Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies with Solutions Set 4 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies Set 4 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours.
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains 34 questions.
- Marks are indicated against each question.
- Answers should be brief and to the point.
- Answers to the questions carrying 3 marks may be from 50 to 75 words.
- Answers to the questions carrying 4 marks may be about 150 words.
- Answers to the questions carrying 6 marks may be about 200 words.
Question 1.
“Aman runs a clothing company. There is lot of chaos in the organisation. He decided to do grouping of similar activities into departments, units, sections, etc., using several criteria as a basis to facilitate specialisation.” Identify the step of organising process referred here.
(a) Identification and division of work.
(b) Departmentalisation.
(c) Assignment of duties.
(d) Establishing reporting relationship.
Answer:
(b) Departmentalisation.
Explanation: Departmentalisation is the process of making departments to bring specialisation in the organisation.
Question 2.
Identify the dimension of business environment, which focuses on laws and regulations on industrial development.
(a) Economic environment
(b) Legal environment
(c) Political environment
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) Legal environment
Explanation: The legal environment includes the laws passed by the government as well as the decisions rendered by the various commissions and agencies at every level of the government. Businessmen have to act according to various legislations. He must have the knowledge for the same.
Question 3.
“Uranus Limited is a company dealing in metal products. The work is mainly divided into functions including production, purchase, marketing, accounts and personnel.” Identify the type of organisational structure followed by the organisation.
(a) Functional Structure
(b) Relational structure
(c) Divisional structure
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Functional Structure
Explanation: Under functional structure the departments are based on functions like production, finance, marketing etc.
Question 4.
Which of the following external dimension is being described in the picture given below?
(a) Natural Environment
(b) International Environment
(c) Political Environment
(d) Technological Environment
Answer:
(d) Technological Environment
Explanation: Technological environment refers to the changes in the output, production methods, use of equipment and quality of the product. It includes force related to scientific innovations and improvements in products as well as production technology.
For example, with recent improvements in technology and computerisation/marketing and selling of products is now possible online leading to increase in sales and output of many firms.
Question 5.
Rahul was running a media company. He observed that the performance of the employees was not up to the mark. So, he performed a function of management which reviews the operations in a business unit. Identify the function of management.
(a) Planning
(b) Organising
(c) Directing
(d) Controlling
Answer:
(d) Controlling
Explanation: Controlling means to compare the actual performance with the standards set during planning. Thus Rahul is performing the control function so as to improve the performance of his employees.
![]()
Question 6.
The Economic Survey, 2019 suggests that the psychological biases can be used for the tax compliance. It is in favour of using religious slogan such as “dying in debt is a sin” to improve tax compliance. Identify the related dimensions of business environment.
(a) Legal dimension and social dimension
(b) Social dimension and economic dimension
(c) Technological dimension and political dimension
(d) Political dimension and economic dimension
Answer:
(b) Social dimension and economic dimension
Explanation: The religious slogan is related to the social dimension which includes forces like traditions, values, social trends, etc. and tax rates relate to economic dimension.
Question 7.
India’s population is expected to grow under 0.5 per cent during 2031-41 due to decline in fertility rate and increase in life expectancy. These changes in India’s demography will also have implications such as the proportion of elementary school-going children will witness significant declines, lack of hospital beds and increase in retirement age. The related feature of business environment being described in the
above lines is:
(a) Totality of external forces
(b) Dynamic nature
(c) Inter-relatedness
(d) Relativity
Answer:
(c) Inter-relatedness
Explanation: Different elements of business environment are closely inter-related and interdependent. A change in one element affects the other elements. The increase in the life expectancy of the people has change the demography of the population as a result demand for different product increased
Question 8.
Management is equally important to rim a political organisation as it is to run an economic organisation. Which feature of management is being highlighted here?
(a) Management is goal oriented
(b) Management is multidimensional
(c) Management is all pervasive
(d) Management is a group activity
Answer:
(c) Management is all pervasive
Explanation: Management is done in every type of organisation, whether it is profit-making, non-profit making , social, political, or any other type of organisation because every organisation comprises of human physical, financial resources which need to be managed properly.
Question 9.
