Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology with Solutions Set 2 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Set 2 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours.
Max. Marks: 70
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has five sections and 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 16 questions of 1 mark each; Section- B has 5 questions of 2 marks each; Section- C has 7 questions of 3 marks each; Section- D has 2 case-based questions of A marks each; and Section- E has 3 questions of 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn.
Section – A (16 Marks)
Question 1.
Filiform apparatus in the embryo sac of an angiosperm is present at the micropylar tip of : [1]
(a) Central cell
(b) Egg cell
(c) Synergids
(d) Antipodals
Answer:
(c) Synergids
Explanation: The synergids have special cellular thickening at the micropylar tip called filiform apparatus, which plays an important role in guiding the pollen tube into the synergids.
Question 2.
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes. [1]
| Column I | Column II | ||
| A | Integuments | (i) | A mass of cells |
| B | Chalaza | (ii) | Stalk of ovule |
| C | Funicle | (iii) | Protective envelopes |
| D | Nucellus | (iv) | Basal part of the ovule |
(a) A-(iii), B-(ii), C-(i), D-(iv)
(b) A-(iv), B-(iii), C-(ii), D-(i)
(c) A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iv), D-(iii)
(d) A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(ii), D-(i)
Answer:
(d) A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(ii), D-(i)
Explanation: Funicle is the stalk through which the ovule is attached to the placenta, integuments are the protective envelopes of an ovule, chalaza represents the basal part of the ovule opposite to the micropyle, and nucellus is the mass of cells enclosed within the integuments.
Question 3.
In a dihybrid cross, if you get 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 ratio it denotes that: [1]
(a) the alleles of two genes are interacting with each other.
(b) it is a multigenic inheritance.
(c) it is a case of multiple allelism.
(d) the alleles of two genes are segregating independently.
Answer:
(d) the alleles of two genes are segregating independently.
Explanation: Cross involving two contrasting characters is called a dihybrid cross. The two flowers of each trait assort at random and independent of their traits and get randomly as well as independently rearranged in the offspring.
Question 4.
In a DNA strand, the nucleotides are linked together by: [1]
(a) Glycosidic bonds
(b) Phosphodiester bonds
(c) Peptide bonds
(d) Hydrogen bonds
Answer:
(b) Phosphodiester bonds
Explanation: In DNA molecule, the nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds whereas the nitrogen bases are held by hydrogen bonds.
Question 5.
Diseases are broadly grouped into infectious and non-infectious diseases. In the list given below, identify the infectious diseases. [1]
I. Cancer
II. Influenza
III. Allergy
IV. Smallpox
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) III and IV
(d) II and IV
Answer:
(d) II and IV
Explanation: Influenza, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Cancer is a non-infectious disease. Smallpox is a serious, highly contagious disease. It is caused by the Variola Virus. Allergy is the exaggerated response of the immune system to certain antigens. It is a non-infectious response.
![]()
Question 6.
Which of the following gas is responsible for the puffed-up appearance of the dough? [1]
(a) NH3
(b) C02
(c) 02
(d) CH4
Answer:
(b) C02
Explanation: The dough which is used for making foods such as dosa and idli is fermented by using bacteria like Saccharomyces. The puffed-up appearance of this dough is due to the production of C02 gas.
Question 7.
Choose the right combination among the following : [1]
| Interaction | Species A | Species B | |
| A. | Commensalism | – | – |
| B. | Parasitism | + | – |
| C. | Mutualism | + | + |
| D. | Competition | 0 | – |
(a) A, B
(b) C, D
(c) A, D
(d) C, B
Answer:
(d) C, B
Explanation:
(a) In commensalism, one is benefited but other has no effect. It is denoted by (+, 0)
(b) In parasitism, one is benefited but other is harmful. It is denoted by (+, -)
(c) In mutualism, both are benefited. It is denoted by (+, +)
(d) Competition is harmful to both the organisms. It is denoted by (-, -).
Question 8.
