Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Accountancy with Solutions Set 2 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Accountancy Set 2 with Solutions
Time: 2 Hrs.
Max. Marks: 40
General Instructions :
- This question paper contains 34 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper is divided into two parts. Part A and Part B.
- Part- A is compulsory for all candidates.
- Part- B has two option i.e. (i) Analysis of Financial Statements and (ii) Computerised Accounting. Students must attempt only one of the given options.
- Question 1 to 16 and 27 to 30 carries 1 mark each.
- Questions 17 to 20. 31 and 32 carries 3 marks each.
- Questions 21, 22 and 33 carries 4 marks each.
- Questions 23 to 26 and 34 carries 6 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 7 questions of one mark, and 2 questions of three marks. 1 question of four marks and 2 questions of six marks.
Part – A
(Accounting for Partnership Firms and Companies)
Question 1.
Ram and Shyam are sharing profit and losses in the ratio of 4: 1. Ajay is admitted as a new partner in \(\frac {1}{3}\) rd share of profit for which he pays ₹3,00,000 as goodwill if Ram and Shyam agree to share future
profits equally. The amount of goodwill to be credited to Ram is:
(a) ₹3,00,000
(b) ₹9,00,000
(c) ₹4,80,000
Answer:
(d) ₹4,20,000
Explanation:
Working Notes:
Calculate New Ratio Ajay’s share = \(\frac {1}{3}\)
\(1-\frac{1}{3}=\frac{2}{3}\)
Ram’s share = \(\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{1}{2}=\frac{1}{3}\)
Shyam = \(\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{1}{2}=\frac{1}{3}\)
New Ratio =1:1:1
Sacrificing Ratio = Old Ratio – New Ratio
Ram’s Sacrificing Ratio = \(\frac{4}{5}-\frac{1}{3}=\frac{12-5}{15}=\frac{7}{15}\)
Shyam Sacrificing = \(\frac{1}{5}-\frac{1}{3}=\frac{3-5}{15}=\frac{-2}{15} \text { [Gain] }\)
Total Goodwill of firm 3,00,000 × \(\frac{3}{1}=9,00,000\)
Ram’s Share in Goodwill = 9,00,000 × \(\frac{7}{15}=₹ 4,20,000\)
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Goodwill belong to be category of Intangible assets such as patents, trade mark, copyrights etc.
Reason(R): Goodwill cannot be seen or touched.
(a) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not correct explanation of (A)
(c) Both (A) and (R) are incorrect.
(d) Both (A) and (R) are correct, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not correct explanation of (A)
Explanation:
Goodwill is an intangible asset that arises when a buyer acquires an existing business. It associated with the purchase of one company by another.
OR
Assertion (A): Purchased goodwill means goodwill for which a consideration has been paid.
Reason(R): It is shown in Balance Sheet as a liability.
(a) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not correct explanation of (A)
(c) Both (A) and (R) are incorrect
(d) Both (A) and (R) are correct, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
(a) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong
Explanation:
Goodwill is an intangible asset that in asssociated with the purchase of one company by another. It will shown in the assets side of balance sheet.
Question 3.
A Ltd. Company issued equity shares of ?100 each. It is called up capital ₹75 on each share but received on ₹60 per share. On forfeiture of these shares the share capital account will be debited with :
(a) ₹60 per share
(b) ₹75 per share
(c) ₹100 per share
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) ₹75 per share
Explanation:
The share capital account will be credited with the called up amount i.e. ₹75.
OR
MMGC Ltd. forfeited 300 shares of ₹10 each, issued at a premium of ₹2 per share for non-payment of final call of ₹3. Out of these 200 shares were reissue at ₹11 per share. How much amount would be transferred to Capital Reserve?
(a) ₹1,400
(b) ₹1,000
(c) ₹2,000
(d) ?600
Answer:
(a) ₹1,400
Explanation:

Question 4.
The amount transferred to Capital Reserve would be ₹1,400 A, B, and C are partners sharing in the ratio 4:3:2, decided to share profit equally. Goodwill of the firm is valued ₹10,800. The adjustment entry will be:
(a) A’s Capital A/c Cr. by ₹4,800; B’s Capital A/c Dr. by ₹3,600; C’s Capital A/c Dr. by 1,200.
(b) A’s Capital A/c Dr. by ₹4,800; B’s Capital A/c Cr. by ₹3,600; C’s Capital A/c Cr. by 1,200.
(c) A’s Capital A/c Cr. by ₹1,200; C’s Capital A/c Dr. by 1,200.
(d) A’s Capital A/c Dr. by ₹1,200; C’s Capital A/c Cr. by 1,200.
Answer:
(c) A’s Capital A/c Cr. by ₹1,200; C’s Capital A/c Dr. by ₹1,200
Explanation: Sacrificing Ratio between A, B and C:
Sacrificing share = Old Share – New Share
A= \(\frac{4}{9}-\frac{1}{3}=\frac{1}{9}\)
B=\(\frac{3}{9}-\frac{1}{3}=\frac{0}{9}\)
C= \(\frac{2}{9}-\frac{1}{3}=\frac{-1}{9} \text { (Gain) }\)
Amount of Goodwill = \(₹ 10,800 \times \frac{1}{9}=₹ 1,200\)

A and B have capitals of ₹2,00,000 and ₹1,00,000 respectively. Interest on capital is to be allowed as per partnership deed @6% per annum. Their profit-sharing ratio is 3 : 2. The profit for the year was ₹15,000. Actual distribution of profit and loss will be:
(a) A ₹12,000 and B ₹6,000
(b) A ₹1,875 and B ₹1,125
(c) A ₹12,000 and B ₹3,000
(d) A ₹10,000 and B ₹5,000
Answer:
(d) A ₹10,000 and B ₹5,000
Explanation:
Net profit = 15,000
Appropriations: Interest on capital of A = 2,00,000 × 6% × 12,000
Interest on capital of B = 1,00,000 × 6% = 6,000
Total appropriation are more than profit, thus profit will be distributed in this ratio of appropriation
= 12,000:6,000 = 2:1
A’s share = 15,000 × \(\frac{2}{3}=10,000\)
B’s share = 15,000 × \(\frac{1}{3}=5,000\)
Question 5.
P, Q and R arc partners sharing profit in the ratio 3: 2: 1. Interest on capital of P, Q, and R ₹1,800, ₹2,100, and ₹1500 respectively is omitted to be provided. The adjustment entry will be:
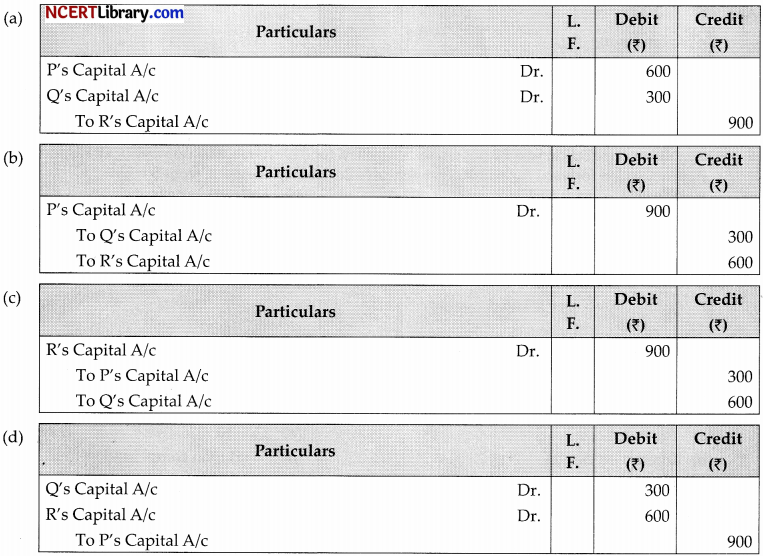
Answer:

Explanation:
Adjustment entry amount (1,800 + 2,100 + 1,500) = 5,400 [loss]
P = 5,400 × \(\frac {3}{6}\) = 2,700 – 1,800 = 90O (Dr.)
