Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry with Solutions Set 5 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Set 5 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions :
Read the following instructions carefully.
- There are 35 questions in this question paper with internal choice.
- SECTION A consists of 18 multiple-choice questions carrying 1 mark each.
- SECTION B consists of 7 very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.
- SECTION C consists of 5 short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.
- SECTION D consists of 2 case-based questions carrying 4 marks each.
- SECTION E consists of 3 long answer questions carrying 5 marks each.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed
Section – A
The following questions are multiple-choice questions with one correct answer. Each question carries 1 mark. There is no internal choice in this section.
Question 1.
When chlorine is passed through propene at 400°C, which of the following is formed?
(a) PVC
(b) Allyl chloride
(c) Vinyl chloride
(d) 1, 2-Dichloroethane
Answer:
(b) Allyl chloride
Explanation: When chlorine gas is reacted with propene at high temperature (400°C) then substitution takes place in place of addition reaction. Hence, allyl chloride is formed.
Question 2.
Acidified potassium dichromate reacts with potassium iodide and oxidises it to I2. What is the oxidation state of chromium in the products of the reaction?
(a) +4
(b) +6
(c) +3
(d) +2
Answer:
(c) + 3
Explanation: K2Cr2O7 + 7H2SO4 + 6KI → 4K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 + 7H2O + 3I2
We have Cr2(SO4)3 in the product in which the oxidation state of Cr is calculated as:
Let, x is the oxidation state of Cr, so,
2x + 3(- 2) = 0
x = + 3
Question 3.
The magnetic moment is associated with its spin angular momentum and orbital angular momentum. Spin only magnetic moment value of Cr3+ ion is:
(a) 2.87 BM
(b) 3.87 BM
(c) 3.47 BM
(d) 3.57 BM
Answer:
(b) 3.87 BM
Explanation: Cr → (Z = 24)
Cr3+ → (Z = 21)
1s², 2s², 2p6, 3s², 3p6, 3d³, 4s0
n = 3(3 unpaired electrons)
μ = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}\) = \(\sqrt{3(3+2)}\)
μ = \(\sqrt{3(5)}\) = \(\sqrt{15}\) = 3.87 BM
![]()
Question 4.
Chlorobenzene on treatment with sodium in dry ether gives diphenyl. The name of the reaction is:
(a) Fittig reaction
(b) Wurtz-Fittig reaction
(c) Sandmeyer reaction
(d) Gattermann reaction
Answer:
(a) Fittig reaction
Explanation: If only aryl halide reacts with sodium in presence of other, the reaction is called ‘Fittig’ reaction.
Question 5.
What weight of glycerol should be added to 600 g of water in order to lower its freezing point by 10°C?
(a) 496 g
(b) 297 g
(c) 310 g
(d) 426 g
Answer:
(b) 297 g
Explanation: Given that,

Question 6.
The reaction is spontaneous if the cell potential is:
(a) Positive
(b) Negative
(c) Zero
(d) Infinite
Answer:
(a) Positive
Explanation: Gibb’s free energy is given by
∆rG = – nFEcell
For spontaneous reaction, we know
∆rG = – ve
Ecell = + ve (∵ F are constant )
Question 7.
Which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) Lowering in vapour pressure is a colligate property.
(b) The depression in freezing point is directly proportional to molality of the solution.
(c) A plant cell swells when placed in hypertonic solution.
(d) A saturated solution will remain saturated at all temperatures.
(b) The depression in freezing point is directly proportional to molality of the solution.
Explanation: We know that,
T = Kf m
So, ∆T ∝ m
Where, m is the molality of the solution.
Thus, the depression of freezing point is directly proportional to the molality of the solution.
Question 8.
Rate law for the reaction A + 2B → C is found to be:
Concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be _______.
(a) The same
(b) Doubled
(c) Quadrupled
(d) Halved
Answer:
(b) Doubled
Explanation: The rate concentration of a reaction does not depend upon concentration of the reactions. Hence, it will remain the same. Even if the equation shows the double concentration level the rate concentration doubles so it is the same throughout.
Following with the equation A + 2B → C
If rate considered as (1) Rate1 = k [A][B]
If rate considered as 2
Then, Rate1 = k [A][2B]
Rate2 = 2 Rate1
Hence, the value of rate constant will be doubled.
![]()
Question 9.
The cell constant of a conductivity cell.
(a) Changes with change of electrolyte
(b) Changes with change of concentration of electrolyte
(c) Changes with temperature of electrolyte
(d) Remains constant for a cell
Answer:
(d) Remains constant for a cell
Explanation: The cell constant of a conductivity cell remains constant for a cell. The cell constant (K) is equal to the distance in cm between the probe’s electrodes divided by the surface area of the electrodes in cm². The cell constant depends on the area of the electrodes, distance between the electrodes and the nature of the electric field between the electrodes.
Cell constant = Length/Area
For a particular conductivity cell, the cell constant remains the same even if:
- The electrolyte is changed.
- The concentration of the electrolyte is changed.
- The temperature of electrolyte is changed.
Question 10.
Which of the following is not a colligative property?
(a) Osmotic pressure
(b) Boiling point
(c) Vapour pressure
(d) Electrical conductivity
Answer:
(d) Electrical conductivity
Explanation: A colligative property may be defined as one which depends on the number of particles in solution and not in any way on the size or chemical nature of the particles.
