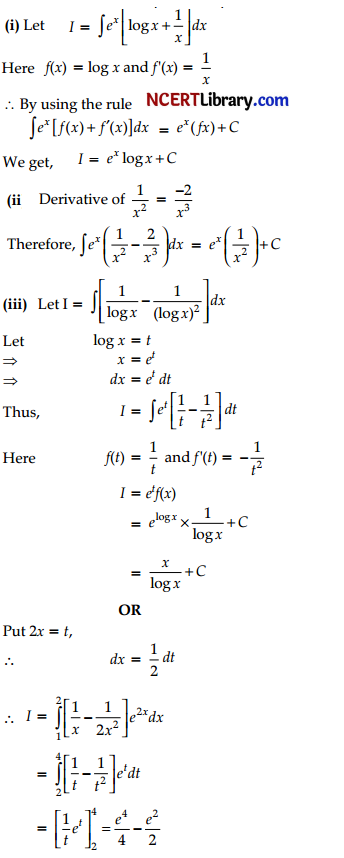Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Applied Mathematics Set 6 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Applied Mathematics Set 6 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains five sections A, B, C, D and E. Each section is compulsory.
- Section – A carries 20 marks weightage, Section – B carries 10 marks weightage, Section – C carries 18 marks weightage, Section – D carries 20 marks weightage and Section – E carries 3 case-based with total weightage of 12 marks.
- Section -A: It comprises of 20 MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section – B: It comprises of 5 VSA type questions of 2 marks each.
- Section – C: It comprises of 6 SA type of questions of 3 marks each.
- Section – D: It comprises of 4 LA type of questions of 5 marks each.
- Section – E: It has 3 case studies. Each case study comprises of 3 case-based questions, where 2 VSA type questions are of 1 mark each and 1 SA type question is of 2 marks. Internal choice is provided in 2 marks question in each case-study.
- Internal choice is provided in 2 questions in Section – B, 2 questions in Section – C, 2 questions in Section – D. You have to attempt only one of the alternatives in all such questions.
Section – A
All questions are compulsory. No internal choice is provided in this section
Question 1.
The compounding if occurs more than once in an annual period then the rate used is ………. [1]
(A) Effective annual rate
(B) Fractional annual rate
(C) Marginal annual rate
(D) Nommai annual rate
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: The compounding if occurs more than once in an annual period then the rate used is effective annual rate.
Question 2.
In the formula S = P + iP, the S is classified as: [1]
(A) Interest Amount
(B) Compound Amount
(C) Discount Amount
(D) Specified Amount
Answer:
(B) Compound Amount
Question 3.
The present value of the cash inflows is ₹ 70,000 and present value of cash outflows is 50,000, then the net present value is: [1]
(A) ₹ 10,000
(B) ₹ – 100000
(C) ₹ 20,000
(D) ₹ – 20,000
Answer:
(C) ₹ 20,000
Explanation:
Net present value = cash outflows – cash inflows
= ₹ 70,000 – ₹ 50,000
= ₹ 20,000
![]()
Question 4.
In calculating interest, any unit of time is classified as: [1]
(A) per unit time
(B) per period
(C) per investment
(D) per rate interest
Answer:
(B) per period
Explanation: In calculating interest, any unit of time is considered as per period.
Question 5.
Prosperity, Recession, and depression in a business is an example of: [1]
(A) Irregular Trend
(B) Secular Trend
(C) Cyclical Trend
(D) Seasonal Trend
Answer:
(C) Cyclical Trend
Explanation: There are 4 phases through which trade cycles are passed. They are prosperity, recession, depression, and recovery. In economic terms, these 4 stages are called economic fluctuations.
Question 6.
If A is a square matrix of order 3 x 3 such that |A| = 4, then |3A| is equal to: [1]
(A) 27
(B) 81
(C) 108
(D) 256
Answer:
(C) 108
Explanation: |3A| = (3)3 |A|
[∵ order of matrix = 3]
= 27 X 4 [Given |A| = 4]
= 108
Question 7.