Q = 5,400 × \(\frac {2}{6}\) = 1,800 -2,100 = Z300 (Cr.)
R = 5400 × \(\frac {1}{6}\) = 900- 1,500 = f600 (Cr.)
Question 6.
A company issued 1,000,12% Debenture of H00 each at 10% premium. 12 % stand for:
(a) Rate of dividend
(b) Rate of tax
(c) Rate of interest
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Rate of interest
Explanation:
When a company issue debentures, a fixed rate of interest will be provided to the debentureholders. Here, 12% stands for that rate of interest.
OR
K Ltd. issued 20,000,8% debentures of ₹10 each at par. The debentures are redeemable at a premium of ₹20% after 5 years. The amount of loss on redemption of debentures should be:
(a) ₹50,000
(b) ₹40,000
(c) ₹30,000
(d) ₹16,000
Answer:
(b) ₹40,000
Explanation:
Amount of loss on redemption = (20,000 × ₹10) × 20%
= 20,000 × 10 × \(\frac{20}{100}=₹ 40,000\)
Question 7.
AK Ltd. had allotted ₹20,000 shares to the applicants of ₹28,000 share on pro rata basis. The amount payable on application was ₹2 per share, S Applied for 840 shares. The number of share allotted and the amount carried forward for adjustment against allotment money due from S will be:
(a) 120 shares; ₹240
(b) 680 shares; ₹320
(c) 640 shares; ₹400
(d) 600 shares; ₹480
Answer:
(d) 600 shares; ₹480
Explanation:
No. of allotted shares to S = \(\frac{840}{28,000} \times 20,000=600 \text { shares }\)
The amount carried forward for adjustment against allotment money = (840 – 600) shares × 2 = ₹480
Question 8.
Dhanya, Dhanvi & Pawna are partners in a firm. Pawna retired from the firm. After making adjustment for reserve and revaluation of assets & liabilities. The balance in capital was ₹1,20,000. Dhanya & Dhanvi paid ₹60,000 more to Pawna for:
(a) Profit & Loss
(b) Interest on capital
(c) Goodwill
(d) Workman compensation fund
Answer:
(c) Goodwill
OR
Net profit before charging commission has been ₹1,20,000. Partner’s commission is 20% of net profit before charging such commission . The amount of partners commission is :
(a) ₹25,000
(b) ₹24,000
(c) ₹20,000
(d) ₹22,000
Answer:
(b) ₹24,000
Explanation:
The amount of partner’s commision = ₹1,20,000 × \(\frac{20}{100}\) = ₹24,000
Read the following hypothetical situation, answer the question no. 9 to 10.
Ram and Gopal were partner in a firm on 1/4/2021 their fixed capital were ₹1,00,000 and ₹1,50,000 respectively on 30-6-2021. Then decided that total capital (fixed) should be ₹3,00,000. It was further decided that capital (fixed) should be in profit sharing ratio. Accordingly they introduced on withdraw the necessary capital. The partnership deed provided the following:
(i) Interest in capital @ 12% p.a.
(ii) Interest on Drawing @ 18% p.a.
(iii) The drawing of Ram and Gopal during the year ₹25,000 and ₹24,000 respectively.
(iv) 10% of profit was to be kept in a reserve.
Fill in the missing figures in the following profit & loss appropriation a/c. Assuming accounts are closed on 31/3/every year.
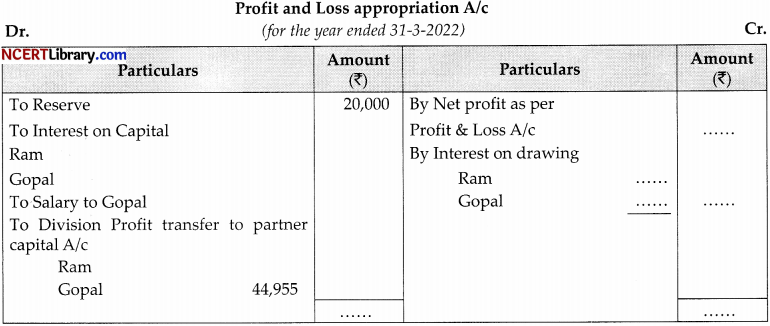
Question 9.
Salary of Gopal will be
(a) ₹ 30,000
(b) ₹60,000
(c) ₹ 40,000
(d) ₹ 20,000
Answer:
(b) ₹60,000
Question 10.
Interest on the capital of Ram.
(a) ₹ 10,000
(b) ₹ 18,000
(c) ₹ 16,500
(d) ₹ 28,000
Answer:
(c) ₹ 16,500
Question 11.
Choose the correct sequence of the following transaction in context of division of partner:
(i) Employee salary
(ii) Manager commission 10% of net profit
(iii) Workers manager commission 10% of gross profit
(iv) Partner commission of net profit after charging such commission
(a) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(b) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(c) (i), (iii), (iii), (iv)
(d) (iii), (i), (ii), (iv)
Answer:
(d) (iii), (i), (ii), (iv)
Question 12.
Bittoo Ltd. offered 30,000 shares of ₹20 each payable as ₹4 on application, ₹7 on allotment, ₹7 on first call and ₹2 On second and Final call. All shares were applied for and allotted. All money duly was received except:
(1) Aditya did not pay allotment and 1st call money on 400 shares which was forfeited.
(2) Vansh Dhaka did not pay 1st call money on 500 shares but paid the same with final call along with interest ₹25.
(3) Rishi could not pay both calls on 600 share which were forfeited .
The amount forfeited on all the above share will be :
(a) ₹10,000
(b) ₹2,000
(c) ₹8,200
(d) ₹7,000
Answer:
(d) ₹7,000
Explanation:
Money forfeited from Aditya = 400 × 4 = 1,600
Money forfeited from Rishi = 600 × (7 + 2) = 5,400
Total amount forfeited = 1,600 + 5,400 = 7,000
Question 13.
A company may issue shares :
(a) By public subscription
(b) By private placement
(c) For consideration other than cash
(d) By any of these
Answer:
(d) By any of these
Explanation:
A company may issue share:
(i) By public subscription
(ii) By private placement
(iii) For consideration other than cash
Question 14.
Risha and Rani were partners in a firm. Ravi was admitted as a new partner for a 1/5 share in the profits of the firm. Ravi brought proportionate capital. Risha and Rani after all adjustments were ₹1,28,000 and ₹92,000. Capital brought by Ravi was:
(a) ₹44,000
(b) ₹55,000
(c) ₹1,10,000
(d) ₹56,000
Answer:
(b) ₹55,000
Explanation:
Total of new capital of Risha and Rani = 1,28,000 + 92,000 = 2,20,000
New capital of firm = 2,20,00 × \(\frac{5}{4}=2,75,000\)
Capital brought in by Ravi = 2,75,000 × \(\frac{1}{5}=55,000\)
Question 15.
Which accounts are opened when partners have fluctuating capitals?