The four principle colligative properties are:
- Lowering of the vapour pressure.
- Elevation of the boiling point.
- Depression of the freezing point.
- Osmotic pressure.
Thus, electrical conductivity is not a colligative property.
Question 11.
If 96500 coulomb electricity is passed through CuSO4 solution, it will liberate:
(a) 63.5 g of Cu
(b) 31.76 g of Cu
(c) 96500 g of Cu
(d) 100 g of Cu
Answer:
(b) 31.76 g of Cu
Explanation: At cathode: Cu2+(aq) + 2e– → Cu(s)
At anode: 4OH–(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g) + 4e–
Faraday’s constant = 96500 C/mol To deposite 1 mole of copper, we need 2 x 96500 C. So,
96500 C will deposite 0.5 moles of copper = 0.5 x 63.5 = 31.75 g.
Hence, 31.76 gm of Cu will be liberated.
Question 12.
Which catalyst is used in the hydrogenation of acetyl chloride to produce ethanal?
(a) Pt over BaSO4
(b) Pt over CuSO4
(c) Pd over BaSO4
(d) Pd over CuSO4
Answer:
(c) Pd over BaSO4
Explanation: Acetyl chlorides are hydrogenated in the presence of catalyst palladium over barium sulphate to produce ethanal. This is known as Rosenmund reaction. The reaction can be represented as follows:
Question 13.
Transition metals, when they form interstitial compounds, the non – metals (H, B, C, N) are accommodated in:
(a) Voids or holes in cubic-packed structure
(b) Tetrahedral voids
(c) Octahedral voids
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Explanation: Transition metals have defects in their crystal lattice. The transition metals form interstial compounds as small atoms like C, H or N are trapped inside the interstial spaces in the crystal lattice of metals. Hence, transition metals, when they form interstial compounds, the non-metals are accomodated in voids.
Question 14.
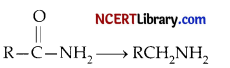
Which one of the following reducing agents is likely to be most effective in bringing about the following change?
(a) H2 – Ni
(b) NaBH4
(c) LiAlH4 ether
(d) Na-Alcohol
Answer:
(c) LiAlH4 ether
Explanation: The given reaction is the reduction of primary amides in the presence of the reducing agent LiAlH4 to primary amines.
Question No. 15 to 18 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Assertion (A): It is not always convenient to determine the instantaneous rate.
Reason (R): Instantaneous rate is measured by the determination of slope of the tangent at point Y in concentration versus time plot.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: It is not always convenient to determine the instantaneous rate, as it is measured by determining the slope of the tangent at point Y in concentration Vs time plot. This generally makes it difficult to determine the rate law and hence, the order of the reaction. Hence, both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 16.
Assertion (A): Ethanol is a weaker acid than phenol.
Reason (R): Sodium ethoxide may be prepared by the reaction of ethanol with aqueous NaOH.
Answer:
(c) A is true, but R is false.
Explanation: Phenol is stronger acid than ethanol as phenoxide ion is stabilized by resonance whereas no such stabilization occurs in ethoxide ion. Sodium ethoxide can be prepared by reaction of ethanol with sodium. Thus, assertion is true but reason is false.
![]()
Question 17.
Assertion (A): When NaCl is added to water a depression in freezing point is observed.
Reason (R): The lowering of vapour pressure of a solution causes no depression in the freezing point.
Answer:
(c) A is true, but R is false.
Explanation: When NaCl is added to water a depression in freezing point is observed. This is due to lowering of vapour pressure of a solution. Thus, assertion is true but reason is false.
Question 18.
Assertion (A): To obtain maximum work from a galvanic cell, charge has to be passed reversibly. Reason (R): The reversible work done by a galvanic cell is equal to decrease in its Gibbs energy.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Electrical work done in one second is equal to electrical potential multiplied by total charge. If we want to obtain maximum work from a galvanic cell then charge has to be passed reversibly. The reversible work done by a galvanic cell is equal to decrease in its Gibbs energy and therefore, if the emf of cell is E and n¥ is the amount of charge passed and AG is the Gibbs energy of reaction then,
∆G = – nFEcell
Thus, both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Section – B
This section contains 7 questions with internal choice in two questions. The following questions are very short answer type and carry 2 marks each.
Question 19.
Why do primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines?
Answer:
In a molecule of tertiary amine, there are no H-atoms whereas in primary amines, two hydrogen atoms are present. Due to the presence of H-atoms, primary amines undergo extensive intermolecular H-bonding. In a molecule of tertiary amine, there are no H-atoms whereas in primary amines, two hydrogen atoms are present. Due to the presence of H-atoms, primary amines undergo extensive intermolecular H-bonding.
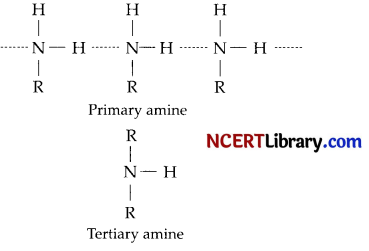
As a result, extra energy is required to separate the molecules of primary amines. Hence, primary amines have higher boiling points than tertiary amines.
