Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry with Solutions Set 6 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Set 6 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions :
Read the following instructions carefully.
- There are 35 questions in this question paper with internal choice.
- SECTION A consists of 18 multiple-choice questions carrying 1 mark each.
- SECTION B consists of 7 very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.
- SECTION C consists of 5 short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.
- SECTION D consists of 2 case-based questions carrying 4 marks each.
- SECTION E consists of 3 long answer questions carrying 5 marks each.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed
Section – A
The following questions are multiple-choice questions with one correct answer. Each question carries 1 mark. There is no internal choice in this section.
Question 1.
The solubility of a gas varies directly with pressure of the gas is based upon:
(a) Raoult’s law
(b) Henry’s law
(c) Nemst’s distribution law
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Henry’s law
Explanation: Henry’s law states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of that gas above the surface of the solution. Hence, the solubility of a gas varies directly with pressure of the gas and is based upon the Henry’s law.
Question 2.
The number of Faradays required to reduce one mol of Cu2+ to metallic copper is:
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
Answer:
(b) Two
Explanation: Faraday’s first law state that “the amount of current passed through the electrode is directly proportional to the number of substances liberated from it.”
The reduction of the one mole of Cu2+ to metallic copper can be represented as:
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
Since, there are two moles of electron involved in this reaction thus the amount of charge required is 2F.
Question 3.
Which of the following is the correct order of arrangement of the first five lanthanides according to atomic number?
(a) La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm
(b) La, Pr, Ce, Pm, Nd
(c) La, Pr, Ce, Nd, Pm
(d) La, Ce, Pr, Pm, Nd
Answer:
(a) La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm
Explanation: The first five elements of Lanthanides are:
Lanthanum (La)-57
Cerium (Ce)-58
Praseodymium (Pr)-59
Neodymium (Nd)-60
Promethium (Pm)-61
![]()
Question 4.
Proteins are denatured in the:
(a) Mouth
(b) Stomach
(c) Small intestine
(d) Large intestine
Answer:
(b) Stomach
Explanation: Proteins are denatured in the stomach due to highly acidic medium.
Question 5.
The IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)3(Br)(NO2)Cl]Cl is :
(a) Triamminebromochloronitroplatinum(IV) chloride
(b) Triamminebromonitrochloroplatinum(lV) chloride
(c) Triamminechlorobromonitroplatinum(IV) chloride
(d) Triamminenitrochlorobromoplatinum(lV) chloride
Answer:
(a) Triamminebromochloronitroplatinum(IV) chloride
Explanation: The ligands are named in the alphabetic order according to the IUPAC nomenclature. For the given complex, the oxidation number of metal is +4. So, the name of [Pt(NH3)3(Br)(NO2)Cl]Cl is Triamminebromochloronitroplatinum(IV) chloride.
Question 6.
Which of the following poisonous gas is formed when chloroform is exposed to light and air?
(a) Mustard gas
(b) Carbon monoxide
(c) Phosgene
(d) Chlorine
Answer:
(c) Phosgene
Explanation: When chloroform is exposed to air and sunlight, it undergoes oxidation and releases a poisonous gas called Phosgene gas (COCl2) and Hydrochloric acid (HCl).
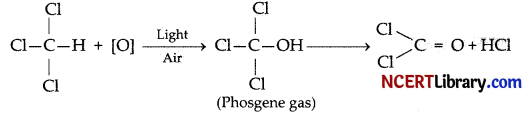
Question 7.
Which of the following statements about benzaldehyde is/are true?
(a) Reduces Tollen’s reagent
(b) Undergoes Aldol condensation
(c) Does not undergo Cannizzaro reaction
(d) Does not form an addition compound with sodium hydrogen sulphite
Answer:
(a) Reduces Tollen’s reagent
Explanation: Benzaldehyde reduces Tollen’s reagent and undergoes Cannizzaro reaction. However, it forms an addition compound with NaHS03 but does not undergo aldol condensation. Thus, the statement which is correct about benzaldehyde is that it reduces Tollen’s reagent.
Question 8.
The coordination number and oxidation state of Cr in K3[Cr(C204)3] are respectively.
