Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Applied Mathematics Set 7 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Applied Mathematics Set 7 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains five sections A, B, C, D and E. Each section is compulsory.
- Section – A carries 20 marks weightage, Section – B carries 10 marks weightage, Section – C carries 18 marks weightage, Section – D carries 20 marks weightage and Section – E carries 3 case-based with total weightage of 12 marks.
- Section -A: It comprises of 20 MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section – B: It comprises of 5 VSA type questions of 2 marks each.
- Section – C: It comprises of 6 SA type of questions of 3 marks each.
- Section – D: It comprises of 4 LA type of questions of 5 marks each.
- Section – E: It has 3 case studies. Each case study comprises of 3 case-based questions, where 2 VSA type questions are of 1 mark each and 1 SA type question is of 2 marks. Internal choice is provided in 2 marks question in each case-study.
- Internal choice is provided in 2 questions in Section – B, 2 questions in Section – C, 2 questions in Section – D. You have to attempt only one of the alternatives in all such questions.
Section – A
All questions are compulsory. No internal choice is provided in this section
Question 1.
20 litres of a mixture contains milk and water in the ratio 3: 1. The amount of milk, in litres, to be added to the mixture so as to have milk and water in the ratio 4: 1, is: [1]
(A) 7
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 6
Answer:
(C) 5
Explanation: In 20 l of mixture,
Quantity of milk = \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) x 20 = 15 l
Quantity of water = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) x 20 = 5l
Let the quantity of milk added be x l.
According to be question.
\(\frac { 15+x }{ 5 }\) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 1 }\)
⇒ 15 + x = 20
⇒ x = 5l
Question 2.
Two athletes Vijay and Samuel finish 100 meters race in 12 seconds and 16 seconds respectively. By how many meters does Vijay defeat Samuel? [1]
(A) 10.2 meters
(B) 15 meters
(C) 25 meters
(D) 33.3 meters
Answer:
(C) 25 meters
Explanation: Since Vijay is faster by 4 seconds.
∴ He beats Sarnuel by = \(\frac { 100 }{ 16 }\) x 4
= 25 meters
Question 3.
If B > A, then which expression will have the highest value, given that A and B are positive integers. [1]
(A) A – B
(B) A x B
(C) A + B
(D) Can’tsay
Answer:
(D) Can’tsay
Explanation: As, B > A
⇒ A < B
⇒ A – B < 0 A + B > 0 and AB > 0
If A = 1, B = 4 then, AB < A + B If A = 2, B = 4 then, AB > A + B
Thus, we can’t say which one of A + B and AB has higher value.
Question 4.
In what ratio must a grocer mix two varieties of pulses costing 15 and 20 per kg respectively so as to get a mixture worth ₹ 16.50 kg? [1]
(A) 3 : 7
(B) 5 : 7
(C) 7 : 3
(D) 7 : 5
Answer:
(C) 7 : 3
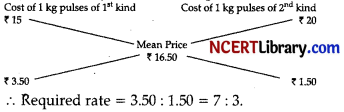
∴ Required rate = 3.50:1.50 7:3.
![]()
Question 5.
The optimal value of the objective function is attained at the points [1]
(A) on X-axis
(B) on Y-axis
(C) which are corner points of the feasible reon
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(C) which are corner points of the feasible reon
Explanation: The optimal value of the objective function is attained at the corner points of feasible region.
Question 6.
Variance of a random variable X is given by [1]
(A) E(X)
(B) E(X2)
(C) E(X2) – (E(X))2
(D) (E(X))2
Answer:
(C) E(X2) – (E(X))2
Explaiatwn: Variance of a random variable is nothing but the expectation of the square of the random variable subtracted by the expectation of X (mean of X) to the power 2. Therefore, the variance is given by E(X2) – (E(X))2.
Question 7.
A table which contains possible value of a random variable and its corresponding probabilities is called [1]
(A) Probability Mass Function
(B) Probability Density Function
(C) Cumulative Distribution Function
(D) Probability Distribution
Answer:
(D) Probability Distribution
Explanation: The given statement is the definition of a probability distribution.
Question 8.