Question 20.
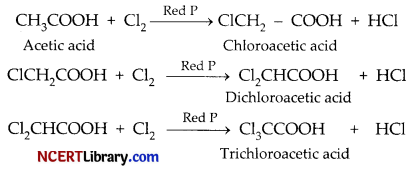
Write chemical equation to illustrate Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction.
Answer:
Hell Volhard Zelinsky (HVZ) reaction involves alpha bromination of carboxylic acids. Carboxylic acids react with chlorine or bromine in presence of small amount of red phosphorous to give alpha halo carboxylic acids.
OR
Write a short note on cross-aldol condensation.
Answer:
Cross aldol condensation: When aldol condensation is carried out between two different aldehydes, or two different ketones, or an aldehyde and a ketone, them the reaction is called a cross-aldol condensation. If both the reactants contain a-hydrogen, four compounds are obtain as products. Atleast one of the reactants should have an a-hydrogen.
For example, ethanal and propanal reacts to give four products.
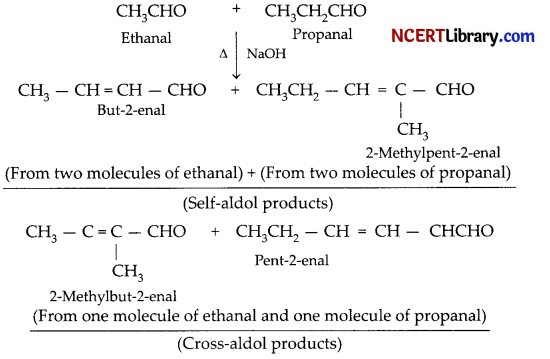
Question 21.
Thermodynamic feasibility of the reaction alone cannot decide the rate of the reaction. Account for the following statement with example.
OR
Consider the following data for the reaction :
A + B → Product
| Experiment | [A] mol L-1) | [B] mol L-1) | [Rate] mol sec-1) |
| 1 | 0.10 M | 1.0 | 2.1 x 10-3 |
| 2 | 0.20 M | 2.0 | 8.4 x 10 |
| 3 | 0.30 M | 3.0 | 8.4 x 10 |
Determine the order of reaction with respect to A and with respect to B and the overall order of reaction.
Answer:
By thermodynamically feasible reaction we mean that the enthalpy of the reaction i.e., ∆Hr is negative. But kinetics of the reaction is also responsible for a reaction to occur. The activation energy of the reaction also plays an important role. The proper orientation of the molecules, so that when they collide, they reach sufficient activation energy to form the product.
Reactants Activated complex Products.
The rate of reactions, i.e., speed of reactions (kinesis) is another factor. Example : Conversion of diamond to graphite is thermodynamically feasible, but in reality because of slow rate of reaction it is not feasible reaction.
OR
The rate of law may be expressed as
Rate = k[A]p[B]q
Comparing experiments 2 and 3
(Rate)2 = k[0.2]p [1.0]q = 8.4 x 10-3 … (i)
(Rate)3 = k[0.2]p [2.0]q = 8.4 x 10-3 … (ii)
Dividing equation by (ii) by (i)
\(\frac{(\text { Rate })_3}{(\text { Rate })_2}=\frac{k[0.2]^p[2.0]^q}{k[0.2]^p[1.0]^q}=\frac{8.4 \times 10^{-3}}{8.4 \times 10^{-3}}\)
[2]q = [2]° or q = 0
Comparing experiments (i) and (ii)
(Rate)2 = k[0.2]p [1.0]q = 8.4 x 10-3 … (iii)
(Rate)1 = k[0.10]p [1.0]q = 2.1 x 10-3 … (iv)
Dividing equation, (iii) by (iv)
\(\frac{(\text { Rate })_2}{(\text { Rate })_1}=\frac{k[0.20]^p[1.0]^q}{k[0.10]^p[1.0]^q}=\frac{8.4 \times 10^{-3}}{2.7 \times 10^{-3}}\) = 4
[2]q = [2]² or q = 2
order with respect to A = 2
order with respect to B = 0
Question 22.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compounds:
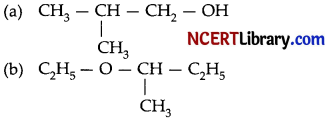
Answer:
(a) 2-Methylpropan-l-ol
(b) 2-Bromo-3-methylbut-2-en-l-ol.
Question 23.
(a) In a cell reaction, the equilibrium constant K is less than one. Is E° for the cell positive or negative?
(b) What will be the value of K if E°cell = 0?
Answer:
(a) For a cell if, E° = \(\frac { 0.0591 }{ n }\)log K (at 298 K)
Let the value of K is less than one i.e., 0.01
E° = \(\frac { 0.0591 }{ n }\) log 0.01 = \(\frac { 0.0591 }{ n }\) log (10-2) [log 10 = 1]
= \(\frac{(-2) \times 0.0591}{n}\) = – ve
Hence E° value of cell will be negative.
(b) E° = 0, hence 0 = log K.
i. e., log K = 0 i.e., K = antilog (0) = 1.
![]()
Question 24.
(a) How is glucose obtained commercially?
(b) Which carbonyl group is present in the structure of glucose?