(a) 3 and +3
(b) 3 and 0
(c) 6 and +3
(d) 4 and +2
Answer:
(c) 6 and +3
Explanation:
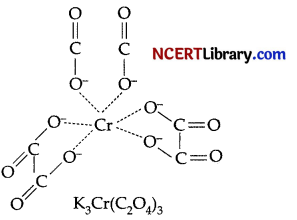
As the number of atoms of the ligands that are directly bound to the central metal is known as coordination number. It is six here.
Oxidation state:
Let oxidation state of Cr be x.
⇒ 3 (+1) x + 3 (-2) = 0
⇒ 3 + x – 6 = 0
⇒ x = 3
Question 9.
Which one of the following aldehyde gives Cannizzaro reaction when heated with strong alkali?
(a) Benzaldehyde
(b) Acetaldehyde
(c) Propionaldehyde
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Benzaldehyde
Explanation: Aldehydes that do not have alpha hydrogen atom will undergo Cannizzaro reaction. Since, benzaldehyde does not have alpha hydrogen atom in its structure, therefore, it will undergo Cannizzaro reaction. The reaction can be represented as:
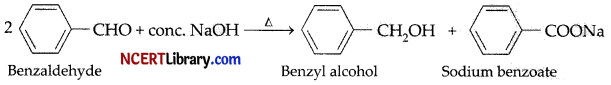
Question 10.
A 5% solution of cane-sugar (molecular weight = 342) is isotonic with 1% solution of substance A. The molecular weight of X is:
(a) 342
(b) 171.2
(c) 68.4
(d) 136.8
Answer:
(c) 68.4
Explanation:
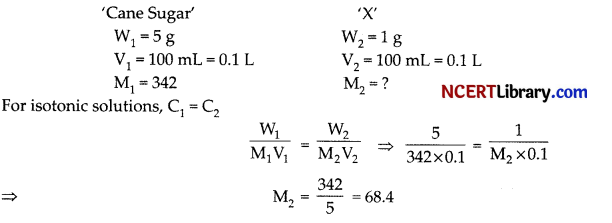
Hence, the molecular weight of X is 68.4.
Question 11.
A catalyst:
(a) Increase the free energy change in the reaction
(b) Decrease the free energy change in the reaction
(c) Does not increase or decrease the free energy change in the reaction
(d) Can either increase or decrease the free energy change depending on what catalyst we use
Answer:
(c) Does not increase or decrease the free energy change in the reaction
Explanation: The characteristics of catalysts are as follows:
- It catalyses the spontaneous reaction but not the non-spontaneous reaction.
- It does not change the equilibrium constant, but only helps in attaining equilibrium faster.
- A small amount of the catalyst can catalyse a large amount of reactants.
- It does not alter the AG (Gibbs free energy) of a reaction.
- It catalyses both forward and backward reactions to the same extent to maintain the equilibrium state in case of reversible reaction.
Hence, a catalyst does not increase or decrease the free energy change in the reaction.
![]()
Question 12.
Osmotic pressure of a solution is 0.0821 atm at a temperature of 300 K. The concentration in moles/litre will be:
(a) 0.33
(b) 0.666
(c) 0.3 x 10-2
(d) 3
Answer:
(c) 0.3 x 10-2
Explanation: Given that
Osmotic pressure at soln (π) = 0.0821 at m
Temperature, T = 300 K
Now, π = CRT
C = \(\frac{0.0821}{0.0821 \times 300}\) = 3.33 x 10-3M
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) x 10-2M
Molarity of the solution,
M = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) x 10-2M
= 0.3 x 10-2
Question 13.

Identify Z.
(a) 2-lodoheptane
(b) Heptane-2-ol
(c) 2-lodohexane
(d) Heptanoic acid
Answer:
(d) Heptanoic acid
Explanation:
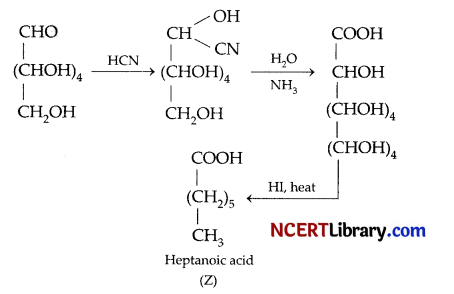
Question 14.
The effect of a catalyst in a chemical reaction is to change the:
(a) Activation energy
(b) Equilibrium concentration
(c) Heat of reaction
(d) Final products
Answer:
(a) Activation energy
Explanation: The effect of a catalyst in a chemical reaction is to change the activation energy because a catalyst provides an alternate pathway or reaction mechanism by reducing the activation energy of reactants.