Study the following list : [1]
| List-I | List-II | ||
| A | Colony hybridisation | (i) | Transfer of recombinant DNA in to a host cell |
| B | Gel electrophoresis | (ii) | Selection of cells containing the desired gene |
| C | Gradient centrifugation | (iii) | Separation of DNA fragments |
| D | Polymerase chain reaction | (iv) | Purification of DNA |
| (v) | Gene cloning | ||
(a) (A) – (iv), (B) – (v), (C) – (ii), (D) – (iii)
(b) (A) – (i), (B) – (ii), (C) – (iii), (D) – (iv)
(c) (A) – (ii), (B) – (iv), (C) – (v), (D) – (iii)
(d) (A) – (ii), (B) – (iii), (C) – (iv), (D) – (v)
Answer:
(d) (A) – (ii), (B) – (iii), (C) – (iv), (D) – (v)
Explanation: The cutting of DNA by restriction endonucleases results in fragments of DNA. These fragments are separated by technique known as gel-electrophoresis.
In colony hybridisation, selected cells with desired genes are grown in culture. In gradient centrifugation, cells/DNA are spinned at very high speed to purify DNA. PCR is amplification or gene donning process used to amplify gene in large amount.
Question 9.
Lichens are well known combination of an algae and fungus where fungus is: [1]
(a) An epiphytic relationship between algae
(b) A parasitic relationship with the algae
(c) A symbiotic relationship with the algae
(d) A saprophytic relationship with algae
Answer:
(c) A symbiotic relationship with the algae
Explanation: Lichens are a well-known combination of an algae and a fungus where the fungus has a symbiotic relationship with the algae. The fungus depends on the algae for food, as fungi cannot perform photosynthesis. In return, they provide shelter to the algae.
Question 10.
Zone of atmosphere near the Earth surface is: [1]
(a) Stratosphere
(b) Mesosphere
(c) Troposphere
(d) Thermosphere
Answer:
(c) Troposphere
Explanation: The troposphere is the lowest layer of our atmosphere. Starting at ground level, it extends upward to about 10 km (6.2 miles or about 33,000 feet) above sea level. After troposphere, stratosphere (up to 50 km), mesosphere (up to 85 km) and thermosphere (between 500 km- 1000 km) are found.
Question 11.
The following flowchart represents the life cycle of malarial parasite. Choose appropriate combination to complete the flow chart.
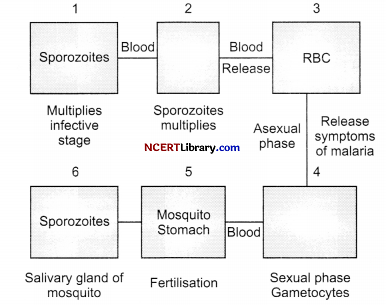
(a) 2: Liver; 4: RBC
(b) 4: Liver; 2: RBC
(c) 2: Spleen; 4: RBC
(d) 2: Liver; 4: Intestine
Answer:
(a) 2: Liver; 4: RBC
Explanation: Plasmodium enters the human body as sporozoites (infectious form) through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquito. The parasites initially multiply within the liver cells and then attack the red blood cells (RBCs) resulting in their rupture.
The rupture of RBCs is associated with release of a toxic substance, hemozoin, which is responsible for the chill and high fever recurring every three to four days.
![]()
Question 12.
Health is not defined by: [1]
(a) Physical well-being
(b) Mental well-being
(c) Social well-being
(d) Genetic disorders
Answer:
(d) Genetic disorders
Explanation: Health is defined as a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being. On the other hand, genetic disorders are the deficiencies or defects which the child inherits from parents by birth, which affect the health of an individual.
Question No. 13 to 16 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question 13.
Assertion (A): In a microsporangium, the tapetal cells possess little cytoplasm and generally have a single prominent nucleus.
Reason (R): During microsporogenesis, the microspore mother cells undergo mitotic divisions to produce haploid microspore tetrads. [1]
Answer:
(d) A is false but R is true.