Answer:
(a) Glucose is obtained commercially by hydrolysis of starch by boiling it with dilute H2SO4 at 393 K under pressure of 2-3 atm.
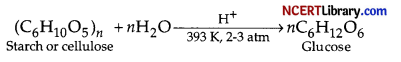
(b) Aldehyde group is present in the structure of glucose.
Question 25.
(a) Write the IUPAC name of following coordination compounds :
1. [CO(H2NCH2CH2NH2)3]2(SO4)3
2. Hg[Co(SCN)4]
(b) Mention the type of hybridisation usually associated with following geometries :
1. Trigonal bipyramidal
2. Square planar
Answer:
(a) 1. Tris(ethane-1, 2-diamine) cobalt(III) sulphate
2. Mercury(I) tetrathiocyanatocobaltate(III)
(b) 1. Trigonal bipyramidal – sp³d
2. Square planar – dsp²
Section – C
This section contains 5 questions with internal choice in two questions. The following questions are short answer type and carry 3 marks each.
Question 26.
(a) Why

is a weaker base than CH3 – CH2 – NH2?
(b) Complete the following chemical equation:
![]()
Answer:
(a) In the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom is involved in resonance with the carbonyl group as follows.
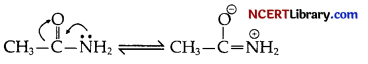
Hence, the electron pair of nitrogen is not easily available for donation. But +1 – effect of – CH2 – CH3 enhances the lone pair availability on ‘N’ atom in CH3 – CH2 – NH2.
That is why IMG is a weaker base than CH3 – CH2 – NH2.
(b) 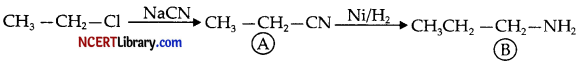
Question 27.
The reaction between A and B is first order with respect to A and zero order with respect to B. Fill in the blanks in the following table:
| Experiment | A (mol L-1) | B (mol L-1) | Initial rate (mol L-1 min-1) |
| I | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.0 x 10-2 |
| II | …………. | 0.2 | 4.0 x 10-2 |
| III | 0.4 | 0.4 | …………. |
| IV | …………. | 0.2 | 2.0 x 10-2 |
Answer:
The given reaction is of the first order with respect to A and of zero order with respect to B.
Therefore, the rate of the reaction is given by,
Rate = k[A]1[B]°
⇒ Rate = k[A]
From experiment I, we obtain
2.0 x 10-2 mol L-1 min-1 = k(0.1 mol L-1)
⇒ k = 0.2 min-1
From experiment II, we obtain
4.0 x 10-2 mol L-1 min-1 = 0.2 min-1 [A]
⇒ [A] = 0.2 mol L-1
From experiment III, we obtain
Rate = 0.2 min-1 x 0.4 mol L-1
⇒ = 0.08 mol L-1 min-1
From experiment IV, we obtain
2.0 x 10-10 mol L-1 min-1 = 0.2 min-1 [A]
⇒ [A] = 0.1 mol L-1
![]()
Question 28.
(a) The standard electrode potential (E°) for the cell containing 0.1 M Ag+ and 4.00 M Cu2+ at 298 K are \(\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{Cu}^2 / \mathrm{Cu}}^{\circ}\) = + 0-34V, \(\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{Ag}^{+} / \mathrm{Ag}}^0\) = + 0.80V.
Calculate the cell potential (E).
(b) How many hours does it take to reduce 3 mol of Fe3+ to Fe2+ with 2.00 A current? [R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1, 1 F = 96500 C]
Answer:
(a) Cell reaction,
Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → 2Ag(s) + Cu2+(aq)
n = 2
Using Nernst equation,
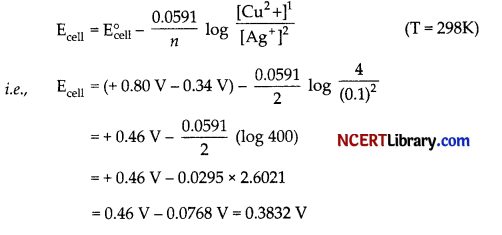
Hence, EcelI = 0.3832 V.
(b) For 3 moles of Fe3+ to convert to Fe2+, we require 1 mol of electron charge per mol.
3Fe3+ + 3e– → 3Fe2+
Hence, 3 moles of electrons are required,
i.e., Q = 3 x IF = 3 x 96500 C.
as, IF = charge of 1 mole of electron.
Also, Q = If
t = \(\frac { Q }{ t }\) = \(\frac{3 \times 96500}{2}\) second
= 144,750 sec [1 hour = 3600 second]
Question 29.
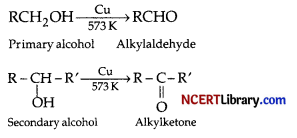
(a) What happens when the vapours of primary and secondary alcohol are passed over heated copper at 573 K?
(b) How to prepare salicylic acid from phenol? Give the reaction sequence as well.
Answer:
(a) When the vapours of primary and secondary alcohol are passed over heated copper at 573 K, dehydrogenation takes place and an aldehyde or ketone is formed.