Question Number: 15 to 18 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Question 15.
Assertion (A): Fibrous protein is a fibre-liked structure formed by the polypeptide chain. These proteins are held together by strong hydrogen and disulphide bonds.
Reason (R): It is usually soluble in water.
Answer:
(c) A is true, but R is false.
Explanation: The proteins which consist of linear, thread-like polypeptide chains arranged or twisted to form fibers are called fibrous proteins. The long chain in fibrous protein is held together by hydrogen bonds and some disulphide bonds. They are insoluble in water. Hence, assertion is true but reason is false.
Question 16.
Assertion (A): Transition metals and their many compounds act as good catalyst.
Reason (R): It is due to variable magnetic property.
Answer:
(c) A is true, but R is false.
Explanation: The transition metals and their compounds are known for their catalytic activity. This is because of their ability to adopt multiple oxidation states and to form complexes. Also, transition metals sometime form unstable intermediate complex which provide a new path with lower activation energy for the reaction.
Transition elements provide a suitable surface for the reaction to take place. Since, the transition metal ions can change their oxidation states, they become more effective as catalysts. Thus, assertion is true but reason is false.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): To obtain maximum work from a galvanic cell, charge has to be passed reversibly.
Reason (R): The reversible work done by a galvanic cell is equal to decrease in its Gibbs energy.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Electrical work done in one second is equal to electrical potential multiplied by total charge. If we want to obtain maximum work from a galvanic cell then charge has to be passed reversibly. The reversible work done by a galvanic cell is equal to decrease in its Gibbs energy and therefore, if the emf of cell is E and nF is the amount of charge passed and AG is the Gibbs energy of reaction then,
∆G = – nFEcell
Question 18.
Assertion (A): Ethanal is soluble in water.
Reason (R): Lower aldehydes form effective hydrogen bond with water molecules.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: : Ethanal is soluble in water in all proportions. The reason for the solubility is that although aldehydes cannot hydrogen bond with themselves, but lower aldehydes can hydrogen bond with water molecules. Thus, both assertion and reason is correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Section – B
This section contains 7 questions with internal choice in two questions. The following questions are very short answer type and carry 2 marks each.
Question 19.
(a) What is meant by ‘limiting molar conductivity’?
(b) Express the relation between conductivity and molar conductivity of a solution held in a cell.
Answer:
(a) The molar conductivity of a solution at infinite dilution is called limiting molar conductivity and is represented by the symbol Am.
(b) The molar conductivity of a given solution is related to conductivity as:
\(\Lambda_m=\frac{\mathrm{K}}{\mathrm{C}}=\frac{\text { Conductivity }}{\text { Concentration }}\)
Question 20.
Write the IUPAC name of :
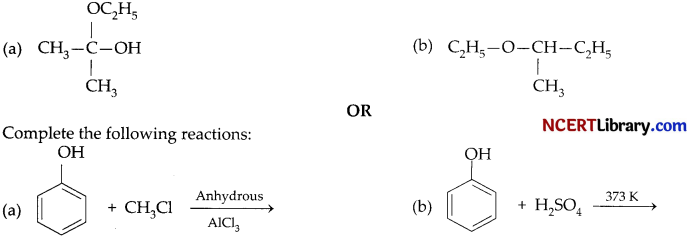
Answer:
(a) 2-Ethoxy-propan-2-ol
(b) 2-Ethoxybutane
OR
Question 21.
(a) What is primary valency of a metal?
(b) Which chelating ligand is used in lead poisoning.
OR
Explain homoleptic and heteroleptic complexes with suitable examples.
Answer:
(a) Primary valency is equal to oxidation state of central atom. It is satisfied by negatively charged ions. It is non-directional and ionisable.
(b) EDTA (Ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) is used in lead poisoning.
OR
Complexes in which metal is bound to only one kind of ligand are know as homoleptic complexes, e.g., [Fe(CH)4]4-
Complexes in which metal is bound to more than one kind of ligand are known as heteroleptic complexes, e.g., [CO(NH3)4Cl2]+.
Question 22.
Given below is the sketch of a plant of carrying out a process.
