Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions Set 7 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 7 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- Question paper comprises Six Sections -A, B, C, D, E, and F. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From question 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Question no. 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words.
- Section C – contains Q.25 to Q.29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words
- Section D – Question no. 30 to 33 are long answer-type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section E – Questions no from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map-based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A
(Multiple Choice Questions)
Question 1.
What was the arrangement made by the European powers to prevent French expansion in future?
(a) Their country’s military was made strong.
(b) An agreement was made with France.
(c) A series of states were set up on the boundaries of France.
(d) Military of France was dissolved.
Answer:
(c) A series of states were set up on the boundaries of France.
This city became the hub of the new print culture, catering to the Western-style schools:
(a) Mumbai
(b) Tokyo
(c) Shanghai
(d) New York
Answer:
(c) Shanghai
![]()
Question 3.
Study the picture and Answer the question that follows:

Which of the following aspects best signifies the above image?
(a) Romanticism
(b) Conservatism
(c) Federalism
(d) Feminism
Answer:
(a) Romanticism
Question 4.
Arrange the following in chronological order:
I. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development was set up reconstruction.
II. The Great Depression was caused by a combination of several factors.
III. Rinderpest killed 90% of the cattle in Africa.
IV. The First World War was fought between two power blocs.
Options:
(a) I, III, IV, II
(b) III, IV, II, I
(c) IV, I, II, III
(d) I, II, III, IV
Answer:
(b) III, IV, II, I
Question 5.
Identify the crop with the help of the following information:
- It is the third most important food crop with respect to area and production.
- It is a rain-fed crop which hardly needs irrigation.
- It has very high nutritional value.
Options:
(a) Maize
(b) Jowar
(c) Rice
(d) Gram
Answer:
(b) Jowar
![]()
Question 6.
Which one of the following options best describe primary sector?
(a) Agriculture
(b) Industry
(c) Banking
(d) Transfer
Answer:
(a) Agriculture
Question 7.
Match the following:
| Dams | Rivers |
| A. Rana Pratap Sagar | I. Bhagirathi |
| B. Hirakud | II. Chenab |
| C. Tehri | III. Mahanadi |
| D. Salal | IV. Chambal |
Options:
(a) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(b) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(d) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
Answer:
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
Question 8.
Which of the following was not one of the initial demands of Sri Lankan Tamils?
(a) Regional autonomy
(b) Recognition of Tamil as an official language
(c) Equal opportunities in securing jobs and education
(d) Creation of an independent Tamil Eelam (state)
Answer:
(d) Creation of an independent Tamil Eelam (state)
Question 9.
In which part of Sri Lanka are the Sri Lankan Tamils concentrated?
(a) North and South
(b) East and West
(c) North and East
(d) South and East
Answer:
(c) North and East
Question 10.
Which form of power-sharing is most commonly referred to as federalism?
(a) Horizontal division of power
(b) Vertical division of power
(c) Division of power among various communities
(d) Sharing of power among political parties
Answer:
(b) Vertical division of power
![]()
Question 11.
Which one among the following pairs is correctly matched?
| List-I | List-II |
| (a) Iron and Steel Industry | Agro based industry |
| (b) Oil India Ltd. | Joint sector industry |
| (c) Cement Industry | Light industry |
| (d) BHEL | Private sector industry |
Answer:
(b) Oil India Ltd.-Joint sector industry
Question 12.
In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): MNCs set up offices and factories for production in different parts of the world.
Reason (R): It makes the cost of production low and the greater profits.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 13.
Who among the following said that religion can never be separated from politics? He believed that politics must be guided by ethics drawn from religion.
(a) B. R. Ambedkar
(b) Rajendra Prasad
(c) Mahatma Gandhi
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru
Answer:
(c) Mahatma Gandhi
Question 14.
Read the given data and find out which state has high HDI.
| State | Infant Mortality Rate per 1000 live births (2016) | Literacy Rate % (2011) |
| Punjab | 21 | 76.68 |
| Kerala | 10 | 93.41 |
| Haryana | 33 | 76.64 |
(a) Haryana
(b) Kerala
(c) Punjab
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Kerala
Question 15.
In which of the following countries, the participation of women is not very large?
(a) Sweden
(b) Norway
(c) India
(d) Finland
Answer:
(c) India
![]()
Question 16.