Explanation:
Tapetum is the innermost wall layer of a microsporangium. It nourishes the developing pollen grains. The tapetal cells enlarge radically and become filled with dense protoplasmic contents as well as nutrients.
Microsporogenesis refers to the process of formation of haploid microspores mother cell or pollen mother cell through meiosis. Thus, assertion is false, but reason is true.
Question 14.
Assertion (A): InMirabilis jalapa, selfing of FI pink flower plants produces same phenotypic and genotypic ratio. [1]
Reason (R): Flower colour gene shows incomplete dominance.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: In Mirabilis jalapa, red and white-coloured flowers are seen. When they are crossed. In the Fj generation. All flowers are pink coloured. This is because of the incomplete dominance of redcoloured flowers. Thus, both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of asssertion.
Question 15.
Assertion (A): In malaria, a person experiences chills and high fever recurring every three to four days. [1]
Reason (R): This is caused by the release of haemozoin with rupture of liver cells.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false.
Explanation: In Malignant malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum is the most serious one and can even be fatal. The parasites initially multiply within the liver cells and then attack the red blood cells (RBCs) resulting in their rupture. The rupture of RBCs is associated with the chill and high fever recurring every three to four days. Thus, assertion is true but reason is false.
![]()
Question 16.
Antibiotics: An antibiotic is an organic substance which is produced by a microorganism which inhibits the growth of other microbes. The very first antibiotic was produced using a fungus by Sir Alexander Fleming in 1929, known as penicillin from fungus Penicillium notatum which is also known as wonder drug.
It has no adverse effects on humans but kills gram positive type bacteria. Streptomycin is another one produced from Streptomyces griseus, effective against gram negative bacteria. Some other antibiotics produced are Chloromycetin, tetramycin and aureomycin.
Various animal and human diseases which are not cured by other drugs are effectively cured by aureomycin. Another mostly used antifungal product isolated from fungi is Grise of ulvin. It is isolated from mycelium of penicillium. It is fungistatic, i.e., diminishes the growth by interfering in the formation of fungal walls, it has dermatological uses in ringworms and athlete’s foot disease.
Some drugs obtained from fungi also work as immunosuppressants, for example cyclosporine A. Psilocybin is a compound found in fungi such as Psilocybe semilanceata and Gymnopilus junonius, which have been used for their hallucinogenic properties by various cultures for thousands of years.
Assertion (A): Discovery of the first antibiotic was a chance discovery.
Reason (R): Penicillin was the first antibiotic. [1]
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Fleming obtained an extract from the mold, naming its active agent penicillin and penicillin was the first antibiotic. Thus, both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Section – B (10 Marks)
Question 17.
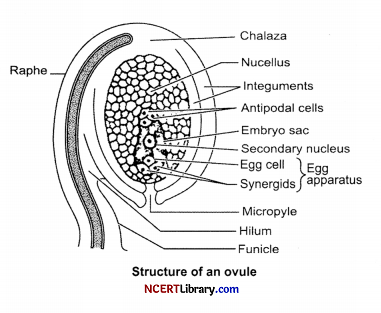
(a) List the function of micropyle and integuments of an angiospermic ovule.
(b) What is the role of the antipodal cells in female gametophytes? [2]
Answer:
(a) (i) Micropyle: It is small opening at the apex of the integuments in the ovule. It serves the function of providing entry to the pollen tube containing male gametes, into the ovule.
(ii) Integuments: Nucellus is surrounded by one or two cellular coats called integuments.
(b) The function of the antipodal cells is to provide nourishment to the egg cell. It is rich in lipid content. They also form the basis of endosperm production.
The synergids consists of filiform apparatus which guides the pollen tube and the pollen tube discharges its content into one of the synergids.
Question 18.
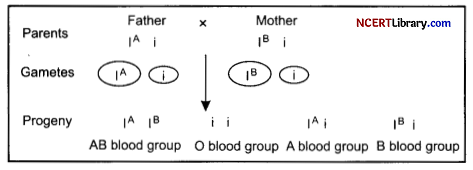
A child has blood group O. If the father has blood group A and mother has blood group B, write the genotypes of the parents and the possible genotypes of other offspring? [2]
Answer:
If the father has blood group A and mother has blood group B, then the possible genotype of the parents will be: Father-Mother:
IA IA / IAi – IB IB/IBi
(a) A cross between homozygous parents will produce progeny with AB blood group.
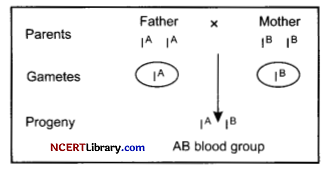
(b) A cross between heterozygous parents will produce progenies with AB blood group (IAIB), O blood group (ii), A blood group (IAi) and B blood group (IBi).
Question 19.
A patient showed symptoms of constipation, abdominal pain and stools with excess mucous and blood clots. Name the disease and its pathogen. Where do these pathogens live in the patient’s body? Name the mechanical carrier that transmits the parasite. [2]
Answer:
According to the symptoms given, the disease that the patient is suffering from is amoebiasis. The pathogen responsible for this disease is Entamoeba histolytica.
The pathogen lives in the large intestine of the human body. The pathogens are carried by houseflies from one place to another and is also directly contacted by the usage of contaminated water and food.
Question 20.
Observe the given figure of 2 types of Insulin labeled as (I) and (II) and answer the following questions:
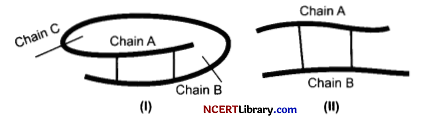
(a) Figure I shown above is insulin or proinsulin. Justify.
(b) How is mature insulin synthesized? [2]
Answer:
(a) Figure I is proinsulin. Proinsulin is the precursor molecule contains three polypepride chains known as the chain A, B and chain C. The mature insulin part contains chain A and B.
(b) The active insulin is formed through the maturation process when the precursor molecule proinsulin undergoes maturation through the action of endopeptidase known as prohormone convertase.
![]()
Question 21.
(a) Which equation express exponential growth in plants?
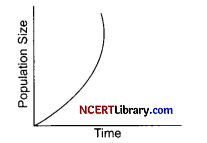
(b) The size of population is not a static parameter. Explain.
OR
The Amazon rainforest is referred to as ‘Lungs of the planet’. Mention any one human activity that causes loss of biodiversity in this region. [2]
Answer:
(a) W1=Woert
express exponential growth in plants
W1 = final size,
Wo = Initial size
r = growth rate
t = time of growth
and e = base of natural logarithm
(b) The size of the population is regulated by the factors like availability of food, predation pressure, adverse climatic conditions and competition. All these entities are dynamic in nature.
Also the four processes that regulate the growth of population are natality, mortality, immigration and emigration. So, all these entities are never static. The size of the population changes as according to these factors, hence it is never static.
OR
As the extent of Amazonian rainforest is too large than any other, it is referred as the ‘Lungs of our planet’. Massive deforestation and conversion of forest land into cultivable land to grow soya has led to rapid decline in the biodiversity of this stretch.
Section – C (21 Marks)
Question 22.
Where are the following structures present in a male gametophyte of an angiosperm? Mention the function of each one of them. [3]
(a) Germ pore
(b) Sporopollenin
(c) Generative cell
Answer:
(a) Germ pore is a prominent aperture on exine of the pollen grain. It is the place where sporopollenin is absent.
Function: The contents of the pollen grain move into the pollen tube through the germ pore.
(b) Sporopollenin is a major component of the tough outer (exine) walls of plant spores and pollen gains. It is chemically very stable and is usually well preserved in soils and sediments.
Function: Sporopollenin can withstand high temperatures and strong acids and alkali. Pollen grains are well preserved as fossils because of the presence of sporopollenin.
(c) Pollen grain on maturity contains two cells, the vegetative cell and generative cell. The generative pell is small and floats in the cytoplasm of the vegetative cell.
Function: In some species, the generative cell divides mitotically to give rise to the two male gametes before pollen grains are shed (3-celled stage).
Question 23.
Name the functions of the following: [3]
(a) Corpus Luteum
(b) Endometrium
(c) Acrosome
Answer:
(a) It is responsible for secretion of progesterone during menstrual cycle. High level of progesterone inhibits FSH and LH and hence prevents ovulation.
(b) It is an inner lining of a uterus. This part undergoes changes during menstrual cycle and gets ready for implantation of an embryo.
(c) It is a cap like structure on the head of the sperm. It contains hvaluronidase enzyme which hydrolyses the outer membrane of an egg and allows the entry of the sperm.
Question 24.
Analyse the diagram given alongside and answer the questions based on it: [3]
(a) What does the below diagrammatic representation concerned about?
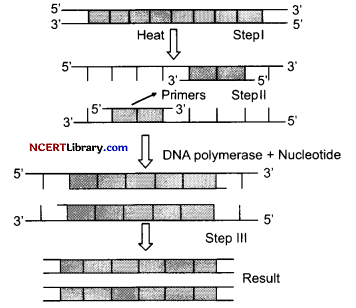
(b) What is the result at the end of the above process?
(c) What are primers?
Answer:
(a) The diagram explains about the steps in PCR technique to amplify the gene of interest.
(b) At the end of PCR the result is an amplified DNA segment at the rate of 1 billion copies. Now, the amplified fragment can be used to ligate with the vector for further cloning.
(c) These are small, chemically synthesized oligonucleotides which are complementary to the regions of DNA.
![]()
Question 25.
(a) Give the Law of Segregation given by Mendel.
(b) In pea plant, the colour of the flower is either violet or white, whereas human skin colour shows many gradations. Explain giving reason how it is possible. [3]
Answer:
(a) The two alternative factors (alleles) of a pair representing a character are separated from each other at the time of gamete formation, so that a gamete contains only one factor (allele) for the character and paired condition is restored during fertilisation.
(b) The colouration of human skin follows quantitative inheritance. It is regulated by at least three genes. There can be seven allelic combinations in the gametes of a person heterozygous for all three genes.
Therefore, as a result, sixty four different combinations of colours are possible. On the other hand, the colour of the flower in pea is controlled by non-allelic complementary genes, which independently shows a simple effect.
Question 26.
| i | P | o | z | y | a |
Given above is the schematic representation of lac operon of E. coli. Explain the functioning of this operon when lactose is provided in the growth medium of the bacteria. [3]
OR
(a) What is operon? Quote some examples of operon.
(b) How are structural genes activated in the lac operon in E. coli1
Answer:
An operon is a part of DNA which acts as a single regulated unit of one or more structural genes, an operator gene, a promoter gene, a regulator gene, a repressor and an inducer or a compressor gene. In lac operon when there is an addition of lactose, it enters the cell with the help of permease.
The lactose binds itself to active repressor and changes its structure. The repressor now fails to bind to the operator. Then the RNA polymerase starts the transcription of the operon by binding to the promoter site. All the three enzymes for digestion of lactose molecules are produced in the whole process of the induction. It can be understood with the help of diagram.
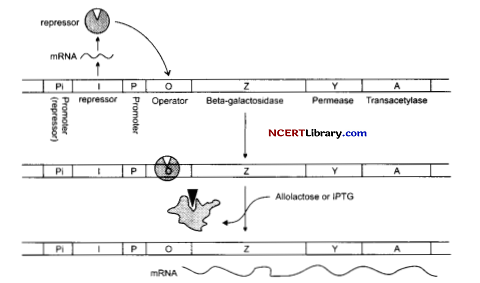
After some time, when the entire lactose is consumed, there is no inducer present so as to bind to the repressor. So the repressor once again activates and attaches itself to the operator and finally switches off the operon.
OR
(a) The arrangement where, a polycistronic structural gene is regulated by a common promoter and regulatory gene. This pattern of arrangement is known as operon. Example: lac operon, trp operon, ara operon, his operon, val operon.
(b) Here, the lactose acts as an inducer. It binds with the repressor protein, free operator gene. Further RNA polymerase freely moves over the structural genes transcribing the lac mRNA which in turn produces the enzymes that areable to digest the lactose.
Question 27.
Analyse the diagram given below and answer the questions based upon it: [3]
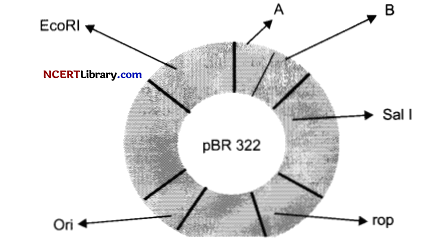
(a) What does the above given diagram represent?
(b) In the diagram, what do A and B stand for?
(c) What does the rop code for?
Answer:
(a) The above given diagram is the £. coli cloning vector pBR322 depicting the restriction sites.
(b) A is Hind III and B shows BamHl which are the restriction sites on the vector.
(c) Rop codes for the proteins that are involved in the replication of the plasmid.
![]()
Question 28.
(a) How has the development of bioreactor helped in biotechnology? [3]
(b) Name the most commonly used bioreactor and describe its working.
Answer:
(a) A larger biomass or large volume of culture can be processed leading to higher yields of desired specific products (proteins or enzymes), under controlled conditions.
(b) Stirring type of biorector is most commonly used.
Working:
(i) Mixing of reactor contents evenly with an agitator system or a stirrer.
(ii) Facilitates 02 availability.
(iii) Temperature, pH and foam are controlled under optimum conditions
Section – D (8 Marks)
Questions No. 29 and 30 are case based questions. Each question has subparts with internal choice in one subpart.
Question 29.
Analyse the following given representation and answer the questions based on it: [4]

(a) What do you understand from the above representation?
(b) What was the concept of “X body” of Henking?
(c) Give an example of XO type of sex determination?
OR
(c) Explain sex determination mechanism in humans.
Answer:
(a) The above representation shows the sex chromosomes in male and female.
(b) Henking carried out experiments on certain entomological species (Insects). During his experiments he focused on the nuclear structure during the process of spermatogenesis. He observed that only fifty percent of sperms received this nuclear structure through spermatogenesis. But he was unable to prove the significance of this nuclear structure and he termed it as “X Body”.
(c) Grasshopper is an example of XO type of sex determination where, males possess single X chromosome whereas females have pair of X chromosome.
OR
(c) The mechanism followed by human beings in determining the sex is of XY type. Out of 23 pairs of chromosome present, 22 are autosomes.
A pair of X chromosomes is present in females on the other hand; X and Y chromosome are present in males. If ovum fuses with sperm carrying X chromosome then the offspring will be a female (XX) and if the ovum fuses with the sperm carrying Y chromosome then the offspring will be male (XY). Hence in human beings, father is said to be the sex determiner and not the mother.
![]()
Question 30.
Analyse the below given chemical structure and answer the questions based on it: [4]
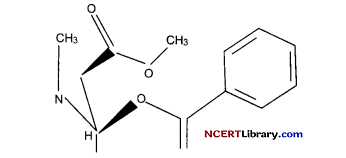
(a) The given structure is of which chemical?
(b) What is the common name of this chemical?
(c) What are the physical attributes of this chemical?
OR
(c) This chemical is obtained from which plant?
Answer:
(a) The chemical structure is of Morphine.
(b) Heroin or Smack.
(c) It is crystalline in nature, bitter in taste, white in colour and is odourless.
OR
(c) It is obtained from Papaver somniferum, commonly called as poppy plant.
Section – E (15 Marks)
Question 31.
What is pollination? Explain various kinds of pollination in brief. Provide suitable examples wherever necessary.