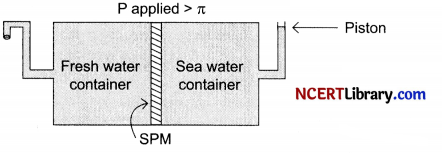
(a) Name the process occurring in the above plant.
(b) Name one SPM which can be used in this plant.
(c) Give one practical use of the plant.
Answer:
(a) Reverse osmosis
(b) Film of cellulose acetate
(c) This can be used as a desalination plant to meet potable water requirements.
Answer the following questions:
Question 23.
(a) La (5d16s2), Gd (4f75d16s²) and Lu (4f145d16s²) have abnormally low third ionisation enthalpies. Why?
(b) Which element among 3d transition elements exhibits the highest oxidation state?
Answer:
(a) La3+, Gd3+ and Lu3+ have stable configuration 4f0, 4f7 and 4f14 respectively. So, they prefer the formation of low energy +3 states and hence third ionisation enthalpies are low.
(b) Among 3d transition elements Manganese (Mn) exhibits the highest oxidation state of (+7).
![]()
Question 24.
Write any three differences between potential difference and EMF.
Answer:
| Potential difference | EMF |
| 1. It is difference between electrode potential of two electrodes when no current is flowing through circuit. | It is difference of potential between electrode in a closed circuit. |
| 2. It is the maximum voltage obtained from a cell. | It is less than maximum voltage obtained from a cell. |
| 3. It is responsible for a steady flow of current. | It is not responsible for a steady flow of current. |
Question 25.
What are azeotropes? Give an example.
Answer:
An azeotrope is a mixture of two or more liquids whose proportions cannot be altered by simple distillation because their composition is unchanged by distillation, azeotropes are also called constant boiling mixture.
Example: 95% ethanol and 5% water mixture has a boiling point 78.17°C. This is a minimum boiling azeotropic mixture.
Section – C
This section contains 5 questions with internal choice in two questions. The following questions are short answer type and carry 3 marks each.
Question 26.
(a) On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if ∆0 < P.
(b) [NiCl4]2- is paramagnetic, while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic, though both are tetrahedral. Why? (Atomic number of Ni = 28)
OR
(a) Which type of compounds show linkage isomerism? What would be the structural formula for linkage isomer of [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2?
(b) How are the inner orbital complexes formed?
(c) What is a chelate ligand? Give one example.
Answer:
(a) On the basis of crystal field theory, for a d4 ion, if ∆0 < P, then the complex is a high spin complex formed by association of weak field ligands with the metal ion. As a result, the fourth electron enters one of the e orbitals, thereby, exhibiting the electronic configuration t2g3 eg1
(b) Though both [NiCl4]2- and [Ni(CO)4] are tetrahedral, their magnetic characters are different. This is due to a difference in the nature of ligands. CL is a weak field ligand and it does not cause the pairing of unpaired 3d electrons. Hence, [Ni(CO)4] paramagnetic.
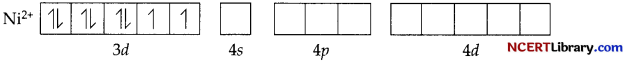
In [Ni(CO)4], Ni is in the zero oxidation state i.e., it has a configuration of 3d8 4s².
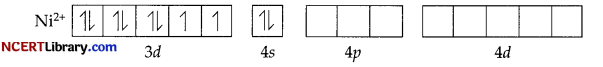
But CO is a strong field ligand. Therefore, it causes the pairing of unpaired 3d electons. Also, it causes the 4s electrons to shift to the 3d orbital, thereby giving rise to sp3 hybridization. Since no unpaired electrons are present in this case. [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic.
OR
(a) Linkage isomerism arises in a coordination compound containing ambidentate ligand. The structural formula for linkage isomer of [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2 would be [Co(NH3)5(ONO)]Cl2.
(b) Inner orbital complexes are coordination compounds composed of a central metal atom having hybridization of the atomic orbitals including d-orbitals of inner shell and s, p-orbitals from the outer shell. In other words, the central metal atom of these complexes uses inner shell d-orbitals for the hybridization of atomic orbitals. Therefore, these d-orbitals are in a lower energy level than s and p-orbitals. The most common hybridization of the metal atom in inner orbital complexes is d²sp³. But there can be some other hybridizations as well, such as dsp².