When securities are not issued directly to the public, but are offered through intermediaries like issuing houses or stock brokers it is called:
(a) offer’through prospectus
(b) offer for sale
(c) private placement
(d) e-IPO
Answer:
(b) offer for sale
Explanation: Under this method, securities are offered for sale through intermediaries like issuing houses or stock brokers. The company sells securities to intermediary/broker at an agreed price and the broker resells them to investors at a higher price.
Question 10.
In a marketing firm, the Finance Manager pays more attention towards an increase of 3% in the marketing cost as compared to a 15% increase in the courier expenses. Identify the concept being used by the manager.
(c) corrective action
(d) none of these
(a) management by exception
(b) critical point control
Answer:
(b) critical point control
Explanation: The concept identified here is critical point control. This is an ideal control technique, therefore he should focus on the key result areas. In the above example, the finance manager pays more attention towards the increase in marketing cost rather than increase in courier expenses because increase in marketing cost is a bigger concern for the organisation.
![]()
Question 11.
Good health limited has decided to launch a new range of water bottles with in-built water purifiers. Instead of marketing the product by its generic name, the company has decided to call it ‘Turifiere’. Identify the type of marketing function being described in the above information.
(a) Packaging and labelling
(b) Branding
(c) Pricing
(d) Promotion
Answer:
(b) Branding
Explanation: The marketing function being described in the above information is branding. A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that identifies one seller’s good or service as distinct from those of other sellers.
Question 12.
Statement I: The principles of management are in the continuous process of evolution.
Statement II: The principles of management are considered to be rigid in nature as principles of pure science.
Choose the correct option from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is true and II is false.
(b) Statement II is true and I is false.
(c) Both the statements are true.
(d) Both the statements are false.
Answer:
(b) Statement I is true and II is false.
Explanation: Statement I is correct and II is wrong because principles of management are in evaluation phase as these principles have evolved over a long period of time with continuous practice and experimentation. Management Principles are very flexible whereas pure science principles are rigid.
Question 13.
Match the Column-I with their respective Statements in Column-II
| Column-I | Column-II |
| (A) Needs and Wants | (i) The process of marketing helps individuals and groups in obtaining what they need and want. |
| (B) Creating a Market Offering | (ii) The process of marketing works through the exchange mechanism. |
| (C) Customer Value | (iii) On the part of the marketers, the effort involves creation of a market offering. |
| (D) Exchange Mechanism | (iv) The process of marketing facilitates exchange of products and services between the buyers and the sellers. |
(A) (B) (C) (D)
(a) (ii) (i) (iii) (iv)
(b) (i) (iii) (iv) (ii)
(c) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
(d) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
Answer:
(a) (i) (iii) (iv) (ii)
Question 14.
The process of estimating the funds requirement of a business and specifying the sources of funds is called __________.
(a) capital structure
(b) financial planning
(c) return on investment
(d) trading on equity
Answer:
(b) financial planning
Explanation: Financial planning is the preparation of financial blueprint, which foresees entire fund requirement in respect to quantum as well as the timing.
Question 15.
__________ is the institution which provides a platform for trading of existing securities having long-term maturity.
(a) SEBI
(b) WTO
(c) Stock exchange
(d) RB
Answer:
(c) Stock exchange
Explanation: Stock Exchange is a place where shares of pubic limited companies are traded. A stock exchange facilitates stock brokers to trade company stocks and other securities. A stock may be bought or sold only if it is listed on an exchange. Thus, it is the meeting place of the stock buyers and sellers.
Question 16.
Which of the following statements is incorrect about the primary market?
(a) Is also known as the old issues market.
(b) It facilitates the transfer of investible funds from savers to entrepreneurs.
(c) It deals with new securities being issued for the first time.
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Is also known as the old issues market.
Explanation: It is a new issue market. New securities are issued by companies directly to investors.
![]()
Question 17.
“They don’t sell what they can make, but they make what they can sell.” Name the marketing philosophy to which this statement is related.
(a) Societal marketing concept
(b) Marketing concept
(c) Product concept
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Marketing concept
Explanation: The marketing concept is consumer oriented marketing. This concept emphasizes on the determination of the requirements of potential consumers and develop strategies not only to satisfy the needs of the customers but also accomplish the goals of the organisation.
Question 18.
Which one of the following is not an element of marketing mix?
(a) Product
(b) Physical distribution
(c) Product pricing
(d) Production process
Answer:
(d) Production process
Explanation: Production process is not a part of marketing mix. The elements of marketing mix are product, price, place, promotion.
Question 19.
Unibix company is a mobile company offers a discount of ₹ 1000 to clear off excess inventory. Identify the method of sales promotion :
(a) Discount
(b) Rebate
(c) Lucky draw
(d) Usable benefit
Answer:
(b) Rebate
Explanation: A rebate is the amount paid by way of reduction, return or refund. It is one of the tools of sales promotion which marketers use for supplement product sales.
Question 20.
Arrange the following steps of Controlling process in correct sequence:
(i) Measurement of Actual Performance
(ii) Analysing Deviation
(iii) Setting Performance Standards
(iv) Comparing Actual Performance with Standard Performance
(a) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(b) (iv), (iii), (ii), (i)
(c) (iii), (i), (ii), (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
Answer:
(c) (iii), (i), (ii), (iv)
Explanation:
Steps in Controlling Process:
1. Setting Performance Standards
2. Measurement of Actual Performance.
3. Analysing Deviations: Some deviation in performance can be expected in all activities.
4. Comparing Actual Performance with Standard Performance.
Question 21.
‘Art is concerned with personal application of knowledge.’ In the light of this statement compare all the features of management with art and prove that it is an art.
Answer :
‘Art is concerned with the personal application of knowledge.’ The features which compare management with art are as follows:
1. There is lot of literature available in various areas of management like marketing, finance and human resources which the manager has to specialise. Thus, there is a existence of theoretical knowledge.
2. A manager applies scientific methods and body of knowledge to a given situation, issue or a problem in his/her own unique manner. A good manager works through a combination of imagination, innovation and initiatives.
3. A good manager learns art of management by continuous practice and training over the years. He/ She is involved in the activities of the organisation, studies critical situations and formulates his/her own theories for use in a given situation.
![]()
Question 22.
Nishant, the director of a garments company, is planning to manufacture bags for the utilisation of waste material from one of his garment units.
He has decided that this manufacturing unit will be set-up in a rural area of Orissa where people have very few job opportunities and labour is available at very low rates. He has also thought of giving equal opportunities to men and women.
For this he wants four different heads for Sales, Account, Purchase and Production. He gives an advertisement and shortlists ten candidates per post after conducting different selection-tests. Identify and state the next three steps for choosing the best candidate out of the shortlisted candidates.
Answer:
The following are the three steps for choosing the best candidate out of the shortlisted candidates:
1. Personal interview: The personal interview is an integral part of the selection process and it is most important and necessary for the organisation.
After the initial round of selection tests, the successful candidates are taken to the subsequent round of personal interviews. This round of screening includes a conversation between the candidate and a manager.
An in-depth conversation is conducted to judge the suitability of the candidate for the job. It also helps the manager to assess the candidate in all the major aspects such as attitude, aptitude, thought process and spirit to cope with challenging tasks.
2. Background check: Once a candidate is successful in the personal interview, his or her documents are verified so that his/her background can be easily identified.
In this round, the work experience and reference given by the candidate in the curriculum vitae are checked. The verification of documents and references (such those as from the previous employer of the candidate) helps in getting additional information about the candidate, which might not have been collected at the personal interview.
3. Selection decision: After the personal interview and background check, the best and most suitable candidate is selected for the job.
Question 23.
Explain how ‘management by exception’ helps in controlling process.
OR
How does controlling help in achieving objectives and improving employers’ morale?
Answer:
The principle of ‘Management by Exception’, emphasises on the fact that an effort to control everything may end up in controlling nothing, i.e., everything cannot be controlled effectively and efficiently.
According to it, rather than controlling each and every deviation in performance, an acceptable limit of deviations in various activities should be set and only those deviations that go beyond the acceptable range should be brought to the notice of the managers and it must be controlled.
In other words, only the major deviations which are beyond permissible limit should be acknowledged. Thus, by emphasising on controlling the major things only, management by exception helps in the controlling process in the organisation.