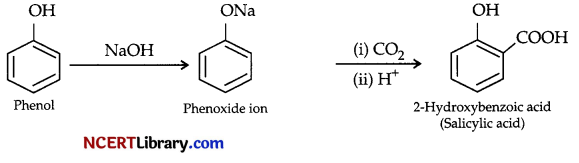
(b) Phenol is converted to ortho-hydroxybenzoic acid via phenoxide ion. Phenoxide ion is generated by treating phenol with sodium hydroxide which is more reactive than phenol towards electrophilic aromatic substitution. Then phenoxide ion is reacted with carbon dioxide followed by acidification to obtain ortho-hydroxybenzoic acid or salicylic acid.
OR
(a) Arrange the following in the increasing order of acidic strength :
n-butanol, 2-methylpropan-1-ol, 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(b) Give a chemical test to distinguish between propanol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol.
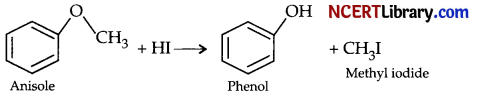
(c) Predict the products:
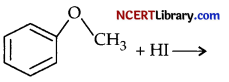
Answer:
(a) As the alkyl groups increase the electron density attached to the carbon bearing the oxygen atom, they destabilise the anion formed after losing proton. Hence, the acidic strength will vary in below order:
2- methylpropan-2-ol < 2-methylpropan-l-ol < n-butanol.
(b) Lucas Test in alcohol is a test used to differentiate between Primary, Secondary and Tertiary alcohols. This test is carried out with the help of Lucas reagent, which is a solution of anhydrous ZnCl2 and cone. HCl.
In case of tertiary alcohols, instantaneous turbidity appears in the solution while in secondary alcohols turbidity appears after 4-5 minutes. Therefore, propanol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol can be distinguished using by Luca’s reagent, (ZnCl2HCl) solution. 2-methylpropan-2-ol react immediately at room temperature to give a white precipitate of corresponding alkyl chloride, whereas in case of propanol turbidity appears after heating.

(c) 2-Methyl propan-2-ol
Question 30.
An aqueous solution freezes at 272.4 K while pure water freezes at 273.0 K. Determine:
(a) The molality of the solution.
(b) Boiling point of the solution.
Given : Kf of water = 1.86 K kg mol-1, Kb = 0.512 K kg mol-1
Answer:
(a) As depression of freezing point (∆Tf) is directly proportional to molality of solution :
∆Tf = Kfm
Now putting the values :
m = ∆Tf = Kfm
m = \(\frac{273.0 \mathrm{~K}-272.4 \mathrm{~K}}{1.86 \mathrm{~K} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}}\)
= 0.323 mol kg-1
(b) Similarly
∆Tb = Kbm
= 0.323 mol kg-1 x 0.512 K kg mol-1 = 0.165 K
As, boiling point of water is 373.15 K, therefore boiling point of solution would be :
373.15 K + 0.165 K = 373.31 K
OR
Determine the amount of CaCl2 dissolved in 2.5 L at 27°C such that its osmotic pressure is 0.75 atm at 27°C (i for 2 for CaCl2 = 2.47).
Answer:
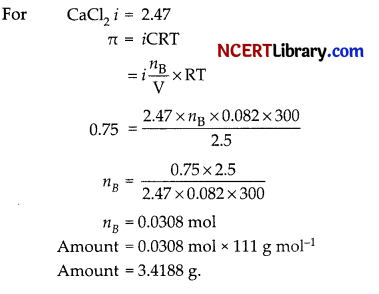
Section – D
The following questions are case-based questions. Each question has an internal choice and carries 4 (1+1+2) marks each. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Question 31.
Magnetic moment, also known as magnetic dipole moment, is the measure of the object’s tendency to align with a magnetic field. “Magnetic Moment is defined as magnetic strength and orientation of a magnet or other object that produces a magnetic field.” The magnetic moment is a vector quantity. The objects have a tendency to place themselves in such a way that the magnetic moment vector becomes parallel to the magnetic field lines.
The direction of the magnetic moment points from the south to the north pole of a magnet. The magnetic field created by a magnet is directly proportional to the magnetic moment.
The magnetic moment is generated by the following two methods:
1. The motion of Electric Charge
2. Spin Angular Momentum
Magnetic moments are typically measured by instruments known as magnetometers. But not all magnetometers are aligned to measure the magnetic moment directly. Some of these devices measure magnetic fields only and from the measured magnetic field, the magnetic moment is measured. Magnetic moment of some co-ordination compounds are measured and given in the table below:
| Co-ordination compounds | Magnetic moment BM |
| Na[Mn(CN)6] | 2.2 |
| [Fe(H2O)6]2+ | 5.3 |
| Na,[MnCl4] | 5.9 |
Answer the following questions:
(a) Which of the above mentioned complex is outer orbital complex ?
(b) What is the geometry of Na2[MnCl4]?
(c) Explain why Na4[Mn(CN)6] is an inner orbital complex?
OR
Explain the hybridisation of [Fe(H2O)6]2+
Answer:
(a) [Fe(H2O)6]2+ is an outer orbital complex.
(b) Na2[MnCl4] Hybridisation is sp³ type and hence geometry is Tetrahedral.