(c) The ligands which can form two co-ordinate covalent bonds through two donor atoms are called bidentate ligands. These bidentate ligands are also called chelate ligands.
Example: C2O4-2,CO3-2 etc.
Question 27.
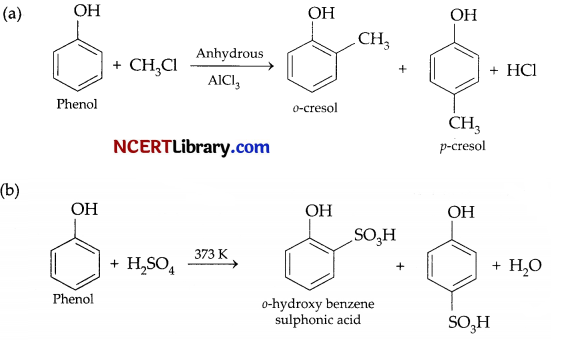
(a) What is Hinsberg reagent?
(b) Complete the following equations:
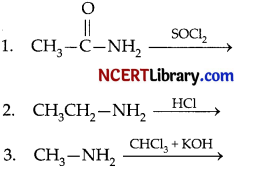
Answer:
(a) Benzenesulphonyl chloride (C6H5 – SO2Cl) is known as Hinsberg reagent.
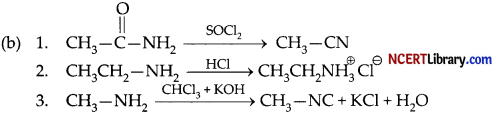
Question 28.
Answer following questions :
(a) What is Lanthanoid contraction? What is the cause of Lanthanoid contraction?
(b) Explain why Cu2+ ion is stable in aqueous solution.
(c) Trivalent Lanthanoid ions are coloured, why?
Answer:
(a) The gradual decrease in atomic radii from La to Lu due to poor screening effect of 4f -electrons is called Lanthanoid contraction.
1. Lanthanoid contraction of 4f-electron.
2. Increased effective nuclear charge.
(b) In an aqueous solution, Cu2+ is more stable than Cu+. Hydration enthalpy of Cu2+ ion is more negative which more than compensates for the second ionisation enthalpy of Cu.
(c) Trivalent lanthanoids are coloured due to the presence of f-electrons which causes f-f electronic transition.
Question 29.
The electrical resistance of a column of 0.05 M NaOH solution of diameter 1 cm and length 50 cm is 5.55 x 10³ ohm. Calculate its:
(a) Resistivity
(b) Conductivity
(c) Molar conductivity
Answer:
(a) Resistivity:
A = πr² = 3.14 (0.5)² cm² = 0.785 cm²
l = 50 cm
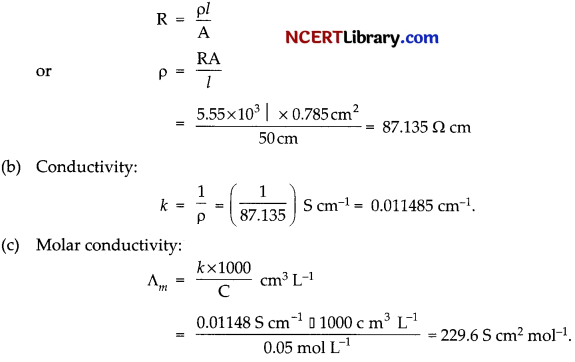
Question 30.
(a) Why C6H5NH2 is a weaker base than NH3?
(b) Give three factors on which basicity of amines in aqueous solution depends upon.
OR
This important class of organic compounds are derived by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia molecule by alkyl or aryl group(s). The nitrogen atom in this class of compound is trivalent. There are many important natural and synthetic compounds of this class. A lot of important drugs also belong to this class of compounds.
(a) Name the class of compounds being discussed. What is the hybridisation state of nitrogen in these class of compounds?
(b) What is ammonolysis?
(c) What are the compounds obtained on?
Answer:
(a) Lone pair on Nitrogen in aniline are involved in resonance with the benzene ring and therefore not available for donation to that extent as in NH3. According to Lewis theory, the species which easily loses a pair of electron is Lewis base. Since ammonia can lose easily electron pair while aniline cannot, thus ammonia is a stronger base than aniline.
(b) Basicity of amines in aqueous solution depends upon:
1. +1 effect of an alkyl group.