OR
During the reproductive cycle of a human female, when, where and how does a placenta develop? What is the function of the placenta during the pregnancy and embryo development? [5]
Answer:
Pollination is a mechanism by which pollen grains are transferred to the receptive stigma of same or another flower, located on same or another plant. Pollination can be categorised into three major types.
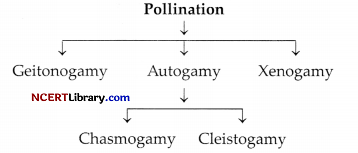
(a) Geitonogamy: It is the transfer of pollen grains from anther to receptive stigma of another flower of a same plant. Though it functionally means cross pollination, but it is genetically similar to autogamy because pollen grains are from the same plant on which stigma is present.
(b) Autogamy: It is a type of pollination that enables pollen grains to transfer to stigma of same flower. Autogamy may be further categorised as:
(i) Chasmogamy: It is transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of other species in which both anther and stigma are open and exposed. For example: Oxalis and Commelina.
(ii) Cleistogamy: It is transfer of pollen from anthers to receptive stigma present in a flower that does not open at all. Such flowers produce assured seed set even in absence of the pollinating
agents.
(c) Xenogamy: It is a kind of pollination where pollen grains from anther to stigma are transferred on the flower present on another plant. It is the only kind of pollination that assures fusion of genetically different anthers and stigma.
OR
Placenta is an organ which connects the developing foetus with uterine wall during pregnancy. It is formed after implantation. Finger like projections appear on the trophoblast called as chorionic villi that are surrounded by uterine tissue and maternal blood. This chorionic villi and uterine tissue jointly form placenta.
Functions of Placenta:
(a) The placenta connects the embryo through the umbilical cord, that transports the nutrients such as oxygen to the developing embryo.
(b) It enables to remove the unwanted waste material from the body produced by foetus.
(c) It also act as an endocrine tissue and produces several hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin, human placental gonadotropin estrogen and progesterone.
Tire production of such hormones is essential for supporting the growing foetus. It also plays a role in maintaining the metabolic changes in mother and maintaining the pregnancy.
Question 32.
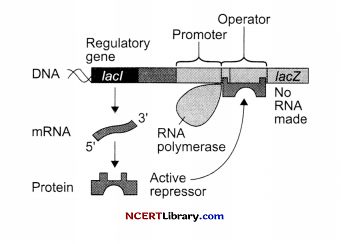
(a) Explain how structural gene of lac operon start on addition of lactose?
(b) What does z,y, a gene codes for? [5]
OR
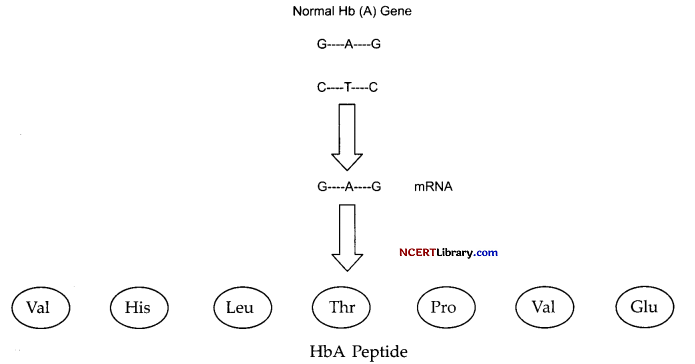
Given above is the representation of amino acid composition of the relevant translated portion if chain of haemoglobin, related to the shape of human red blood cells.
(a) Is the representation indicating a normal human or a sufferer from certain genetic disease? Give reason in support of your answer?
(b) What difference would be noticed in the phenotype of a normal and a sufferer related to this gene? Who are likely to suffer more from the defect related to the gene represented: the male, the female or both equally and why?
Answer:
(a) E. coli prefers to use glucose as an energy source when both glucose and lactose are available. Lactose is an alternative energy source that can be used if glucose is absent.