In the measurement of the secular trend, the moving averages: [1]
(A) Smooth out the time series
(B) Given the trend in a straight line
(C) Measure the seasonal Variations
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(A) Smooth out the time series
Explanation: Moving averages is a series of arithmetic means of variate values of a sequence. This is another way of drawing a smooth curve for a time series data.
Question 9.
A set of observations recorded at an equal interval of time is called. [1]
(A) Array data
(B) Data
(C) Geometric Series
(D) Time series data
Answer:
(D) Time series data
Explanation: A time series is a set of observations taken at specified times, usually at equal intervals.
Question 10.
A specific characteristics of a sample is known as [1]
(A) population
(B) parameter
(C) statistic
(D) variance
Answer:
(C) statistic
Question 11.
If we reject the null hypothesis, we might be making: [1]
(A) Type-I error
(B) Type-II error
(C) A correct decision
(D) A wrong decision.
Answer:
(A) Type-I error
Explanation: Type I error: The error of rejecting hypothesis (H0) when it is true.
![]()
Question 12.
A sample of 50 pens is taken at random. Out of 50 pens we found 15 pens are of Cello, 17 are of Parker and 18 are of Reynolds. What is the point estimate of population proportion of Parker. [1]
(A) 0.3
(B) 0.34
(C) 0.36
(D) 0.4
Answer:
(B) 0.34
Explanation: Population proportion of Parker = \(\frac { 17 }{ 50 }\) = 0.34.
Question 13.
The function f(x) = ax is increasing on R, if: [1]
(A) a > 0
(B) a < 0
(C) 0 < a < 1 (D) a > 1
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Explanation: Given, f(x) = ax
∴ f'(x) = ax log a
for increasing function, f'(x) > 0
∴ ax loga > 0
⇒ ax > 0 and log a > 0 or ax < 0 and log a < 0 But log function is always positive ⇒ log a > 0
⇒ a > 1
Question 14.
If the total revenue (₹) received from the sale of x units of a product is given by: [1]
R(x) = 3x2 + 36x + 5
then the marginal revenue.when x = 15, is
(A) ₹ 116
(B) ₹ 96
(C) ₹ 90
(D) ₹ 126
Answer:
(D) ₹ 126
Explanation: R(x) = 3x2 + 36x + 5
Marginal Revenue, R’(x) = \(\frac { dR }{ dx }\) = 6x + 36
∴ Marginal Revenue at x = 15 is \(\frac { dR }{ dx }\)|x=15
= 6(15) + 36 = ₹ 126
Question 15.
The interest earned plus principal amount is considered as: [1]
(A) Semiannual Amount
(B) Compound Amount
(C) Discount Amount
(D) Annual Amount
Answer:
Option (B) is correct.
Explanation: The sum of principal and its interest is known as Compound Amount.
Question 16.
The stated annual rate of interest is referred as: [1]
(A) Classified rate
(B) Fractional Rate
(C) Marginal rate
(D) Nominal rate
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Explanation: The stated interest rate of a bond payable is also known as the face interest rate, nominal interest rate, contractual interest rate, and the coupon interest rate.
![]()
Question 17.
The negative cash flows are classified as: [1]
(A) Present cash
(B) Future cash
(C) Cash outflows
(D) Cash inflows
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: Negative cash flow describes a situation in which a firm spends more cash than it takes in.
Question 18.
The process of loan repayment by installment payments dassified as: [1]
(A) Depreciation loan
(B) Appreciation of investment
(C) Appreciation of loan
(D) Amortizing a loan
Answer:
Option (D) is correct.
Explanation: An amortized loan pays all the interest expenses for the period of principal. This is applicable before the principal of the loan is paid and reduced. Theref ore, the process of loan by installment process is classified as amortizing a loan.
DIRECTION: For questions 19 and 20, two statements are given – one labelled Assertion(A) and the other labelled
Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C) and (D) as given below:
(A) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(B) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(C).Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Question 19.
Assertion (A): An electric pump can fill a tank in 3 hours. Because of a leak in the tank it took 3\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) hours to fill the tank. If the tank is full, the leak will empty the tank in 21 hours.