2. Extend of hydrogen bonding with H2O.
3. Steric effects of alkyl groups.
OR
(a) The class of compounds here is ‘amines’. Hybridisation state of nitrogen in these class of compounds is sp³.
(b) The process of cleavage of C-X bond of an alkyl halide molecule by ammonia molecule is known as ammonolysis. The halogen atom of alkyl or benzyl halide gets replaced by an amino (-NH2) group. The primary amine thus obtained behaves as a nucleophile and in subsequent reactions, secondary amine, tertiary amine and quaternary ammonium salts are produced.
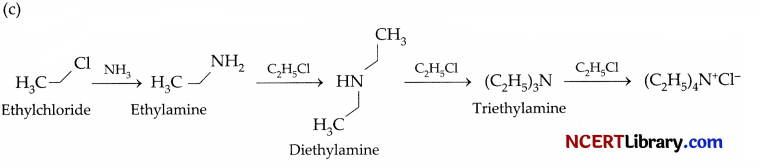
Section – D
The following questions are case-based questions. Each question has an internal choice and carries 4 (1+1+2) marks each. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Question 31.
The reaction of ethanol with cone. H2SO4 was carried out under different thermal conditions and following results are obtained as furnished below:
| Reactant | Temperature | Product |
| Ethanol + Conc. H2SO4 | 25°C (Room temperature) | CH3CH2OSO3H (Ethyl hydrogen sulphate) |
| Ethanol + Conc. H2SO4 | 140°C | CH3-CH2-O-CH2-CH3 (diethyl ether) |
| Ethanol + Conc. H2SO4 | 170°C | CH2 = CH2 (Ethylene) |
Answer the following questons:
(a) Predict the product when ethanol is treated with cone. H2SO4 at O°C.
(b) At 170°C, the product formed in the table follow substitution or elimination pathway?
(c) Write the reaction mechanism involved in the above mentioned reaction at 170°C.
OR
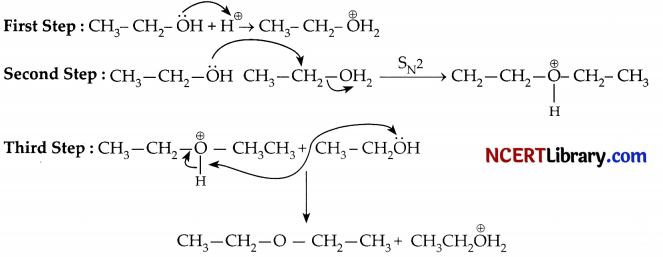
Write the reaction mechanism involved in the above mentional reaction at 140°C.
Answer:
(a) ![]() (Ethyl oxonium hydrogen sulphate)
(Ethyl oxonium hydrogen sulphate)
(b) Elimination pathway is followed by the product formed at 170°C
(c) H2SO4 → H+ + HSO4–
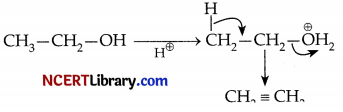
OR
The reaction actually takes place through the following three steps:
Question 32.
Water solubility of some organic compounds alongwith some carbohydrates were investigated and observations are furnished as follow:
| Organic compound | Solubility in H2O |
| Glucose | ✓ |
| Sucrose | ✓ |
| Benzene | ✗ |
| Cyclohexane | ✗ |
Answer the following questions:
(a) How many -OH groups are present in a suerose molecule?
(b) What happens when glucose is treated with dilute NaOH?
(c) Why Glucose or Sucrose is water soluble?
OR
Why cyclohexane or benzene is water insoluble?
Answer:
(a) Eight -OH groups are present in the sucrose molecule.
(b) When glucose is treated with dilute NaOH, it forms a mixture of D-glucose, D-Fructose and D-Mannose due to reversible isomerisation.
(c) There are five -OH groups present in the glucose molecule and right -OH groups in the sucrose molecule. These -OH groups link to water molecules strongly by hydrogen bonds. That is why glucose and sucrose are water soluble.
OR
Cylohexane and benzene are hydrocarbons lacking any -OH group. So, these compounds can not form hydrogen bonds with water and hence, are water insoluble.
Section – E
The following questions are long answer type and carry 5 marks each. Two questions have an internal choice.
Question 33.
What happens when:
(a) Bromobenzene is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether.