If A2 – A + I = 0, then the inverse of matrix A is: [1]
(A) A2
(B) A + 1
(C) l – A
(D) A – l
Answer:
(C) l – A
Explanation: We have,
A2 – A + I = 0
⇒ A-1(A2 – A + I) = A-1(0)
⇒ A-1A2 – A-1A + A-1 I = 0
⇒ A – I + A-1 I = 0
⇒ A-1 = I – A
Question 8.
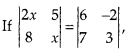
then the value of x is: [1]
(A) 3
(B) ±3
(C) ±6
(D) 6
Answer:
(C) ±6
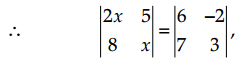
⇒ 2x2 – 40 = 18 + 14
⇒ 2x2 = 32 + 40
⇒ x2 = \(\frac { 72 }{ 2 }\) = 36
∴ x = ± 6
![]()
Question 9.
Two pipes A and B can fill a cistern in 8 hours and 12 hours respectively. The pipes when opened simultaneously takes 12 minutes more to fill the cistern due to leakage. Once the cistern is full, it will get emptied due to leakage in ………… [1]
(A) 5 hours
(B) 20 hours
(C) 60 hours
(D) 120 hours
Answer:
(D) 120 hours
Explanation: Portion of cistern filled by both pipes in 1 hour
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 8 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 12 }\)
= \(\frac { 5 }{ 24 }\)
Time taken by both pipes to fill the cistern
= 4 h 48 minutes
Time taken to fill tank due to leakage
= 5h
Cistern empty by leakage in 1 h = \(\frac { 5 }{ 24 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 120 }\)
Time taken by leakage to empty the cistern
= 120 h
Question 10.
If p > q and r < 0, then which of the following is true? [1]
(A) pr < qr
(B) p – r < q – r
(C) p + r < q + r
(D) Noneof these
Answer:
(A) pr < qr Explanation: Since, given p > q and r < 0 then pr < qr (inequality sign is reversed when multiplied by a negative integer)
Question 11.
A dishonest milkman professes to sell his milk at cost price but he mixes it with water and thereby gains 25%. The percentage of water in the mixture is: [1]
(A) 4%
(B) 6%
(C) 20%
(D) 25%
Answer:
(C) 20%
Explanation: Let C.P. of 1 litre milk be ₹ 1
Then, S.P. of 1 litre of mixture = ₹ 1,
Gain = 25%
C.P. of 1 litre mixture = ₹ ( \(\frac { 100 }{ 125 }\) x 1) =
By the rule of alligation, we have:
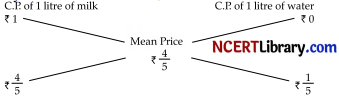
∴ Ratio of milk to water = \(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) = 4 : 1
Hence, percentage of water in the mixture = (\(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) x 1oo)% = 20%.
![]()
Question 12.
A team played 40 games in a season and won in 24 of them. What percent of games played did the team win? [1]
(A) 70%
(B) 40%
(C) 60%
(D) 35%
Answer:
(C) 60%
Explanation: Number of games played = 40
Number of games won = 24
Percentage of games played = (\(\frac { 24 }{ 40 }\) x 100)
= 60%
Question 13.
A variable that can assume any value between two given points is called ……….. [1]
(A) Continuous Random Variable
(B) Discrete Random Variable
(C) Irregular Random Variable
(D) Uncertain Random Variable
Answer:
(A) Continuous Random Variable
Explanation: This is the definition of a continuous random variable.
Question 14.
For a Poisson distribution with mean λ,
![]()
is equai to. [1]
(A) – 1
(B) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(D) 1
Answer:
(D) 1
![]()
= 1
Question 15.
The total aiea under the normal distributed cune above the base line i.e., [1]
![]()
(A) 0
(B) 0.5
(C) 0.75
(D) 1
Answer:
(D) 1
Explanation: The total area under the normal distribution curve above the base line is 1.
Question 16.