(a) Capital A/c
(b) Current A/c
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer:
(a) Capital A/c
Explanation:
When partners have fluctuating capitals then only a single account is prepared, Partners’ Capital A/c
OR
L, M and N are partners in a firm sharing profits itn the ratio 2 : 2 :1. N is guaranteed a minimum profit of ₹40,000 by L profit for the year amounted to ₹1,60,000. The profit credited to each partner will be:
(a) ₹40,000, ₹80,000. ₹40,000
(b) ₹56,000 ₹64,000, ₹40,000
(c) ₹64,000 ₹64,000₹32,000
(d) ₹60,000, ₹60,000,₹40,000
Answer:
(b) ₹56,000 ₹64,000, ₹40,000
Explanation:
The profit credited to each partner:
L = ₹1,60,000 × \(\frac {2}{5}\) = ₹64,000 – ₹8,000 (guarantee given to L)
= ₹56,000
M = ₹1,60,000 × \(\frac {2}{5}\) = ₹64,000
N = ₹1,601,000 × \(\frac {1}{5}\) = ₹32,000 + ₹8,000 (guarantee by L) = ₹40,000
Question 16.
Lakshay, Roni and Ravi are partners sharing profit in the ratio of 3 : 2 : 2. As per the partnership agreement, Ravi is to get minimum amount of ₹1,00,000. As his share of profit every year and any deficiency on this account is to be personally borne by Lakshay. The net profit for the year ended 31st March, 2022 amounted to ₹2,80,000. Calculate the amount of net profit due to Lakshay after bearing deficiency is:
(a) ₹1,20,000
(b) ₹1,40,000
(c) ₹1,00,000
(d) ₹90,000
Answer:
(c) ₹1,00,000
Explanation:
Amount of net profit = ₹2,80,000 × \(\frac {3}{7}\)
Due to Lakshav = ₹1,20,000 – 20,000 (gurantee to Ravi) = ₹1,00,000
Question 17.
X, Y, Z are partners in a firm sharing profit in the ratio of 5 : 3 : 2. Z Died on 30th September, 2022 and his share of profit till the date of death was to be calculate on the basis of sales. Sales for the year ended 31st March, 2022 amounted to ₹1,50,000 and that from 1st April to 30th September, 2022 amounted to ₹90,000. The profit for the year ended 31st March, 2022 was ₹50,000. Calculate Z ‘s share of profit upto the date of death and pass necessary Journal entry if:
Case 1: X and Y decided not to change their future profit-sharing ratio
Case 2: X and Y decided to share future profit in the ratio of 7: 3
Answer:

Working Notes:
Last Year profit =50,000
Last Year sale =1,50,000
1.4 .2022 to 30.8 .2022= Sales 90,00
Profit = \(\frac{50,000}{1,50,000} \times 90,000=₹ 30,000\)
Z’s share = \(30,000 \times \frac{2}{10}=₹ 6,000\)

When there is a change in profit sharing ratio containing partners give profit to retiring partner in their gaining ratio.
X’s gain = \(\frac{7}{10}-\frac{5}{10}=\frac{2}{10}\)
Y = \(\frac{3}{10}-\frac{3}{10}=0\)
Question 18.
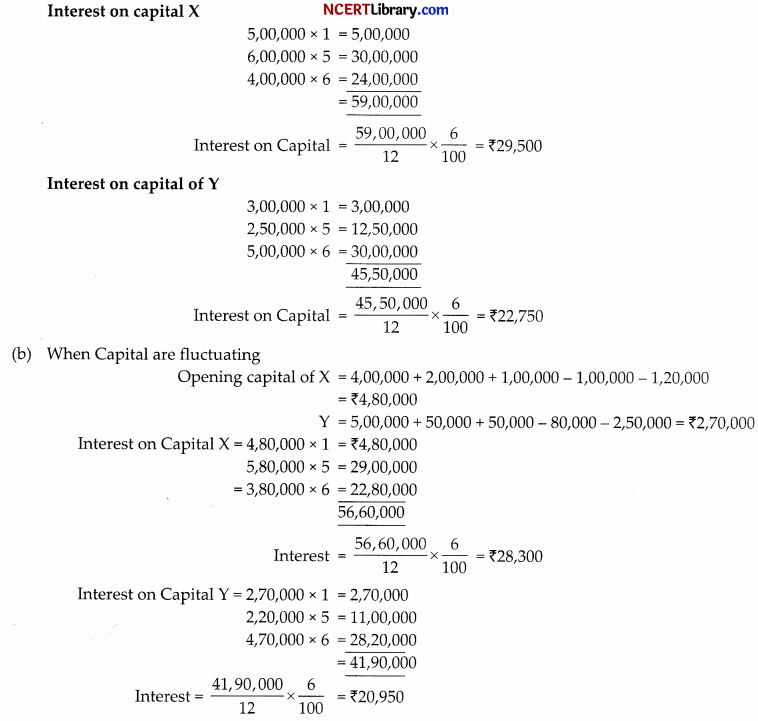
On 31st March, 2012 after the closing of the accounts, the capital accounts of X and Y stood in the books of the firm at ₹4,00,000 and ₹5,00,000 respectively. On 1st May 2011, X introduced an additional capital of 1,00,000 and Y withdrew ₹50,000 from his capital. On 1st October 2011, X withdrew ₹2,00,000 from his capital and Y introduced ₹2,50,000. Interest on capital is allowed @ 6% p.a. Subsequently, it was discovered that interest on capital @ 6% p.a. had been omitted. The profits for the year ended 31st March, 2012 amounted to ?2,00,000 and the partners drawings had been: X ₹1,00,000 and Y ₹50,000. The profit sharing ratio of X and Y was 3 : 2.
Required: Calculate the interest on Capital if the Capitals are (a) fixed (b) fluctuating.
OR
X and Y are partners sharing the profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2. X being a non-working partner contributed ₹5,00,000 as his capital on 1st April, 2011. Y being a working partner agreed to work for the firm. The partnership deed provides for interest on capital @ 8% and salary to every working partner @ 2,000 p.m. On 31st October 2011, X advanced 2,00,000 by way of loan to the firm. Net profit before providing for any interest and partner’s salary for the year 2011-12 was 25,000. Show the distribution of profit.
Answer:
(a) When capital are fixed
Calculation of Interest on Capital:
Opening capital X = 4,00,000 + 2,00,000 – 1,00,000 = 5,00,000
Y = 5,00,000 + 50,000 – 2,50,000 = ₹3,00,000
OR
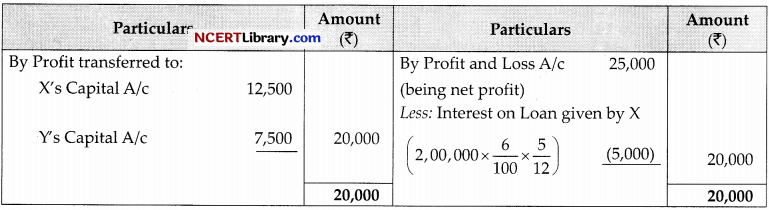
Calculation of Interest on Capital:
Interest on Capital of X = 5,00,000 × \(\frac{8}{100}=₹ 40,000\)
Salary to Y = 2,000 x 12 = ₹24,000
Total of appropriation = ₹(40,000 + 24,000) = ₹64,000
Which is more than profit.
Thus profit will be distributed in the ratio of appropriation.
40,000: 24,000
⇒ 5:3
Question 19.