(b) Chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis.
(c) Ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH.
(d) Methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether.
(e) Methyl chloride is treated with KCN.
OR
(a) Complete the following reactions:
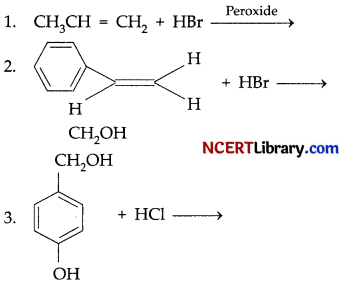
(b) 1. Why does ammonolysis of alkylhalides does not yield pure amines?
2. Why do haloalkanes dissolve in organic solvents.
Answer:
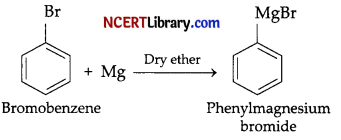
(a) When bromobenzene is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether, phenylmagnesium bromide a Grignard’s reagent is formed.
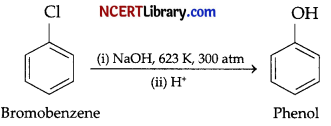
(b) Chlorobenzene does not undergo hydrolysis under normal conditions. It only undergoes hydrolysis when heated in an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at a temperature of 623 K and a pressure of 300 atm to form phenol.
(c) When ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH, it undergoes hydrolysis to form ethanol.
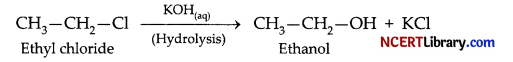
(d) When methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether, ethane is formed. This reaction is known as the Wurtz reaction.
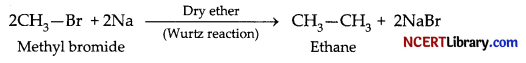
(e) When methyl chloride is treated with KCN, it undergoes a substitution reaction to give methyl cyanide.

OR
(b) 1. Ammonolysis of alkylhalides does not give a single amine but gives a mixture of primary, secondary and tertiary amines which further react with alkyl halide to form quaternary ammonium salt as follow:
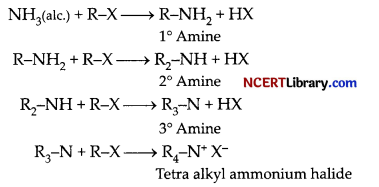
It is difficult to separate this mixture into individual amines therefore, it is difficult to prepare pure amines by ammonolysis of alkylhalides. The ammonolysis of alkyl halide with ammonia is a nucleophilic substitution reaction in which ammonia acts as a nucleophile by donating the electron pair on nitrogen atom.
2. Haloalkanes dissolve in organic solvents because the new intermolecular attraction between haloalkanes and organic solvent molecules have the same strength as the one being broken in the separate haloalkanes and solvent molecules.
Question 34.
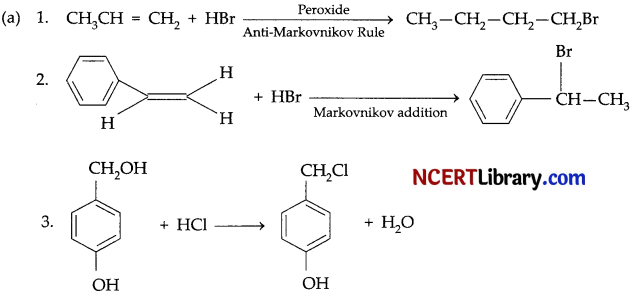
(a) What would be effect of a ‘substitution of phenyl ring’ on acidity of an aromatic carboxylic acid?
(b) During preparation of aldehydes, acids are found as impurities in reaction mixture. Give a reagent for preparation of aldehydes starting from alcohol by their controlled oxidation.
(c) Biologists preserve their samples of animals and plants in chemical called Formalin. What is the chemical composition of formalin?
(d) What happens when CH3CHO is treated with K2Cr2O2 in presence of H2SO4?
(e) Write a test to distinguish between pentanal and pentanone.
OR
(a) An organic compound X has molecular formula C5H10O. It does not reduce Fehling’s solution but forms a bisulphate compound. It also gives positive iodoform test. What are possible structures of X? Explain your reasoning relating structure.