(c) In Na4[Mn(CN)6, CNΘ is a strong field ligand and forces the pairing of electrons in the 3d orbitals of Mn. The hybridisation is d²sp³ type hence it is inner orbital complex.
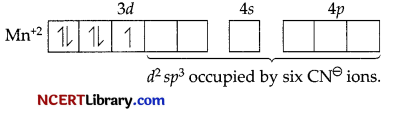
In [Fe(H2O)6]2+ complex ion, H2O is a weak field ligand and the electrons in 3d orbitals remain as such. The hybridisation is sp³d² type.
Question 32.
Solvolysis, is a chemical reaction in which the solvent, such as water or alcohol, is one of the reagents and is present in great excess of that required for the reaction. Solvolytic reactions are usually substitution reactions i.e., reactions in which an atom or a group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms.
The solvents act as or produce electron-rich atoms or groups of atoms (nucleophiles) that displace an atom or group in the substrate molecule. At high temperatures or in the presence of strong bases, some solvents act as eliminating agents, producing alkenes from alkyl halides. It is common practice to name solvolysis reactions after the specific solvent, such as “hydrolysis” when water is the reagent.
In ethanol, the compound 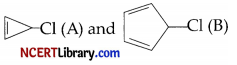 were studied for solvolysis and results are furnished below:
were studied for solvolysis and results are furnished below:
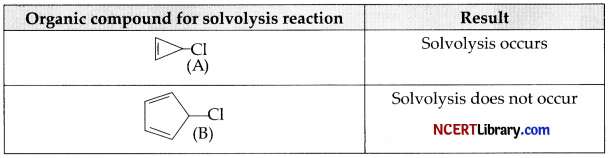
Answer the following questions:
(a) The above mentioned solvolysis is Sn1 or SN2 type reaction?
(b) What is reason for the difference in solvolysis reaction?
(c) Why the compound (A) undergoes solvolysis reaction?
OR
Why the compound (B) does not undergo solvolysis reaction?
Answer:
(a) SN1 type reaction.
(b) Difference in solvolysis reaction is due to the stability of carbocation formed during the course of reaction.
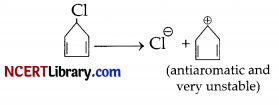
(c) The carbocation obtained from C-Cl bond cleavage of the compound (A) is a very stable aromatic compound [cyclopropenyl cation having (4n+2)π electrons, where n = 0.
For this reason, the compound (A) undergoes solvolysis (SN1) at a faster rate.
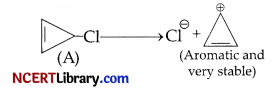
OR
The carbocation expected to be obtained on C-Cl bond cleavage of ‘B’ in an unstable anti-aromatic carbocation [cyclopentadienyl cation, having 4nπ electrons, where n = 1]. There, the compound ‘B’ does not undergo solvolysis (Sn1) in ethanol.
Section – E
The following questions are long answer type and carry 5 marks each. Two questions have an internal choice.
Question 33.
Write the various reactions of glucose to answer the following and justify your answer based on its structure.
(a) Glucose forms mono glucoxime.
(b) Glucose contains 6-carbon chain.
(c) Glucose forms pentaacetate, but not hexacetate.
(d) Glucose pentaacetate does not reacts with NH2OH
(e) Glucose does not give positive Schiff’s test or NaHSO3 addition product in spite of having an aldehyde group.
OR
(a) Describe the mechanism of enzyme activity.
(b) What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose?
Answer:
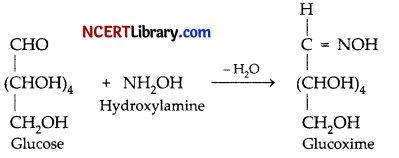
(a) Due to the presence of a single carbonyl group glucose forms glucoxime.
(b) Glucose on reduction with HI in presence of red P at about 373 K produces n-hexane. This reaction confirms the presence of 6-carbon chain in glucose.
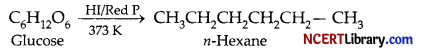
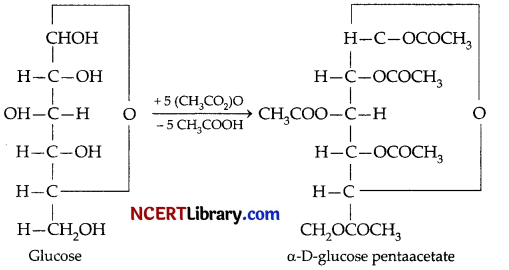
(c) In glucose all the hydroxy (- OH) i.e., 5 groups react with acetic anhydride to form a pentaacetate except the aldehydic group. This product indicates presence of 5, hydroxyl group in normal structure of D-glucose.
(d) The aldehydic group is absent in the a-D-glucose pentaacetate or p-D-glucose pentaacetate. It is involved in the cyclic bond between first and the 5th carbon of the chain. Hence, glucose pentaacetate does not give any reaction with NH2OH.
(e) The open chain form of glucose is responsible for the positive tests of aldehyde given by glucose. But in case of Schiff s reagent and NaHSO3 which are weak reagents, the reactions are reversible and the equilibrium cannot be shifted to get more and more open chain form, which is smaller in amount in the mixture of a and p cyclic glucose forms.