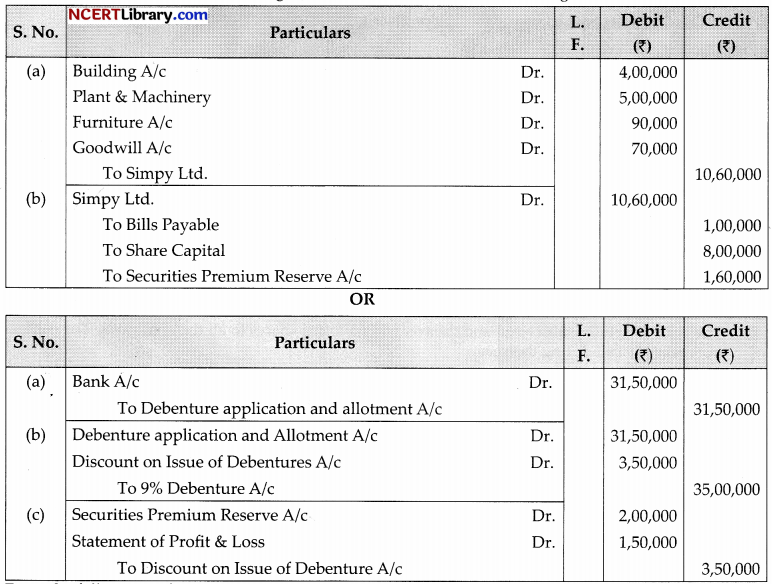
Ak Ltd. purchases the following assets from Simpy Ltd.:
| Building | ₹3,70,000 at ₹4,00,000 |
| Plant and Machinery | ₹5,10,000 at ₹5,00,000 |
| Furniture and Fitting | ₹75000 at ₹90,000 |
AK Ltd decided to accept Bills Payable for ₹1,00,000 and issued 8,000 equity share of ₹100 each at 20% Premium to Simpy Ltd. To discharge consideration. Give necessary journal entries in the books of AK Ltd.
OR
Pooja ltd issued 35,000, 9% debentures of ₹100 each at a discount of 10% to the public. The debentures were to be redeemed by draw of lot in following ways:
| By the end of 1st Year | 10,000 |
| By the end of 2nd Year | 5,000 |
| By the end of 3 Year | 10,000 |
| By the end of 4th Year | 5,000 |
| By the end of 6thYear | 5,000 |
The company had a balance of Securities Premium Reserve of ₹2,00,000. Give necessary Journal Entries for the issue of debenture and writing off discount on issue of debentures, ignore interest.
Question 20.
From the following information, calculate the value of goodwill of M/s Shrama and Gupta:
(i) At three year’s purchased of super profit.
(ii) On the basis of capitalisation of average profit.
Information:
(a) Average capital employed in the business ₹7,00,000.
(b) Net trading result of the firm for the past year’s; profit 2007 ₹1,47,600; loss 2008 – ₹1,48,100; profit 2009- ₹4,48,700.
(c) Rate of interest expected from capital having regard to the risk involved 18%.
(d) Remuneration to a partner for his service – ₹500 per month
(e) Assets (excluding goodwill) ₹7,54,762; liabilities – ₹31,329.
Answer:
Calculation of Goodwill simple profit method
(i) Average Profit = \(\frac{1,47,600-1,48,100+4,48,700}{3}=₹ 1,49,400\)
Average Profit = 1,49,400 – 12,000 (remuneration) = ₹1,37,400
Normal Profit = Capital employed × \(\frac{\text { Rate }}{100}\)
= \(7,00,000 \times \frac{18}{100}=1,26,000\)
Superprofit = 1,37,400 – 1,26,000=₹ 11,400
Goodwill = 11,400 × 3=₹ 34,200
(ii) Calculation of goodwill on the basis of capitalisation of average profit:
Average profit = \(=\frac{1,47,600-1,48,100+4,48,700}{3}=₹ 1,49,400\)
Capitalised values of average profit = \(=\frac{\text { Average profit }}{\text { Normal rate of return }} \times 100\)
= \(1,49,400 \times \frac{100}{18}=₹ 8,30,000\)
Goodwill = Capitalised value of average profit Actual capital Employed
= 8,30,000 – 7,00,000 = 1,30,000
Question 21.
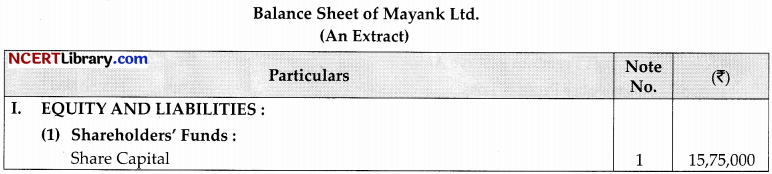
On 1st April 2022, Mayank Ltd. was formed with an authorised capital of ₹25,00,000 divided into 50,000 shares of ₹50 each. The company issued prospectus inviting application for 45,000 shares. The issue price was payable as under:
On application ₹15
On allotment ₹20
On call balance
The issue was fully subscribed and the company allotted shares to all the applicants. The company did not make the call during the year.
Show the following:
(a) Share capital in the Balance Sheet of the company as per revised Schedule III, part 1 of the Company Act, 2013.
(b) Also prepare ‘notes to accounts’ for the same.
Answer:
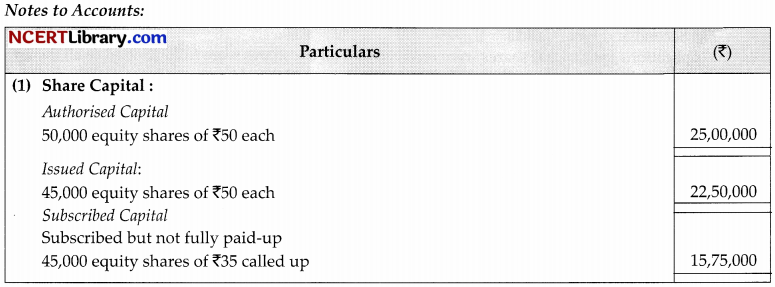
Question 22.
Pass the necessary journal entries for the following transactions on the dissolution of the firm of K and L after the various assets (other than cash) and outside liabilities have been transferred to Realisation Account:
(i) Bank Loan ₹15,000 was paid.
(ii) Stock worth ₹20,000 was taken over by L.
(iii) K paid ₹9,000 to a creditor.
(iv) A liability not appearing in the books was settled at ₹3,700.
(v) Expenses of realisation ₹900 were paid by L.
(vi) Loss on realisation ₹7,100 was divided among the partners K and L in 7 : 3 ratio.
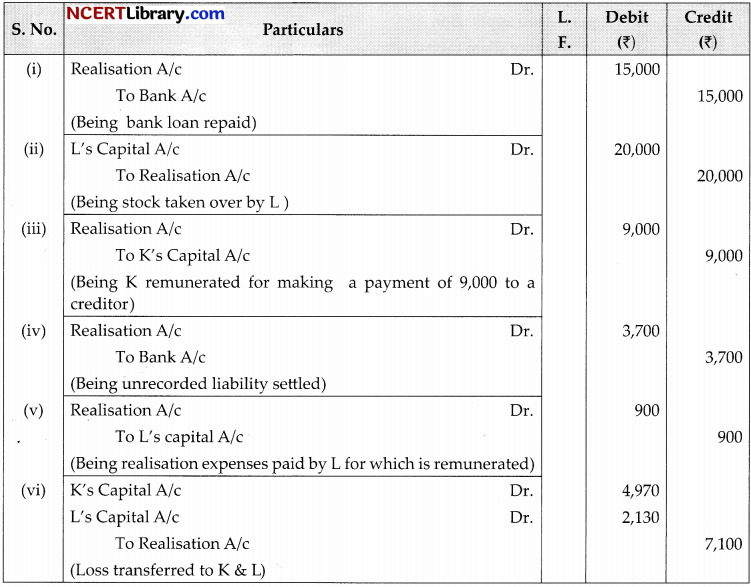
Question 23.
Gupta Ltd. invited applications for issuing 1,12,000 equity share of ?10 each at par. The amount per share was payable as follows:
On Applications ₹1
On Allotment ₹2
On First Call ₹3
On Second and Final Call ₹4
Applications for 1,00,000 shares were received and all the shares were fully allotted to all the applicants. Ramesh failed to pay his allotment money which was ₹2,000. His shares were forfeited immediately. Suresh did not pay the first call on 500 shares applied by him. His shares were forfeited after the first call. The forfeited shares of Ramesh and Suresh were re-issued at ₹9 per share fully paid-up. Afterwards the second and final call was made and was duly received.