(b) Write IUPAC name of the following:
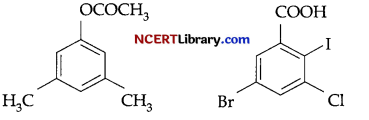
(c) How are following obtained:
1. Benzoic acid from ethyl benzene
2. Benzaldehyde from toluene.
Answer:
(a) The substituted group on phenyl ring would be either an electron with drawing or electron donating group. The presence of electron with drawing group on the phenyl ring of aromatic carboxylic acid increases their acidity while electron donating groups decrease their acidity.
(b) Primary alcohols can be oxidised using combination of pyridiniumchlorochromate and chromic oxide (CrO3) to obtain aldehydes only and further oxidation to carboxylic acid does not happen to give acidic impurities.
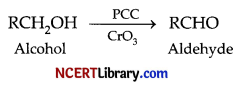
(c) Chemical composition of formalin is 40% aqueous solution of formaldehyde (HCHO).
(d) CH3CHO is oxidised to acetic acid when it is treated with K2Cr2O7 in presence of H2SO4.
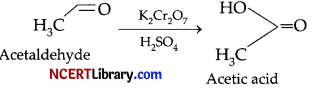
(e) Pentanal being an aldehyde would give the silver mirror test with Tollen’s reagent whereas pentanone being a ketone does not reduce Tollen’s reagent and hence does not give the silver mirror test.
OR
(a) As the compound gives adduct with bisulphite, i.e., bisulphate compound, it contains a carboxyl group. But it does not reduce Fehling’s solution so it must be a ketone. Now, as this gives a positive test with iodoform, it is methyl ketone.
So, based on the above information the following structures for a 5 carbon atom containing methyl ketone.
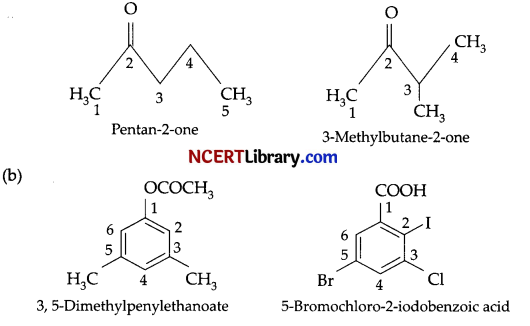
(c) 1. Benzoic acid from ethyl benzene:
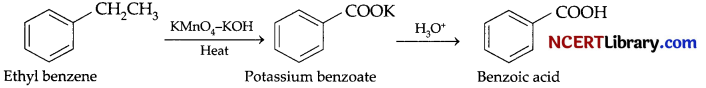
2. Benzaldehyde from toluene: It can be obtained by Etard reaction.
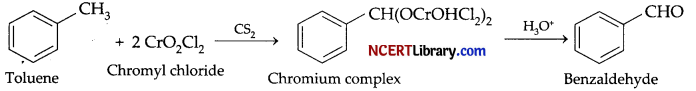
Question 35.
For the hydrolysis of methyl acetate in aqueous solution, the following results were obtained:
| t/s | 0 | 10 | 20 |
| [CH3COOCH3]/mol L-1 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.025 |
(a) Show that it follows pseudo first order reaction, as the concentration of water remains constant.
(b) Calculate the average rate of reaction between the time interval 10 to 20 seconds.
(Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 4 = 0.6021)
(c) For a reaction A + B → P, the rate is given by Rate = k [A][B]².
1. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of B is double?
2. What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess?
(d) A first order reaction takes 30 minutes for 50% completion. Calculate the time required for 90% completion of this reaction.
Answer:
(a) [A]o = 0.01 mol/L
[A] = 0.05 mol/L at time t = 10 s.

Thus, its pseudo first order reaction.
(b) The average rate constant is:
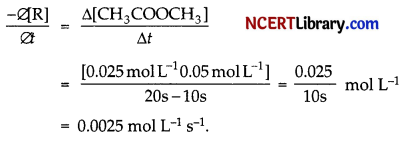
(c) 1. Since the given reaction has order two with respect to reactant B, thus it the concentration of B is doubled in the given reaction, then the rate of reaction will become four times.
2. If the concentration of B is doubled i.e., [B]² the overall reaction will be two, because if A is present in large excess, then the reaction will be independent of the concentration of A and will be dependent only on the concentration of B. Order of reaction 2.
(d) we have,