OR
(a) (i) Enzymes are very specific in their actions. They bind to the active site of the substrate and form enzyme substrate complex (E + S = ES).
(ii) The complex ES, promotes the chemical reaction generally by bringing down the activation energy required for the reaction to occur.
Once the products are formed the enzyme returns back to its original shape.
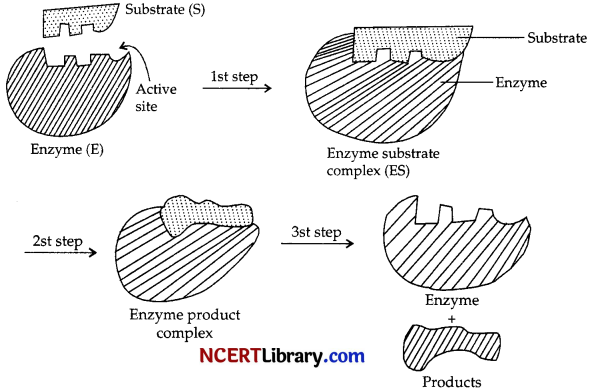
Also enzymes work best under optimal pH and temperature. They are required in very small quantity.
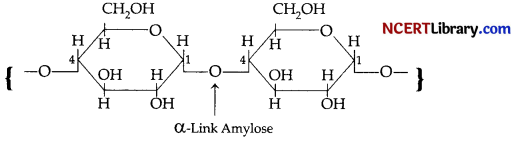
(b) Starch consists of two components amylose and amylopectin. Amylose is a long linear chain of 200-1000 units of α-D-(+)-glucose units joined by C1-C4 glycosidic linkage (α-link).
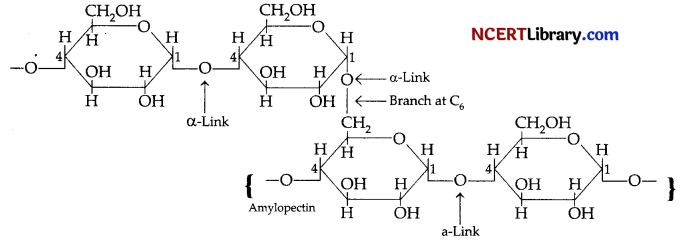
Amylopectin is a branched-chain polymer of α-D-glucose units, in which the chain is formed by C1-C4 glycosidic linkage and the branching occurs by C1-C6 glycosidic linkage.
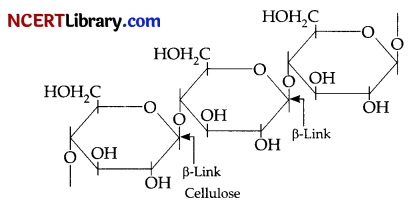
On the other hand, cellulose is straight-chain polysaccharide of ß-D-glucose units joined C1-C4 glycosidic linkage (ß-link).
Question 34.
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entities on the basis of valence bond theory.
(a) [Fe(CN)6]4-
(b) [FeF6]3-
(c) [Co(C2O4)3]3-
(d) [CoF6]3-
OR
Using valence bond theory, explain the following for the complexes given below:
[Mn(CN)6]3-, [Co(NH3)6]3+, [FeCl6]4-.
(a) Type of hybridisation
(b) Geometry
(c) Magnetic behaviour
(d) Inner or outer orbital complex
(e) Spin only magnetic moment value.
Answer:
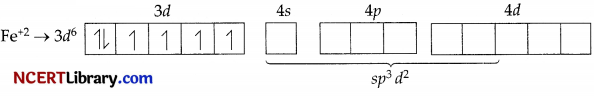
(a) [Fe(CN)6]4-
In the above coordination complex, iron exists in the +2 oxidation state.
Fe2+ : Electronic configuration is 3d6 orbitals of Fe2+ ion.
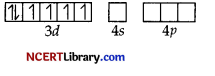
As CN– is a strong field ligand, it causes the pairing of the unpaired 3d electrons.
![]()
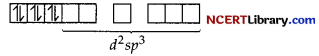
Since there are six ligands around the central metal ion, the most feasible hybridisation is d²sp³.
6 electron pairs from CN ions occupy the six hybrid d²sp³ orbitals.
Then,
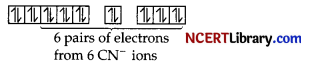
Hence, the geometry of the complex is found to be octahedral, strongly paramagnetic and outer orbital complex.
(b) [FeFd6]3-
In this complex, the oxidation state of Fe is + 3.
Orbitals of Fe+3 ion:
![]()
There are 6F– ions. Thus, it will undergo sp³d² hybridization as F– is a weak field ligand and it does not cause the pairing of the electrons in the 3d orbital. Hence, hybridisation is sp³d². sp³d² hybridized orbitals of Fe3+ are:
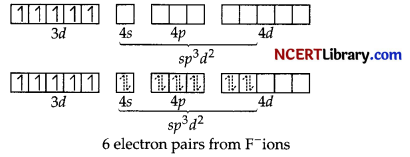
Hence, the geometry of the complex is found to be octahedral, strongly paramagnetic and outer orbital complex.
(c) [Co(C2O4)3]3-
Cobalt exists in the +3 oxidation state in the given complex.
Orbitals of Co3+ ion : 4s°3d6 configuration.
