Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry with Solutions Set 2 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Set 2 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions :
Read the following instructions carefully.
- There are 35 questions in this question paper with internal choice.
- SECTION A consists of 18 multiple-choice questions carrying 1 mark each.
- SECTION B consists of 7 very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.
- SECTION C consists of 5 short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.
- SECTION D consists of 2 case-based questions carrying 4 marks each.
- SECTION E consists of 3 long answer questions carrying 5 marks each.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed
Section – A
The following questions are multiple-choice questions with one correct answer. Each question carries 1 mark. There is no internal choice in this section.
Question 1.
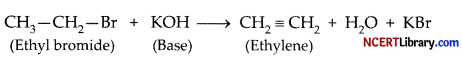
Conversion of ethyl bromide to ethylene is an example of: [1]
(a) Substitution
(b) Dehydrohalogenation
(c) Dehydration
(d) Hydration
Answer:
(ii) Dehydrohalogenation
Explanation: Dehydrohalogenation is a type of elimination reaction in which a hydrogen atom and a halogen are removed together. Usually, this reaction is used for making alkenes from alkyl halides. The conversion of ethyl bromide to ethylene is an example of dehydrohalogenation reaction.
During the reaction, ethyl bromide is treated with a strong base like KOH to convert it into ethylene. The base attacks the Hydrogen on the ß-Carbon, forming H2O. This leads to bromine leaving the a-Carbon to combine with K+. The leftover electrons from both carbons make another bond, so ethylene is formed.
Question 2.
Which of the following is isotonic to red blood cells? [1]
(a) 0.9% NaCl solution
(b) Distilled water
(c) 0.9% glucose solution
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) 0.9% NaCl solution
Explanation: At 0.9% NaCl solution, there will be no net movement of water through osmosis between a red blood cell and the solution. If observed through a light microscope, the red blood cells will appear normal in their shape. Thus, by definition, a 0.9% NaCl solution will be isotonic to the red blood cell as there is no net movement of water in or out of the cell.
Question 3.
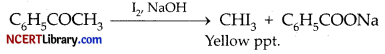
The reagent(s) which can be used to distinguish acetophenone from benzophenone is/are: [1]
(a) 2,4-dinitrophenythydrazine
(b) aqueous solution of NaHSO3
(c) Benedict reagent
(d) I2 and NaOH
Answer:
(d) I2 and NaOH
Explanation: Acetophenone reacts with NaOH and I2 to give yellow ppt of CHI3 but benezophenone (C6H5COC6H5) does not. Hence, it can be used to distinguish between them.
Question 4.
Which of the following compound is an organometallic compound? [1]
(a) C2H5ONa
(b) C2H5SNa
(c) C2H5MgI
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) C2H5MgI
Explanation: An organometallic compound is the one that contains atleast one direct bond between metal and carbon.
For C2H5ONa: There is a bond between, carbon and oxygen. So, it is not an organometallic compound (Non-metal)
For C2H5SNa: There is a bond between carbon and sulphur. So, it is not on organometallic compound. (Non-metal)
For C2H5MgI: There is a bond between carbon and Magnesium. So, it is an organometallic compound (Metal)
Hence, from the given options C2H5MgI is an organometallic compound.
Question 5.
Identify the correct IUPAC name of CH3 – CH = CH – CHO. [1]
(a) But-2-enal
(b) 2-Butenal
(c) Buten-2-al
(d) Butenal
Answer:
(a) But-2-enal
Explanation: The carbon atom of the CHO group is assigned the first number. So, in this case, the double bond occurs at second carbon and hence, the prefix 2- is used for the naming of double bonden. Hence, the correct IUPAC name of the given compound is But-2-enal.
![]()
Question 6.
Of the following terms used for denoting concentration of a solution, the one which does not get affected by temperature is: [1]
(a) Molarity
(b) Molality
(c) Normality
(d) Formality
Answer:
(b) Molality
Explanation: Molality is defined as the “total moles of a solute contained in a kilogram of a solvent.”
Molality (M) = \(\frac{\text { Number of moles of solute }}{\text { Mass of solvent in kgs }}\)
Molality (M) = \(\frac{g \times 1000}{\mathrm{~W} \times m}\)
Both numerator and denominator contains mass terms only and mass is not affected by temperature. On the other hand, molarity, normality and formality contains volume terms and hence, are affected by temperature.
Question 7.
Which of the following is used to prepare ketone from acyl chloride? [1]
(a) R-MgX
(b) R2Cd
(c) CO + HCl
(d) CrO3
Answer:
(b) R2Cd
Explanation: Acyl chlorides upon treatment with Grignard reagent and a metal halide, yield ketones. For example: when cadmium chloride is reacted with the Grignard reagent, dialkyl cadmium is formed.
Question 8.
Zr and Hf have almost equal atomic and ionic radii because of: [1]
(a) Diagonal relationship
(b) Lanthanoid contraction
(c) Actinoid contraction
(d) Belonging to the same group
Answer:
(b) Lanthanoid contraction
Explanation: Due to lanthanide contraction Zr and Hf have almost similar atomic radii. It can be explained on the basis of shielding effect. In case of post lanthanide elements like Hf, 4f subshell is filled and it is not very effective at shielding the outer shell electrons. Therefore, Zr and Hf have almost similar atomic radii.
Question 9.
The reagent which does not react with both, acetone and benzaldehyde? [1]
(a) Sodium hydrogen sulphite
(b) Phenyl hydrazine
(c) Fehling’s solution
(d) Grignard reagent
Answer:
(c) Fehling’s solution
Explanation: Aromatic aldehydes such as benzaldehyde and ketones such as acetone does not respond to Fehling’s test. This is because benzaldehyde does not contain alpha hydrogen so intermediate enolate formation does not take place. Thus, it does not react with Fehling’s solution. On the other hand, ketone does not react with the Fehling’s solution unless they are alpha-hydroxy ketones. Acetone is not alpha-hydroxy ketone so it will also not reduce the Fehling’s solution.
![]()
Question 10.
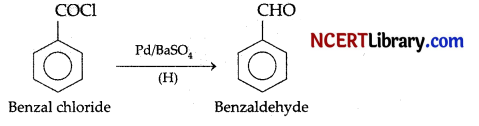
The reduction of benzoyl chloride with Pd and BaSO4 produces: [1]
(a) Benzoyl chloride
(b) Benzaldehyde
(c) Benzoic acid
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Benzaldehyde
Explanation: The reduction of benzoyl chloride with Pd and BaSO4 produces benzaldehyde. This reaction is called Rosenmund reaction.
Question 11.
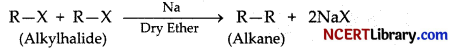
The action of sodium on alkyl halide to form an alkane is called: [1]
(a) Grignard reaction
(b) Wurtz coupling reaction
(c) Isocyanide reaction
(d) Halogenation reaction
Answer:
(b) Wurtz coupling reaction
Explanation: The action of sodium on alkyl halide to form an alkane is called as Wurtz coupling reaction. This reaction provides a method for the synthesis of higher alkanes from alkylhalides by treating with metallic sodium in dry ether.
Question 12.
Which one of the following is diamagnetic ion? [1]
(a) CO2+
(b) Ni2+
(c) Cu2+
(d) Zn2+
Answer:
(d) Zn2+
Explanation: Electronic configuration of CO2+ is [Ar]4s03d7. Unpaired electrons are present. Paramagnetic.
Electronic configuration of Ni2+ is [Ar]4s03d8. Unpaired electrons are present. Paramagnetic.
Electronic configuration of Cu2+ is [Ar]4s03d9. Unpaired electrons are present. Paramagnetic.
Electronic configuration of Zn2+ is [Ar]4s03d10. No unpaired electrons are present. Diamagnetic.
Hence, from the following options, Zn2+ is dimagnetic ion.
Question 13.
Curdling of milk is an example of: [1]
(a) Breaking of peptide linkage
(b) Hydrolysis of lactose
(c) Breaking of protein into amino acids
(d) Denaturation of protein
Answer:
(d) Denaturation of protein
Explanation: The major components of milk are lactose, protein, and fats. During the curdling process, the lactose present in the milk is fermented by lactic acid bacteria and produces lactic acid which causes a decrease in the pH of milk. At low pH, the proteins present in the milk are denatured and get precipitated
Question 14.
Cannizzaro’s reaction is not given by ________. [1]
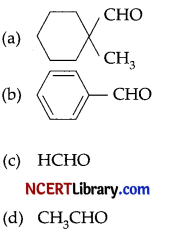
Answer:
(d) CH3CHO
Explanation: CH3CHO will not give Cannizzaro’s reaction because it contains a-hydrogen while other three compounds have no a-hydrogen. Hence, they will give Cannizzaro’s reaction.
Question No. 15 to 18 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Question 15.
Assertion (A): Azeotropic mixtures are formed only by non-ideal solutions and they may have boiling points either greater than both the components or less than both the components.
Reason (R): The composition of the vapour phase is same as that of the liquid phase of an azeotropic mixture. [1]
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Azeotropic mixtures are formed only by non-ideal solutions and they may have boiling points either greater than both the components or lesser than both the components. The composition of the vapour phase is same as that of the liquid phase of an azeotropic mixture. Thus, both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
Question 16.
Assertion (A): Halogen acids react with alcohols to form haloalkanes
Reason (R): Order of reactivity of halogen acids HCl > HBr > HI. [1]
Answer:
(c) A is true, but R is false.
Explanation: Halogen acids react with alcohols to form haloalkanes. For a given alcohol the order of reactivity of halogen acids follows the sequence HI > HBr > HCl. It is because of the fact that I- is a stronger nucleophile than Br– which in turn is a stronger nucleophile than Cl–. Thus, assertion is true but reason is false.
![]()
Question 17.
Assertion (A): 2, 2-Dimethylpropanal undergoes Cannizzaro reaction with concentrated NaOH.
Reason (R): Cannizzaro reaction is a disproportionation reaction. [1]
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Aldehydes which do not contain a-hydrogen undergo Cannizzaro reaction. 2,2-Dimethylpropanal undergoes Cannizzaro reaction with concentrated NaOH because it does not contain a-hydrogen atom.
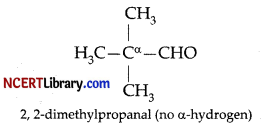
Cannizzaro reaction is a disproportionation reaction because it involves the base-induced disproportionation of two molecules of a non-enolizable aldehyde to give a primary alcohol and carboxylic acid. Thus both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 18.
Assertion (A): When a solution is separated from the pure solvent by a semi- permeable membrane, the solvent molecules pass through it from pure solvent side to the solution side.
Reason (R): Diffusion of solvent occurs from a region of high concentration solution to a region of low concentration solution. [1]
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: When a solution is separated from the pure solvent by a semipermeable membrane, the solvent molecules pass through it from pure solvent side to the solution side. Diffusion is the process of movement of solvent molecules from the region of higher concentration to region of low concentration. Thus, both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Section – B
This section contains 7 questions with internal choice in two questions. The following questions are very short answer type and carry 2 marks each.
Question 19.
(a) Complete the reaction: [2]

(b) Suggest the most probable product:
![]()
Answer:
Question 20.
Write down the number of 3d electrons in each of the following ions: [2]
Ti2+, V2+, Cr3+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, CO2+, Ni2+ and Cu2+.
Indicate how would you expect the five 3d~ orbitals to be occupied for these hydrated ions (octahedral).
OR
Complete the following:
(a) Na2CrO4 + H2SO4 →
(b) MnO2 + KOH + O2 →
(c) HgCl3 + SnCl2 →
Answer:
| Metal ion | Number of d-electrons | Filling of d-orbitals |
| Ti2+ | 2 | t²2g |
| V2+ | 3 | t³2g |
| Cr3+ | 3 | t³ 2g |
| Mn2+ | 5 | t³2g e²g |
| Fe2+ | 6 | t42g e²g |
| Fe3+ | 5 | t³2g e²g |
| Co2+ | 7 | t52g e²g |
| Ni2+ | 8 | t62g e²g |
| Cu2+ | 9 | t62g e³g |
(a) 2Na2CrO4 + H2SO4 (conc.) → Na2Cr2O7 + Na2SO4 + H2O
(b) MnO2 + 4KOH + O2 → 2K2MnO4 + H2O
(c) HgCl3 + SnCl2 → Hg2Cl2– + SnCl4
Question 21.
What is crystal field splitting energy? [2]
Answer:
Crystal field splitting energy (∆) is the energy difference between two sets of d-orbitals (of metal atom) formed after splitting in presence of ligands. For example, in octahedral complexes d-orbitals split in two energy levels eg (higher than degenerate level) and t2g (lower than degenerate level). The eg level has dx²-y² and dz² (pointing towards the axes along the direction of the ligand) and t2g level has dxy, dyz and dxz orbitals (directed between the axes).
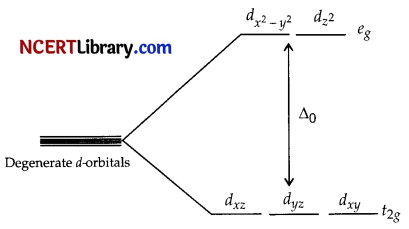
OR
Which the IUPAC name of the following complexes.
(a) [Co(NH3)6] (SO4)3
(b) K4 Ni(CN)4]
Answer:
(a) Hexaammine cobalt (III) Sulphate
(b) Potassium hexacyanide ferrate (II)
Question 22.
A first order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 x 10-3 s_1. How long will 5 g of this reactant take to reduce t° 3 g? [2]
Answer:
Initial amount = 5 g
Final concentration = 3 g
Rate constant = 1.15 x 10-3 s-1
We know that for a first order reaction,

Question 23.
Calculate the e.m.f. of the following cell at 298 K: [2]
Mg | Mg2+ (0.001 M) || Cu2+ (0.001 M) | Cu
Given : E°Mg2+ = – 2.36 V; E°Cu2+/Cu = + 0.34V
Answer:
The half cell reactions can be written as :
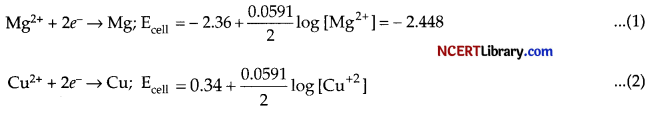
Cu2+ + Mg (s) → Mg2+(aq) + Cu (s), as the cell reaction.
So, Ecell will be: Ecell = 0.251 V – ( – 2.448) V
= – 2.69 V
Question 24.
Write the equation of the reactions of ethanal with the following: [2]
(a) Fehling’s solution
(b) Phenylhydrazine
Answer:
(a) Fehling’s solution is a tartaric acid complex of cupric ions. When acetaldehyde is heated with Fehling’s solution, it gives a red precipitate of Cu20. During the reaction, acetaldehyde is oxidized to acetate ion and cupric ions are reduced to cuprous oxide.
![]()
(b) When acetaldehyde is treated with phenyl hydrazine, the Nitrogen atom of the phenylhydrazene serves as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon of the acetaldehyde and removes water to give acetaldehyde phenylhydrazone.
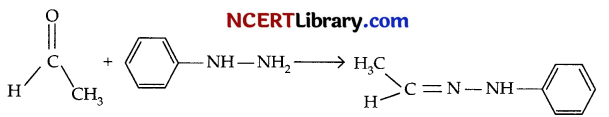
Question 25.
Provide a method to convert: [2]
(a) Benzene to aniline.
(b) Aniline to benzoic acid
Answer:
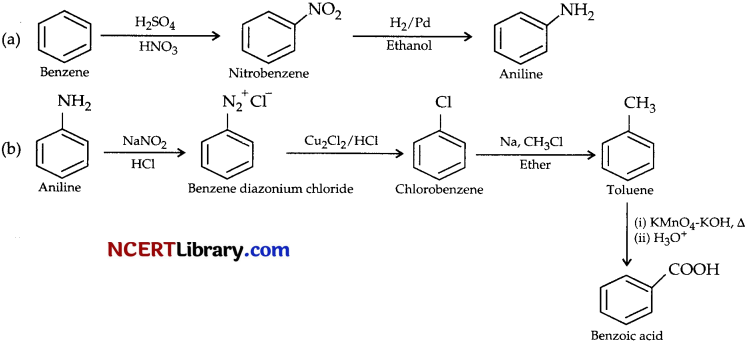
Section – C
This section contains 5 questions with internal choice in two questions. The following questions are short answer type and carry 3 marks each.
Question 26.
What would be the weight of glucose which when dissolved in 100 g of water will cause lowering of vapour pressure by 0.23 mm of Hg. Vapour pressure of pure water is 54.2 mm of Hg. [3]
Answer:
The given information is:
P1 (Vapour pressure of solvent) = 54.2 mm Hg;
Molecular weight of glucose (C6H12O6), M2 = 180 g mol-1;
Lowering of vapour pressure (i.e. P1 – p1) = 0.23 mm Hg;
M1 = 18 g; w1 = 100 g
Relative lowering of vapour pressure can be given the below formula :
\(\frac{\mathrm{P}_1-w f_1}{\mathrm{P}_1}=\frac{w_2 \times \mathrm{M}_1}{\mathrm{M}_2 \times w_1}\)
Here, P1 and p1 are vapour pressure of solvent and solution respectively, w1 and w2 are masses and M1 and M2 are molar masses of the solute and solvent respectively.
Now, putting the values in equation:
\(\frac{0.23 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}}{54.2 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}}=\frac{w_2 \times 18 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}}{180 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \times 100 \mathrm{~g}}\)
w2 = 4.24 g
Hence, weight of glucose is 4.24 g.
![]()
Question 27.
State clearly what are known as nucleosides and nucleotides. [3]
Answer:
Nucleoside: A nucleoside contains only two basic components of nucleic acids i.e., a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base. During their formation 1-position of the pyrimidine or 9-position of the purine moitey is linked to C1 of the sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) by a ß-linkgae.
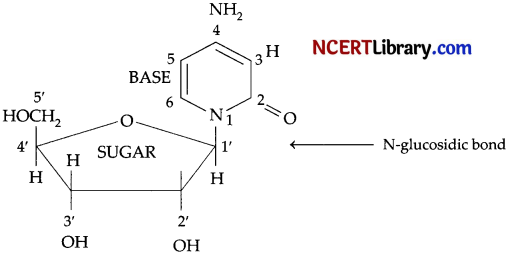
Nucleotides: A nucleotide contains all the three basic components of nucleic acids, i.e., a phosphoric acid group, a pentose sugar and nitrogenous base. These are formed by esterification of C5‘-OH of the sugar of the nucleoside with phosphoric acid.
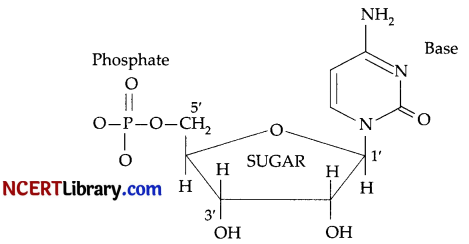
Question 28.
The cell in which the following reaction occurs: [3]
2Fe3+(aq) + 2I–(aq) → 2Fe2+(aq) + I2(s)
has E°cell = 0.236 V at 298 K.
Calculate the standard Gibbs energy and the equilibrium constant of the cell reaction.
Answer:
Here, n = 2, E°cell = 0.236 V, T = 298 K We know that:
∆rG° = – nEF°cell
= – 2 x 96487 x 0.236
= – 45541.864 J mol-1
= – 45.54 kJ mol-1
Note : Generally we take value of F as 96500 C. Then
∆rG° = – 2 x 96500 x 0.236
= – 45548.00 J mol-1
= – 45.548 kJ mol-1
Again, ∆rG° = – 2.303 RT log Kc
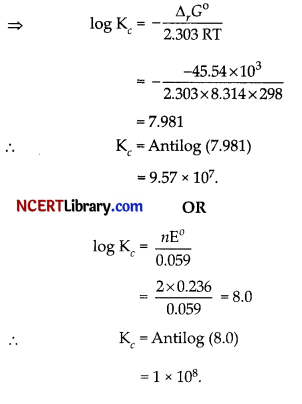
Question 29.
(a) The ‘silver’ UK coins are made up of which material? [3]
(b) Give the outer electronic configuration of Uranium (Z = 92), and U3+ ion.
(c) electrons can participate in bonding to a far great extent compared to 4f electrons. Why?
OR
(a) It is difficult to separate the lanthanoid elements, why?
(b) Transition metals exhibit higher enthalpies of atomisation, why?
(c) Transition metals have high enthalpy of hydration, why?
Answer:
(a) The ‘silver’ UK coins are made up of Cu/Ni alloy.
(b) The electronic configuration of Uranium (Z = 92) is : [Rn]5f³6d17s²
The electronic configuration of U3+ ion is : [Rn]5f³
(c) Although the 5/orbitals resemble the 4/orbitals in their angular part of wave function, they are not as buried as 4/orbitals hence, 5/electrons can participate in bonding to a far great extent compared to 4/electrons.
OR
(a) Due to lanthanide contraction, the change in the atomic or ionic radii of these elements is very small. Hence, their chemical properties are similar. This makes their separation difficult.
(b) The greater the number of unpaired electrons greater is interatomic interaction and greater will be the enthalpy of atomisation. Since transition elements have unpaired electrons they have greater interatomic interaction and exhibit higher enthalpies of atomisation.
(c) Transition elements have a high enthalpy of hydration because of the presence of strong metallic bonds which is a result of the unpaired electron in the (n -1) d subshell. The atoms in these elements are tightly packed. The strong bonds basically attribute to the elements having high enthalpies
Question 30.
(a) Why amino acids behave like salts? [3]
(b) How is protein different from polypeptide?
(c) Name one optically inactive amino acid.
Answer:
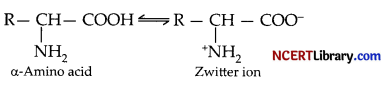
(a) Amino acids behave like salt due to the pressure of both acidic and basic groups in the same molecule.
In aqueous solution, the carbonyl group loses a proton and amino accepts a proton. Thus, the carboxyl and amino group neutralize each other to form a salt like structure called dipolar ion or switter ion.
(b) A peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by peptide bonds, and a polypeptide is a chain of many amino acids. A protein contains one or more polypeptides. Therefore, proteins are long chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds.
(c) Glycine is optically inactive amino acid.
Section – D
The following questions are case-based questions. Each question has an internal choice and carries 4 (1+1+2) marks each. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
Question 31.
MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula CH3CN and structure H3C- C ≡ N. This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile (hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not classed as organic). It is produced mainly as a by-product of acrylonitrile manufacture. It is used as a polar aprotic solvent in organic synthesis and in the purification of butadiene.
The N ≡ C- C skeleton is linear with a short C ≡ N distance of 1.16 Å. Acetonitrile was first prepared in 1847 by the French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas. Acetonitrile is used mainly as a solvent in the purification of butadiene in refineries. Specifically, acetonitrile is fed into the top of a distillation column filled with hydrocarbons including butadiene, and as the acetonitrile falls down through the column, it absorbs the butadiene which is then sent from the bottom of the tower to a second separating tower. Heat is then employed in the separating tower to separate the butadiene.
Solubility of methyl cyanide and methyl isocyanide in water was checked and different results were observed as given below : [3]
| Compound | Solubility in water |
| Methyl cyanide | ✓ |
| Methyl isocyanide | ✗ |
Answer the following questions:
(a) What type of isomerism in found in between methyl cyanide and methyl isocyanide?
(b) How methyl amine can be converted to methyl isocyanide?
(c) Why methyl cyanide shows significant solubility in water?
OR
Why methyl isocyanide is almost insoluble in water?
Answer:
(a) Functional isomerism is found in between methyl cyanide and methyl isocyanide as both have same molecular formula but different functional groups.

(c) N-atom in the molecule of methyl cyanide in partially negative charged. So, it can easily participate in the hydrogen bond formation with the water molecules as follow:
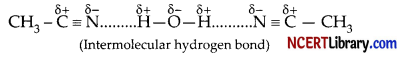
That is why, methyl cyanide shows significant solubility in water.
OR
N-atom in the molecule of methyl isocyanide becomes partially positive charged and hence it fails to form H-bond with water molecules. So, it is almost insoluble in water.
Question 32.
The most familiar commercial cells are dry cells. These are based on Leclanche cell invented by G. Leclanche in 1868. A dry cell is one type of electric battery, which is generally used for the home and portable electronic devices. A battery is a device that consists of one or more electrochemical cells, which converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
It was developed by the “German scientists Carl Gassner” in 1886, after the development of wet zinc-carbon batteries by Georges Leclanche in 1866. Nowadays, the most commonly used batteries are dry cell batteries, which vary from large flashlight batteries to minimized flashlight batteries and are mostly used in wristwatches or calculators.
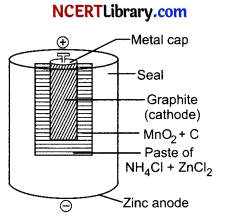
A dry cell is an electrochemical cell consisting of low moisture immobilized electrolytes in the form of a paste, which restricts it from flowing. Due to this, it is easily transportable. These are used in used in torches, toys, flash lights, calculators and other many devices.
Answer the following questions:
(a) Why dry cell is called a primary cells ?
(b) Give another example of primary cell.
(c) Why dry cell does not have an indefinite life?
OR
Write the overall reaction taking place in the above mentioned dry cell. [3]
Answer:
(a) Dry cell is called a primary cells a is in these cells, the electrode reactions can not be reversed by an external electric energy source.
(b) Mercury cell is the example of primary cell.
(c) Dry cell does not have an indefinite life because NH4Cl being acidic corrodes the zinc container even when not in use.
OR
Overall reaction: Zn + 2NH4+(aq) + 2MnO2(s) → Zn+2 + 2NH3 + 2MnO(OH)
Section – E
The following questions are long answer type and carry 5 marks each. Two questions have an internal choice.
Question 33.
(a) Draw figure to show the splitting of d-orbitals in an octahedral crystal field.
(b) [Fe(H2O)6]3+ is strongly paramagnetic whereas [Fe(CN)6]3- is weakly paramagnetic. Explain.
OR
(a) What is meant by stability of a coordination compound in solution? State the factors which govern the stability of complexes.
(b) Using valence bond theory, explain the following for the complexes given below:
[Mn(CN)6]3-, [Co(NH3)6]3+, [FeCl6]4-.
(i) Type of hybridisation
(ii) Geometry
(iii) Magnetic behaviour
(iv) Inner or outer orbital complex
(v) Spin only magnetic moment value. [5]
Answer:
(a)
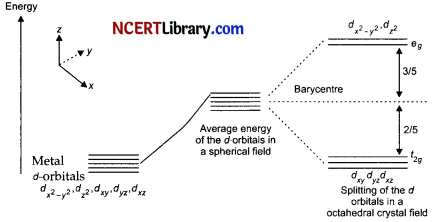
The splitting of the d-orbitals in an octahedral field takes place in such a way that dx²-y², dz² experiences a rise in energy and forms the eg level, dxy, dyz and dzx experience a fall in energy and forms the t2g level.
(b) In both [Fe(H2O)6]3+ and [Fe(CN6)3-, Fe exists in the +3 oxidation state i.e., in d5 configuration.
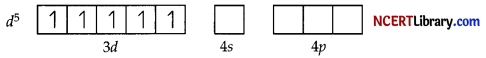
Since CN– is a strong field ligand, it causes the pairing of unpaired electrons. Therefore, there is only one unpaired electron left in the d-orbital.
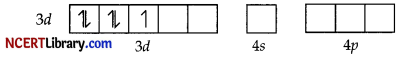
Therefore,
µ = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}=\sqrt{1(1+2)}\)
= \(\sqrt{3}\) = 1.732 BM
On the other hand, H2O is a weak field ligand. Therefore, it cannot cause the pairing of electrons. This means that the number of unpaired electrons is 5.
Therefore,
µ = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}\)=
= \(\sqrt{5(5-2)}\)
= \(\sqrt{35}\) = 5.916 BM
Hence, [Fe(H2O)6]3+ is strongly paramagnetic, while [Fe(CN)6]3- is weakly paramagnetic.
OR
(a) The stability of a complex in a solution refers to the degree of association between the two species involved in a state of equilibrium. Stability can be expressed quantitatively in terms of stability constant (K) or formation constant (kf).
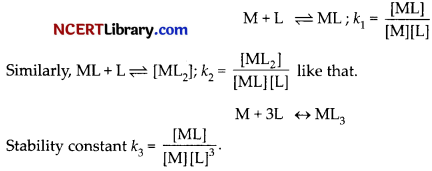
For this reaction, the greater the value of the stability constant, the greater is the proportion of Ml3 in the solution. Also ß is = K1 x K2 x K3 where K1, K2 and K3 are stability constant of individual steps in the formation of final complex.
Stability can be of two types :
1. Thermodynamic stability: The extent to which the complex will be formed or will be transformed into another species at the point of equilibrium is determined by thermodynamic stability.
2. Kinetic stability: This helps in determining the speed with which the transformation will occur to attain the state of equilibrium.
Factors that affect the stability of a complex are:
1. Charge on the central metal ion: The greater the charge on the central metal ion, the greater is the stability of the complex.
2. Basic nature of the ligand: A more basic ligand forms a more stable complex because ligands donate electron pairs, hence more basic the ligand more will be the ease with which it can donate its lone pair to central metal. Thus F–, CN– and NH3– act as good ligands, whereas H20 is a weak ligand.
3. Presence of chelate rings: Chelation increases the stability of complexes. This is called chelation effect and is found to be maximum in five and six membered rings.
Example : [Ni(en)3]2+ is more stable than [Ni(NH3)6]2+.
(b) 1. [Mn(CN)6]3- oxidation state of Mn is (+ 3)
[Co(NH3)6]3+ oxidation state of Co is (+ 3)
[FeCl6]4- – oxidation state of Fe is (+ 2)
In [Mn(CN)6]3+ CN is strong field ligand.
In [CO(NH3)6]4-, NH3 is weak field ligand.
In [FeCl6]4-, Cl– is a weak field ligand.
Now [Mn(CN)6]3- Mn3+(3r4).
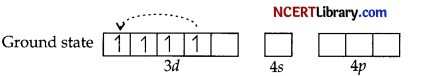
Pairing will take place due to strong field ligand CN–
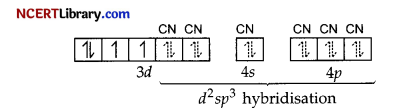
(i) Hybridisation d²sp³
(ii) Octahedral geometry
(iii) Paramagnetic
(iv) Inner orbital complex
(v) μ = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}\) = \(\sqrt{2(2+2)}\)
= \(\sqrt{8}\)
= 2.87 BM
2.
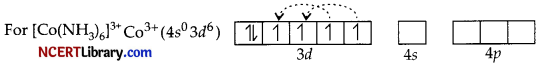
Pairing will take place due to strong field ligand NH3
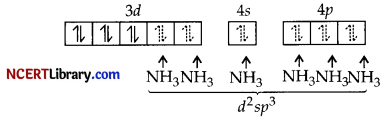
(i) Hybridisation d²sp³
(ii) Octahedral
(iii) Diamagnetic
(iv) Inner orbital complex
(v) μ = \(\sqrt{0(0+2)}\) = 0
3.
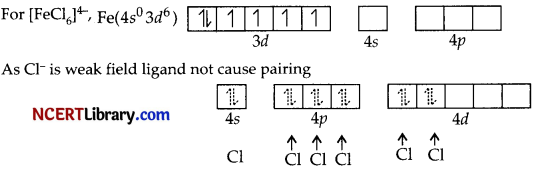
(i) Hybridisation sp³d²
(ii) Octahedral
(iii) Paramagnetic
(iv) Inner orbital complex
(v) μ = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}\) = \(\sqrt{4(4+2)}\)
= \(\sqrt{24}\)
= 4.9 BM
![]()
Question 34.
(a) The slope of a line in the graph of log10 K (K = rate constant) versus 1/T for a reaction is – 5841 K. Calculate the energy of activation for this reaction (R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1).
(b) Explain the ‘intermediate complex theory’ of catalyst action.
(c) What are ‘complex reactions’?
(d) Does a zero order reaction has molecularity equal to zero?
OR
(a) A first order reaction is 20% completed in 10 minutes. Calculate:
(i) The specific rate constant.
(ii) The time taken for the reaction to reach 75% completion.
(b) What is the order of photochemical reactions?
(c) Name three factors which can affect the rate of reaction?
(d) In a graph between ‘fraction of molecules’ and ‘kinetic energy’, what does the peak of graph corresponds to? [5]
Answer:
(a) The plot of In k Vs. 1/T gives a straight line according to the equation given below :
In k = \(\frac{-\mathrm{E}_a}{\mathrm{RT}}\) + ln A
Activation energy can be calculated by the value of slope (- Ea/R) of the graph.
Given : Slope = – 5841 K and R = 8.314 J thin K-1 mol-1
Putting the values
Slope = \(\frac{-\mathrm{E}_a}{\mathrm{R}}\)
– Ea = – 5841 K x 8.314 J thin K-1 mol-1
= 48562 J mol-1
(b) The action of the catalyst can be explained by intermediate complex theory. According to this theory a catalyst participates in a chemical reaction by forming temporary bonds with the reactants resulting in an intermediate complex. This has a transitory existence and decomposes to yield products and catalysts. This explains that catalysts are obtained as such from reaction mixture.
(c) Reactions which do not take place in a single step but take place in a sequence of a number of elementary steps are called as complex reactions. In some complex reactions, products are not formed in steps directly involving the reactants.
(d) Order of a reaction can be zero but molecularity of a reaction can never be equal to zero because number of molecules colliding with each other in a reaction can never be zero.
OR
(i) If reaction is 20% completed then the remaining reactant is 80%,
Hence, R1 = 100; R2 = 80
For a first order reaction, rate constant is given by :
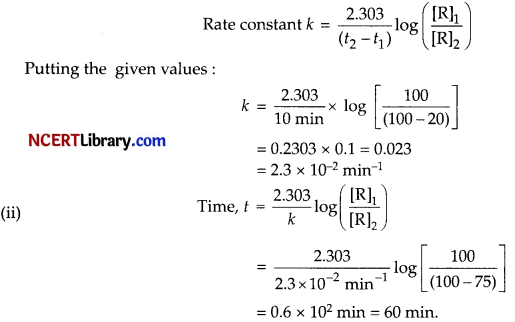
(b) The order of all photochemical reactions is zero as it does not depend upon the concentration of reactants.
(c) Temperature, concentration of reactants and catalyst affect the rate of reaction.
(d) In a graph between ‘fraction of molecules’ and ‘kinetic energy’, the peak of graph corresponds to the ‘most probable kinetic energy’ of the molecules.
Question 35.
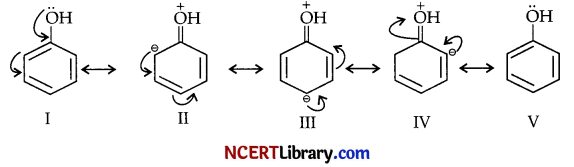
(a) Draw the resonating structures of phenol.
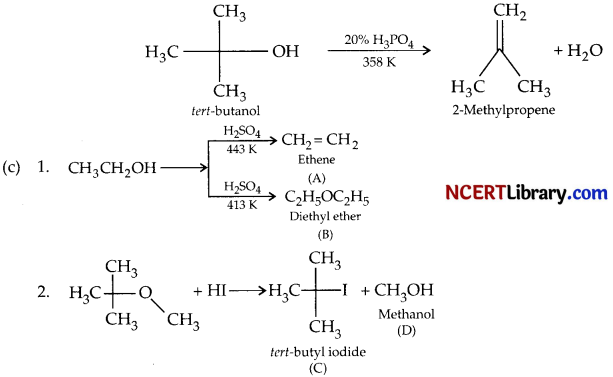
(b) What happens when tert-butanol is treated with 20% H3PO4 at 358 K?
(c) Predict the products A, B, C, and D
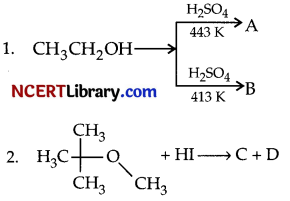
(d) Diethyl ether was widely used as an anaesthetic. Give reason for discontinuation of its use? [5]
Answer:
(a) Resonating structures of phenol can be shown as :
(b) fert-butanol undergoes dehydration when it is treated with 20% H3PO4 at 358 K.
(d) Diethyl ether was widely used as an anesthetic before because it was cheap and easy to use and most importantly, it is soluble in water. Although, because of some major drawbacks its use was discontinued, first, it’s bad smelling and can cause coughing, salivation, lacrimation, etc. Second, it is explosive, so it can result in fire. Third and the most important is its slow effect and unpleasant recovery period.