The function y – \(\frac { 1 }{ x }\) is strictly decreasing In the interval(s) [1]
(A) (0, ∞)
(B) ( – ∞,0)
(C)(- ∞,0)aswellas(0,∞)
(D) R
Answer:
(C)(- ∞,0)aswellas(0,∞)
y = \(\frac { 1 }{ x }\)
\(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = – \(-\frac{1}{x^2}\)| < 0 [x ≠0]
for ( – ∞,0) and (0, ∞)
Question 17.
Find the second derivative of x3 – 5x2 + x = 0 [1]
(A) 10x – 5
(B) 6x – 10
(C) 3x + 10
(D) 3x2 – 5x
Answer:
(B) 6x – 10
Explanation:
Let f(x) = x3 – 5x2 + x
So, f’(x) = 3x2 – 10x + 1
and f”(x) = 6x – 10
![]()
Question 18.
The order and degree (If defined) of differential equation [1]
![]()
(A) 1, 2
(B) 2, 1
(C) 1, 1
(D) 4, 2
Answer:
(B) 2, 1
Explanation: The highest order derivative present is \(\frac{d^2 S}{d t^2}\) and it is raised to power 1. So, its order is 2 and degree is 1.
DIRECTION: For questions 19 and 20, two statements are given – one labelled
Assertion(A) and the other Labelled
Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C) and (D) as given below:
(A) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(B) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is faLse.
(D) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Question 19.
Assertion (A): If A and B are invertible matrices of order 3, |A| = 2 and |(AB)-1| = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\), then find |B| = – 3.
Reason (A): If A and B are invertible matrices of order 3, |A| = 2 and |(AB)-1| = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\), then find |B| = 3. [1]
Answer:
Option (C) is correct.
Explanation:
\(\frac { 1 }{ |AB| }\) = – \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ |A||B| }\) = – \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
⇒|B| = – 3
Question 20.
Assertion (A): The differential equation of the family of lines passing through the origin is: [1]
x \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) – y = 0
Reason (A): If the equation of the family of curves is given then its differential equation is obtained by eliminating arbitrary constants occurring in equation with the help of equation of the curve and the equations obtained by differentiating the equation of the curve.
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: General equation of family of lines passing through origin is
y = mx
m = \(\frac { y }{ x }\)
\(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = m
\(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = \(\frac { y }{ x }\)
x \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) – y = 0
Section – B
All questions are compulsory. In case of internal choice, attempt any one question only
Question 21.
Wholesaler in ceiling fans claints that only 8% of the ceiling fans supplied by him are defective. A random sample of 1200 ceiling fans contained 56 defective ceiling fans. Calculate the standard error concerning good ceiling fans. [2]
Answer:
Sample size = 1200
No. of defective ceiling fans = 56
Sample proportion, P = \(\frac { 56 }{ 1200 }\) = 0.46
Population proportion, P = probability of defective
ceiling fans = 8% = 0.08
Q = 1 – P
= 1 – 0.46 = 0.54
The S.E. for sample proportion is given by S.E.
![]()
= \(\sqrt{0.000207}\)
= 0.0144
Question 22.
Write the value of the determinant: [2]

OR
Prove that the diagonal elements of a skew symmetric matrix are all zero.
Answer:
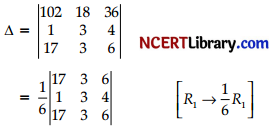
= 0 ( ∵ R1 and R3 are identical)
OR
LetA be a skew-symmetric matrix. Then by definition
A’= – A
or the (i, j)th element of A’ = the (i, j)th element of
(-A)
or the (j, i)th element of A’ = – the (i, j)th element of A
For the diagonal elements i = j op the (i, j)th element
of A = – the (i, j)th element of A
or the (i, j)th element of A = O
Hence the diagonal elements are all zero.
![]()
Question 23.
The random variable X has a probability distribution P(X) of the following form, where k is some number: [2]
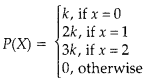
(i) Find the value of k
(ii) Find P(x < 2)
Answer:
Here,
(i) Since P(0) + P(1) + P(2) = 1, we have
k + 2k + 3k = 1
i.e., 6k = 1, or k = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
(ii) P(X < 2) = P(O) + P(1)
= k + 2k = 3k = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
Question 24.
What causes secular trend? [2]
Answer:
The effect of long term causes is reflected in the tendency of a behaviour, to move in an upward or downward direction, termed as Trend or Secular Trend.
The secular trends could reflect environmental improvements, specifically changes in health practice and living conditions leading to improvements in mortality rates and life expectancy. These factors are interrelated with those concerning family size.
Question 25.
The total cost function (in thousands) for manufacturing x manipulators per year is given [2]
C(x) = 375 + 25x – 0.25x2 0 ≤ x ≤ 50
(a) Use the marginai cost function to approximate the cost of producing the 31 manipulator.
(b) Use the total cost function to find the exact cost of producing the 315t manipulator. 2
Answer:
(a) The marginal cost is C(x) = 25 – 0.5x.
Thus, C’(30) = 25 – 03(30) = 1o.
The cost of producing of the 31st manipulator is approximately ₹ 10,000.
(b) The exact cost of producing the 31st manipulator is
C(31) – C(30) = 909. 75 – 900 = 9.75, i.e. ₹ 9,750.
The marginal cost of ₹ 10,000 per manipulator is a close approximation to his exact cost.
Section – C
All questions are compulsory. In case of internal choice, attempt any one question only
Question 26.
Solve the following LPP graphically: [3]
Maximize Z = 1000x + 600y
Subject to the constraints:
x + y ≤ 200
x ≥ 20
y – 4x ≥ 0
x, y ≥ 0
Answer:
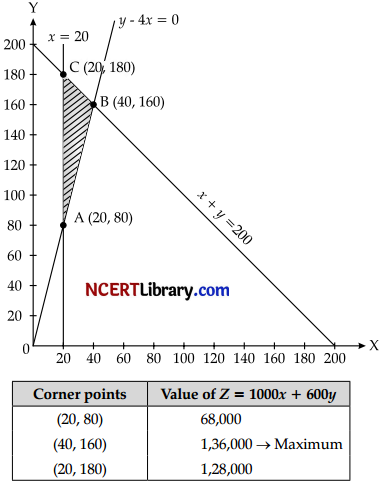
∴ Maximum value, Z = 1,36,000
at x = 40,y = 160
![]()
Question 27.
Madhu exchanged her old car valued at ₹ 1,50,000 with a new one priced at ₹ 6,50,000. She paid ₹ x as down payment and the balance in 20 monthly equal instalments of ₹ 21,000 each. The rate of interest offered to her is 9% pa. Find the value of x. [3]
[Gven that: (1.0075)1 = 0.86118985]
Answer:
Cash down price = ₹ (6,50,000 – 1,50,000)
= ₹ 5,00,000
Now, Cash down price = down payment (x) + present value (PV) of 21,000 for 20 months at 9% compounded monthly 1/2

= ₹ 388,668.42
∴ Down payment (x) = Cash down price – PV
= 5,00,000 – 388,668.42
= ₹ 111,331.58
Question 28.
Fit a straight line trend by the method of least square to the following data on sales (₹ in lakhs) for the period 2011 – 2018.[3]
| years | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| Sales(₹lakhs) | 76 | 80 | 130 | 144 | 138 | 120 | 174 | 190 |
OR
Country A has an average farm size of 191 acres, while Country B has an average farm size of 199 acres. Assume the data were attained from two samples with standard deviations of 38 and 12 acres and sample sizes of 8 and 10, respectively. is it possible to infer that the average size of the farms in the two countries is different at a = 0.05? Assume that the populations are normally distributed. [3]
Answer:
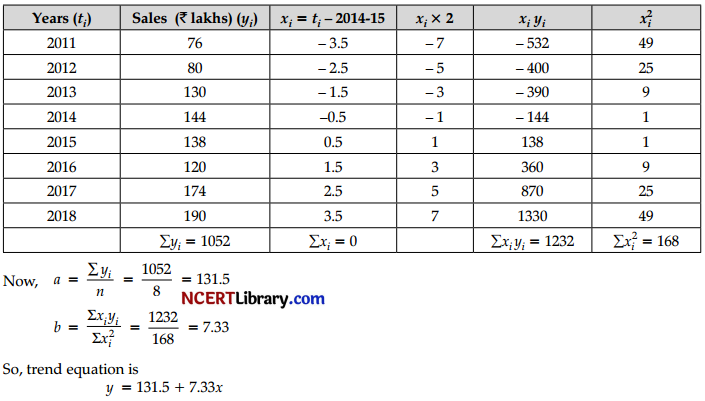
OR
Step 1: Hypothesis H0: = μ1 = μ2
and H1 : μ1 ≠ μ2 (claim)
Step 2: Find the critical values. The test is two-tailed
and α = 0.05, also variances are unequal, the degrees
of freedom are the smaller of n1 – 1 or n2 – 1.
In this case, the degrees of freedom are 8 – 1 = 7. Hence,
from t-table F, the critical values are – 2.365 + 2.365.
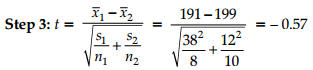
Step 4: Make the decision.
Do not reject the null hypothesis, since – 0.57 > – 2.365.
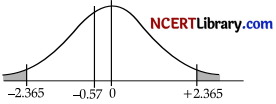
Step 5: Make conclusion, There is not enough evidence to support the claim that the average size of the farms is different.
![]()
Question 29.
It is claimed that the average weight of a bag of biscuits is 250 grams with the standard deviation 20.5 grams. Would you agree lo this claim if random sample of 50 bags of biscuits showed an average weight of 240 grams, using a 0.05 level of significance? [3]
Answer:
Let the null hypothesis be H0: μ = 250.
Let the alternative hypothesis be H1 : μ ≠ 250.
Assume that the population standard deviation is
σ = 20.5.
The population standard deviation is known and the
sample size n is large (n ≥ 30).
Hence, the test statistic is

The test is two tailed (because H1 contains inequality ≠) and the critical values are
Z-0.025 = – 1.96 and Z0.025 = 1.96.
Since z ← z0.025, i.e. the z lies to the left of the critical value, we reject the null hypothesis.
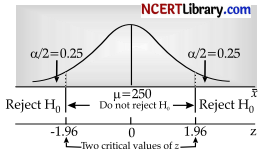
We would not agree with a claim, the true average weight of a bag of biscuits is not 250 grams.
Question 30.
Find the remainder when 281 is divided by 17.
OR
If n! denotes the product of the integers 1 through n, what is the remainder when (1! + 2! + 3! + 4! + 5! + 6! + …) is divided by 9? [3]
Answer:
281≡x(mod 17)
We know that,
23≡8(mod 17)
29 ≡(8)3 (mod 17)
29≡512(mod 17)
29 ≡2(mod 17)
(29)9 ≡ (2)81 (m0d 17)
281 ≡ 512 (mod 17)
281 ≡ 2(mod 17)
So, when 281 is divided by 17,remainder is 2.
OR
We know that k! ≡ 0 (mod 9) for all k ≥ 6.
Thus, we need to find
(1! +2! + 3! + 4! +5!)(mod 9).
1! ≡ 1 (mod 9)
2! ≡ 2 (mod 9)
3! ≡ 6 (mod 9)
4! ≡ 24 ≡ 6(mod 9)
5! ≡ 5 6 ≡ 30 ≡ 3(mod 9)
Thus,
(1! + 2! + 3! + 4! + 5!) ≡ 1 + 2 + 6 + 6 + 3
≡ 18 ≡ 0 (mod 9)
So, the remainder is 0.
![]()
Question 31.
A biased die is such that P(4) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\) and other scores are equally likely. The die is tossed twice. If X is the number of fours obtained’, find the variance of X.
OR
It is known from the past experience that the number of telephone calls made daily in a certain community between 3 p.m. and 4 p.m. has a mean of 352 and a standard deviation of 31. What percentage of the time will there be more than 400 telephone calls made in the community between 3 pm to 4 pm? [Use : P(0 ≤ Z ≤ 1.5) = 0.4394] [3]
Answer:
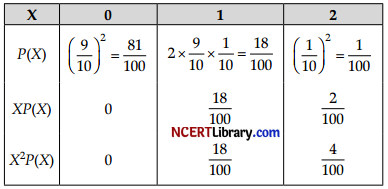
Variance = ∑X2P(X) – [∑XP(X)]2
= \(\frac { 22 }{ 100 }\) – (\(\frac { 22 }{ 100 }\))2
= \(\frac { 18 }{ 100 }\) = 0.18
OR
Let Z= \(\frac { x – μ }{ σ }\) = \(\frac { x – 352 }{ 31 }\)
Now, when x = 400,
Z = \(\frac { 400 – 352 }{ 31 }\)
Z = \(\frac { 48 }{ 31 }\)
Z = 1.55
Probability (more than 400 telephone call are made)
= p(x > 400) = p(z > 1.55)
= p(z ≥ 0) – p(0 ≤ z ≤ 1.55)
= 5 – 4394
= .0606
(given p(0 ≤ z ≤ 1.55) = .4394)
= .0606
Required % = .0606 X 100
= 6.06%
Section – D
All questions are compulsory. In case of internal choice, attempt any one question only
Question 32.
(i) At what rate of interest will the present value of a perpetuity of ₹ 300 payable at the end of each quarter be ₹ 24000?
(ii) What sum of money invested now could establish a scholarship of ₹ 5000 which is to be awarded at the end of every year forever, if money is worth 8% per annum.
(iii) Rehaan invested ₹ 7000 in a Term Deposit Scheme that fetches interest 7.5% per annum compounded semi
annually. What will be the interest after 3 years? Given (1.0375)6 = 1.2472 A [5]
Answer:
(i) Let the rate of investment be r% per annum, the
i = \(\frac { r }{ 4 x 100 }\) = \(\frac { r }{ 400 }\)
Given, perpetuity, ₹ = 300
and payment, ₹ = 24000
Using, P = \(\frac { R }{ i }\)
⇒ i = \(\frac { R }{ P }\)
⇒ \(\frac { r }{ 400 }\) = \(\frac { 300 }{ 2400 }\)
⇒ r = \(\frac { 300 x 400 }{ 2400 }\) = 5%
Hence, rate of interest = 5% per annum.
(ii) It is a flat perpetuity, so Present value of perpetuity

= \(\frac{\frac{5000}{8}}{\frac{8}{100}}\)
= \(\frac { 5000 x 100 }{ 8 }\)
= ₹ 62500
(iii) We know that, Compound interest
I = P[(1 + i)n – 1]
i = 7.5% p.a.
= 0.075 p.a.
= 0.075 x \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) per six months
= 0.0375 per six months
I = 7000[(1 + 0.0375)6 – 1]
= 7000[(1.0375)6 – 1]
= 7000[1.2472 – 1]
= 7000 x 0.2472
= ₹ 1730.4
Question 33.
A wire of length 50 m is cut into two pieces. One piece of the wire is bent in the shape of a square and the other in the shape of a cirde. What should be the length of each piece so that the combined area of the two is minimum? [5]
Answer:
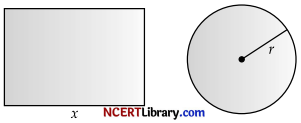
Length of wire = 50 m (Given)
Let length of one piece for shape of square = x m
∴ Length of other piece for shape of cirde
= (50 – x) m
Now perimeter of square = 4 a = x
a = \(\frac { x }{ 4 }\)
and ciicumference of circle = 2πr = 50 – x
r = \(\frac { 50 – x }{ 2π }\)
Combined Area = a2 + πr2
= \(\frac{x^2}{16}\) + π . (\(\frac { 50 – x }{ 2π }\))2
= \(\frac{x^2}{16}\) + π . (\(\frac { (50 – x)^2 }{ 4π^2 }\))
A = \(\frac{x^2}{16}\) + π . (\(\frac { (50 – x)^2 }{ 4π }\))
Differentiating w.r.t.x, we get
\(\frac { dA }{ dx }\) = \(\frac { 2x }{ 16 }\) + \(\frac { 2(50 – x)(-1) }{ 4π }\)
= \(\frac { x }{ 8 }\) + \(\frac { (x – 50) }{ 2π }\)
= \(\frac { πx + 4x – 200 }{ 8π }\)
= \(\frac { x (4 + π) – 200 }{ 8π }\)
For maximum and minimum value of A, \(\frac { dA }{ dx }\) = 0
∴ x(4 + π) – 200 = 0
x = \(\frac { 200 }{ 4 + π }\)
At x = \(\frac { 200 }{ 4 + π }\), \(\frac { d^2A }{ dx^2 }\) > 0
A is minimum at \(\frac { 200 }{ 4 + π }\)
∴ Length of square wire, x = \(\frac { 200 }{ 4 + π }\) m
and lengh of circle wire = 50 – x
= 50 – x
= 50 – \(\frac { 200 }{ 4 + π }\)
= \(\frac { 50π }{ 4 + π }\)m
![]()
Question 34.
Two cards are drawn simultaneously (without replacement) from a well-shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the mean and variance of the number of red cards. [5]
Answer:
Number of red cards = 26
Let X be a random variable which can take values 0, 1,2, where X is the no. of red cards selected
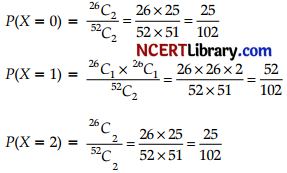
Probability distribution of random variable X is
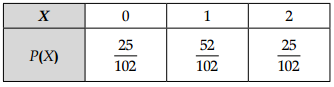
Mean = ∑xP(X) = \(\frac { 52 + 50 }{ 102 }\) = 1
Variance ∑x2P(X) – {xP(X)}2
= \(\frac { 152 }{ 102 }\) – 1
= \(\frac { 50 }{ 102 }\) or \(\frac { 52 }{ 51 }\)
Question 35.
Two tailors P and Q earn ₹ 150 and ₹ 200 per day respectively. P can stitch 6 shirts and 4 trousers a day, while Q can
stitch 10 shirts añd 4 trousers per day. How many days should each work to produce at least 60 shirts and 32 trousers at
minimum labdur cost? [5]
Answer:
Iet the tailor P work for x days and the tailor Q work for y days respectively.
Here, the problem can be formulated as an L.PP as
follows:
Minimize Z = 150x + 200y
Subject to the constraints:
6x + 10y ≥ 60
or 3x + 5y ≥ 30
4x+4y ≥ 32
or x + y ≥ 8 …………..(ii)
and x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 …………..(iii)
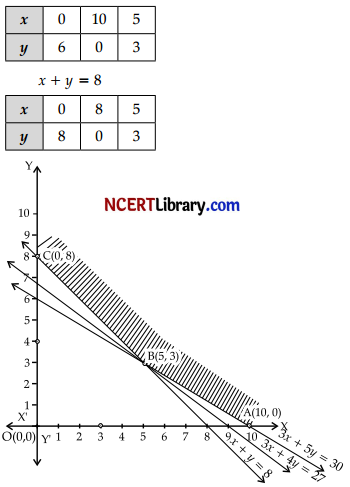
The shaded region in the diagram represent the feasible region.
The corner points are
A(10, 0), B(5, 3) and C(0, 8)
At the corner point the value of Z = 150x + 200y
At A (10, 0) Z = 1500
At B (5,3) Z = 150 x 5 + 200 x 3
= 750 + 600 = 1350
At C (0,8) Z = 1600
As the feasible region is unbounded, we draw the graph of the half-plane.
150x + 200y < 1350
3x + 4 < 27
There is no point common with the feasible region, therefore, Z has minimum value.
Minimum value of Z is ₹ 1350 and it occurs at the point B(5, 3).
Hence, the labour cost is ₹ 1350 when P works for 5 days and Q works for 3 days.
Section – E
All questions are compulsory. In case of internal choice, attempt any one question only
CASE STUDY-I
Question 36.