Find the odd one out from the following:
(a) MTNL, Indian Railways, Jet Airways, All India Radio
(b) Cobbler, Washerman, Tailor, Potter
(c) Teacher, Doctor, Tourist guide, Lawyer
(d) Postman, Bank cashier, Soldier, and Police constable Answer: (a) MTNL, Indian Railways, Jet Airways, All India Radio
Question 17.
Fill in the blank:
| Sector | Related Economic Activity |
| Secondary | Manufacturing |
| Tertiary | ? |
Options:
(a) Agriculture
(b) Weaving
(c) Teaching
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Teaching
Question 18.
Zafra always complains about her weight. She believes that she is overweight. She tries different methods to lose her weight. She uses to search on internet about her problem. Her papa and mummy say to her that she is not overweight. One day, they took her to consult doctor. Doctor asked her age. Then she checked her weight and height. She told her about a scientific calculation on nutrition. This is used to know whether a person is undernourished or overweight. Analyse the information given above, considering one of the following correct
Options:
(a) Human Development Index
(b) Body Mass Index
(c) Life Expectancy
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Body Mass Index
![]()
Question 19.
Which of the following is marked by “Regular, free and fair elections”?
(a) Dictatorship
(b) Democracy
(c) Monarchy
(d) Military Rule
Answer:
(b) Democracy
Question 20.
Identify the correct statement/s about MGNREGA:
I. It was passed by the Parliament in August 2005.
II. It was implemented in about 725 districts of India.
III. It is also referred to as ‘Right to Work’.
IV. On annual basis, it provides guaranteed 150 days of employment to the unemployed people in rural areas.
Options:
(a) I & II
(b) I & III
(c) III & IV
(d) I, II & III
Answer:
(b) I & III
Section – B
(Very Short Answer-Based Questions)
Question 21.
State any two problems that were faced in transfer sorting food over long distances till the 1870s.
Answer:
- Till the 1870s, animals were shipped live from the starting point and then slaughtered at the destination. But they took up a lot of ship space.
- In voyage, many died, fell ill, lost weight, or became unfit to eat. Hence, meat was an expensive food item for the poor.
- High prices in turn kept demand and production down. (Any two)
Question 22.
Mention any two functions of a Gram Sabha.
Answer:
- Gram Sabha elects the members of the Gram Panchayat.
- It supervises the overall working of the Gram Panchayat.
Question 23.
What are basic industries? Give one example.
OR
Mention any three physical factors for the location of an industry.
Answer:
Basic or key industries are those which supply their products as raw materials to various industries which manufacture other goods. For example, the iron and steel industry supplies steel to the automobile industry which uses it as a raw material.
OR
The three physical factors for the location of an industry are:
- Availability of raw materials
- Water and power supply
- Suitable climate
Question 24.
What is money? Why is it called a medium of exchange?
Answer: Money is something that can act as a medium of exchange in transfer actions. Before the introduction of coins, a variety of objects was used as money. It is called a medium of exchange because it acts as an intermediate in the exchange process.
Section – C
(Short Answer-Based Questions)
Question 25.
Discuss rabi cropping season in India.
OR
Explain the important characteristics of Intensive Subsistence Farming.
Answer:
Rabi cropping season:
(i) Time for sown and harvesting: Seeds for rabi crops are sown in winter from October to December. Crops are harvested in summer from April to June.
(ii) Important rabi crops: Wheat, barley, peas, gram and mustard are some of the important rabi crops.
(iii) Areas where rabi crops are grown: These crops are grown mainly in the north and north-western parts of India. States of Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh are important producers of wheat and other rabi crops.
(iv) Climate and other required conditions: Rabi crops require precipitation during winter months. This precipitation is generally caused by the western temperate cyclones. In Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan, the success of the green revolution has also been an important factor in the growth of the rabi crops.
OR
Intensive Subsistence Farming has following important characteristics:
(i) Intensive Subsistence Farming is mostly prevalent in areas of high population.
(ii) To obtaining maximum output from the land, high doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation are used. It also required intensive labour.
(iii) Due to the ‘right of inheritance’, land gets divided between successive generations. It causes decrease in land-holding size with every generation and ultimately a time reaches when it becomes uneconomical. Still, farmers try to take maximum output from the limited land in the absence of alternative source of livelihood. It creates high pressure on agricultural land.
![]()
Question 26.
Explain some economic effects of the Non-Cooperation Movement.
Answer:
In the economic sphere, the effects of the Non-Cooperation Movement are as follows:
- Foreign goods were boycotted and eliminated from the market.
- Liquor shops were picketed and foreign cloths were burnt in large bonfires.
- The import of foreign cloth reduced to half between 1921 and 1922.
- In large number of places, merchants, peasants and traders refused completely to trade in foreign good or finance foreign trade.
Question 27.
How does democracy produce an accountable, responsive and legitimate government?
Answer:
(i) Democracy produces an accountable government: The people have the right to chose their representatives who participate in the decision-making process. In case the people are not satisfied with the working of the elected representatives, they have a chance to not to elect them in the next elections.
(ii) Democracy produces a responsive government: It is elected by the people and is responsible towards the needs of the people. It promotes the formation of public opinion and takes care of the needs and desires of the people.
(iii) Democracy produces a legitimate government: Elections are held regularly and people get a chance to elect their representatives. The party which gets majority votes forms the government rules and it has to resign if it is not able to win majority in the next elections. Moreover, there is trAnswer:arency in the decision making process.
Question 28.
What are the different goals that people desire for their development?
Answer:
Goals that people desire for their development:
- Most people desire for more income. They want regular work, better wages and decent price for their crops or other products that they produce.
- But more income is not the only thing that people desire. They also want to enjoy equal treatment, freedom, security and respect of others. They resent discrimination. All these are important goals.
- In some instances, more income or more consumption becomes less significant than these goals because money can buy material goods only and there are some non-material things important to live.
- Money or material thing is one factor on which our life depends. But non-material things also affect
the quality of our life. (Any three)
Question 29.
What is demand deposit? How does it share essential features of money?
Answer: People who have deposited their money in the banks have provision to withdraw it when they require.
These deposits of people with the banks are called demand deposits. It shares the essential features of money because:
- With demand deposits we can directly settle payments without the use of cash. The facility of cheques helps in this manner.
- Along with currency, demand deposits are commonly accepted as a menswear of payment. Thus, they constitute money in the modern economy.
Section – D
(Long Answer-Based Questions)
Question 30.
Who hosted Vienna Congress in 1815? Analyse the main changes brought by the Vienna Treaty?
OR
Who was Giuseppe Mazzini? Why did his visions frighten the conservatives?
Answer:
In 1815, major European powers-Britain, Russia, Prussia and Austria who jointly defeated Napoleon, assembled at the Vienna Congress. The Austrian Chancellor, Duke Metternich hosted the Vienna Congress. The representatives concluded the treaty, which brought about the following changes:
- The Bourbon Dynasty that was deposed during the French Revolution was reinstated.
- France lost all the territories it had captured and annexed under the reign of Napoleon.
- An array of states was established on the fringes of France to restrict expAnswer:onist policies of France in future.
- Prussia was granted important new territories on its western frontiers. At the other end of the spectrum, Northern Italy was ceded to Austria.
- In the east, Russia was granted a part of Poland and Prussia was given the portions of Saxony.
- The main intention was to reinstate the monarchies that had been toppled by Napoleon and to create a new conservative order in Europe.
OR
Giuseppe Mazzini was an Italian revolutionary:
(i) He was born in Genoa in 1807. He became a member of the secret society of the Carbonari. In 1831, at the age of 24, he attempted a revolution in Liguria. For this, he was sent into exile.
(ii) Being underground he founded two more societies namely Young Italy in Marseilles and Young Europe in Berne. Their members included the like-minded young men from Poland, France, Italy and the German states.
(iii) According to Mazzini, God had planned nations to be the natural units of mankind. Thus, Italy could not remain divided in small states and kingdoms. It had to become a single unified republic within a wider alliance of nations. Italian could attain its liberty on the name of its unification only.
(iv) His model was adopted in different countries like Germany, France, Switzerland and Poland and secret societies were set up in these countries. Mazzini persistently opposed the monarchy. Conservatives used to frighten from his vision of democratic republics. This was the reason why. Metternich described him as ‘the most dangerous enemy of our social order.’
![]()
Question 31.
Discuss the different functions performed by political parties.
OR
What are the different types of party system prevailing in the world? Explain with examples.
Answer:
Political parties perform following functions:
(i) Contesting elections: In most democratic countries, political parties choose candidates who contest elections. However, process of choosing candidates is not same in all countries. For example, in the USA, candidates are chosen by members and supporters of a party. On the other hand in India, candidates are chosen by top party leaders.
(ii) Forward policies and programmes to voters: In a democracy, a party reduces the opinions of large mass into a few basic positions which it supports. When a party wins in election and forms government, these basic positions use to provide a direction in which policies can be formulated.
(iii) Make laws for a country: Most of the members of legislature belong to a party. They debate and pass laws in the legislature. They go by the direction of the party leadership, irrespective of their personal opinions.
(iv) Form and run governments: Parties selects leaders, train them and then make them ministers to run the government in the way they want.
(v) Work as opposition parties: Parties which lose in the elections function as opposition to the parties in power. They criticise government for its failures or wrong policies.
(vi) Shape public opinion: Lakhs of members and activists of the parties have spread throughout the country. They come from different sections of society. Many of the pressure groups are the extensions of political parties. Parties sometimes also launch movements for the resolution of problems faced by the people.
(vii) Provide access to government machinery and welfare schemes: Parties provide people access
to government machinery and welfare schemes implemented by governments. For an ordinary citizen, it is easy to approach a local party leader than a government officer. That is why, they feel close to parties even when they do not fully trust them. (Any five)
OR
There are three types of party systems prevailing in the world:
(i) One party system: In one-party system, the government is controlled and run by only one party. All other parties are not allowed to take part in electoral competition. For example, China is ruled by only the Communist Party. The electoral system of China does not permit free competition for power. One-party system is not good for democracy because in any democratic system there must be at least two parties to compete in elections and have fair chance to come to power.
(ii) Two party system: In this system, power usually changes between two main parties. Other parties may also exist, contest elections and win a few seats in the national legislatures. But only the two main parties have a serious chance of winning majority of seats to form government. For example, the United States of America and the United Kingdom.
(iii) Multi-party system: In this system several parties compete for power, and more than two parties have a reasonable chance of coming to power either on their own strength or in alliance with others. For example, in India there is a multi-party system. Government can be formed by various parties coming together in a coalition after election or by making an alliance or a front before the elections. The multi-party system is seemed as very messy and it often leads to political instability. But a variety of interests and opinions are allowed in this system to enjoy political representation.
Question 32.
What is manufacturing? How is manufacturing industry important for India?
OR
What are the factors affecting the location by Industries in India?
Answer: Manufacturing is the production of goods in large quantity after processing raw material into more
valuable products. Manufacturing sector is considered the backbone of development particularly in
general and economic development because:
(i) Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy but they also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
(ii) Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country. This was the main philosophy behind the set-up of public sector industries and joint sector ventures in India. It was also aimed at bringing down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas.
(iii) Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings in much needed foreign exchange.
(iv) Countries that trAnswer:orm their raw materials into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value are prosperous. India’s prosperity lies in increasing and diversifying its manufacturing industries as quickly as possible.
OR
Factors affecting the location of industries in India are:
(i) Raw Material:
The easy availability of raw materials is an important factor that affects the location of the industry. In the early days industries in India developed near the sources of raw material. For instance, the textile mills of Bombay (now Mumbai) had supply of cotton coming from Gujarat and Vidarbha and the jute mills of Hooghly region got the raw material from the delta region of the Ganga. The nature of raw material also has a bearing on the location.
(ii) Energy:
Energy is another important factor that affects the location of an industry. For example, the iron and steel industry has been traditionally tied with the coal resources, as it uses coal as cooking fuel. Similarly, the electro-metallurgical and electro-chemical industries, being power intensive, have been located where electricity is easily available.
![]()
(iii) TrAnswer:ort:
A cheap and effective trAnswer:ort system is another factor that determines the location of an industry. TrAnswer:ort is required for carrying raw materials to manufacturing units and finished products to the market. The earliest industries developed near the port towns of Kolkata, Mumbai and Chennai, since these ports were linked with rail and road to the hinterland. This infrastructure for trAnswer:ort was further developed after independence.
(iv) Labour:
Easy availability of cheap labour is another factor for the determination of the location of an industry. Unskilled labour is easily available in urban locations due to large rural-urban migration. One characteristic feature of the labour factor is its mobility. The industrial belt around Mumbai attracts labour from all over the country. Some of the small-scale industries, traditionally associated with labour are glasswork (Firozabad), brass-work (Moradabad), utensils (Yamunanagar in Haryana), silk sarees (Varanasi), carpets (Mirzapur), etc.
(v) Market:
High demand and satisfactory purchasing power give impetus to industrial development. Government policies facilitate expAnswer:on of the market and, thus, of the industry. Markets may be local, national or international.
Question 33.
Discuss the achievements of Grameen Bank of Bangladesh.
OR
What are the reasons why the banks might not be willing to lend to certain borrowers?
Answer:
Achievements of Grameen Bank of Bangladesh:
(i) Grameen Bank of Bangladesh is one of the rural banks in the world which is successfully meeting the credit needs of the poor at reasonable rates.
(ii) Grameen bank was launched as a small project during 1970s but in 2018 it had more than 9 million members in about 81,600 villages spread throughout the Bangladesh.
(iii) Women coming from the poorest sections of the society constitute the largest borrowers of the banks.
(iv) Success of this bank proved that poor women are reliable borrowers as well as they can start and run a variety of small income-generating activities successfully. Whereby socially weaker sections and women are represented in the legislatures and administration. This type of arrangement is meant to give space in the government and administration to diverse social groups who otherwise would feel alienated from the government. This method is used to give minority communities a fair share in power.
OR
The banks might not be willing to lend to certain borrowers due to the following reasons:
- The borrower might not have proper guarantee or collateral.
- The previous track record of the borrower regarding loan repayment is not good.
- The purpose for which the borrower wants to take loan involves very high risks or uncertainty and the bank has the doubt of getting its loan back.
- The bank is not satisfied with the purpose for which the borrower is taking the loan.
- The borrower is not able to present a proper project report showing convincing returns on investment.
- If the amount of the loan is very high which the bank is not willing to lend to a single borrower.
- The RBI has put restrictions on the bank to lend to certain category of borrowers.
Section – E
(Case-Based Questions)
Question 34.
Read the source given below and Answer:er the questions that follows:
The earliest factories in England came up by the 1730s. But it was only in the late eighteenth century that the number of factories multiplied. The first symbol of the new era was cotton. Its production boomed in the late nineteenth century. In 1760, Britain was importing 2.5 million pounds of raw cotton to feed its cotton industry. By 1787, this import soared to 22 million pounds. This increase was linked to a number of changes within the process of production. Let us look briefly at some of these.
A series of inventions in the eighteenth century increased the efficacy of each step of the production process (carding, twisting and spinning, and rolling). They enhanced the output per worker, enabling each worker to produce more, and they made possible the production of stronger threads and yam. Then Richard Arkwright created the cotton mill. Till this time, as you have seen, cloth production was spread all over the countryside and carried out within village households. But now, the costly new machines could be purchased, set up and maintained in the mill.
(i) When did the industrial revolution begin in Britain?
Answer:
The industrial revolution began in Britain during the late eighteenth century when the factories got multiplied suddenly.
(ii) How the import of cotton increased in Britain during the 1760 to 1787?
Answer: The import of cotton increased tremendously in Britain during this period. In the year 1760, Britain was importing nearly 2.5 million pounds of raw cotton which increased tremendously to 22 million pounds in 1787 as industrialisation began in Britain.
(iii) What were some of the processes involved in the production of textiles?
Answer:
Some of the steps involved in the production of the textiles were carding, twisting, spinning and rolling. These processes were automated by the improvements in the technology. One of the most important inventions was the cotton mill which was developed by Richard Arkwright.
Question 35.
Read the given extract and Answer:er the following questions.
In June 1992, more than 100 heads of states met in Rio de Janeiro in Brazil, for the first International Earth Summit. The Summit was convened for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socio-economic development at the global level. The assembled leaders signed the Declaration on Global Climatic Change and Biological Diversity. The Rio Convention endorsed the global Forest Principles and adopted Agenda 21 for achieving Sustainable Development in the 21st century.
It is the declaration signed by world leaders in 1992 at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), which took place at Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It aims at achieving global sustainable development. It is an agenda to combat environmental damage, poverty, disease through global co-operation on common interests, mutual needs and shared responsibilities. One major objective of the Agenda 21 is that every local government should draw its own local Agenda 21.
1. When and where was the first International Earth Summit held?
Answer:
It was held from 3 June to 14 June, 1992 in Rio de Janeiro in Brazil.
2. Analyse the reason for adopting Agenda 21 for achieving Sustainable Development in the 21st century.
Answer:
The reason for adopting Agenda 21 was to fight environmental damage, poverty, disease through global
cooperation on common interests, mutual needs and shared responsibilities.
3. Mention the aims of United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), which took place at Rio de Janeiro.
Answer:
(i) To address urgent problems of environmental protection and socio-economic development at the global level.
(ii) To achieve global sustainable development.
![]()
Question 36.
Read the given extract and Answer:er the following questions.
Boys and girls are brought up to believe that the main responsibility of women is housework and bringing up children. This is reflected in a Sexual Division of Labour in most families; women do all work inside the home such as cooking, cleaning, washing clothes, tailoring, looking after children, etc., and men do all the work outside the home. It is not that men cannot do housework they simply think that it is for women to attend to these things.
When these jobs are paid for, men are ready to take up these works, Most tailors or cooks in hotels are men. Similarly, it is not that women do not work outside their home. In villages, women fetch water, collect fuel and work in fields. In urban areas, poor women work as domestic helper in middle class homes, while middle class women work in offices. In fact the majority of women do some sort of paid work in addition to domestic labour. But their work is not valued and does not get recognition.
1.”Our society is still male-dominated patriarchal society”. Give an example to support the statement.
Answer:
In India, the literacy rate among women is only 54% compared to 76% among men. A smaller proportion of girl students go for higher education. This is because parents prefer to spend their resources for their boys’ education rather than spending equally on their sons and daughters.
2. Mention any one feature of a patriarchal society.
Answer:
In many parts of India, parents prefer to have sons and find ways to have the girl child aborted before she is bom. Such sex-selective abortion is an example of patriarchal society.
3. How does the Indian Constitution ensure equal representation for women?
Answer:
(i) The Equal Wages Act provides that equal wages should be paid to equal work.
(ii) One-third of seats in local government bodies – in panchayats and municipalities are reserved for women.
Section – F
(MAP Skill-Based Question)
Question 37.
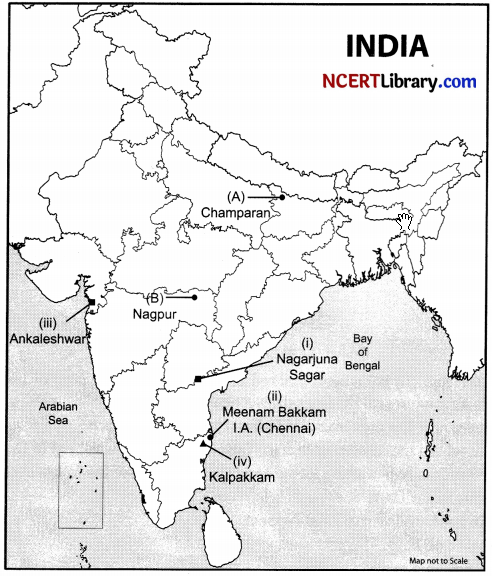
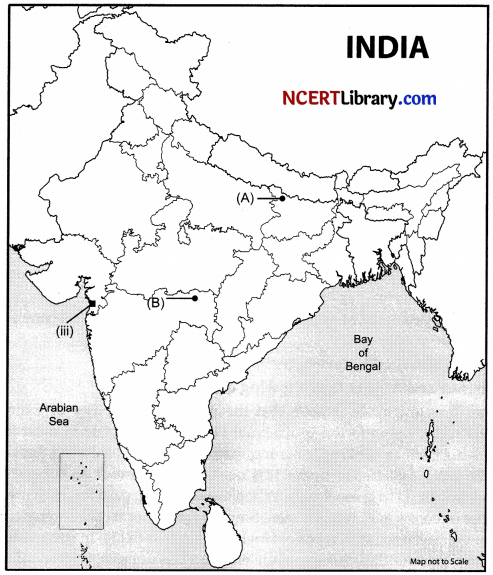
(a) Two places (A) and (B) have been marked on the given outline map of India. Identify them and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them:
(A) The place where the movement of Indigo Planters took place.
(B) The place where the session of Indian National Congress was held in December 1920.
(b) On the same outline map of India locate and label any three of the following with suitable symbols:
(i) Nagarjuna Sagar Dam.
(ii) Meenam Bakkam International Airport.
(iii) Identify the oil field.
(iv) Kalpakkam Nuclear Power Plant.
Answer: