% while imports have shown annual growth rate of 5.1%. There is not much gap between exports and imports with Pakistan. It indicates less trade with Pakistan due to political reasons as compared to China.
Comparison with China:
Exports have shown annual growth rate of 2.6% while imports have shown annual growth rate of 10.3%. There is a huge gap between exports and imports with China. It indicates that India is becoming over-dependent on Chinese products which is a threat for domestic industries.
Question 31.
(a) Name any one Maharatana company.
(b) ‘Land ceiling promotes equity.’ Support the given statement with valid explanation. [4]
OR
Discuss briefly, how institutional reforms (land reforms) have played a significant role in transforming Indian agriculture. [4]
Answer:
(a) Maharatna Company- ONGC ( Oil and Natural Gas Corporation limited).
(b) Land Ceiling promotes equity:
(i) Land ceiling means fixing the maximum size of land which could be owned by an individual, beyond which it would be taken over by the government and would be allotted to landless and small farmers.
(ii) This policy is meant to bridge the gap between haves and haves not or to promote equitable distribution of resources.
OR
Institutional Reforms (Land Reforms):
Abolition of intermediary system: Zamindari, Mahalwari and Ryotwari System were abolished. Tillers of the soil were made owners of the land so that the actual cultivators could pay attention to the farm productivity and modern technology.
Land ceiling: It refers to fixation of maximum size of land holding. Excess land taken away was redistributed to the landless farmers. Beyond this limit, owners of land had to give up the land.
Consolidation of land holdings: Land holdings of farmers were small and scattered. Land holdings were consolidated i.e., these scattered pieces of land were converted to a single big one. It reduced the cost of production.
Cooperative fanning: It implies that number of farmers could work together on a large scale and reap the benefits of pooling the resources. It reduced the cost of production and promoted the investment in modem technology.
Question 32.
State whether the following statements are true/false, with valid arguments:
(a) Human Capital and Human Development are one and the same thing.
(b) India has a poor stock of technical manpower. [4]
Answer:
(a) False
(i) Human capital and Human Development is not the same thing.
(ii) Human capital refers to the stock of skills, knowledge, abilities and expertise possessed by the population of a country at a given point of time.
(iii) Human development is the ultimate goal of economic progress and considers human being as an end. It is an index of human welfare.
(iv) Human capital is a narrow concept and Human Development is a broad concept.
(b) False
(i) India has a largest stock of technical manpower.
(ii) From the last few years, there has been an immense interest of people in the technical education.
(iii) Every year, lacs of graduates and post graduates having technical know-how enter in the production sector in India or outside India.
(iv) That is why; India has become an outsourcing hub for MNCs.
![]()
Question 33.
(a) Define agricultural marketing.
(b) Discuss briefly the importance of micro-credit programmes in rural development.
(c) Enlist any two problems faced by farmers in the initial years of organic farming. [6]
OR
(a) “India has failed to implement the recommendations of Education Commission of 1964 – 66.” Give valid arguments in support of the given statement.
(b) ‘Casual wage work is the major source of employment in rural India ‘. Defend or refute the given statement with valid reason. [6]
Answer:
(a) Agricultural Marketing:
(i) Agricultural Marketing is a process that involves the assembling, storage, processing, transport, packaging, grading and distribution of different agricultural goods across the country and abroad.
(ii) It ensures a reasonable price to the farmer.
(iii) It has become quite essential for the agricultural and rural development.
(b) Importance of Micro-credit Programmes in Rural Development:
(i) Pooling of Resources: In rural areas, Self-Help Groups (SHGs) have emerged as a micro-credit programme. Members of SHGs pool their resources with small savings and this is used to give credit to those who need it.
(ii) No Need of Collateral: Loans can be taken at reasonable rates from SHGs without any collateral or security. Also, loan is paid back in easy installments.
(c) Problems faced by Farmers:
(i) Lower yield at Higher Cost: The cost of production of organic products is much higher than the produce. So, these products have high prices which is the main problem faced by farmers.
(ii) Shorter Life Span: Organic products have shorter life span than chemically produced products as plants are not forced to grow more. So, people do not take much interest in buying these products.
(iii) Limited choice: There is a limited choice of food products in off-season in case of organic products. But it is not so in case of non-organic products. Various choices of non-organic products are available in the market in off-season.
OR
(a) The given statement is appropriate. Over the years India has not been able to raise the educational standards to the desired level. Education Commission of 1964-66 had recommended that at least 6 % of GDP should be spent on education so as to make a noticeable rate of growth in educational achievements. However, the current expenditure level has been quite inadequate. Thus, necessary steps must be taken by the government in this direction.
(b) The given statement is refuted. In rural areas, non-farm job opportunities are limited. People generally do not show preference to acquire skill and training for non-farm occupation. They prefers to stay on family farms and fields as self-employed.
Question 34.
Read the following text carefully and answer the given questions on the basis of the same and common understanding:
The Green Revolution in India began in the mid-1960s marking a transition from traditional agriculture in India to high-yielding varieties of seeds and the associated modem agricultural techniques. The need for introduction of Green Revolution in India arose due to a shortage of food grains in the post-independent period.
The government in the post-independent India wanted to ensure self-dependence in terms of food-grain production. Such efforts coincided with the development of high-yielding varieties of seeds of wheat developed by Dr. Norman Borlung and his associates in Mexico. These seeds also necessitated changes in farming techniques such as the addition of fertilizers, pesticides and better irrigation facilities.
High-yielding varieties of seeds were first introduced in India in the states of Punjab, Haryana and parts of western Uttar Pradesh. In the early period of the green revolution in India, the focus was to acclimatise the new system with the more resource-intensive agricultural methods. The argument for introducing the new crop varieties was to increase agricultural production in terms of higher crop yields.
The seeds introduced during the early period of the green revolution in Punjab were not high-yielding by themselves. These high yields were possible due to the seeds being highly responsive to certain inputs such as irrigation water and fertilizers. The green revolution in India, thus, necessitated a resource-intensive process whereby, those who could make significant capital investments could benefit, whereas, those others became more marginalized in regions affected by practices of the green revolution in India.
On one hand, the results derived from the green revolution helped farmers to increase their yield and income and on the other hand, it helped the government to procure and preserve more food grains through agencies like Food Corporation of India. These food grain reserves were helpful in creation of buffer stocks in India, which helped in the situations of adversities.
(a) Why was Green revolution implemented and how did it benefit the farmers?
(b) Justify the following statement with valid explanation:
‘Green revolution enabled the government to procure sufficient food grains to build its stocks that could be used during time of shortage’. [6]
Answer:
(a) Cause of Implementation of Green Revolution:
(i) Acute food Shortage: After Independence, India was facing shortage of food grains. Green revolution is associated with use of HYV seed, fertilisers, irrigation facilities and modern technology. To make country self-sufficient in production of good grains, green revolution was implemented.
Benefits to Farmers:
(ii) Increase in productivity and production: Introduction of HYV seeds and modem technology in farming, production of food grains increased up to nearly 25% in second phase.
(iii) Increased marketable surplus: Farmers were encouraged to sell their excess produce in the government-established regulated market and get reasonable prices. It led to increase in income of farmers.
(b) (i) Introduction of HYV seeds, chemical fertilizers, irrigation facilities and improved technology led to increase in both productivity and production of food grains.
(ii) Marketable surplus is purchased by government agencies like Food Corporation of India.
(iii) Procurement of sufficient food grains by FCI is stocked. This is called buffer stock.
(iv) This buffer stock is used whenever there is a shortage of food grains in the country.