You may never have heard of modular arithmetic, but you use it every day without the slightest difficulty. In this system, numbers wrap around when they reach a certain size called the modulus; it is the arithmetic of remainders. When reckoning hours, we count up to 12 and start again from one. Thus, four hours after 9 o’clock it is 1 o’clock. Numbers that differ by a multiple of the modulus 12 are said to be congruent modulo 12.
A similar situation arises for the days of the week, which are computed modulo seven. Suppose today is Thursday. What weekday will it be 1,000 days from today? We don’t have to count through the thousand days, just calculate the remainder when 1,000 is divided by seven, which is six. It is much the same for other time measurements. With 52 weeks in a year, the week number is reset to I at the beginning of each year, so it is confined to the range 1 to 52. Likewise, for the months, we use modulo 12 arithmetic.
(i) Assume it is 18:00 hours. What time will it be 59 hours from now ? [1]
(ii) What is the time 15 hours before ii p.m. ? [1]
(iii) Which month is it 721 months from now if this month is November? [2]
OR
Which day after 110 days if today is Friday?
Answer:
(i) Here, we use the 24 hour dock.
i.e., (18 + 59) (mod 12)
= 77 (mod 12)
= 5
So, time will 5:00 hours.
(ii) 15 = 11 – x(mod 12)
(we take (mode 12) in case of docki
15 – 11 + x = 12n for some integern
4+ x = 12n
4 + x is a multiple of 12.
Therefore, the least positive value of x must be 8.
Since, 4 + 8 = 12 is a multiple of 12.
Hence, the time 15 hours before 11 p.m. is 8 a.m.
(iii) Months wrap around after 12 months. We have 721 mod 12 = 1.
Since, December is one month after November,
months from now, it will be December.
OR
The days of the week wrap around after seven days.
So, 110 mod 7 = 5 days
Thus, 110 days after Friday is the same day of the
week as 5 days after Friday, i.e., Wednesday.
CASE STUDY – II
![]()
Question 37.
In a city there are two factories A and B. Each factory produces sports clothes for boys and girls. There are three
types of clothes produced in both the factories type I, type II and type III. For boys the number of units of types I, II and III respectively are 80, 70 and 65 in factory A and 85, 65 and 72 are in factory B. For girls the number of units of types I, II and III respectively are 80, 75, 90 in factory A and 50, 55, 80 are in factory B.

(i) Write the matrices P and Q, if P represents the matrix of number of units of each type produced by factory A for both boys and girls. [1]
(ii) Write the matrix Q, if Q represents the matrix of number of units of each type produced by factory B for both boys and girls. [1]
(iii) Find the total production of sports clothes for boys. [2]
OR
Find the total production of sports clothes for girls
Answer:
(i) In factory A, number of units of type I, II and III for boys are 80, 70, 65 respectively and for girls number of units of type I, II and III are 80, 75,90 respectively.
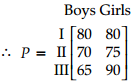
(ii) In factory B, number of units of type I, II and III for boys are 85, 65, 72 respectively and for girls number of units of type I, II and III are 50, 55, 80 respectively.
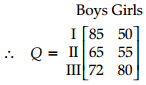
(iii) Let matrix X represent the number of units of each type produced by factory A for boys and matrix Y represents the number of units of each type produced by factory B for boys.
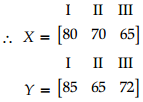
Now, total production of sports clothes of each type for boys = X + Y
= [80 70 65] + [85 65 72]
= [165 135 137]
OR
For girls, let matrix S represents the number of units of each type produced by factory A and matrix T represents the number of units of each type produced by factory B.
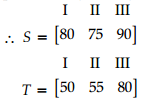
Now, required matrix = S + T
= [80 75 90] + [50 55 80]
= [130 130 170]
CASE STUDY – III
Question 38.
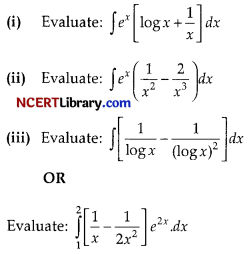
Rishi and Nifish were discussing integration, in there discussion following points were discussed. In question like ∫ [f(x) + f'(x)]dx we should result exf(x) + C
If we have irrational terms in integration question, then we should try doing rationalising these terms.

Answer: