Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Applied Mathematics Set 8 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Applied Mathematics Set 8 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains five sections A, B, C, D and E. Each section is compulsory.
- Section – A carries 20 marks weightage, Section – B carries 10 marks weightage, Section – C carries 18 marks weightage, Section – D carries 20 marks weightage and Section – E carries 3 case-based with total weightage of 12 marks.
- Section -A: It comprises of 20 MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section – B: It comprises of 5 VSA type questions of 2 marks each.
- Section – C: It comprises of 6 SA type of questions of 3 marks each.
- Section – D: It comprises of 4 LA type of questions of 5 marks each.
- Section – E: It has 3 case studies. Each case study comprises of 3 case-based questions, where 2 VSA type questions are of 1 mark each and 1 SA type question is of 2 marks. Internal choice is provided in 2 marks question in each case-study.
- Internal choice is provided in 2 questions in Section – B, 2 questions in Section – C, 2 questions in Section – D. You have to attempt only one of the alternatives in all such questions.
Section – A
All questions are compulsory. No internal choice is provided in this section
Question 1.
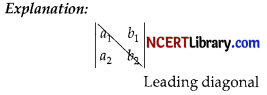
For a determinant containing 4 elements a1, b1, a2 and b2; what will the elements of leading diagonals? [1]
(A) a1,b1
(B) a1, b2
(C) a2, b1
(D) a2, b2
Answer:
(B) a1, b2
Question 2.
If
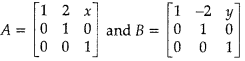
and AB = I3, then (x + y) equals: [1]
(A) 0
(B) – 1
(C) 2
(D) -2
Answer:
(A) 0
Question 3.
Assume X,Y,Z,W and Pare matrices of order 2 x n, 3 x k, 2 x p, n x 3 and p x k,respectively. The restriction on n. k and p so that PY + WY will be defined are: [1]
(A) k – 3, p = n
(B) k is arbltraryp = 2
(C) p is arbitrary, k = 3
(D) k = 2, p = 3
Answer:
(A) k – 3, p = n
Explanation: Matrices P and Y are of the orders p x k and 3 x k, respectively. Therefore, matrix PY will be defined if k = 3. Consequently, PY will be of the order p x k. Matrices W and Y are of the orders n x 3 and 3 x k respectively.
Since the number of columns in W is equal to the number of rows in Y, matrix WY is well-defined and is of the order n x k. Matrices PY and WY can be added only when their orders are the same.
However, PY is of the order p x k and WY is of the order n x k. Therefore, we must have p = n. Thus, k = 3 and p = n are the restrictions on n, k, and p so that PY + WY will be defined.
Question 4.
Pipe A can fill a tank 6 times faster than a pipe B. If B can fill a tank in 21 minutes, then the time taken by both the
pipes together to fill the tank is:
(A) 3 minutes
(B) 4\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) minus
(C) P minutes
(D) 9 minutes
Answer:
(A) 3 minutes
Explanation: Given, slower pipe filled the tank in 21 minutes.
Then faster pipe filled the tank in minutes \(\frac { 21 }{ 6 }\) Thus, tank filled by both the pipes in 1 minute = \(\frac { 1 }{ 21 }\) + \(\frac { 6 }{ 21 }\) = \(\frac { 7 }{ 21 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
Hence, time taken by both pipes together to fill the tank is 3 nnnutes.
![]()
Question 5.
The solution set of the inequation |x + 2| ≤ 5 is: [1]
(A) ( – 7, 5)
(B) [ – 7, 3]
(C) [ – 5, 5]
(D) ( – 7, 3)
Answer:
(B) [ – 7, 3]
Explanation: |x + 2| ≤ 5
⇒ – 5 ≤ x + 2 ≤ 5
⇒ [∴ |x| ≤ a,then – a ≤ x ≤ a]
⇒ – 5 – 2 ≤ x ≤ 5 – 2
⇒ – 7 ≤ x ≤ 3
⇒ x ∈ [- 7, 3]
Question 6.
A person can row in still water at the rate of 8 km/h. ¡fit takes him thrice as long to row upstream as to row downstream then the speed of the stream is: [1]
(A) 2km/h
(B) 3km/h
(C) 4km/h
(D) 6km/h
Answer:
(C) 4km/h
Explanation: Let x be the speed of the stream
\(\frac{V_d}{t}\) = 3\(\frac{V_u}{t}\)
8 + x = 3(8 – x)
4x = 16
x = 4km/h
Question 7.
A retailer buys 250 kg of rice, a part of which he sells at 10% profit and the remaining at 5% loss. If the net profit made by the retailer in the whole transaction is 7%, then the quantity of rice sold at 10% profit is …………… [1]
(A) 200kg
(B) 150kg
(C) 100kg
(D) 50kg
Answer:
(A) 200kg
Explanation: C = – 5 % d = 10%, m = 7%
(d – m):(m – c) = 1 : 4
Quantity sold at 10 % profit
= \(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\) x 250
= 200 kg
![]()
Question 8.
The best-fitted trend line is one for which sum of squares of residuals or errors is: [1]
(A) Positive
(B) Minimum
(C) Negative
(D) Maximum
Answer:
(B) Minimum
Explanation: The line is termed as the line of best fit form which the sum of squares of distances from the points is minimized.
Question 9.
The variable cost of producing x units is V(x) = x2 + 2x. If the company incurs a fixed cost of 10,000, then the level of output where the average cost is minimum is ……………. [1]
(A) 10 units
(B) 50 units
(C) 100 units
(D) 200 units
Answer:
(C) 100 units
Explanation: TC = VC + FC
= x2 + 2x + 10000
AC = x + 2 + \(\frac { 10000 }{ x }\)
\(\frac { d(AC) }{ dx }\) = 1 – \(\frac { 10000 }{ x^2 }\)
∴ [\(\frac { d(AC) }{ dx }\) = 0]
1 – \(\frac { 10000 }{ x^2 }\) = 0
x = 100 units
Question 10.
Let h(x) = f(x) – [f(x)]2 + [f(x)]3 for eve real number x. Then [1]
(A) h is increasing whenever f is increasing
(B) h is increasing wheneverf is decreasing
(C) h is decreasing whenever f is increasing
(D) Nothing can be said in general
Answer:
(A) h is increasing whenever f is increasing
Explanation: For the given relation h is increasing whenever is increasing as:
h(x) = f(x) – [f(x)]2 + [f(x)]3
[f(x)]3 > [f(x)]2
Question 11.
The value of: ∫(x + 3)(x + 2)dx is: [1]
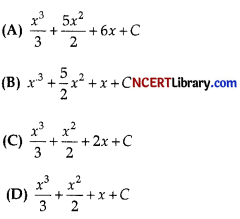
Answer:
![]()
Explanation:
I = ∫(x + 3)(x + 2)dx
= ∫(xsup>2 + 5x + 6)dx
= ∫xsup>2dx + 5 ∫xdx + 6 ∫dx
= \(\frac{x^3}{3}\) + \(\frac{5x^2}{2}\) + 6x + C
![]()
Question 12.
Let X represent the difference between the number of heads and the number of tails obtained when a coin is tossed 6 times. Then the possible values of X are: [1]
(A) 0, 1, 3, 5
(B) 0, 2, 4, 6
(C) 0, 2, 5, 6
(D) 1, 3, 4, 5
Answer:
(B) 0, 2, 4, 6
Explanation: The coin is tossed six times and X represents the difference between the number of heads and the number of tails.
∴ X(6H,OT) = |6 – 0| =6
X(5H, 17) = |5 – 1| = 4
X(4H,2T) = |4 – 2| =2
X(3H,3T) = |3 – 3| =0
X(2H,4T) = |2 – 4| = 2
X(1H,5T) = |1 – 5| =4
X(0H,6T) = |0 – 6| = 6
Thus, possible values are 0, 2, 4, 6.
Question 13.
If the mean of a binomial distribution is 81, then the standard deviation lies in the interval: [1]
(A) (0,9)
(B) (0,9]
(C) [0, 3]
(D) (0, 3]
Answer:
(A) (0,9)
Explanation: Standard deviation, σ = \(\sqrt{npq}\) > 0
Now, mean = np = 81 and q < 1
So, σ = \(\sqrt{npq}\) < \(\sqrt{np}\) = \(\sqrt{81}\) = 9
∴ 0 < σ < 9
Hence, a lies in [0, 9)
Question 14.
If ‘m’ is the mean of a Poisson Distribution, then variance is given by …………. [1]
(A) m2
(B) m1/2
(C) m
(D) \(\frac { m }{ 2 }\)
Answer:
(C) m
Explanation: Mean and variance of Poisson distribution are equal.
![]()
Question 15.
The money borrowed or lent for a certain period is:
(A) Amount
(B) Principal
(C) Interest
(D) Loan
Answer:
(B) Principal
Explanation: Money borrowed or lent out for a certain period is called the principal or the sum.
Question 16.
The simple interest on sum for one year is 60. What will he the compound on the same sum and at the same rate of interest for one year? [1]
(A) 60
(B) 66
(C) 70
(D) 76
Answer:
(A) 60
Explanation: If the period for the calculation of interest is 1 year, then the compound interest and the simple interest are same.
Question 17.
The interest rate per year is 16 and the compounding occurs every quarter then interest rate per compounding period is: [1]
(A) 0.4
(B) 0.04
(C) 0.004
(D) 40
Answer:
(B) 0.04
Explanation:
Interest Rate = \(\frac { 16 }{ 4 x 100 }\) = 0.04
Question 18.
The nominal rate which is compounded more frequently than annually is equal to interest rate [1]
(A) Compounded monthly
(B) Discounted monthly
(C) Compounded annually
(D) Discounted annually
Answer:
(B) Discounted monthly
DIRECTION: For questions 19 and 20, two statements are given – one labelled Assertion(A) and the other labelled
Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C) and (D) as given below:
(A) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(B) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
![]()
Question 19.
Assertion (A): If A and B are matrices of order 3 and |A| = 5, |B| = 3, then find |3AB| = 405. [1]
Reason (R): |3AB| = (3)3 |AB|
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: We know that,
|AB| = |A|.|B|
|3AB| = (3)3 |AB|
= 27 |AB|
= 27 |A|.|B|
= 27 x 5 x 3
= 405
Question 20.
Assertion (A): The general solution of the differential equation \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = ex+y is e-y = – ex + c.
Reason (R): The given equation is solved by apply variable separation method. [1]
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: Given differential equation is
\(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = ex+y
\(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = ex ey
\(\frac{dy}{e^y}\) = (ex)dx
(e-y)dy = (ex)dx
Integrating both sides, we get
∫(e-y)dy = ∫(ex)dx
– e-y = ex + c’
e-y = – ex + c [where c = – c’]
Section – B
All questions are compulsory. In case of internal choice, attempt any one question only
Question 21.
If A is a skew-symmetric matrix of order 3, then prove that det A = O.
OR
Without expanding at any stage, find the value of
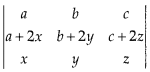
Answer:
∴ Since A is a skew-symmetric matrix
∴ |AT| = A
|AT| = |- A| = ( – 1)3.|A|
or |AT| = – |A|
2|A| = 0 or |A| = 0.
OR
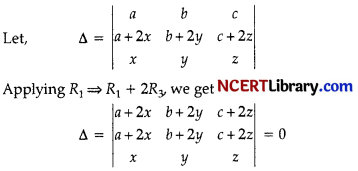
Since, R1 and R2 are identical, therefore value of is zero.
![]()
Question 22.
The following table shows the annual rainfall (in mm) recorded for Cherrapunji. Meghalaya:
| Year | Rainfall (in mm) |
| 2001 | 1.2 |
| 2002 | 1.9 |
| 2003 | 2 |
| 2004 | 1.4 |
| 2005 | 21 |
| 2006 | 1.3 |
| 2007 | 1.8 |
| 2008 | 1.1 |
| 2009 | 1.3 |
Determine the trend of rainfall by 3-years moving average. [2]
Answer:
| Year | Rain fall (in mm) | Three year moving total | Three year moving average |
| 2001 | 12 | – | |
| 2002 | 1.9 | 5.1 | 1.7 |
| 2003 | 2 | 5.3 | 1.766 |
| 2004 | 1.4 | 5.5 | 1.833 |
| 2005 | 2.1 | 4.8 | 1.6 |
| 2006 | 1.3 | 5.2 | 1733 |
| 2007 | I .8 | 4.2 | I .4 |
| 2008 | 1.1 | 4.2 | 1.4 |
| 2009 | 1.3 | – |
Question 23.
A random sample of 60 observations was drawn from a large population and its standard deviation was found to
be 2.5. Calculate the suitable standard error that this sample is taken from a population with standard deviation 3? [2]
Answer:
Given sample size n = 60
Sample standard deviation = 2.5
Population standard deviation σ = 3
The S.E. is given by
\(\sqrt{\frac{\sigma^2}{2 n}}\) = \(\sqrt{\frac{9}{120}}\)
= \(\sqrt{0.075}\)
= 0.2739
Question 24.