Reason (A): An electric pump can fill a tank in 3 hours. Because of a leak in the tank it took 3\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) hours to fill the tank. If the tank is full, the leak will empty the tank in \(\frac { 1 }{ 21 }\) hours. [1]
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation:
Work done by the leak in 1 hour
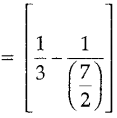
= (\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) – \(\frac { 2 }{ 7 }\)) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 21 }\)
∴ The leak will empty the tank in 21 hours.
Question 20.
Assertion (A): A server channel monitored for an hour was found a have an estimated mean of 20 txansactions transmitted per minute. The variance is known to be 4. The standard error is 0.2582.
Reason (A): Standard Error = \(\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}\) [1]
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: Given σ2 = 4 which implies σ = 2, n = 1 hour = 60, min. \(\bar{X}\) = 20/mm
Standard Error = \(\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}\) = \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{60}}\)
= 0.2582
Section – B
All questions are compulsory. In case of internal choice, attempt any one question only
Question 21.
Find the least positive value of x such that 5 x ≡ 4 (mod 6). [2]
OR
Today is Tuesday. My uncle will come after 45 days. In which day my uncle will be coming?
Answer:
5x – 4 (mod 6)
5x – 4 = 6n for sorne integer n
x = \(\frac { 6n + 4 }{ 5 }\)
When we put n = 1, 6, 11, 16 ………..; then 6n + 4 is divisible by 5.
When n = 1, x = \(\frac { 6 x 1 + 4 }{ 5 }\) = 2
Therefore, the least positive value of x is 2.
OR
Number of days in a week = 7
So, 45 ≡ x(mod7)
45 ≡ 3(mod 7)

The value of x must be 3.
Thus, three days after Tuesday is Friday. So, uncle will corne on Friday.
![]()
Question 22.
If the matrix
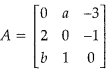
is skew symmetric. Find the values of ‘a and ‘b’. [2]
OR
If
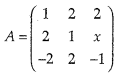
is a matrix satisfying AA’ = 9I, find x.
Answer:
A is a skew symmetric matrix
⇒ A’= – A
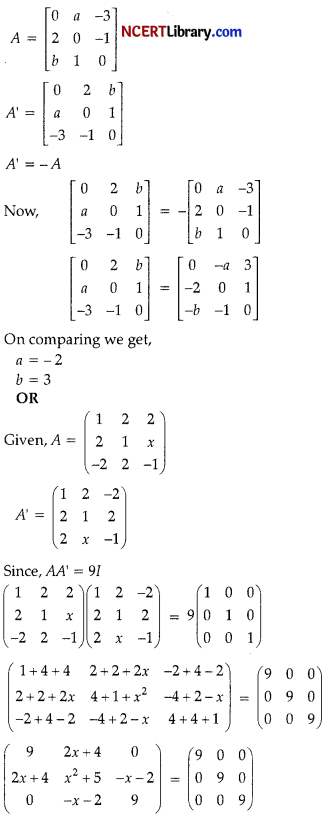
Now, x2 + 5 = 9
x2 = 9 – 5
x2 = 4
x = \(\sqrt{4}\)
x = ± 2
Also,
2x + 4 = 0
2x = – 4
x = – \(\frac { 4 }{ 2 }\)
So, x = – 2
Question 23.
The feasible solution for a LPP is shown in given figure. Let Z = 3x – 4y be the objective function. Find the minimum and maximum value of Z.
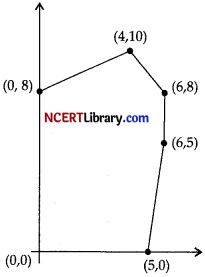
Answer:
| Corner points | Corresponding value of Z = 3x – 4y |
| (0, 0) | 0 |
| (5, 0) | 15 ← Maximum |
| (6, 5) | – 2 |
| (6, 8) | – 14 |
| (4,10) | -28 |
| (0,8) | -32 ← Maximum |
Hence, the minimum of Z occurs at (0, 8) and its minimum value is ( – 32).
And, the maximum of Z occurs at (5, 0) and its maximum value is 15.
Question 24.
