Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology with Solutions Set 4 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Set 4 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours.
Max. Marks: 70
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has five sections and 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 16 questions of 1 mark each; Section- B has 5 questions of 2 marks each; Section- C has 7 questions of 3 marks each; Section- D has 2 case-based questions of A marks each; and Section- E has 3 questions of 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn.
Section – A (16 Marks)
Question 1.
Micropyle occurs in: [1]
(a) Ovary
(b) Ovule
(c) Seed
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Explanation: Micropyle is the small minute pore which is differentiated from the surface of the egg. It is formed by the projection of integuments into which the male gamete through pollen tube enters into the egg of the ovule. It is usually located at the top of the seed or ovule.
Question 2.
Match the structures of male reproductive system given in column I with their features given in column II and select the correct match from the options given below. [1]
| Column I (Structures) | Column II (Features) | ||
| A | Rete testis | (i) | Facilitates insemination |
| B | Leydig cells | (ii) | Meiosis and sperm formation |
| C | Seminiferous tubules | (iii) | Connects seminiferous tubules to vasa efferentia |
| D | Penis | (iv) | Secrete androgens |
(a) A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iii), D-(iv)
(b) A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(ii), D-(i)
(c) A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iv)
(d) A-(ii), B-(iv), C-(iii), D-(i)
Answer:
(d) A-(ii), B-(iv), C-(iii), D-(i)
Explanation: Rete testis carries sperms from the seminiferous tubules (where sperms are produced through meiosis) of the testes into the vasa efferentia. Leydig cells synthesise and secrete testicular hormones called androgens. The penis is the male external genitalia that facilitates insemination.
Question 3.
A dihybrid for qualitative trait is crossed with homozygous recessive individual of its type, the phenotype ratio is: [1]
(a) 1: 2: 1
(b) 3: 1
(c) 1: 1: 1: 1
(d) 9: 7
Answer:
(c) 1: 1: 1: 1
Explanation: The given cross is a test cross. The ratio for a test cross is always 1:1 for a monohybrid cross and 1:1:1:1 for a dihybrid cross.
Question 4.
Discontinuous synthesis of DNA occurs on one strand because: [1]
(a) DNA molecule being synthesized is very long
(b) DNA dependent DNA polymerase catalyses polymerisation only in one direction (5′ → 3′)
(c) it is a more efficient process
(d) DNA ligase has to play some role
Answer:
(b) DNA dependent DNA polymerase catalyses polymerisation only in one direction (5′ → 3′)
Explanation: DNA dependent DNA polymerase catalyses polymerization only in one direction (5’→ 3′)- Consequently the replication on template with polarity 3′ to 5′ is continuous while the other template with polarity 5′ to 3′ is discontinuous and is synthesized in Okazaki fragments which later join by DNA ligase.
Question 5.
Match the following columns: [1]
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Lady bird | 1. Methanobacterium |
| B. Mycorrhiza | 2. Trichoderma |
| C. Biological control | 3. Aphids |
| D. Biogas | 4. Glomus |
Choose the correct match:
Codes:
| A | B | C | D | |
| (a) | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| (b) | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| (c) | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| (d) | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| (b) | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
Answer:
Explanation: Ladybird is a very familiar beetle with red and black markings, used to get rid of Aphids. Fungi form symbiotic association with the roots of higher plants called mycorhiza, e.g., Glomus. A biological control being developed for use in the treatment of plant disease in the fungus Trichoderma.
Methanogens, particularity Mcthanobacterium, are found in cowdung. These bacteria grow anaerobically on cellulosic material and produce large amount of methane along with Co2 and H2.
![]()
Question 6.
Which of the following is the most fatal noninfectious disease? [1]
(a) AIDS
(b) Cancer
(c) Diabetes
(d) Obesity
Answer:
(b) Cancer
Explanation: Cancer is the most fatal non-infectious disease. In 2017, 9.6 million people were estimated to have died from various forms of cancer. While AIDS is the most fatal infectious disease affecting nearly 36.9 million people world-wide. Diabetes and obesity are also non-infectious diseases but not the most fatal.
Question 7.
Match column-I with column-II and select the correct option from the codes given below. [1]
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| A | Lungs of the planet | (i) | Lantana camara |
| B | Reserpine | (ii) | Amazon rain forests |
| C | Anti-cancer drug | (iii) | Yew tree |
| D | Exotic species | (iv) | Rauwolfia |
(a) A-(ii), B-(iv), C-(iii), D-(i)
(b) A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(iv), D-(i)
(c) A-(iv), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(ii)
(d) A-(ii), B-(iv), C-(i), D-(iii)
Answer:
(a) A-(ii), B-(iv), C-(iii), D-(i)
Explanation: Amazon forest called lungs of planet because they generally draw in carbon dioxide and breathe out oxygen. Reserpine It is an indole alkaloid obtained from Rauwolfia serpentina. Lantana camara is exotic species. Anti-cancer drugs are obtained from Yew tree.
Question 8.
Gel electrophoresis is used for: [1]
(a) Construction of recombinant DNA by joining with cloning vectors
(b) Isolation of DNA molecule
(c) Cutting of DNA into fragments
(d) Separation of DNA fragments according to their size
Answer:
(d) Separation of DNA fragments according to their size
Explanation: Gel electrophoresis is a method that is widely used in laboratories to separate the molecules such as DNA, RNA, or proteins, based on their size, under the influence of an electric field.
Question 9.
Match List-I with List-II and choose the correct options : [1]
| List-I | List-II | ||
| A. | dN/dt = \(r \mathrm{~N}\left(1-\frac{\mathrm{N}}{\mathrm{K}}\right)\) | 1. | A large no of small size |
| B. | Oyster | 2. | Exponential growth |
| C. | Nt = Noert | 3. | Breeds only ones in lifetime |
| D. | Pacific Salmon fish | 4. | Verhulst-Pearl logistic growth |
(a) (A)- 1, (B)- 3, (C)- 2, (D)- 4
(b) (A)- 1, (B)- 2, (C)- 3, (D)- 4
(c) (A)- 4, (B)- 1, (C)- 2, (D)- 3
(d) (A)- 3, (B)- 2, (C)- 1, (D)- 4
Answer:
(c) (A)- 4, (B)- 1, (C)- 2, (D)- 3
Explanation: In a finite world, no population can grow exponentially for very long. Sooner or later every population must encounter either difficult environmental conditions or shortages of its requisites for reproduction.
This is explained by the Verhulst-Pearl Logistic growth equation which is given in the form of dN/dt = rN(K-N/K), where N denotes population, K is the carrying capacity and r shows the rate of increase in the population.
There are variations found in the production of offspring in different animals. Some of the animals produce small sized offsprings which are many in number. The examples of such animals are oysters and pelagic fishes.
The exponential function appears when original quantity grows exponentially over time. If a quantity N increases at a rate proportional to the amount present at time t, then the quantity can be written as Nt = Noert, where N0 is the value of N at time t = 0 and N increases as t increases and k is called an exponential growth function.
Pacific salmon fish is called as a semelparous type of fish. These fishes live in the ocean water. They swim and then lay eggs in the freshwater. They spawn and then die. These type of animals spawn only once in their lifetime and die after spawning.
![]()
Question 10.
Identify the possible link “A” in the following food chain: [1]
Plant → Insect → Frog → “A” → Eagle.
(a) Rabbit
(b) Wolf
(c) Cobra
(d) Parrot
Answer:
(c) Cobra
Question 11.
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) in a river water: [1]
(a) Has no relationship with concentration of oxygen in the water
(b) Gives a measures of Salmonella in the water
(c) Increase when sewage gets mixed with river water
(d) Remains unchanged when algal bloom occurs
Answer:
(c) Increase when sewage gets mixed with river water
Explanation: If the water is more polluted, more will be the BOD because more will be the organic matter present in it and hence, more oxygen will be required to decompose it. Hence, BOD in a river water will increase if sewage gets mixed up with the river water.
Question 12.
Identify a, b and c in the schematic diagram of an antibody given below and answer the questions: [1]
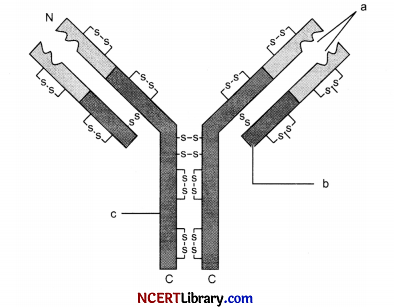
(a) “a”: Antigen binding site, “b”: Light Chain/’c”: Heavy chain
(b) “a”: Light Chain, “b”: Antigen binding site/’c”: Heavy chain
(c) “a”: Antigen binding site, “b”: Heavy chain/’c”: Light chain
(d) “a”: Heavy chain, “b”: Light chain, “c”: Antigen binding site
Answer:
(a) “a”: Antigen binding site, “b”: Light Chain/’c”: Heavy chain
Explanation: Each antibody molecule has four peptide chains, two small, called light chains and two, longer called heavy chains. Hence, is represented as H2L2.
Question No. 13 to 16 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question 13.
Assertion (A): The development of embryo sac from a single functional megaspore is monosporic development. [1]
Reason (R): In monosporic type of embryo sac development, usually the megaspore which is situated towards micropylar end remains functional.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false.
Explanation: In monosporic type of development of embryo sac, only one megaspore situated towards chalazal end remains functional. This type of embryo sac development occurs in a majority of flowering plants and the common example is Polygonum. Thus assertion is true, but reason is false.
Question 14.
Assertion (A): A single mRNA strand is capable of forming a number of different polypeptide chains. [1]
Reason (R): The mRNA strand has termination codons.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: A single mRNA strand is capable of forming different polypeptide chains because it has different reading frame, (the way through which reading of mRNA done by tRNA). Thus both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 15.
Assertion (A): Immunoglobin molecules have a basic structure composed of four polypeptide chains. [1]
Reason (R): The polypeptide chains consist of two identical heavy and light chains connected by disulphide bonds.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: In the structure of Immunoglobulin, two heavy and light chains are present and connected by disulphilde linkages. Thus both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 16.
Bio-fertilizers are introduced in seeds, roots, or soil to mobilise the availability of nutrients. Thus, they are extremely beneficial in enriching the soil with organic nutrients. Many species of bacteria and cyanobacteria have the ability to fix free atmospheric nitrogen. Rhizobium is a symbiotic bacteria found in the root nodules of leguminous plants.
Azospirillium and Azotobacter are free living nitrogen fixing bacteria, whereas Anabaena, Nostoc and Oscillitoria are examples of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria. Bio-fertilizers are cost effective and eco-friendly as they don’t harm the microbial flora and pH of soil whereas chemical fertilizers can harm microbes present in the soil and also alter the pH.
Assertion (A): Chemical fertilizers are preferred over Bio-fertilizers.
Reason (R): Chemical fertilizers are generally more expensive and hazardous to the environment. [1]
Answer:
(d) A is false but R is true.
Explanation: Biofertilizers are eco-friendly as they don’t hamper the microbial flora and pH of soil which chemical fertilizers can harm microbes present in the soil and alter the pH which will not be suitable for the growth of plants. Thus bio-fertilizers are preferred over Chemical fertilizers. Thus assertion is false but reason is true.
Section – B (10 Marks)
Question 17.
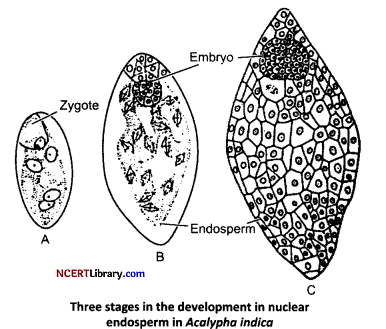
(a) What is endosperm?
(b) How endosperm is formed? Explain. [2]
Answer:
(a) Endosperm accumulates the food reserves and functions as the nutritive tissue for the developing embryo. It develops from the triploid primary endospermal cell by repeated cell divisions. Its development starts shortly before the development of the embryo.
(b) Endosperm is formed by three methods:
(i) Nuclear Type: In this, primary endosperm nucleus divides repeatedly by mitosis and number of free nuclei arrange themselves at the periphery of embryo sac, leaving a central vacuole.
The nuclear division is not accompanied by the cell wall formation. But later on, protoplast collects around each nucleus and then walls are formed. So the endosperm becomes cellular at the maturity e.g., wheat, rice, maize and sunflower.
(ii) Cellular Type: In this, the repeated mitotic division of primary endosperm nucleus is followed by cytogenesis around each nucleus, so the endosperm becomes cellular from the beginning. e.g., Datura and Petunia.
(iii) Helobial Type : In this, the first mitotic division of primary endosperm nucleus is followed by incomplete cytokinesis and the endosperm is formed both by cellular and nuclear type. E.g. Eremurus.
![]()
Question 18.
Using a Punnett square, work out the distribution of phenotypic features in the first filial generation after a cross between a homozygous female and a heterozygous male for single locus. [2]
Answer:
To explain the concept, we can take an example of body colour Grey (G) and Albino (g). As per the question a homozygous female (gg) having albino colour is crossed with heterozygous male (Gg) having Grey colour. By using punnett square the following conclusions can be derived,
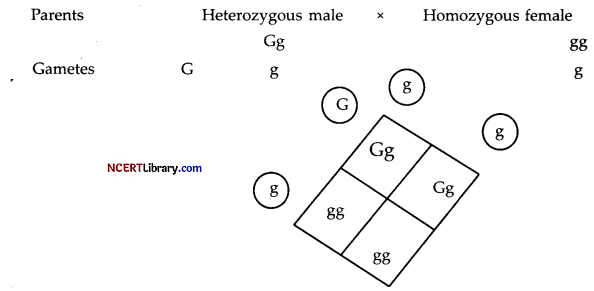
Conclusion F1 generation will show 2 : 2 Albino : Grey as the phenotypic ratio.
Question 19.
Choose any three microbes from the following which are suited for the organic farming and which are in great demand these days for various reasons. Mention one application of each chosen one. Mycorrhiza, Monascus, Anabaena, Rhizobium, Methanobacterium, Trichoderma. [2]
Answer:
The three microbes efficiently used are:
(a) Rhizobium: The root nodules of leguminous plants are formed by the symbiotic association of Rhizobium bacteria. These microbes fix atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms that is used by plant as a nutrient.
(b) Anabaena: It is a cyanobacterium that is used as a biofertilizer that fixes atmospheric nitrogen.
(c) Trichoderma: It is free living fungal species that is able to control certain plant pathogens. Specifically, it is present in root zone.
(d) Mycorrhiza: It is symbiotic associated fungal species. It is phosphorus fixing fungi. It is resistant to root borne pathogens and shows tolerance to salinity and drought conditions.
Question 20.
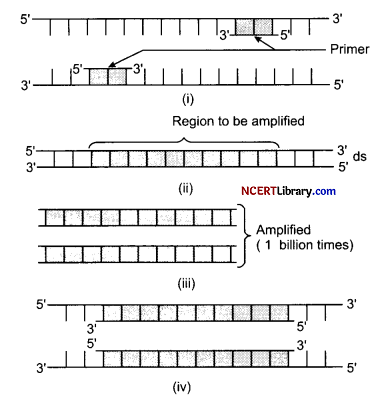
(a) The sample under investigation was very less in quantity to give desired results. It was amplified using PCR. What are the correct steps of PCR which would give desired results?
(b) Write any two significance of PCR. [2]
Answer:
(a) The correct steps of PCR which would give desired results are:
(ii) → (i) → (iv) → (iii)
The DNA sample to be amplified is taken and suitable primers are added which will bring polymerization of DNA resulting many copies at the end of cycle.
(b) (1) The amplification of gene fragments as fast alternative of cloning.
(2) The modification of DNA fragments.
Question 21.
Give the binomials of two types of yeast and the commercial bioactive products they help to produce. [2]
OR
What are fermented beverages?
Answer:
(a) Saccharomyces cerevisiae → ethanol
(b) Monascus purpureus → statin.
OR
These are those fermented products that are produced from malted cereals and fruit juices by fermenting them using Saccharomyces cerevisiae which is a brewer’s yeast to produce ethanol. Such products are known as fermented beverages. For example, wine, beer, whisky, brandy and rum.
Section – C (21 Marks)
Question 22.
(a) Explain the process of double fertilization in angiosperms. [3]
(b) Why does the development of endosperm precede that of embryo?
(c) List the parts of a typical dicot embryo.
Answer:
(a) Double fertilization:
(i) One male gamete fuses with the egg cell in the embryo sac to form zygote (2n) by the process of syngamy.
(ii) The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuceli to form PEN (Primary Endospern Nucleus) (3n) by the process of triple fusion.
(iii) Both syngamy and triple fusion together are known as double fertilisations.
(b) The endosperm contains reserve food material which is used for nutrition of developing embryo.
(c) A typical dicot embryo consists of an embryonal axis and two cotyledons. The portion of the embryonal axis above the level of cotyledons is the epicotyl which terminates with the plumule.
The portion below the level of the cotyledons is the hypocotyl that terminates at its lower end with the radical which is covered by a root cap.
![]()
Question 23.
(a) Explain any two ways by which apomictic seed can develop. [3]
(b) List one advantage and one disadvantage of a apomictic crop.
(c) Why do farmers find production of hybrid seeds costly?
Answer:
(a) (i) A diploid egg is formed without reductional division which directly develops into embryo without fertilisation.
(ii) Some diploid cells of the nucellus start dividing and develop into a embryo.
(b) Advantage: No segregation of characters in hybrid progeny.
(i) Apomictic hybrid can be used to grow crop year after year.
(ii) It is economical as ordinary hybrid seeds that are costly.
Disadvantage:
(i) They lack ability to adapt to changing environment.
(ii) Cannot control deleterious genetic mutation.
(c) Hybrid seeds are costly as farmers have to purchase seeds year after year. Production of hybrid seeds is a highly technical and expensive method. It requires intensive labour and is not easily feasible.
Question 24.
Analyse the diagram and answer the following questions. [3]
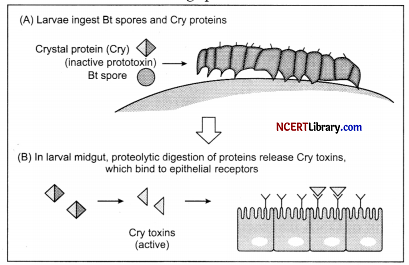
(a) What is Bt-cotton?
(b) Is Bt-cotton really selectively toxic to insects?
(c) How does Bt-cotton kill insects?
Answer:
(a) Bt-cotton has been genetically modified by the insertion of one or more genes from a common soil bacterium, Bacillus thuringiensis. These genes encode for the production of insecticidal proteins and thus, genetically transformed plants produce one or more toxins as they grow.
(b) Yes, Bt-toxins are highly specific. The toxins produced by Bt-cotton and coin are toxic to a selected number of arthroped species because cotton is primarily a fiber crop, the contamination of food with toxins from cotton is highly unlikely.
(c) Bacillus thruingiensis forms protein crystals during particular phase of growth. These crystals contain toxic insecticidal protein which exist as inactive protoxins but once insect ingest inactive toxin it is converted into an active form of toxin due to alkaline pH of the gut which solubilise crystals. Activated toxin binds surface of midgut epithelial cells and excrete pore.
Question 25.
(a) Linkage or crossing-over of genes is alternative of each other. Justify with the help of an example. [3]
(b) Why are grasshopper and drosophila said to show male heterogamety? Explain.
Answer:
(a) In Drosophila, a yellow bodied and white eyed female was crossed with brown bodied and red eyed male. The progeny produced and inter-crossed gave second filial generation, the phenotypic ratio of which significantly deviated from Mendel’s 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 ratio.
The genes regulating colour of an eye and colour of the body are closely situated on X choromosome that shows linkage and hence inherited together. Thus, recombinants were produced due to crossing over at low percentage.
(b) In male grasshopper they have one X chromosome only. In drosophila males have one X and one Y chromosome. The males in both produce two different kinds of gametes hence they show heterogamety.
Question 26.
List the criteria a molecule that can act as genetic material must fulfill. Which one of the criteria are best fulfilled by DNA or by RNA thus making one of them a better genetic material than the other? Explain. [3]
OR
(a) Give an example of an autosomal recessive trait in humans Explain its pattern of inheritance with the help of a cross.
(b) A couple with normal vision bear a colour blind child. Work out a cross to show how it is possible and mention the sex of the affected child.
Answer:
(a) The genetic material should be able to carry out replication or generate a replica.
(b) It should be chemically or structurally stable.
(c) It should provide scope for slow mutation.
(d) It should be able to express itself as characters.
Out of the two, clearly, DNA is more stable because of the following factors:
(a) Presence of H and not OH at 2′ position.
(b) Presence of thymine instead of uracil.
(c) It is less reactive.
(d) It is structurally more stable because of its double stranded structure with hydrogen bonding.
(e) DNA is slower to mutate than RNA.
(f) Complementary strands of DNA further resist changes by evolving a process of repair.
OR
(a) Sickle cell anaemia is an autosomal recessive trait disease than can be transmitted from parents to the offspring when both the partners are carrier for the gene. The disease is controlled by a single pair of allele, HbA and HBS. Out of three possible genotypes only homozygous individuals for Hbs (Hbs Hbs) show the diseased phenotype while heterozygous (HbAHbs) individuals are carrier of the disease.
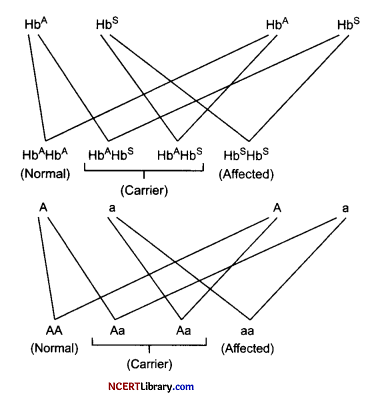
(b)
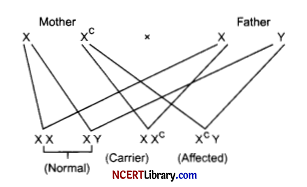
The affected child is male.
Question 27.
Answer the following questions by analyzing the figure below. [3]
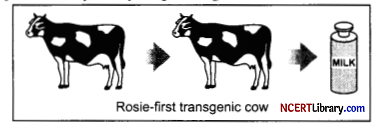
(a) Name the first transgenic cow. Which gene was introduced in this cow?
(b) How is ‘Rosie’ considered different from a normal cow? Explain.
Answer:
(a) Rosie was the first transgenic cow and it was produced in 1997. The gene for human protein a-lactalbumin was introduced in this cow. Thus, the cow could produce protein-enriched milk.
(b) Rosie cow was considered different from a normal cow as it produced human protein enriched milk. The milk contained ‘human alpha-lactalbumin’ and was nutritionally a more balanced product for human babies than a normal cow milk.
![]()
Question 28.
(a) What is a GMO?
(b) List any five possible advantages of GMO to a farmer.
Answer:
(a) Those plants, bacteria, fungi or animals whose genes have been altered by manipulation are called Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)
(b) Advantages of GMO to a farmer:
(i) Tolerance to abiotic stresses like cold, drought, salt, heat, etc.
(ii) Reduce reliance on chemical pesticides.
(iii) Reduced post harvest losses.
(iv) Increased efficiency of mineral usage by plants.
(v) Enhanced nutritional value.
(vi) To create tailor-made plants.
Section – D (8 Marks)
Questions No. 29 and 30 are case based questions. Each question has subparts with internal choice in one subpart.
Question 29.
Study the following diagram and and answer the following questions [4]
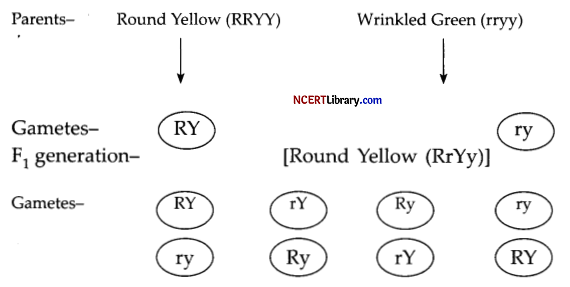
(a) Draw Punnett Square for F2 generation.
(b) Write the Conclusion of the cross.
(c) Mention the possible cross carried.
OR
Find the genotypic ratio for the F0 generation.
Answer:
(a) F2 generation:
| Gametes | RY (male) | rY (male) | Ry (male) | iy (male) |
| RY
(Female) |
RRYY
Round Yellow |
RrYY
Round Yellow |
RRYy
Round Yellow |
RrYy
Round Yellow |
| rY
(Female) |
RrYY
Round Yellow |
rrYY
Wrinkled Yellow |
RrYy
Round Yellow |
rrYy
Wrinkled Yellow |
| Ry
(Female) |
RRYy
Round Yellow |
RrYy
Round Yellow |
RRyy
Round Green |
Rryy
Round green |
| iy
(Female) |
RrYy
Round Yellow |
rrYy
Wrinkled Yellow |
Rryy
Round Green |
rryy
Wrinkled Green |
(b) Conclusion of the cross is:
Round Yellow = 9 Round Green = 3 Wrinkled yellow = 3 Wrinkled green = 1
Hence, the phenotypic Ratio is 9: 3: 3: 1.
(c) The result of the genetic cross indicates probability of all genotypes and phenotypes along with their ratio.
OR
The genotype is genetic struture. The genotype ratio of Punnet Square is1:2:2:4:1:2:1:1:2 ( i.e., RRYY- 1, RRYy-2, RrYY-2, RrYy-4, RRyy-1, Rryy-2, rrYY-l,rryy – 1 and rrYy-2).
![]()
Question 30.
Organic farming is increasing the production of pollutant-free crops. It involves the use of biofertilizers and biopesticides which increase the nutrient quality of the crop and controls any kind of pest and pathogen.
Biofertilizer are defined as preparations containing living cells or latent cells of efficient strains of microorganisms that help crop plants for the uptake of nutrients by their interactions in the rhizosphere.
Biofertilizers are the microorganisms that add to the nutrient quality of the soil. Bacteria, fungi, and algae are some of the beneficial microorganisms that help in improving the fertility of the soil. These are introduced to seeds, roots, or soil to mobilise the availability of nutrients by their biological activity.
Thus, they are extremely beneficial in enriching the soil with organic nutrients. Many species of bacteria and cyanobacteria have the ability to fix free atmospheric nitrogen. Biofertilizers are cost effective and eco-friendly. Application of biofertilizers results in increased mineral and water uptake, root development, vegetative growth and nitrogen fixation.
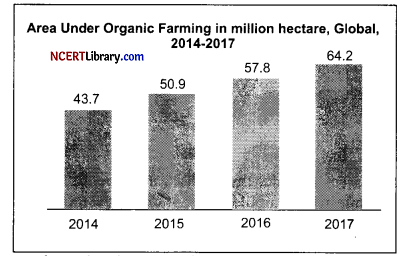
(a) What do you observe from the above graph?
(b) Define Biofertilizers.
(c) Why is organic farming beneficial to us. Describe. [4]
OR
(c) Why should we prefer biofertilizers instead of chemical fertilizers? Explain.
Answer:
(a) The graph shows the increasing demand for organic food, worldwide, farming and also shows the area under global organic farming increased from 43.7 million hectares in 2014 to 64.2 million hectares in 2017.
(b) Biofertilizer are defined as preparations containing living cells or latent cells of efficient strains of microorganisms that help crop plants for the uptake of nutrients by their interactions in the rhizosphere.
(c) Organic farming beneficial to us because it involves the use of biofertilizers and biopesticides which increase the nutrient quality of the crop and controls any kind of pest and pathogen.
OR
(c) We should prefer biofertilizers instead of chemical fertilizers because Biofertilizers are the microorganisms that add to the nutrient quality of the soil. Bacteria, fungi, and algae are some of the beneficial microorganisms that help in improving the fertility of the soil. They are also cost effective and eco-friendly.
Section – E (15 Marks)
Question 31.
(a) As a senior biology student you have been asked to demonstrate to the students of secondary level in your school, the procedure(s) that shall ensure cross-pollination in a hermaphrodite flower. List the different steps that you would suggest and provide reasons for each one of them.
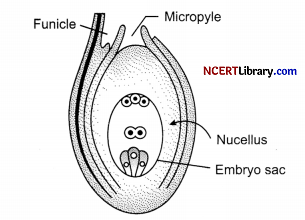
(b) Also draw a diagram of a section of a megasporangium of an angiosperm and label funiculus, micropyle, embryosac and nucellus. [5]
OR
What is spermatogenesis? Briefly describe the process of spermatogenesis by giving a schematic representation showing the events of spermatogenesis in human male.
Answer:
(a) The different steps that would suggest for cross-pollination in a hermaphrodite flower are:
Removal of anthers from the flower bud before the anther dehisces using a pair of forceps is necessary to avoid self pollination. It is referred as emasculation. Emasculated flowers covered with a bag of suitable size to prevent contamination of its stigma is called bagging.
(i) Removal of anthers from the flower bud before the anther dehisces using a pair of forceps is necessary to avoid self pollination. It is referred as emasculation.
(ii) Emasculated flowers covered with a bag of suitable size to prevent contamination of its stigma is called bagging
(iii) When the stigma of bagged flower attains receptivity, mature pollen grains collected from anther of the male parent are dusted on the stigma and the flowers are rebagged to allow the fruit to develop.
(b)
OR
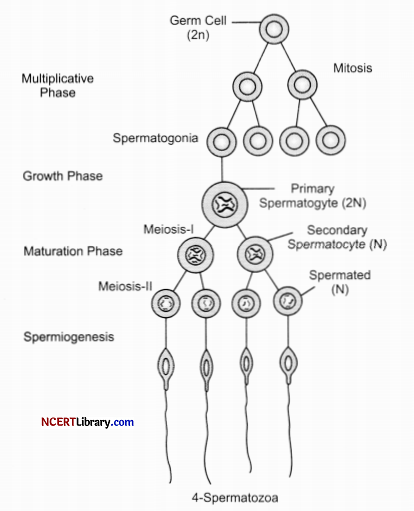
Spermatogenesis is the process by which the production ofsperms from the immature germ cells in males takes place. It occurs in seminiferous tubules present inside the testis. In the process of spermatogenesis, diploid spermatogonia increase its size to form a diploid primary spermatocyte.
This diploid primary spermatocyte undergoes first meiotic division to form two equal haploid secondary spermatocytes. Each secondary spermatocyte further undergoes second meiotic division to form two equal haploid spermatids. Hence, diploid spermatogonia produce four haploid spermatids. These spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa or sperms by the process called spermiogenesis.
Question 32.
Occasionally, situations arise in which people require concrete, scientific evidence of parent age, whether it be their own or that of someone else. In most instances, maternity is easy to determine.
Unfortunately, questions of paternity aren’t so easy to answer. In order to make a determination of fatherhood, scientists almost always work backwards-from the child to the potential parent-to ascertain the actual nature of the relationship. The process of DNA fingerprinting first became available for paternity testing in 1988.
Before this sort of DNA analysis was available, blood types were the most common factor considered in human paternity testing. Blood groups are a popular example of Mendelian genetics at work. After all, there are numerous human blood groups with multiple alleles, and these alleles exhibit a range of dominance patterns.
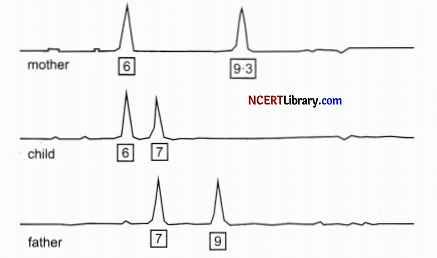
(a) Above test shows samples from the mother (top row), the child (middle row), and the alleged father (bottom row). What can be concluded from the above figure?
(b) Explain DNA finger printing . [5]
OR
Sex chromosomes of some animals and man besides having genes for sex character also possess gene for non-sexual(somatic) characters. These genes for non-sexual characters being linked with sex chromosomes are carried with them from one generation to the other.
Such non-sexual (somatic) characters linked with sex chromosomes are called sex linked characters or traits, genes for such characters are called sex linked genes and the inheritance of such characters is called sex linked inheritance.
The concept of sex-linked inheritance was introduced by T. H. Morgan in 1910, while working on Drosophila melanogaster.
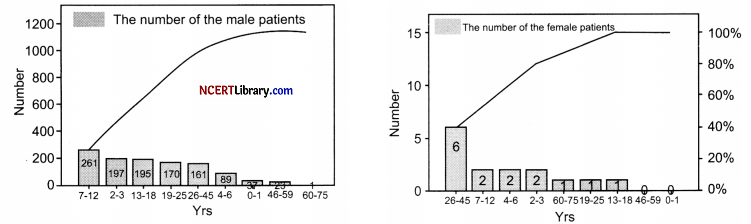
(a) What conclusion can be drawn from above graphs?
(b) Briefly explain the contribution of T.H. Morgan in genetics?
(c) In a family of four including a normal mother, a normal father, a colourblind son and a normal son; who do you think has the defective X gene other than the affected son?
Answer:
(a) The above mentioned test shows the maternal marker that has been passed to the child is 6 and the alleged father matches the child, since one of his markers is indeed 7.
(b) DNA finger printing: DNA finger printing is a technique that shows the genetic makeup of living things. It is a method of finding the difference between the satellite DNA regions in the genome.
Alec Jeffreys developed this technique in which he used satellite DNAs also called VNTRs (Variable Number of Tandem Repeats) as a probe because it showed the high level of polymorphism.
Following are the steps involved in DNA fingerprinting:
Isolating the DNA.
↓
Digesting the DNA with the help of restriction endonuclease enzymes.
↓
Separating the digested fragments as per the fragment size by the process of electrophoresis.
↓
Blotting the separated fragments onto synthetic membranes like nylon.
↓
Hybridising the fragments using labelled VNTR probes.
↓
Analysing the hybrid fragments using autoradiography
OR
(a) The graphs above show the number of the male (a) and female (b) with hemophilia in different age intervals. The possibility of a female becoming a haemophilic is extremely rare.
(b) Morgan’s work is founded on the basis of the observations during experiments on fruit flies that is Drosophila melanogaster. He structured the chromosomal theory of linkage. He defined linkage as the co-existence of two or more genes in the same chromosome and performed dihybrid crosses in Drosophila to show that linked genes are inherited together and are located on X-chromosome.
His experiments have also justified that tightly linked genes show very low recombination while loosely linked genes show higher recombination.
(c) The mother has the defective X gene other than the affected son.
![]()
Question 33.
Analyse the graph given below and answer the questions based upon it: [5]
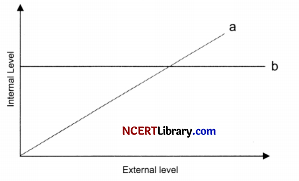
(a) Name the organisms depicting the pattern A and B and state the reason for growth pattern seen in A.
(b) Write the effects of growth pattern seen above.
(c) What are the major causes of the formation of above graph?
OR
Two types of aquatic organisms in a lake show specific growth patterns as shown below, in a brief period of time. The lake is adjacent to an agricultural land extensively supplied with fertilizers. Answer the questions based on the facts given above:
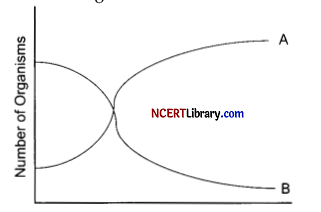
(a) Name the organisms depicting the pattern A and B and state the reason for growth pattern seen in A.
(b) Write the effects of growth pattern seen above.
(c) What are the major causes of the formation of above graph?
Answer:
(a) It is the response given by the organism to the abiotic factors. When plotted on the graph they can be represented as above. In above graph ‘a’ denotes the conformer organisms whereas ‘b’ denotes regulator organisms.
(b) It is the process of maintaining consistency of internal environment by the organism according to the changing external environment. Organisms either thermoregulate (Regulation of temperatures) or osmoregulate (Regulation of osmotic pressure) to maintain homeostasis.
(c) Tiny organisms expose maximum surface area through which large amount of heat produced in the body is given out. So in order to generate the energy again, they have to expand much more energy. Therefore, they are not found in the polar region.
OR
(a) A depicts the algal or phytoplankton population whereas B depicts aquatic animals. The growth pattern of A is because of excessive lodging of nutrients from the adjacent agricultural land leaching the nutrients here.
(b) The result of above graph will be eutrophication, decrease in BOD, unpleasant odour and death of aquatic ecosystem.
(c) Above graph formation occurs when the water body becomes overly enriched with nutrients. Various factors like excessive use of fertilisers, untreated sewage, usage of detergents containing phosphorous and industrial discharge of waste may contribute to eutrophication.