Evaluate:
![]()
OR
There are 1000 birds on an island. They breed with a Constant growth rate of 10% per year. How many birds will be on the island after seven year. [Given e0.7 = 2.010] [2]
Answer:
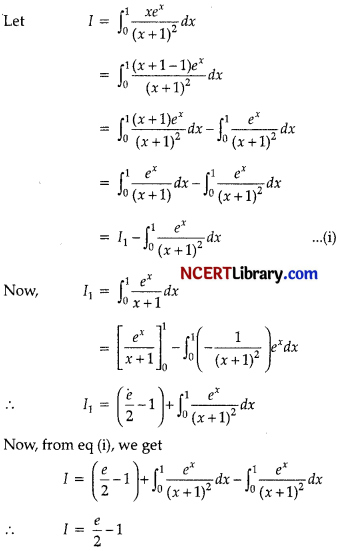
OR
Let x be the number of the birds on the island after 1
year with continuous growth rate k = 10% = 0.1
C = 1000
\(\frac { dx }{ dt }\) = 0.1x
We have dt
Solving the diff. eq.
x(t) = Ce0.1t
x(t) = 1000 e0.1t
t = 7
x(7) = 1000 e0.7
= 2010
Question 25.
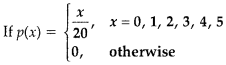
Find (i) P(X < 3) and (ii) P(2 < X ≤ 4) [2]
Answer:
(i) P(X < 3) = P(X = 0) + P(X = 1) + P(X = 2)
= 0 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 20 }\) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 20 }\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 20 }\)
(ii) P(2 < X ≤ 4) = P(X = 3) + P(X = 4)
= \(\frac { 3 }{ 20 }\) + \(\frac { 4 }{ 20 }\) = \(\frac { 7 }{ 20 }\)
Section – C
All questions are compulsory. In case of internal choice, attempt any one question only
Question 26.
Prove that 2n + 6 x 9n is always divisible by 7 for any positive integer n.[3]
OR
Solve \(\frac { |x| – 1 }{ |x| – 2 }\) ≥ 0 x ∈R, x ≠ ± 2
Answer:
2n + 6 x 9n ≡ (mod 7)
2n + 6 x 9n ≡ 7n for sorne integer n
So, 2n + 6 x 9n is a multiple of 7.
When n = 0, then 20 + 6 x 90 = 1 + 6 = 7 is a multiple of 7.
When n = 1, then 2 + 6 x 91 = 2 + 54 = 56 is a multiple of 7.
When n = 2,then 22 + 6 x 92 = 4 + 486 = 490 is a multiple of 7.
Hence, 2n + 6 x 9n is always divisible by 7 for any positive integer n.
OR
Wehave, \(\frac { |x| – 1 }{ |x| – 2 }\) ≥ 0
⇒ \(\frac { y – 1 }{ y – 2 }\) ≥ 0 where y = |x|
⇒ y ≤ 1 or y > 2

⇒ |x| ≤ 1 or |x| > 2
⇒ (- 1 ≤ x ≤ 1) or (x < – 2 or x > 2)
⇒ x ∈ [- 1, 1] or x ∈ [- ∞, – 2) ∪ (2, ∞)
⇒ x ∈ [ – 1, 1] ∪ ( – ∞, – 2) ∪ (2, ∞)
Hence, solution set of the given inequalion is [ – 1, 1]
∪ ( – ∞, – 2) ∪ (2, ∞).
![]()
Question 27.
Maximize Z = 3x + 4y, if possible, subject to the constraints: [3]
x – y ≤ – 1
– x + y ≤ 0
x, y ≥ 0
Answer:
Given LPP is
Max. Z = 3x + 4y
Subject to constraints
x – y ≤ – 1
– x + y ≤ 0
x, y ≥ 0
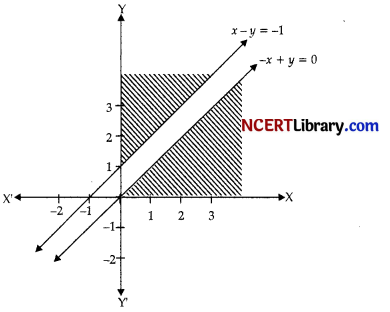
The region determined by the constraints is shown in above figure.
It is clear, there is no feasible region and thus, Z has no maximum value.
Question 28.
Fit a straight line trend by the method of least squares and find the trend value for the year 2008 for the following data: [3]
| Year | Production
(in lakh tonnes) |
| 2001 | 30 |
| 2002 | 35 |
| 2003 | 36 |
| 2004 | 32 |
| 2005 | 37 |
| 2006 | 40 |
| 2007 | 36 |
Answer:
| Year | Production (y) (in lakh tonnes) | x = t – 2004 | xy | x2 |
| 2001 | 30 | – 3 | – 90 | 9 |
| 2002 | 35 | – 2 | – 70 | 4 |
| 2003 | 36 | – 1 | – 36 | 1 |
| 2004 | 32 | o | 0 | 0 |
| 2(X)5 | 37 | 2 | 37 | 1 |
| 2006 | 40 | 3 | 80 | 4 |
| 2007 | 36 | ∑x = o | 108 | 9 |
| n = 7 | ∑y = 246 | x = t – 2004 | ∑xy = 29 | ∑x2 = 28 |
Now, a = \(\frac { ∑y }{ n }\)
= \(\frac { 246 }{ 7 }\)
= 35.14
b = \(\frac{\sum x y}{\sum x^2}\)
= \(\frac { 29 }{ 28 }\)
= 1.035
∴ Trend equation is:
yt = a + bx
yt = 35.14+ 1.035 x
Trend value at 2008 is
y2008 = 35.14 + 1.035 (4)
= 35.14 + 4.140
= 39.28
![]()
Question 29.