What do you understand by useful life and scrap value? [2]
Answer:
The time period in which an asset is expected to be functional and fit for purpose is called useful life. It is generally measured in years. The value of a depreciable asset at the end of its useful life is called scrap value or salvage value or depreciated value.
Question 25.
Assume that the year-end revenues of a business over a three-year period, are mentioned in the following table:
| Year-End | 31-12-2017 | 31-12-2020 |
| Year End Revenue | 9,000 | 13,000 |
Calculate the CAGR of the revenues over the three-years period spanning the mend” of 2017 to the ‘end’t of 2020.
Given’that \(\left(\frac{13}{9}\right)^{\frac{1}{3}}\) = 1.13. [2]
Answer:
The CAGR of the revenues over the three – year period spanning the “end’ of 2017 to the end’ of 2020 is:
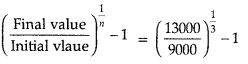
= 1.13 – 1
= 0.13
= 13%
Section – C
All questions are compulsory. In case of internal choice, attempt any one question only
Question 26.
A trust fund has ₹ 35,000 is to be invested in two different types of bonds. The first bond pays 8% interest per annum which will be given to orphanage and second bond pays 10% interest per annum which will be given to an N.G.O. (Cancer Aid Society). Use matrix multiplication, determine how to divide 35,000 among two types of bonds if the trust fund obtains an annual total interest of ₹ 3,200. [3]
OR
Show that the matrix BT AB is symmetric or skew-symmetric accordingly when A is symmetric or skew-symmetric.
Answer:
Let investment in first type of bond be ₹ x.
∴ The investment in second type of bond
= ₹ (35,000 – x)
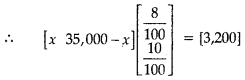
or \(\frac { 8 }{ 100 }\) x + (35,000 – x)\(\frac { 10 }{ 100 }\) = 3,200
or x = ₹ 15,000
Investment in first bond = ₹ 15,000
and Investment in second bond
= ₹ (35,000 – 15,000)
= ₹ 20,000
OR
Case I: Let A be a symmetric mathx. Then AT = A.
Now, (BTAB)T = BTAT(BT)T[By reversal law]
= BTATB [∵(BT)T = B]
or (BTAB)T = BTAB [∵ AT = A]
∴ BT AB is a symmetric matrix.
Case II: Let A be a skew-symmetric matrix. Then,
AT = – A.
Now, (BT AB)T = BTAT(BT)T[By reversal law]
or (BTAB)T = BTATB [∵ (BT)T = B]
or (BTAB)T = BT( – A)B [∵ AT = – A]
or (BTAB)T = BTAB
∴ BT AB is a skew-symmetric matrix.
![]()
Question 27.
Find the maximum value of (\(\frac { 1 }{ x }\))x. [3]
Answer:
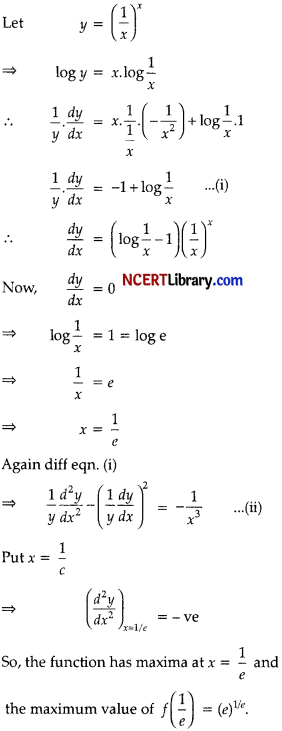
Question 28.
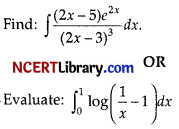
Answer:
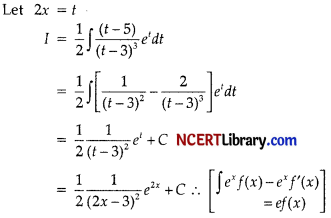
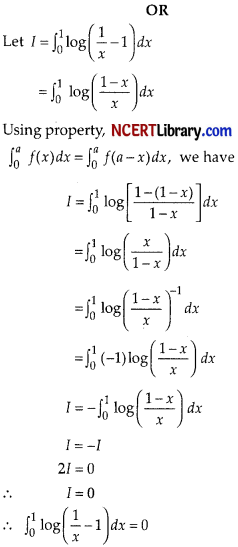
Question 29.