OR
Controlling helps in achieving objectives and improving employers’s morale by following ways: Controlling helps in achieving objectives by continuously measuring the performance in the light of organisational goals to brings out the deviations, if any and indicates the corrective actions to be taken. Thus, controlling keeps the organisation on the right track.
Controlling improves employers’s morale as implementation of controlling mechanism makes all the employees to work with complete dedication because they are aware that their performance will be evaluated and they will have a chance to build their reputation in the organisation. The employees who show good performance are rewarded by giving them promotions, cash prizes, etc.
Question 24.
What are the features of secondary market/stock exchanges?
OR
What are the features of money market?
Answer:
The features of secondary market/stock exchanges are:
1. It is the market for old/existing securities.
2. Both buying and selling of securities take place.
3. The forces of demand and supply determine prices of the securities.
4. It involves dealings between two investors.
5. Stock exchanges exist at fixed locations.
OR
The features of money market are:
1. The main participants are institutional investors.
2. Since the cost of securities may be high, investment in the money market may require a huge capital outlay.
3. The money market enjoys high liquidity as The Discount Finance House of India works as a compulsory market maker.
4. The instruments in the money market carry low risk as the expected return is low on securities.
![]()
Question 25.
Define the staffing process and the various steps involved in it.
OR
Explain the steps in the process of selection of employees.
Answer:
Staffing process of the management is concerned with acquiring, developing, employing, remunerating and retaining people or we can say it is the timely fulfillment of the manpower requirements within an organisation.
The following steps are involved in staffing process:
1. Estimating the manpower requirements: The first step in the staffing process is determining the present manpower inventory and assessing the present and future manpower requirements of the organisation keeping in mind the production schedule, demand etc.
2. Recruitment: Recruitment may be defined as the process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organisation. For this various sources can be used like transfer, promotion, advertising, job consultants etc.
3. Selection: Selection is the process of choosing from among the pool of the prospective candidates who have applied at the stage of recruitment. It involves a host of tests and interviews.
4. Placement and Orientation: Orientation is introducing the selected employee to other employees and familiarising him with the rules and policies of the organisation.
He is taken around the work place and given the charge of the job for which he has been selected. Placement refers to the employee occupying the position or post for which the person has been selected.
5. Training and development: All organisations have either in-house training centres or have forged alliances with training and educational institutes to ensure continued learning of their subordinates.
By offering the opportunities for career advancement to their employees, organisations are not only able to attract but also retain its talented staff.
6. Performance appraisal: After the employees have undergone a period of training and they have been on the job for some time, there is a need to evaluate their performance.
The employee is expected to know what the standards are and the superior is the one who provides the employee feedback on his/her performance. The performance appraisal process, therefore, will include defining the job, appraising performance and providing feedback.
7. Promotion and career planning: It is very important for all organisations to address career related issues and promotional avenues for their employees. They must provides opportunities to everyone to show their potential and in return promotions can be provided.
8. Compensation: All organisations need to establish wage and salary plans for their employees. There are various ways to prepare different pay plans depending on the worth of the job. Compensation therefore, refers to all forms of pay or rewards going to employees.
OR
The important steps in the process of selection are as follows:
1. Preliminary screening: It helps the manager eliminate unqualified or unfit job seekers based on the information supplied in the application forms.
2. Selection tests: An employment test is a mechanism that attempts to measure certain characteristics of individuals. These range from aptitudes, such as manual dexterity, to intelligence to personality.
3. Employment interview: Interview is a formal, in depth conversation conducted to evaluate the applicant’s suitability for the job.
4. Reference and background checks: Many employers require names, addresses and telephone numbers of references for the purpose of verifying information and gaining additional information about an applicant.
5. Selection decision: The final decision has to be made among the candidates who qualify the tests, interviews and reference checks.
6. Medical examination: Before the candidate is given a job offer he/she is required to go through a medical test.
7. Job offer: Job offer is made through a letter of appointment to confirm his acceptance. Such a letter generally contains a date by which the appointee must report on duty.
8. Contract of employment: After the job offer has been made and candidate accepts the offer, certain documents need to be executed by the employer and the candidate. There is also a need for preparing a contract of employment. It includes job title, duties, responsibilities, date, effects joining, etc.
![]()
Question 26.
Explain the principles of directing.
OR
Differentiate between formal and informal communication.
Answer:
Principles of directing are:
1. Maximum individual contribution: This principle emphasises that directing techniques must help every employee to contribute to his maximum potential in order to achieve the organisational goals.
It should help in bringing out unused or dormant potential of an employee to improve the efficiency of the organisation, e.g., suitable and appropriate incentives should be given to encourage employees to improve their performance.
2. Harmony of objectives: Most of the time it happens that the organisational objectives and individual objectives move in opposite directions. The person in charge of a team of workers should guide and instruct his team in such a manner that they realise the importance of both the objectives,
3. Unity of command: This principle insists that a person in the organisation should receive instructions from one superior only. If instructions are received from more than one, it creates confusion, conflict and disorder in the organisation. Adherence to this principle ensures effective direction.
4. Appropriateness of direction technique: According to this principle, appropriate motivational and leadership technique should be used while directing the people based on subordinate needs, capabilities, attitudes etc., e.g., combination of both monetary and non-monetary incentives should be used to elicit the right response from the employees.
OR
| Basis of Difference | Formal Communication | Informal Communication |
| 1. Meaning | It refers to official interactions of information following the chain of command. | It refers to unofficial communication occurring between different people across different groups. |
| 2. Path followed | Definite path. | Indefinite path. |
| 3. Identity the source of information | Known source. | Unknown source. |
| 4. Media | Written, verbal. | Only verbal. |
| 5. Mutual relations | Issuer and receptor have some organisational relations. | Issuer and receptor have some personal relations. |
| 6. Distortion | Less distortions. | High distortions. |
| 7. Authenticity | Mostly authentic information. | May not be authentic information. |
| 8. Rigidity | Very rigid. | Information can be clarified flexibly. |
Question 27.
Discuss Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory of Motivation.
Answer:
Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory of Motivation: Motivation is a psychological term and the needs of an employee play an important role in motivation. In order to study motivation various researchers developed theories on them. Among them Abraham Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory is considered of worth. In this opinion, their exists a Hierarchy of five needs. These are:
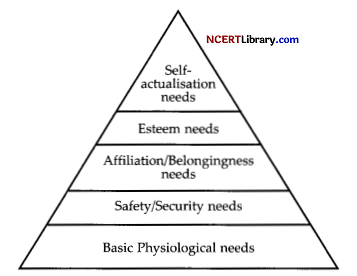
1. Basic Physiological Needs: These needs are most basic in the hierarchy and correspond to primary needs. Food, clothing, shelter are a few examples of this type of need. Basic salary helps to fulfill these needs.
2. Safety/Security Needs: When the basic needs are satisfied, people start thinking of future. These needs provide security and protection from physical and emotional harm in coming future e.g., job security, pension plans etc.
3. Affiliation/Belonging Needs: These needs refer to human feeling of belongingness. We all as human beings look forward to being accepted in the society e.g., friendship.
4. Esteem Needs: These include factors such as self-respect, autonomous status, attention. In this need an individual wants respect and recognition from others.
5. Self-actualisation Needs: It is the highest level of need in the hierarchy. It refers to the drive to become what one is capable of becoming. The needs include growth self-fulfillment and achievement of goals etc.
Question 28.
“Capital structure decision is essentially optimisation of risk-return relationship.” Comment.
Answer:
Capital structure refers to the mix between owners, and borrowed funds. It can be calculated as Debt/ Equity. Debt and equity differ significantly in their cost and risk involved for the firm.
The cost of debt is lower than the cost of equity for a firm because the lender’s risk is lower than the equity shareholder’s risk since lenders earn on assured return and repayment of capital.
Therefore they should require a lower rate of return. Debt is cheaper but is riskier for a business because payment of interest and the return of principal is obligatory for the business. Any default in meeting these commitments may force the business to go into liquidation.
There is no such compulsion in the case of equity, which is, therefore, considered riskless for the business. Higher use of debt increases the fixed financial charges of a business. As a result, increased use of debt increases the financial risk of a business.
The capital structure of a business thus affects both the profitability and creates the financial risk. Therefore, a capital structure will be said to be optimal when the proportion of debt and equity is such that it increases the value of the equity share.
![]()
Question 29.
Kay Ltd. is a company manufacturing textiles. It has a share capital of ₹ 60 lakhs. In the previous year its earning per share was ₹ 0.50. For diversification, the company requires additional capital of ₹ 40 lakhs.
The company raised funds by issuing 10% debentures for the same. During the year the company earned profit of ₹ 8 lakhs on capital employed. It paid tax @ 40%.
(i) State whether the shareholders gained or lost, in respect of earning per share on diversification. Show your calculations clearly.
(ii) Also, state any three factors that favour the issue of debentures by the company as part of its capital structure.
Answer:
(i) Profit before Interest and Tax = ₹ 8,00,000.
Interest on 10% Debentures = ₹ 4,00,000 \(\left(40,00,000 \times \frac{10}{100}\right)\)
Profit before Tax = Profit before Interest and Tax- Interest
= 8,00,000 – 4,00,000
= ₹ 4,00,000
Tax @ 40% = ₹ 1,60,000
profit after Tax = Profit before Tax – Tax
= 4,00,000 – 1,60,000 \(\left(40,00,000 \times \frac{40}{100}\right)\)
= ₹ 2,40,000
\text { EPS } &=\frac{\text { Profit after Tax }}{\text { Number of Equity Shares }} \\
&=\frac{2,40,000}{6,00,000}=₹ 0.4
\end{aligned}\)
(The face value of equity share is assumed to be ₹10 each. Hence, the share capital is ₹ 6,00,000) This clearly shows that the shareholders have incurred a loss after the issue of debentures.
(ii) The three factors that favour the issue of debentures by the company as part of its capital structure are:
1. Tax deductibility: Interest paid by the company to its debenture holders is tax deductible. In the above scenario, the company is paying tax @40%. Thus, it is beneficial for the company to issue debentures.
2. Say in management: In the given scenario, the company already has a share capital of ₹ 60,00,000. Issuing more shares will dilute the control of management. Thus, companies that are apprehensive of the dilution of control, opt for more of debt and less of equity.
3. Relatively low cost: For a company, cost of raising capital through debentures is relatively lower than that through equity. This is due to guaranteed repayment that debenture holders require lower rate of returns. Besides this, interest amount repayable to debenture holders is a deductible expense.
Question 30.
What role can you as a student play to contribute to the cause of consumer protection?
Answer:
A student can play an active role in bringing out an awareness campaign on ‘Consumer Protection’.
1. Special assemblies can be organised to show the display of consumer rights and responsibilities, e.g.,
Right to the satisfaction of basic needs, Right to safety, Right to be informed and protected, responsibility to be aware of the quality and safety of goods and services before purchasing, responsibility to think independently and make choices about well-considered needs and wants etc.
2. When the school organises any exhibition, the commerce students can put a stall and demonstrate the responsibilities of a consumer.
3. The Biology and Chemistry laboratories can test adulterated goods (e.g., milk, paneer, spices etc.).
4. Essay writing competitions, debate competitions, and quizzes can be organised to promote awareness of consumer protection.
5. Encourage students to boycott goods/ eatables which are adulterated or defective, in the school canteen.
6. To set up a voluntary complaint centre for consumer guidance and counselling.
Question 31.
Explain the following principles of Fayol with the help of one example for each.
(i) Discipline
(ii) Unity of Command
(iii) Scalar Chain
(iv) Stability of Tenure of Personnel
OR
Explain ‘Science, not rule of thumb’, ‘Harmony, not discord’, and ‘Development of each and every person to his or her greatest efficiency and prosperity’ as principles of Scientific Management given by F.W.Taylor.
Answer:
(i) Discipline: It is the obedience to organisational rules and employment agreement, which are necessary for the working of an organisation. Discipline requires good supervisors at all levels, clear and fair agreements and judicious application of penalties.
For example, if workers took an unauthorised and non-sheduled break in the middle of the day from work, they would have to pay a penalty for wasting time which should be actually meant for work.
(ii) Unity of Command: According to Fayol there should be one and only one boss for every individual employee. It implies that every worker should receive orders from one superior only, otherwise it will create confusion, conflict and duplication of work.
For example, the workers responsible for manufacturing steering wheels should receive orders from the foreman managing the steering wheel unit and not from the foreman managing the frame of the car in a car production plant.
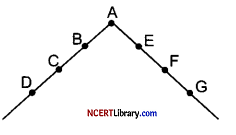
(iii) Scalar Chain: According to Fayol, Scalar Chain refers to the chain of authority and communication that runs from top to bottom and should be followed by managers and their subordinates.
The given figure illustrates the process of scalar chain. If D and G want to communicate, the message should usually move up through C, B, A, E, F and then G whereas, the manager is communicating with all levels and all departments, without following the scalar chain.
(iv) Stability of Personnel: Employees, once selected, should be kept at their post for a minimum fixed tenure and be given reasonable time to show results.
It will help to minimise employee turnover and maintain organisational efficiency. Any unfavour in this regard will create instability/ insecurity among employees.
They would tend to leave the organisation. For example, if a hard-working employee is dissatisfied with his monotonous job, he can be retained by providing a new position (or responsibility) in another department within the company that requires him to explore and advance his capabilities.
OR
Science not rule of thumb:
1. This principle states that there may be only one best way/method to maximise efficiency.
2. This method can be developed through scientific study and analysis of each element of a job and should substitute ‘Rule of Thumb’.
3. This standard method should be followed throughout the organisation.
Harmony, not discord:
1. The principle emphasises that there should be complete harmony between the management and the workers.
2. This requires ‘Mental revolution’ on the part of both management and workers. Both management and the workers should transform their thinking.
3. Management should share gains of the company if any with the workers and workers should work hard and always be willing to embrace change for the good of the company.
Development of each and every person to his or her greatest efficiency and prosperity:
1. This principle is concerned with efficiency of employees which could be built in right from the process of employee selection.
2. The work assigned to employees should suit their capabilities. They should be given the required training to increase their efficiency.
3. Efficient employees would produce more and earn more. This will ensure their greatest efficiency and prosperity for both the company and the workers.
![]()
Question 32.
What are the main aspects in the definition of planning?
OR
“It is decided in advance what to do and how to do it. It is one of the basic managerial functions. It requires that before doing something, the manager must formulate an idea of how to work on a particular task.
This function is closely connected with creativity and innovation. It seeks to bridge the gap between where we are and where we want to go and is performed at all levels of management. In spite of this, the function of management referred above has a number of limitations.” What are the limitations highlighted in the above case?
Answer:
Planning is a process of analysing and deciding in advance regarding the tasks that need to be done and the way it should be done. It is a type of mental exercise in which a manager decides the goals that need to be achieved and the means through which those goals can be accomplished.
It involves looking ahead at the future. It can also be defined as setting up of objectives and goals, setting up alternatives and deciding on the appropriate action that needs to be taken.
Following are some of the main aspects of planning:
1. Planning must be done with fulfilling a certain objective. There needs to be certain objective which needs to be accomplished with the planning.
2. Plan must be defined for a certain period of time. If planning is not done within a set time period, it can become useless, as the business environment can change which will lead to changes in existing plan and new set of actions to be implemented.
3. Once an objective is decided, the next part is deciding on how the objectives need to be achieved. Achieving the objective can be done through various alternative courses of action. Hence, those alternative options need to be determined appropriately.
4. The best alternative should be chosen among the available alternatives in order to get the best result.
OR
The following are the limitations of planning:
1. Planning leads to rigidity: A well-defined plan is put up in an organisation with specified goals to be completed within a specific time frame, but management may not be able to change it.
These plans decide the future course of action and managers may not be in a position to change it. This kind of rigidity in plans may create difficulty.
Managers need to be given some flexibility to be able to cope with the changed circumstances. Following a pre-decided plan, when circumstances have changed, may not turn out to be in the organisations interest.
2. Planning may not work in a dynamic environment: The business environment is dynamic, nothing is constant. The environment consists of a number of dimensions, economic, political, physical, legal and social dimensions.
The organisation has to constantly adapt itself to changes. It becomes difficult to accurately assess future trends in the environment if economic policies are modified or political conditions in the country are not stable or there is a natural calamity.
Competition in the market can also upset financial plans, sales targets may have to be revised and, accordingly, cash budgets also need to be modified since they are based on sales figures. Planning cannot foresee everything and thus, there may be obstacles to effective planning.
3. Planning reduces creativity: Top management does planning and middle management does implementation of plan but they are not allowed to deviate from the plan and thus creativity of these managers are reduced.
Planning is an activity which is done by the top management. Usually the rest of the members just implements these plans As a consequence, middle management and other decision makers are neither allowed to deviate from plans nor are they permitted to act on their own.
Thus, much of the initiative or creativity inherent in them also gets lost or reduced. Most of the time, employees do not even attempt to formulate plans.
They just carry out orders. Thus, planning in a way reduces creativity since people tend to think along the same lines as others. There is nothing new or innovative.
![]()
Question 33.
State any five points which highlight the importance of delegation of authority.
Answer:
The following points highlight the importance of delegation of authority:
1. Managerial efficiency: Delegation of work to subordinates helps a manager to concentrate on other relevant areas of operation. Besides, it provides him the opportunity to explore new work techniques.
For example, if a manager delegates the basic work to his subordinate, he can put his mind into exploring new ways to improve efficiency.
2. Employee development: Delegation causes subordinates to accept accountability and exercise judgement for solving problems. Thus improves self-confidence and willingness to take decisions.
3. Motivation: Delegation motivates the employees to work with greater responsibility. Delegation shows the trust and confidence of superior on his subordinates. It provides them satisfaction in terms of recognition and use of authority.
4. Growth: Delegation facilitates easy growth and expansion. Delegation helps in preparing efficient and experienced managers that can take up leading positions at times of growth of the organisation.
In other words, workers trained and prepared through delegation contribute towards the expansion and growth of the organisation.
5. Better coordination: The three elements of delegation viz. authority, responsibility and accountability help to define powers, duties and answerability related to various job positions.
It provides clarity in duties to be performed and avoids overlapping and duplication of work. Such clarity helps in bringing effective coordination among the departments, levels and functions of management.
Question 34.
Ramesh was watching television. He saw many advertisements. Within a span of five hours, he saw advertisements of five toothpaste selling companies.
He noticed that every toothpaste selling company was claiming its toothpaste to be the best toothpaste recommended by dentists. He decided to go to his friend who was a personal selling agent of FMCG.
After meeting him he got assured of the best toothpaste available in the market. However, he also liked the quality of the toothpaste of his friend’s company as his friend gave him some very logical reasons for it.
After returning home Ramesh couldn’t sleep as he could see his friend’s struggle in convincing him for half an hour and compared it with the mass reach of an advertisement. Next day he was on an off from his office.
He went to a mobile shop and decided to purchase a mobile worth ₹ 40,000. The company offered him a scheme in which he could purchase the mobile in interest free ten instalments of ₹ 4,000 to be paid every month. However, when he was asked to fill a form, a file charge of ₹2,000 was taken from him.
He purchased the phone because of the good quality of the phone and the continuous efforts of the salesman in the mobile shop.
(i) Which objection to advertising has been highlighted in the above case?
(ii) Which quality of a good salesman do you think his friend possessed?
(iii) Which limitation of personal selling did Ramesh find in comparison to advertisement?
(iv) Did Ramesh pay any interest on the phone he purchased?
(v) Which quality do you think existed in the salesman in the mobile shop?
Answer:
(i) The objection to advertising which is highlighted in the above case is ‘Advertising confuses the buyers’. He found that every toothpaste selling company was claiming its toothpaste to be the best toothpaste recommended by dentists.
(ii) The quality of ‘convincing customers and building trust’ was possessed by his friend. However, he also liked the quality of the toothpaste of his friend’s company as his friend gave him some very logical reasons for it.
(iii) The limitation of personal selling is to reach only a limited number of people due to time and cost considerations. After returning home, Ramesh couldn’t sleep as he could see his friend’s struggle in convincing him for half an hour and compared it with the mass reach of an advertisement.
(iv) No, he has not paid any interest for the purchase of the mobile phone. However, at the time of filling a form, a file charge of ₹ 2,000 was taken from him.
(v) The quality which existed in the salesman in the shop was ‘persistence’. He purchased the phone because of the good quality of the phone and the continuous efforts of the salesman at the mobile shop.