In a sample of 400 population from a village 230 are found to be eaters of vegetarian items and the rest non – vegetarian items. Compute the standard error assuming that both vegetarian and non-vegetarian foods are equally popular in that village? [3]
OR
Ten cartons are taken at random from an automatic packing machine. The mean net weight of the ten cartons is 11.8 kg and standard deviation is 0.15 kg. Does the sample mean differ significantly from the intended mean of 12 kg?
[Given that for d.f. = 9, t0.05 = 2.26]
Answer:
Given sample size 400 and 230 are vegetarian eaters.
So sample proportional = \(\frac { 230 }{ 400 }\) = 0.575
Population proportion P = Prob. (vegetarian eaters from the village) =
(Since vegetarian and non-vegetarian foods are equally popular),
Q = 1 – P
= 1 – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
The standard error S.E. = \(\frac{PQ}{N}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)}{400}}\)
= \(\frac{0.25}{400}\)
= \(\sqrt{0.000625}\)
= 0.025
OR
Given,
Population mean (μ) = 12
Sample mean \(\bar{x}\) = 11.8
Standard deviation (σ) = 0.15
Sample size (n) = 10
Let H0, ; μ = \(\bar{x}\) ≠ 11.8
and H1 : μ ≠ \(\bar{x}\) =11.8
The test statistic is
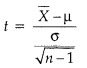
At 0.05 level of significance, for a 2 – tail test, for 10 – 1 = 9 degrees of freedom if the calculated value is greater than 2.262 or less than – 2.262, we reject H0 else retain it. Substituting known values of parameters, we get
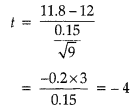
Since, t = – 4 is less than – 2.262, so we reject H0 at 5% level of significance.
Thus, the sample mean differences significantly from the intended weight of 12 kg.
Question 30.
A company borrowed ₹ 60,000 for renovation. The company plans to set up a sinking fund that will pay back the loan at the end of 5 years. Assuming a rate of 10% compounded semiannually, and the sinking fund of the ordinary annuity. Given that (1.05)10 = 1.6288. [3]
Answer:
Given, A = ₹ 60,000, r = 10% or 0.10
Number of years (n) = 5
Number of payments per year (m) = 2
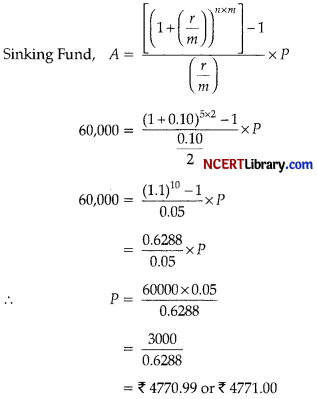
Question 31.
Mr. Lal took a car loan of 10 lakhs at an 11% interest for a 15 years loan tenure. What would be his EMI ? Given
(1.0091)180 = 5.1069. [3]
Answer:
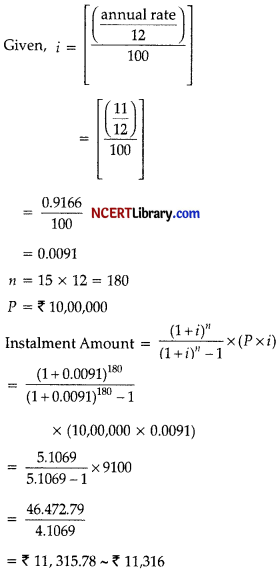
Section – D
All questions are compulsory. In case of internal choice, attempt any one question only
Question 32.
A dietician wishes to mix two types of food F1 and F2 in such a way that the vitamin content of the mixture contains at least 8 units of vitamin A and 10 units of vitamin C. Food F1 contains 2 units/kg of vitamin A and 1 unit/kg of vitamin C, while Food F2 contains 1 unit/kg of vitamin A and 2 units/kg of vitamin C. It costs ₹ 5 per kg to purchase Food F1and ₹ 7 per kg to purchase Food F2.
Based on the above information, answer the following questions:
(a) To find out the minimum cost of such a mixture, formulate the above problem as a LPP
(b) Determine the minimum cost of the mixture. [5]
Answer:
(a) let the mixture contain x kg. of food F1 and y kg of Food F2.
Clearly x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0. We make the following table from the given data:
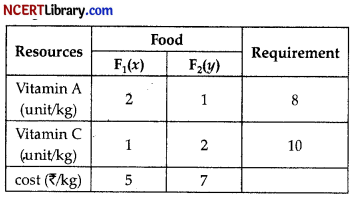
Since the mixture must contain atleast 8 unit of
vitamin A and 10 units of vitamin C.
∴ 2x + y ≥ 8
and x + 2y ≥ 0
Total cost Z of purchasing x kg of food F1 and y kg of food F2 is
Z = 5x + 7y
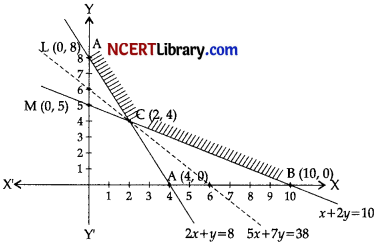
Since, feasible region is unbounded.
∴ We are to check whether this value is minimum
For this, we draw the graph of 5x + < 38 …………(i)
Since (1) has no common point with feasible region.
∴ Minimum vaLue = 38 at (2, 4)
(b) ∴ Cost is minimum when the dietician mixed 2 kg of food F1 and 4 kg of Food F2.
Minimum cost is ₹ 38.
| Corner print | Z = 5x + 7y |
| P(0,8) | Z = 0 + 56 = 56 |
| B(10, 0) | Z = 50 + 0 = 50 |
| C(2, 4) | Z = 10 + 28 = 38 |
![]()
Question 33.
If x cos (a + y) = cos y, then prove that \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = \(\frac{\cos ^2(a+y)}{\sin a}\) . Hence, show that sin a \(\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2}\) + sin 2 (a + y) \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = 0.
OR
An open topped box is to be made by removing equal squares from each corner of a 3 m by 8 m rectangle sheet of aluminium and by folding up the side. Find the volume of the largest such box.
Answer:
Given, x cos (a + y) = cos y
or x = \(\frac { cosy }{ cos(a+y) }\)
On differentiating both sides wr.t. y. we get
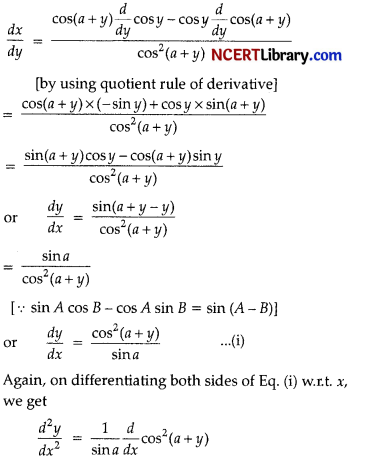
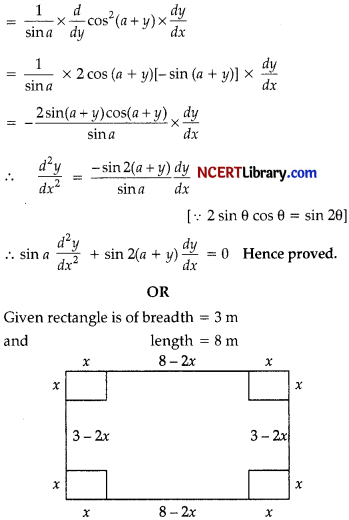
Let x be the length of each square removed from the corners
Volume of bo V(x) = (8 – 2x)(3 – 2x)x
= x(24 – 16x – 6x + 4x2)
= 24x – 22x2 + 4x3
V’(x) = 24 – 44x + 12x2
For max. and min. volume
V'(x) = 0
12x2 – 44x + 24 = 0
3x2 – 11x + 6 = 0
3x2 – 9x – 2x + 6 = O
(x – 3) (3x – 2) = 0
x = 3 (not possible) or 3x = 2
x = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
Now, V”(x) = – 44 + 24x
at x = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) V”(\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)) = -44 + 24 (\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)) < 0
∴ Volume is maximum when x = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
Volume (V) = (8 – 2(\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)))(3 – 2(\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)))(\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\))
= (8 – \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\)) (3 – \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\))(\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\))
= \(\frac { 20 }{ 3 }\) x \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 }\) x \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
= \(\frac { 200 }{ 27 }\) m3
Question 34.
If X is a normal variate with mean 30 and SD 5. Find the probabilities that (i) 26 ≤ X ≤ 40 (ii) X > 45. [5]
OR
In the proportion of defective in a bulk is 4%. Find the probability of not more than 2 defective in a sample of 1o. It is known that e-4 = 0.6703.
Answer:
Here mean μ = 30 and
standard deviation σ = 5
(i) When X = 26
z = \(\frac { (X – μ) }{ σ }\)
= \(\frac { (26 – 30) }{ 5 }\) = – 0.8
And when X = 40,
z = \(\frac { 40 – 30 }{ 5 }\) = 2
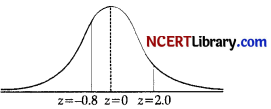
Therefore,
P(26 < X < 40) = P(- 0.8 ≤ Z < 2)
= P( – 0.8 ≤ Z ≤ 0) + P(0 ≤ Z ≤ 2)
= P(0 ≤ Z ≤ 0.08) + P(0 ≤ Z ≤ 2)
= 0.2881 + 0.4772 (By tables)
= 0.7653
(ii) The probability that X ≥ 45
When X = 45
x= \(\frac { (X – μ) }{ σ }\) = \(\frac { 45 – 30 }{ 5 }\) = 3
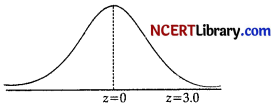
P(X ≥ 45) = P(Z ≥ 3)
= 0.5 – 0.49865
= 0.00135
OR
Proportion of defective units
p = \(\frac { 4 }{ 100 }\) = 0.04
m = np = 0.04 x 10 = 0.4
Probability of not more than 2 defective means the sum of probabilities of 0, 1 and 2 defectives:
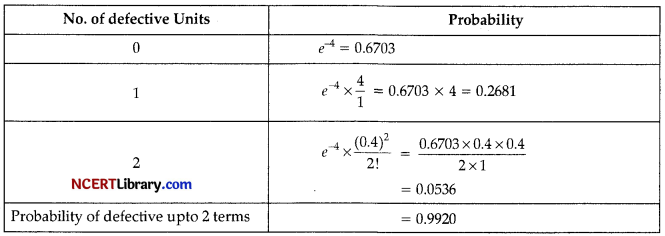
Hence the probability of not more than 2 defectives = 0.9920 or 99.2%
Question 35.
A person amortizes a loan of ₹ 15,00,000 for renovation of his house by 8 years mortgage at the rate of 12% p.a. compounded monthly. Find
(i) the equated monthly instalment
(ii) the principal outstanding at the beginning of 40th month.
(iii) the interest paid in 40th payment.
[Given (1.01)96 = 2.5993, (1.01)57 = 1.7633] [5]
Answer:
Given, P = ₹ 15,00,000, i = \(\frac { 12 }{ 12 x 100 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 100 }\) = 0.01
and, n = 8 x 12 = 96

Section – E
All questions are compulsory. In case of internal choice, attempt any one question only
CASE STUDY – I
Question 36.
The demand function for a popular make of 12- speed bicycle is given by p = D(x) = – 0.001x2 + 250, where p is the unit price in Rupees and x is the quantity demanded in units of a thousands. The supply function for the same
product is given by p = S(x) = 0.0006x2 + 0.02x + 100, where p is the unit price in Rupees and x is the quantity supplied in units of a thousands.

(i) Write the formula for consumer’s surplus. [1]
(ii) Write the formula for producer’s surplus. [1]
(iii) Find point of intersection. [2]
OR
Find producer’s profit in Rs.
Answer:
(i) Formula for Consumer’s Surplus is
![]()
Where, D(x) Demand Function
Pe = Equilibrium Price
Qe = Equilibrium Quantity
(ii) Formula for Producer’s Surplus is
![]()
Where, S(x) = Supply Function
Pe = Equilibrium Price
Qe = Equilibrium Quantity
(iii) At equilibrium, the intersection point (x,y) of demand curve and supply curve represents equilibrium quantity (Qe) and equilibrium price (Pe), respectively.
At equilibrium, D(x) = S(x)
⇒ – 0.001x2 + 250 = 0.0006x2 + 0.02x + 100
⇒ (0.0006 + 0.001)x2 + 0.02x + (100 – 250) = 0
⇒ 2x2 + 25x – 187500 = 0.
⇒ 2x2 + 625x – 600x – 187500 = 0
⇒(2x + 625)(x – 300) = 0
⇒ x = \(\frac { – 625 }{ 2 }\) or x = 300
The value of x cannot be negative, So
x = 300
Now, substituting x = 300 in D(x) or S(x),
we get p = 160
Thus, point of intersection is (300, 160).
OR
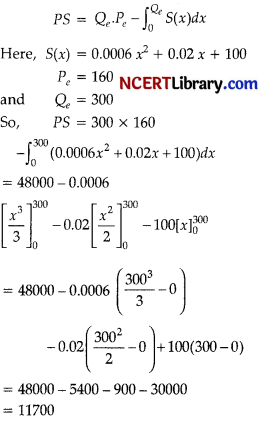
Since, the quantity supplied in units of a thousands,
so, PS = 11,700 x 1000 = 11,700,000
CASE STUDY-II
![]()
Question 37.
The 12 hour clock is most commonly represented on an analogue clock with number 1 – 12, when shown on a digital clock, it usually accompanied by a.m. or p.m. The 24 hour clock is more often shown on digital clocks and is written in a 4 digit form, with the first two digits representing the hours and the last two digits representing the minutes. There is no need for a.m. or p.m. as each time represents each hour in a 24 hour day.
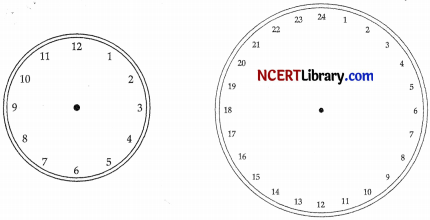
(i) What time in 24 hour clock is equivalent to 7 a.m. in 12 hour clock ? [1]
(ii) Which of two times are same in 12 hours and 24 hours clocks respectively? [1]
1: 00 pm., 13 : 00; 3 : 00 p.m., 03 : 00; 02 : 00 a.m., 14 : 00 and 04 : 00 a.m., 16 : 00
(iii) It is currently 7:00 a.m. in 12 hour dock.
What will be the time In next 493 hours? [2]
OR
If the time after 640 hours from now will be 9 a.mq then what Is current time?
Answer:
(i) 7 : 00 hour in 24 hour dock is equivalent to 07 : 00 a.m. in 12 hour clock.
(ii) Here, 3 : 00 p.m. in 12 hour clock
= 15 : 00 in 24 hour clock
2 : 00 a.m. in 12 hour clock
= 02 : 00 in 24 hour clock
4 : 00 a.m. in 12 hour clock
= 04 : 00 in 24 hour clock
Now,
1:00 p.m. in 12 hour dock is same as 13 : 00 in 24 hour clock
(iii) We know that time repeat after every 24 hours.
So, we find 493 (mod 24)
So, 493(mod24) = 13
∴ 493 hours is equivalent to 13 hours.
Now, 7 : 00 a.m. + 13 hours = 8 p.m.
So, the time in next 493 hours is 8 p.m.
OR
Here, we find 640 (mod 24)
640 (mod 24) 16
∴ 640 hours is equivalent to 16 hours
Now,
9 : 00 a.m – 16 hours = 5 p.m.
So, current time is 5 p.m.
CASE STUDYe III
Question 38.
Three schools A, B and C organised a ,neia for collecting funds for helping the rehabilitation of flood victims. They
sold hand made fans, mats and plates from recycle material at a cost of ₹ 25, ₹ 100 and ₹ 50 each. The number of articles sold are given below:
| School Articles | A | B | C |
| Fans | 40 | 25 | 35 |
| Mats | 50 | 40 | 50 |
| Plates | 20 | 30 | 40 |

(i) Which approach will you use to solve the given problem? [1]
(ii) Find the value of fund collected by School A. [1]
(iii) Find the values of fund collected by School B and School C. [2]
OR
Find the total fund collected by all three Schools.
Answer:
(i) We will use Matrix Multiplication to solve the given problem.
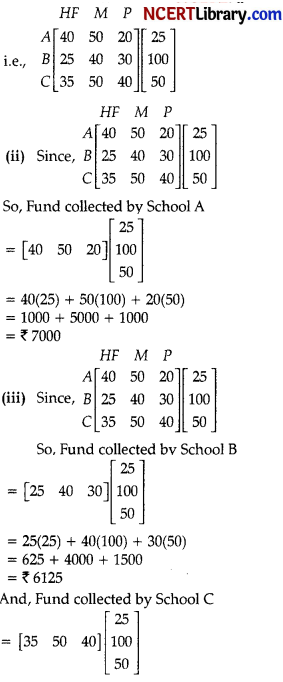
= 35(25) + 50(100) + 40(50)
= 875 + 5000 + 2000
= ₹ 7875
OR
Total collection: ₹ 7,000 + ₹ 6,125 + ₹ 7,875
= ₹ 21,000