![]()
Oxalate is a strong field ligand so, it causes the pairing of the unpaired 3d orbital electrons. As there are 6 ligands, hybridisation has to d²sp³ hybridisation of Co3+
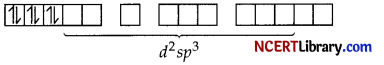
The 6 electron pairs from 3 oxalate ions (oxalate anion is a bidentate ligand) occupy these d²sp³ orbitals.
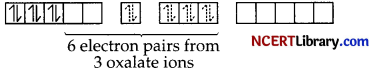
Hence, the geometry of the complex is found to be octahedral, inner orbital, diamagnetic.
(d) [CoF6]3-
Cobalt exists in the +3 oxidation state.
Orbitals of Co3+ ion:
![]()
Again, fluoride is a weak field ligand. It cannot cause the pairing of the unpaired 3d electrons.
As a result, the Co3+ ion will undergo sp³d² hybridisation. sp³d² hybridised orbitals of Co3+ ion are:
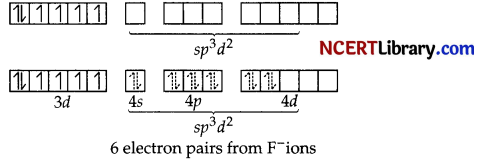
Hence, the geometry of the complex is octahedral and paramagnetic and outer orbital complex.
OR
[Mn(CN)6]3- oxidation state of Mn is (+ 3)
[CO(NH3)6]3+ oxidation state of Co is (+ 3)
[FeCl6]4- oxidation state of Fe is (+ 2)
In [Mn(CN)6]3-, CN is strong field ligand.
In [CO(NH3)6]3+, NH3 is weak field ligand.
In [FeCl6]4- Cl– is a weak field ligand.
(a) Now [Mn(CN)6]3-, Mn3+(3d4).
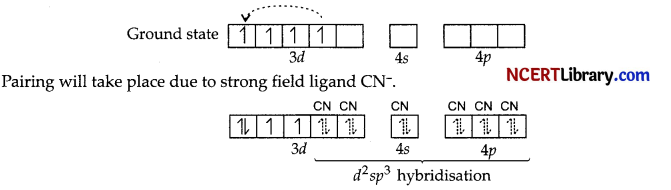
(i) Hybridisation d²sp³
(ii) Octahedral geometry
(iii) Diamagnetic
(iv) Inner orbital complex
(v) μ = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}=\sqrt{2(2+2)}\)
= \(\sqrt{8}\)
= 2.87 BM
(b)
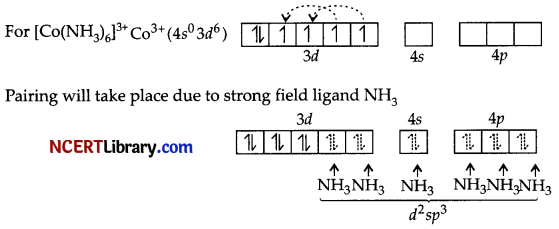
(i) Hybridisation d²sp³
(ii) Octahedral
(iii) Diamagnetic
(iv) Inner orbital complex
(v) p = \(\sqrt{0(0+2)}\) = 0
(c)
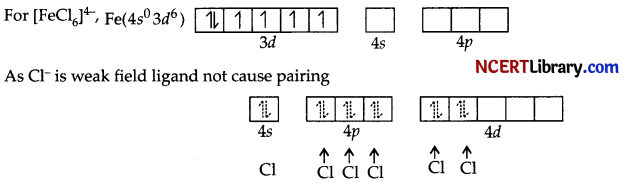
(i) Hybridisation sp³d².
(ii) Octahedral
(iii) Paramagnetic
(iv) Outer orbital complex
(v) μ = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}=\sqrt{4(4+2)}\)
= \(\sqrt{24}\)
= 4.9 BM
![]()
Question 35.
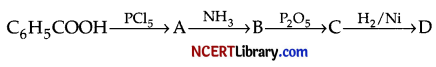
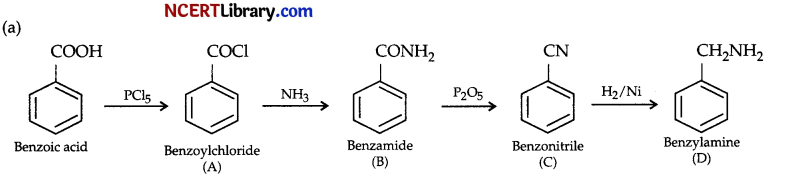
(a) Identify A, B, C and D and complete the reaction sequence :
(b) Explain why the a-hydrogen in aldehydes and ketones are acidic in nature?
(c) Convert:
(i) Benzene to acetophenone
(ii) Acetaldehyde to methane.
(iii) Acetaldehyde to acetone.
(d) Give the reaction sequence for conversion of acetaldehyde to acetamide.
(e) Give the IUPAC name for the following compound :
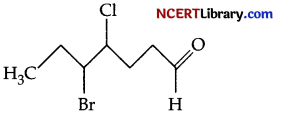
Answer:
(b) The acidity of a-hydrogen in carbonyl compounds is due to the strong electron withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group and resonance stabilisation of the conjugate base.