The overall rate of messenger RNA synthesis from the lac operon, and from other operons is indirectly regulated by the concentration of glucose in the cell. cAMP is the second messenger used directly in the regulation of lac operon expression in response to changing levels of glucose.
The lac operon consists of:
(i) Regulatory gene i – It codes for the repressor protein.
(ii) Structural gene
Normally, the lac operon is turned off. A repressor protein binds the operator (control) region upstream of the operon preventing transcription. When lactose is present outside the cell, it crosses the cell membrane and acts as an inducer of the operon.
It does so once lactose is broken down to create allolactose. The lac operon is then membrane facilitating lactose transport into the cell, and & beta-galactosidase, which eats up lactose to make glucose moleclues and beta-galactosidase also makes allolactose. This leads to a positive feedback loop.
(b) (i) z gene — It codes for beta-galactosidase which catalyzes the hydrolysis of lactose into glucose and galactose.
(ii) y gene — It codes for permease which regulates the lactose permeability in the cell.
(iii) a gene — It codes for transacetylase which assists the enzyme beta galactosidase.
OR
(a) The correct representation of a normal person is given below.
The HbA peptide given is incorrect. The peptide shown in the diagram is of a Sickle cell HbS peptide. The correct HbA peptide is:

(b) The sufferer’s RBC’s become elongated and sickle shaped as compared to the normal biconcave RBC. Both males and females are likely to suffer from the disease equally, as this is not a sex linked disease. It is an autosomal linked recessive trait.
![]()
Question 33.
India is the seventh largest country in the world and Asia’s second largest nation, encompassing a varied landscape rich in natural resources. India has a great diversity of natural ecosystems from the cold and high Himalayan ranges to the sea coasts, from the wet north eastern green forests to the dry north western arid deserts, different types of forests, wetlands, islands and the oceans The world comprises a huge diversity of the types of environments which are divided and grouped into different types of biomes and are mainly based on the adaptations, range of temperature, weather, and climatic conditions.
(a) Define Niche density.
(b) Explain biotic and abiotic factors with examples.
(c) Give the brief explanation about xerocoles and ecotype. [5]
OR
The flow of energy in ecosystems is vitally important to the thriving of life on Earth. Nearly all of the energy in Earth’s ecosystems originates within the Sun. Once this solar energy reaches Earth, it is distributed among ecosystems in an extremely complex manner. All organisms, dead or alive, have potential for energy transfer in an ecosystem. For example, a leaf is eaten by a caterpillar, which is eaten by a small bird, which is eaten by a hawk. A food chain catalogues the movement of this energy and nutrients from one organism to another.
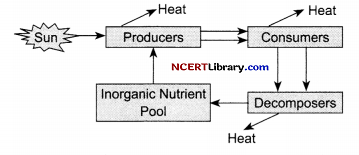
(a) Name the organisms that manufacture organic compounds from simple inorganic compounds without using sunlight?
(b) Explain energy flow in ecosystem.
(c) What is PAR? Also write the percentage of PAR captured by plants.
Answer:
(a) Niche density is the number of a particular species in a given area or suitable habitat.
(b) The biotic factors refer to all the living beings present in an ecosystem. It consists of plants and animals which are found on the earth. The abiotic factors of an ecosystem include various physical and chemical factors. Examples: heat, sunlight, water, temperature, humidity, etc.
(c) Xerocole are animals adapted to live in a desert while, genetically different population with the same physical features is known as ecotype.
OR
(a) Chemotrophs are the organisms that manufacture organic compounds from simple inorganic compounds without using sunlight.
(b) Energy flow in an ecosystem is always unidirectional or one way, i.e., solar radiations- producers herbivores- carnivores. It cannot pass in the reverse direction. There is a decrease in the content and flow of energy with the rise in trophic levels.
(c) Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) is light of wavelengths 400-700 nm and is the portion of the light spectrum utilised by plants for photosynthesis. 2-10 % of PAR is captured by plants.