Anna owns a produce truck, invested ₹ 700 in purchasing the truck, some other initial admin related and insurance expenses of ₹ 1500 to get the business going, and has now a day to day expense of ₹ 500/p.m. Consider hypothetically that her everyday profit is ₹ 550/p.m. (ideally, it will be based on sales). At the end of 6 months, Anna takes up her accounts and calculates her rate of return. [3]
Answer:
Total Initial Investment: ₹ 700 + ₹ 1,500 = ₹ 2,200
day to day
Expenses: ₹ 500/month
Total Expenses for 6 months: ₹ 3,000
day to day Returns: ₹ 550/month
Total Returns for 6 months: ₹ 3,300
So, Rate of Return
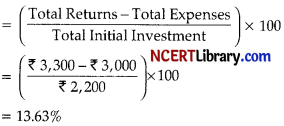
Question 30.
A textile company has raised funds in the form of 5,000 zero-coupon bonds worth ₹ 1,100 each. The company wants to set up a sinking fund for repayment of the bonds, which will be after 7 years. Determine the amount of the periodic contribution if the annualised rate of interest is 6%, and the contribution will be done quarterly.
[Given (1.015)28 = 1.5172]
Answer:
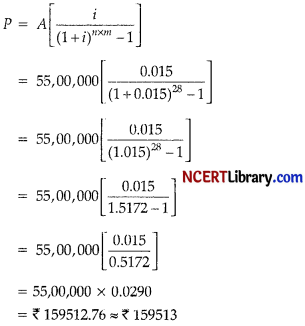
Given, Sinking fund,
A = Par value of bond x No. of bonds
= ₹ 1,100 x 5,000 = ₹ 5,500,000
No. of years, n = 7
No. of payments per year, m = 4
Annualized rate of interest, r = 6%
∴ i = \(\frac { 6 }{ 400 }\) = 0.015
Therefore, the amount of the periodic contribution can be calculated using the above formula as,
Question 31.
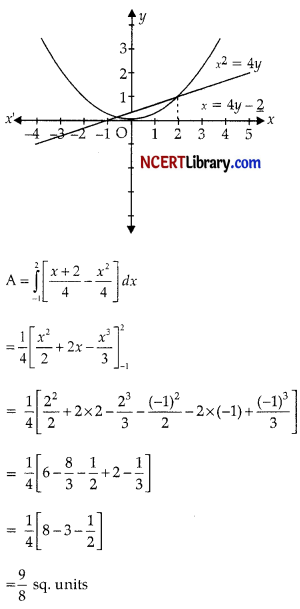
Find area of the region bounded by the curve x2 = 4y and the straight-line x = 4y – 2. [3]
Answer:
x2 = x + 2
x2 – x – 2 = 0
(x – 2)(x + 1) = 0
x = – 1, 2
For x = – 1, and for x = 2, y = 1
Points of intersection are (- 1, \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)) and (2, 1).
Graphs of parabola x2 = 4y and the straight line
x = 4y – 2 are shown in the following figure:
Section D
All questions are compulsory. In case of internal choice, attempt any one question only
Question 32.
Prove that
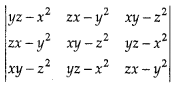
is divisible by (x + y + z), and hence find the quotient. [5]
OR
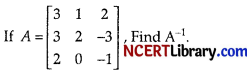
Hence, solve the system of equations:
3x + 3y + 2z = 1
x + 2y = 4
2x – 3y – z = 5
Answer:

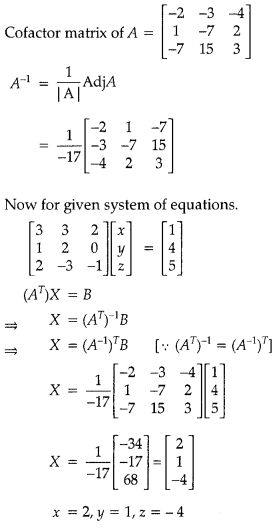
![]()
Question 33.
A farmer has a supply of chemical fertilizer of type A which contains 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and of type B which contains 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After soil test, it is found that atleast 7 kg of nitrogen and same quantity of phosphoric acid is required for a good crop. The fertilizer of type A costs ₹ 5.00 per kg and the type B costs ₹ 8.00 per kg. Using Linear Programming, find how many kilograms of each type of the fertilizer should be bought to meet the requirement and for the cost to be minimum. Find the feasible region in the graph. [5]
Answer:
Let the fertilizer of type A be x kg and type B be y kg
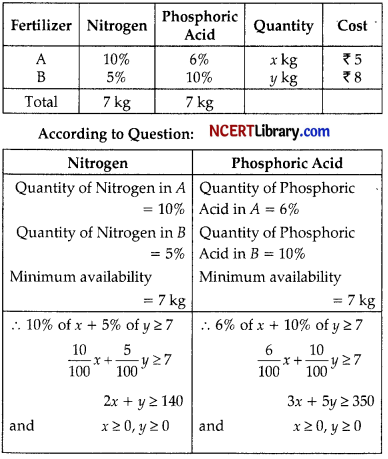
∴ Min. Z = 5x + 8y
Subject to constraints
it 2x + y ≥ 140
3x + 5y > 350
x ≥ O, y ≥ 0
2x + y = 140 ………….(i)
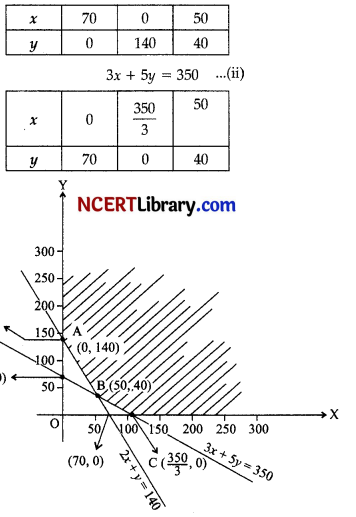
We draw the lines 2x + y = 140 and 6x + y = 70 and obtain the feasible region (unbounded and convex) as shown in figure. Thus, corner points are A(0, 140), B(50, 40), c(\(\frac { 350 }{ 3 }\), o).
The values of Z at these points are given in following table:
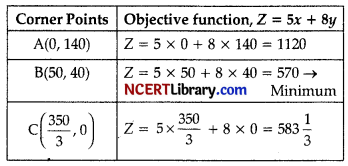
As the feasible area is unbounded, Hence, 500 may
or may not be the minimum value of Z.
For this, we need to graph inequality.
5x + 8y < 570
| x | 114 | 0 | 50 |
| Y | 0 | 71.25 | 40 |
Since, there is no common point between the feasible region and 5x + 8y < 570 Hence, the cost will be minimum, if
Fertilizer of type A used = 50 kg
Fertilizer of type B used = 40 kg
Minimum cost = ₹ 570
Question 34.
A box has 20 pens of which 2 are defective. Calculate the probability that out of 5 pens drawn one by one with replacement, at most 2 are defective. [5]
Answer:
Let X be a random variable that denotes the number of defective pens is a draw of 5 pens.
Then, X can take values 0, 1, 2, 3,4 and 5.
Here, p = probabiLity of getting a defective pen in
a single draw = \(\frac { 2 }{ 20 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\) and q = probability of not
getting a defective pen in a single draw
= 1 – p = 1 – \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 }\)
Clearly, X follows binomial distribution with
parameters n = 5, p = \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\) and q = \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 }\)
∴ P (X = r) = 5Cr ( \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\))r ( \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 }\))5-r
r = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Now, P(getting at most 2 defective pen)
= P (x ≤ 2)
= P (X = 0) + P (X = 1) + (X = 2)
= 5C0 ( \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\))0 ( \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 }\))5 + 5C1 ( \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\)) ( \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 }\))4 + 5C2 ( \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\))2 ( \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 }\))3
= \(\frac{9^3}{10^5}\) [92 + 5 x 9 + 10] = \(\frac { 729 }{ 100000 }\)[81 + 45 + 10]
= \(\frac { 729×139 }{ 100000 }\) = \(\frac { 99144 }{ 100000 }\) = 0.99144
Question 35.
Suppose the demand for the certain product is given by p = – 0.01x2 – 0.1x + 6, where p is the unit price given in rupees and x is the quantity demanded per month given in the units of 1000. The unit market price for the product is ₹4 per unit.
(a) Find the quantity demanded at the given price.
(b) Find the consumer’s surplus if the market price for the product is 4 per unit.
OR
Assume that a spherical raindrop evaporates at a rate proportional to its surface area. If its radius originally in 3 mm and 1 hour later has been reduced to 2 mm, find an expression for the radius of the rain drop at any time.
Answer:
(a) First we find the point of intersection of demand curve and market price for the product i.e., (D, g).
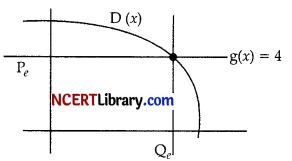
Since, p is the unit price so we put p = 4 in demand
curve, p = – 0.01x2 – 0.1x + 6,
i.e., 4 = – 0.01x2 – 0.1x + 6
0.01x2 + 0.1x – 2 = 0
x2 + 10x – 200 = 0
= (x + 20)(x – 10) = 0
x = 10 (Neglecting x = – 20)
So, (D,g) = (10, 4)
Hence, the quantity demanded at the given price
(Qe,Pe)(1000,4)
(b) Consumer’s surpius is given by
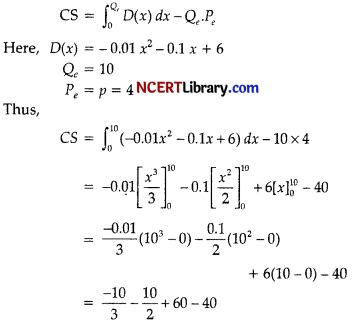
For 1000 units, 11.6667 x 1000 = 11666.7 =11667
OR
Let r(t) denotes the radius of the raindrop after t minutes.
Since, given the radius is decreasing as t increases, the rate of change of r must be negative.
Let V be the volume of the raindrop and S be its surface area
i.e. V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) πr3 and S = 4πr2
Also given, \(\frac { dv }{ dt }\) ∝ S
\(\frac { dv }{ dt }\) = – kS
[∴ as the rate of change of radius with time is negative]
\(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\)π3r2\(\frac { dr }{ dt }\) = – k 4πr2
[∵\(\frac { dv }{ dt }\) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\)π(3r2)]
\(\frac { dr }{ dt }\) = – k ………….(i)
Integrating (i), we get
∫\(\frac { dr }{ dt }\) = – ∫k
∫dr = – ∫k dt
r = -kt + C ……………(ii)
Let at time t = 0, radius is r0
∴ From (ii), r0 = 0 + C = C
Hence, r = – kt + r0 is the required expression.
When t = 0, r0 = 3 mm C= 3
When t = 1hr, r = 3 mm ∴ k = 1
∴ r = – t + 3
Section – E
All questions are compulsory. In case of internal choice, attempt any one question only
CASE STUDY – I
Question 36.
Riya is doing her Mathematics homework given in the class. Her teacher gave a problem related to the topic ‘Boats and Streams’. She is very confused in this topic, the question given by the teacher is “A man can row 5km/h in still water. If in a river running at 2 km an hour, it takes him 40 minutes to row to a place and return back”.

(i) What is the downstream speed? [1]
(ii) What is the upstream speed? [1]
(iii) A man rows downstream 30 km and upstream 12 km. If he takes 4 hours to cover each distance, Lhen find the speed of the stream. [2]
OR
A boat travels at 9 kmjh along the stream and 6 km/h against the stream, Find the speed of the boat in still water.
Answer:
(i) Speed of the man in still water = 5km/h
and speed of the river = 2 km/h
Downstream speed = Speed of man in still water + Speed of the river
= 5 + 2 = 7km/h
(ii) Upstream speed
= Speed of man in still water – Speed of the river
= 5 – 2 = 3km/h
(iii) Downstream speed Distance travelled downstream / Time taken
= \(\frac { 30 }{ 4 }\) Km/h
Upstream speed = Distance travelled in upstream /Time taken
\(\frac { 12 }{ 4 }\)
Speed of the stream = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (Downstream speed – upstream speed)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ( \(\frac { 30 }{ 4 }\) – \(\frac { 12 }{ 4 }\))
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (\(\frac { 18 }{ 4 }\))
= 2.25 km/h
OR
Downstream speed of the boat = 9km/h
Upstream speed of the boat = 6 km/h
Speed of the boat in still water = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (Downstream speed + Upstream speed)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ( 9 + 6)
= 7.5 km/h
CASE STUDY – II
![]()
Question 37.
Mr. Rama Roy a owner of a factory lives in Karnataka. In his factory, he manufactures razor blades. There is a smali
chance that \(\frac { 1 }{ 500 }\) for any blade to be defective. The blades are in the packets of 10.
(i) Find the probability that packet contain no defective blade. [1]
(ii) The probability that packet contain one defective blade. [1]
(iii) Find the probability that packet contain two detective blade, when it is given that e-0.02 = 0.9802.
Also, find the approximate number of packets containing no defective blade, when there are 10000 packets in a consignment. (Use e-0.02 = 0.9802) [2]
OR
Find the approximate number of packets containing one defective blade, when there are 20,000 packets in the consignment. (Use e-0.02 = 0.9802)
Answer:
(1) Here given N 1000, n = 10, p = \(\frac { 1 }{ 500 }\)= 0.002
m = np = 10 x 0.0002
m = 0.02
P(No defective blade) = P(X = 0)
= e-0.02 (0.002)2 = e-0.02
(ii) P(one defective blade) = P(X = 1)
\(\frac{e^{-0.02}(0.02)^1}{1 !}\)
= 0.02e-0.02
(iii) P(two defective blade) = P(X = 2)
\(\frac{e^{-0.02}(0.02)^2}{2 !}\)
\(\frac{0.9802 \times 0.0004}{2}\)
= 0.000196
= 0.0002
P (no defective blade) = e-0.02
= 0.9802
So, the approximate number of packets containing no defective blade
= 10,000 X 0.9802 = 9802
OR
P(one defective blade)
= O.02e-0.02
= 0.02 x 0.9802
= 0.0196
So, the approximate nunther of packets containing defective blade = 20,000 x 0.0196
= 392.
CASE STUDY – III
Question 38.
Today in class Mr. Agarwal is teaching the Method of Least Squares to measure the trend in time series. After explaining the method, he had taken an example which is as follows:
Given below are the data relating to the sales of a product in a district.
| Year | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
| Sales | 6.7 | 5.3 | 4.3 | 6.1 | 5.6 | 7.9 | 5.8 | 6.1 |
(i) If the straight line is yt = a + bx, then find the value of ‘a’. [2]
OR
If the straight line is yt = a + bx, then find the value of ‘b’.
(ii) Write the trend equation. [1]
(iii) Find the trend value for year 2016. [1]
Answer:
(i) ∑y = 6.7 + 5.3 + 4.3 + 6.1 + 5.6 + 7.9 + 5.8 + 6.1
a = \(\frac { ∑y }{ n }\)
Here, n = 8 and ∑y = 47.8
So, a = \(\frac { 47.8 }{ 8 }\)
= 5.975 2
OR
∑xy = – 46.9 – 26.5 – 12.9 – 6.1 + 5.6 + 23.7 + 29.0 + 42.7
= 8.6
= \(\frac{\Sigma x y}{\Sigma x^2}\)
Here, n = 8 and ∑xv = 8.6 and ∑x2 = 168
So, b = \(\frac { 8.6 }{ 168 }\)
= 0.051
(ii) Since, a = 5.975
and b = 0.051
Thus, trend equation is given by
yt = 5.975 + 0.051 x
(iii) For year 2016, x = – 5
yt = 5.975 + 0.051 (- 5)
t = 5.975 – 0.255
= 5.720