Pass necessary journal entries for the above transactions in the books of Gupta Ltd.
OR
LCM Ltd. invited applications for issuing 2,00,000 equity shares of ₹10 each at a premium of ₹3 per share. The amount was payable as follows:
On application and allotment-₹8 per share (including premium)
On first and final call-the balance amount applications for 3,00,000, shares were received. Applications for 50,000 shares were rejected and money refunded. Shares were allotted on pro-rate basis to the remaining applicants. The first and final call was made. The amount was duly received except of 2,500 shares applied by Kanwar. His shares were forfeited. The forfeited shares were re-issued at ₹7 share fully paid-up.
Answer:
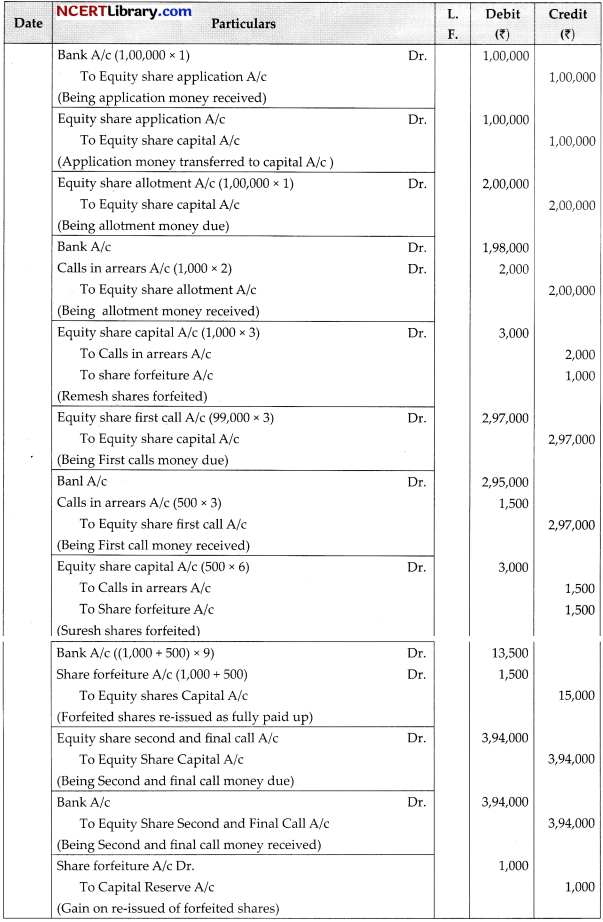
OR
| 3,00,000 | 2,00,000 |
| 50,000 | Nil |
| 2,50,000 | 2,00,000 |
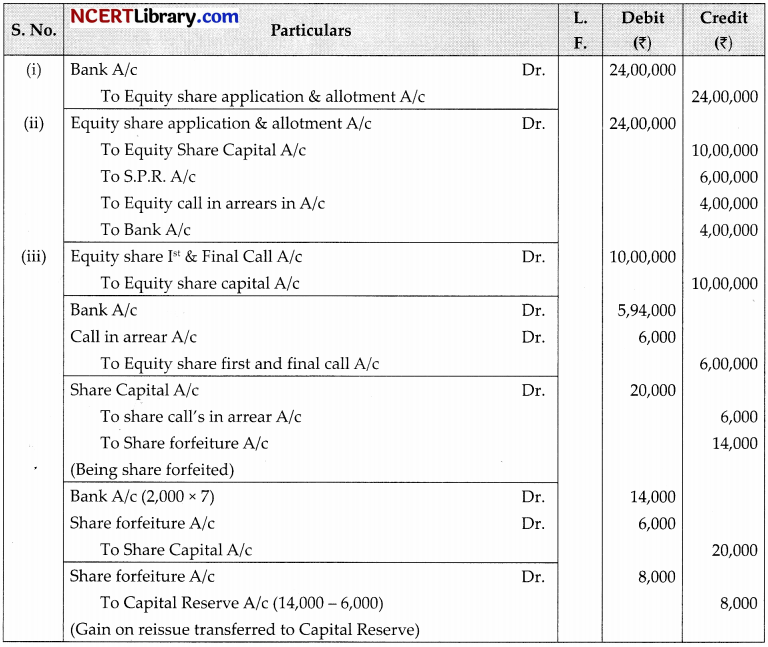
Working Notes:
Kanwar Applied 2,500

Question 24.
Om, Ram and Shanti were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3:2:1. On 1st April, 2022, their balance sheet was as follow.
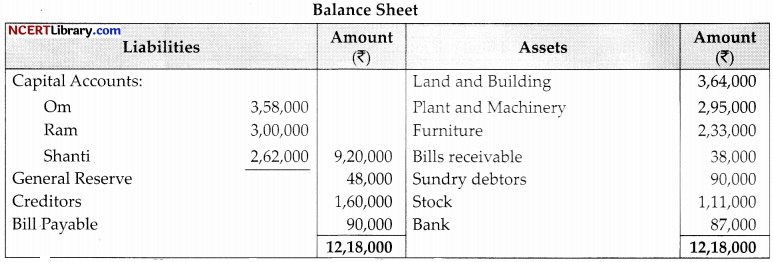
On the above date, Shyam was admitted on the following basis:
(i) He will bring ₹1,00,000 for his capital and will get 1/10th share in the profits.
(ii) He will bring necessary cash for his share of goodwill premium. The goodwill of the firm was valued at ₹3,00,000.
(iii) A liability of ₹18,000 will be created against bill receivable discounted.
(iv) The value of stock and furniture will be reduced by 20%.
(v) The value of land and building will be increased by 10%.
(vi) Capital accounts of the partnership will be adjusted on the basis of partner’s’s capital in their profit sharing ratio by opening current accounts.
Prepare revaluation account and partners’ capital accounts.
OR
Following is the balance sheet of Jain, Gupta and Malik as on 31st, March 2022.
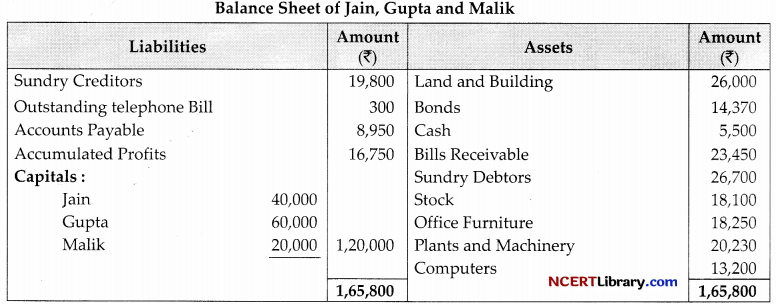
The partners have been sharing profits in ratio of 5 : 3 : 2. Malik decides to retire from business on lsl April, 2022 and his amount in the business is to be calculated as per the following terms of revaluation of assets and liabilities
| ₹ | |
| Stock | 20,000 |
| Office Furniture | 14,250 |
| Plant and Machinery-v | 23,530 |
| Land and Building | 20,000 |
A provision of 1,700 to be created for doubtful debts. The goodwill of the firm is valued at ₹9,000. The continuing partners agrees to pay ₹16,500 as cash on retirement of Malik by bringing in money in new ratio to be continuing partners in the ratio of 3 : 2. The balance in the capital accounts of Malik will be treated as loan. Pepare revaluation account, Capital accounts and Balance Sheet of the reconstituted firm.
Answer:
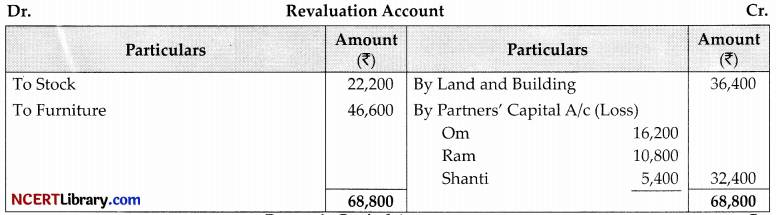
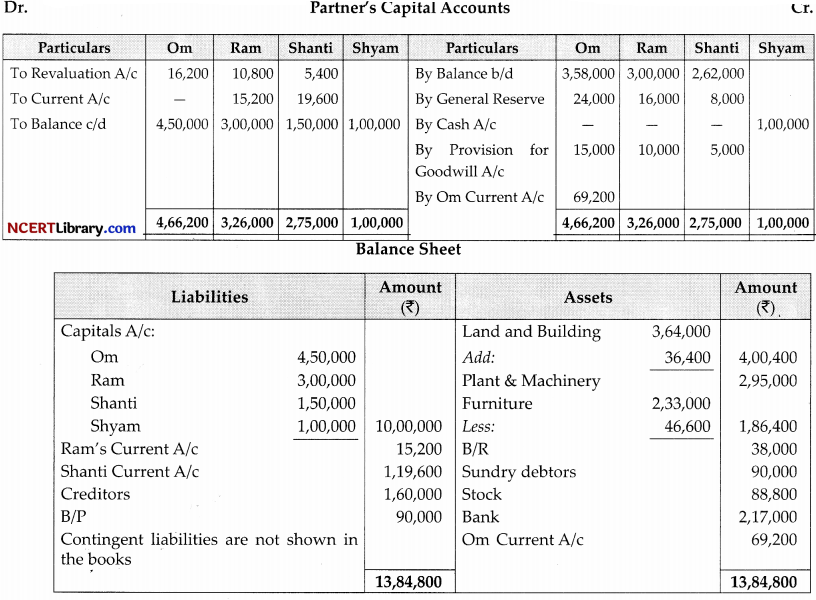
Working Notes:
Shyam’s Capital = 1,00,000
Ram = \(\frac {1}{10}\)
Total Capital = \(=\frac{10}{1} \times 1,00,000=₹ 10,00,000\)
Calculation New Ratio:
Let Profit be = 1
Shyam Share = \(\frac{1}{10}=1-\frac{1}{10}=\frac{9}{10}\)
0m = \(\frac{9}{10} \times \frac{3}{6}=\frac{27}{60}\)
Ram = \(\frac{9}{10} \times \frac{2}{6}=\frac{18}{60}\)
Shanti = \(\frac{9}{10} \times \frac{1}{6}=\frac{9}{60}\)
Shyam = \(\frac{1}{10} \times \frac{6}{6}=\frac{6}{60}\)
27 : 18: 9: 6
9 : 6: 3: 2
New Capital of 0m = \(10,00,000 \times \frac{9}{20}=₹ 4,50,000\)
Ram = \(10,00,000 \times \frac{6}{20}=₹ 3,00,000\)
Shanti = \(10,00,000 \times \frac{3}{20}=₹ 1,50,000\)
OR
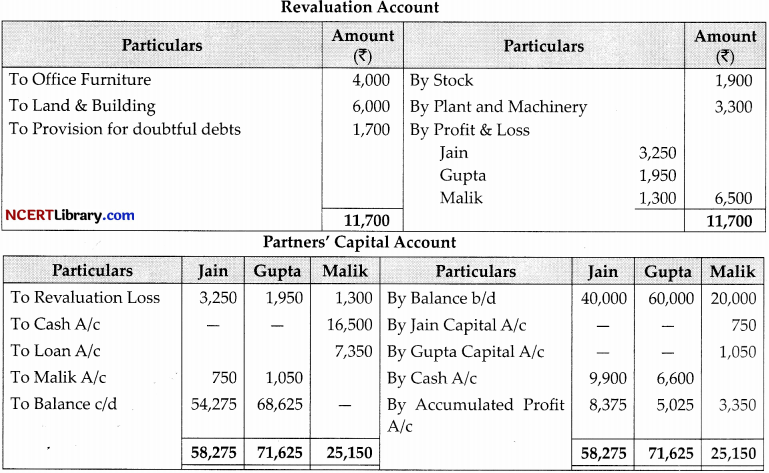
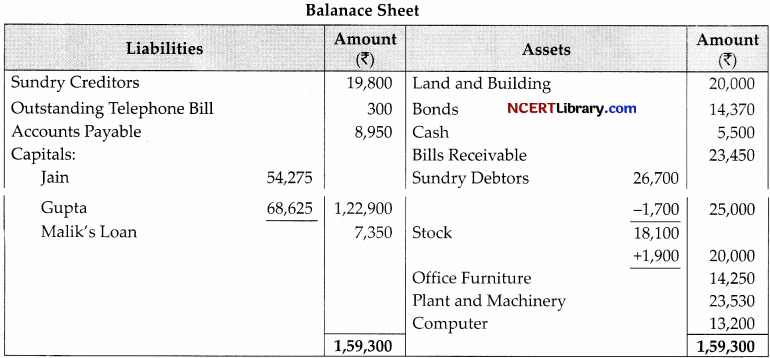
Working Notes:
Goodwill = \(9,000 \times \frac{2}{10}=₹ 1,800\)
Jam’s gain = \(\frac{5}{8}-\frac{5}{10}=\frac{50-40}{80}=\frac{10}{80}\)
Gupta’s gain = \(\frac{3}{8}-\frac{2}{10}=\frac{30-16}{80}=\frac{14}{80}\)
Gaining Ratio = = 10 : 14 = 5 : 7
Jam’s share of goodwill to Malik = \(1,800 \times \frac{5}{12}=₹ 750\)
Gupta = \(1,800 \times \frac{7}{12}=₹ 1,050\)
Cash bring by partners
Jam = \(16,500 \times \frac{3}{5}=₹ 9,900\)
Gupta = \(16,500 \times \frac{2}{5}=₹ 6,600\)
Question 25.
Pranav, Karan, Rahim were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1. On 31sl March, 2022 their Balance Sheet was as follows.
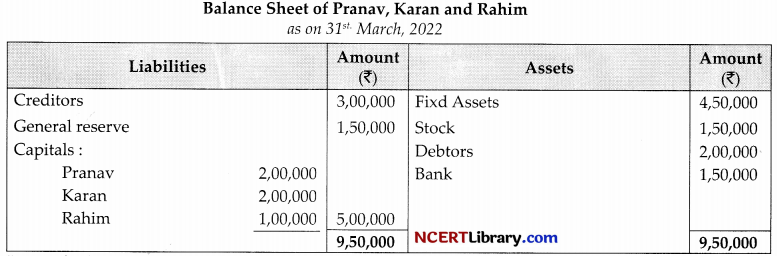
Karan died on 12.06.2022 accounting to the partnership deed, the legal representative of the deceased partner were entitled to the following:
(i) Balance in his capital account
(ii) -Interest on capital @ 12% p.a.
(iii) Share of goodwill. Goodwill of the firm on Karan’s death was revalued at ₹60,000
(iv) Share in the profit of the firm till the date of his death, calculated on the basis of last year’s profit, the profits of the firm for the year ended 31.03.2022 was ₹5,00,000.
Prepare Karan’s capital account to be presented to his representative .
Answer:
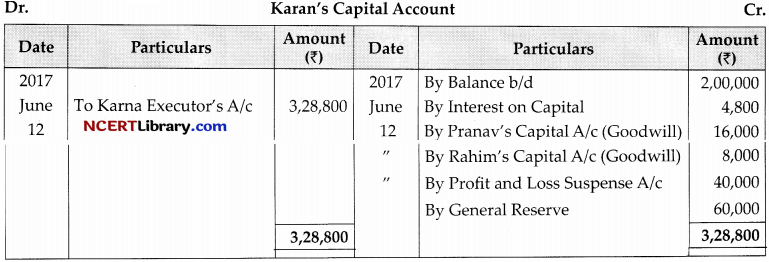
Working Notes:
(a) Interest on Capital = \(2,00,000 \times \frac{12}{100} \times \frac{73}{365}=4,800\)
(b) Karrta’s Goodwill = \(60,000 \times \frac{2}{5}=₹ 24,000\) (will be given by Pranav arid Rahim)
(c) Profit & Loss = \(5,00,000 \times \frac{73}{365} \times \frac{2}{5}=₹ 40,000\)
Question 26.
(a) Q. Ltd., took over the assets and liabilities of PS Ltd. of ₹28,00,000 and ₹3,20,000 respectively. For the purchase consideration, a cheque of ₹10,00,000 and ₹12,000, 12% debenture of ₹100 each were issued at a premium of 25 % . Pass the necessary journal entries for the above transactions.
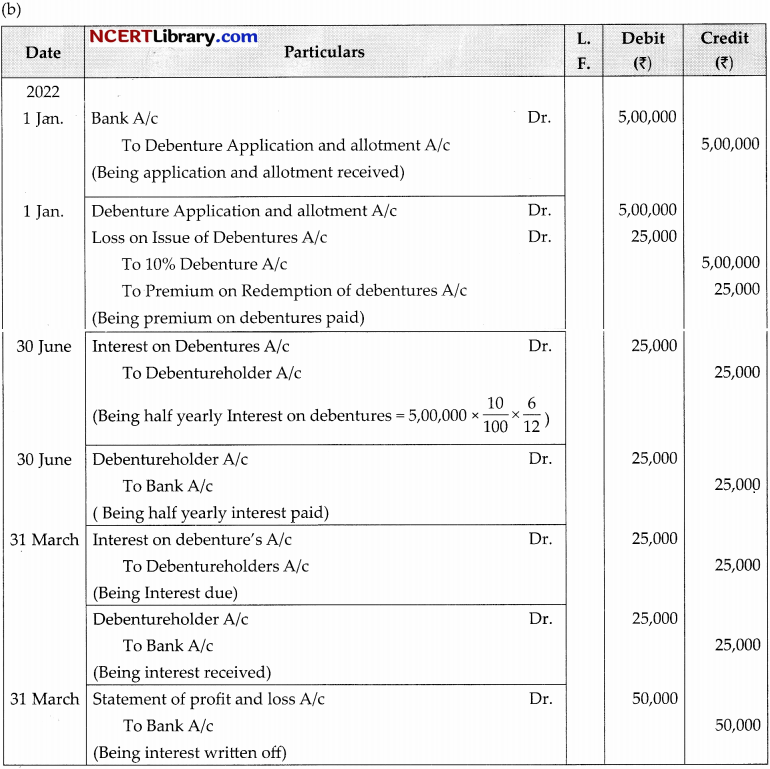
(b) On 1st January 2022, K ltd., issued 5,000, 10% debenture of 100 each at par to be redeemed at a premium of 5% at the end of seventh year out of profit. Pass the necessary journal entries for issue of debenture and interest on debenture for the year ending 31st March, 2022.
Answer:
Part – B
(Analysis of Financial Statement)
(Option-1)
Question 27.
Under what headings will you show the following item? Interest Accrued and due on Unsecured Loan:
(a) Fixed assets
(b) Current assets
(c) Current liabilities
(d) Non-Current liabilities
Answer:
(c) Current liabilities
Explanation:
Interest accrued and due on borrowings shall be shown under other current liabilities because it is paid with in 12 months. Therefore it is shown under current liabilities.
OR
Higher the ratio, the more favourable it is, does not stand true for:
(a) Liquidity Ratio
(b) Net Profit Ratio
(c) Operating Ratio
(d) Inventory turnover ratio
Answer:
(a) Liquidity Ratio
Explanation:
The higher the liquidity ratio the better it is because the firm will be able to pay its current liabilities more easily.
Question 28.
Opening Inventory T19,000; Closing Inventory ₹2’1,000; Revenue from Operations ₹2,00,000; Gross Profit Ratio 25%. Calculate Inventory Turnover Ratio.
(a) 7.5 times
(b) 10 Times
(c) 5 times
(d) 4.5 times
Answer:
(a) 7.5 times
Explanation:
Inventory turnover ratio = \(=\frac{\text { Cost of Revenue from operation }}{\text { Average inventory }}\)
Cost of Revenue from operations = \(2,00,000-\left(2,00,000 \times \frac{25}{100}\right)=₹ 1,50,000\)
Average inventory \(=\frac{\text { Opening inventory }+\text { closing inventory }}{2}\)
= \(=\frac{19,000+21,000}{2}=\frac{40,000}{2}=₹ 20,000\)
inventory turnover Ratio = \(=\frac{1,50,000}{20,000}=7.5 \text { times }\)
Question 29.
Classify the cash sales into:
(a) Operating Activities
(b) Investing Activities,
(c) Financing Activities, and
(d) Cash Equivalents while preparing a Cash Flow Statement
Answer:
(d) Cash Equivalents while preparing a Cash Flow Statement
OR
If fixed tangible assets whose original cost is ₹40,000 having accumulated depreciation ₹12,000 were sold for ₹34,000. Then while preparing cash flow statement its effect on cash flow will be:
(a) Cash flow from Financing activity ₹34,000
(b) Cash flow from Financing activity ₹6,000
(c) Cash flow from Investment activity ₹34,000
(d) Cash flow from Investment activity ₹6,000
Answer:
(c) Cash flow from Investment activity ₹34,000
Explanation:
Question 30.
ABC Ltd. had investment of ₹68,000 as on 31.3.2019 and investment of ₹56,000 as on 31.3.2020. During the year ABC Ltd. sold 40% of its investment being held in the beginning of period at a profit of ?16,800. Determine cash flow from investing activities.
(a) ₹59,200
(b) ₹28,800
(c) ₹72,800
(d) ₹44,000
Answer:
(d) ₹44,000
Explanation:
Cost of investments sold = 68,000 × 40% = 27,200
Cash flow from investing activities = 27,200 + 16,800 (Profit) = 44,000
Question 31.
State the major headings under which the following items will be put as per as per Schedule VI Part-I of Companies’ Act, 1956:
(i) Long-term Investments:
(ii) Bills receivables
(iii) Motor Car:
(iv) Discount on Issue of Shares:
(v) Securities Premium reserve
(vi) Unclaimed dividend.
Answer:
| Items | Major heads |
| (i) | Noncurrent Assets |
| (ii) | Current Assets |
| (iii) | Non-Current Assets – Fixed Tangible Assets |
| (iv) | Reserves and Surplus, by way of deduction from statement of profit & loss or securities |
| (v) | premium reserve A/c |
| (vi) | Shareholders fund Reserves & Surplus |
Question 32.
Accounting ratios ignore qualitative factors and are also not comparable if different firms follow different accounting policies”. Comment.
Answer:
These may be different accounting policies adopted by different firms with regards to providing
depreciation, creation of provision for doubtful debts, etc. For instance on firm may adopt the policies
of changing depreciation or straight line basis, while other may change on written down value method.
Such differences make the accounting ratio are incomparable.
Question 33.
(A) Current Assets of a Company are 4,00,000 and its Current Liabilities are ₹1,25,000. It purchased
goods for 75,000 on credit. Calculate the revised current ratio.
(B) Current Liabilities of a Company were 1,20,000 and its Current ratio was 2.4. After this it made payment of a B/P for 10,000. Calculate the Current ratio after the payment.
OR
From the given information, Calculate the Inventory Turnover Ratio:
Revenue from Operations: 2,00,000; Gross Profit : 25%; Opening Inventory was 1/4th of the value of Closing Inventory. Closing Inventory was 40% of Revenue from Operations.
Answer:
(a) Current Assets = 400,000
Current Liabilities = 1,25,000
Goods purchase on credit 75,000
Current Ratio (Revised) = \(\frac{\text { Current Assets }}{\text { Current Liabilities }}=\frac{4,00,000+75,000}{1,25,000+75,000}=\frac{4,75,000}{2,00,000}\)
= 2 : 375: 1
(b) Current Liabilities = 1,20,000
Current Ratio = 2 : 4
Current Ratio = \(=\frac{\text { Current Assets }}{\text { Current Liabilities }}\)
2 : 4 = \(=\frac{\text { Current Assets }}{1,20,000}\)
Current Assets = : 1,20,000 × 24 = 2,88,000 After Pay able for B/P 10,000
Current Ratio = \(\frac{2,88,000-10,000}{1,20,000-10,000}=\frac{2,78,000}{1,10,000}=2 \cdot 52: 1\)
OR
Revenue from Operations = 2,00,000
Gross Profit = 25%
Gross Profit = \(2,00,000 \times \frac{25}{100}=50,000\)
Cost of goods sold =
Closing Inventory = \(2,00,000 \times \frac{40}{100}=80,000\)
Opening Inventory = \(80,000 \times \frac{25}{100}=20,000\)
Average Inventory = \(\frac{80,000+20,000}{2}=50,000\)
Inventory Turnover Ratio = \(=\frac{\text { Cash of Revenue }}{\text { Average Inventory }}=\frac{1,50,000}{50,000}=3 \text { times }\)
Question 34.
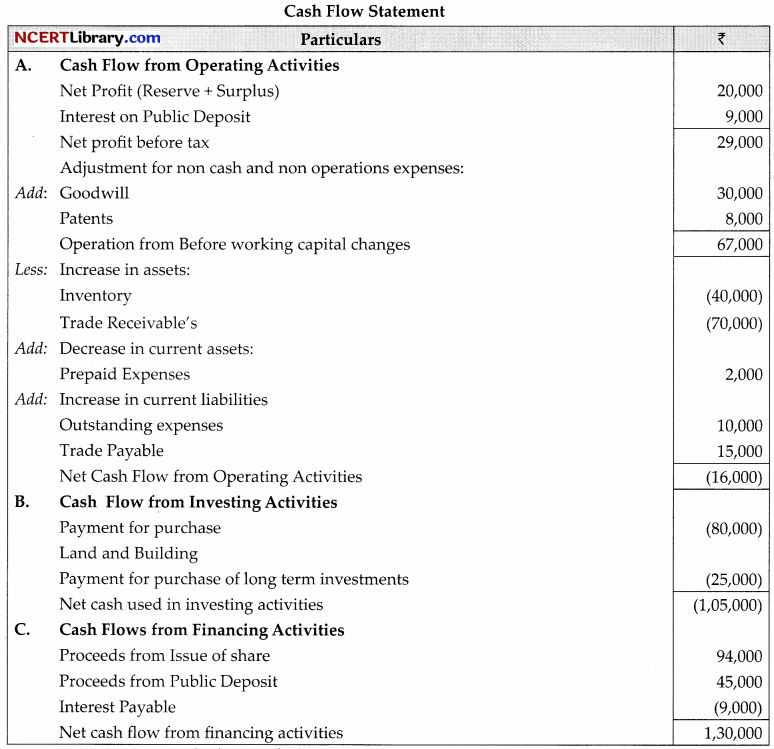
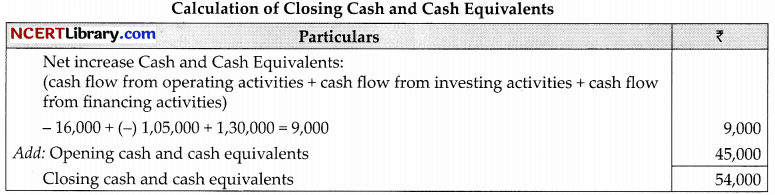
From the following Balance Sheet of MMGC Ltd.
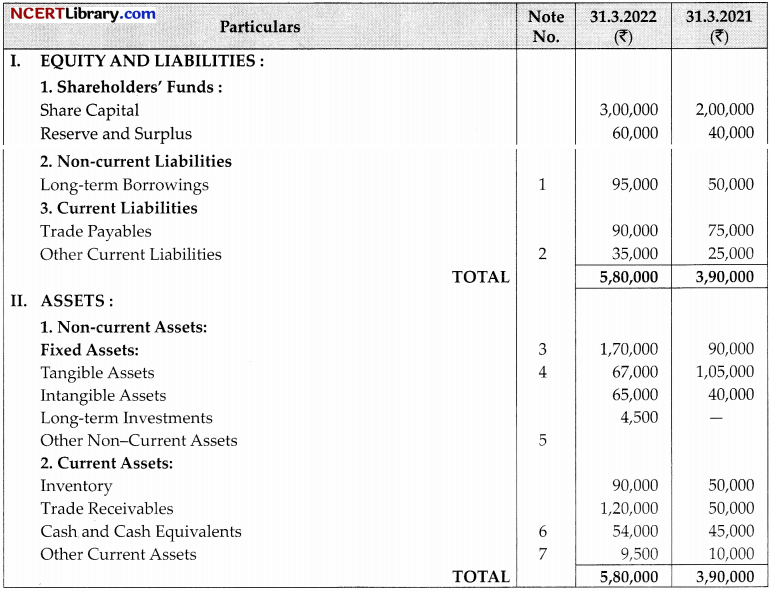
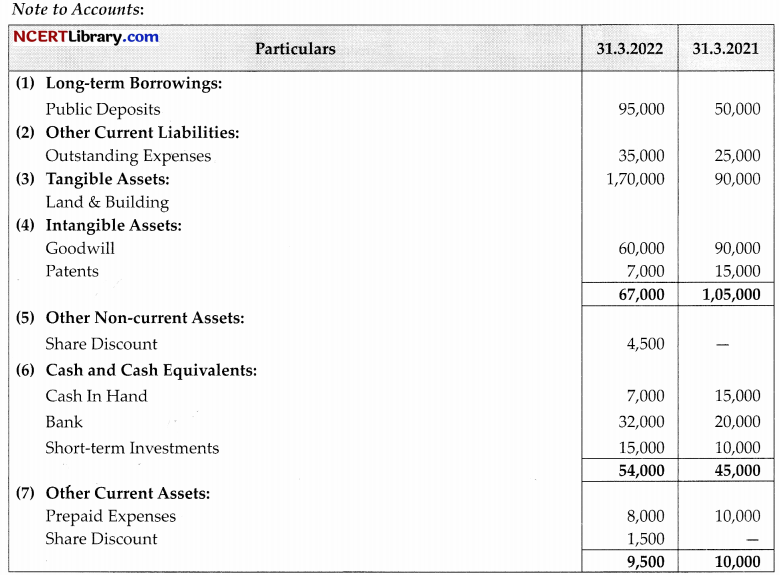
Additional Information:
(1) Interest paid on public deposits amounted to ₹9,000.
(2) On 1st April, 2021,10,000 shares of ₹10 each were issued at 6% discount.
1. Calculate Net Profit before tax and extraordinary items ₹29,000
2. Calculate Operating profit before working capital changes ₹67,000.
3. Calculate Cash flow from Investing activities. Cash uses ₹1,05,000
4. Calculate Cash flow from Financing activities. XI,30,000
5. Calculate closing cash and cash equivalents. ₹9,000
Answer:
Working Notes