Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions Set 6 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 6 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- Question paper comprises Six Sections -A, B, C, D, E, and F. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From question 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Question no. 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words.
- Section C – contains Q.25 to Q.29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words
- Section D – Question no. 30 to 33 are long answer-type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section E – Questions no from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map-based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A
(Multiple Choice Questions) 1 × 20 = 20
Questions 1.
Which of the following incidents was the reason to stop the Non- Cooperation Movement?
(a) Violent clash of Chauri-Chaura.
(b) Jallianwala Bagh Massacre.
(c) Assault by the British police during the demonstration against the Simon Commission.
(d) Attack by Gudem rebels.
Answer:
(a) Violent clash of Chauri-Chaura.
![]()
Questions 2.
Germany was unified by:
(a) The military actions
(b) Revolutionary upsurge
(c) Peasants uprising
(d) Liberals revolution
Answer:
(a) The military actions
Questions 3.
Look at the picture given below and answer the question that follows.
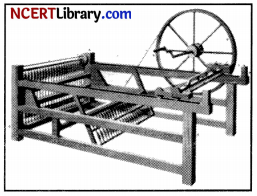
What is the name of this machine and who invented it?
(a) Weaving machine by Charles
(c) Cotton Gin by Eli Whitney
(b) Flying shuttle by John key
(d) Spinning Jenny by James Hargreaves
Answer:
(a) Weaving machine by Charles
Questions 4.
Arrange the following in chronological order:
I. The T- Model Ford was the world’s first mass-produced car.
II. China became an attractive destination for investment by foreign MNCs competing to capture world markets.
III. During the Great Depression, agricultural regions and communities were the worst affected.
IV. The Second World War caused an immense amount of economic devastation and social disruption.
Options:
(a) I, II, III, IV
(b) IV, I, II, III
(c) III, IV, II, I
(d) I, III, IV, II
Answer:
(d) I, III, IV, II
Questions 5.
Identify the crop with the help of the following information:
- It is the second most important cereal crop.
- It is rabi crop which requires a cool growing season and bright sunshine at the time of ripening.
- It requires 50 to 75 cm of annual rainfall evenly distributed over the growing season.
- It grows best in a well-drained loamy soil.
Options:
(a) Wheat
(b) Ragi
(c) Rice
(d) Gram
Answer:
(a) Wheat
Questions 6.
Which one of the following types of resources is iron ore?
(a) Renewable
(b) Flow
(c) Biotic
Answer:
(d) Non-renewable
Questions 7.
Match the following:
| Common Names | Botanical Names |
| A. Mango | I. Bassia latifolia |
| B. Kadamba | II. Mangifera indica |
| C. Tamarind | III. Anthocaphalus cadamba |
| D. Mahua | IV. Tamarindus indica |
Options:
(a) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(b) A-H, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(d) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
Answer:
(b) A-n, B-III, C-IV, D-I
Questions 8.
Consider the following statements regarding democracy and identify the incorrect one from the following:
(a) It brings improvement in the quality of decision-making.
(b) It provides room to correct mistakes.
(c) It respects public opinion.
(d) Decision-making is much faster and quicker.
Answer:
(d) Decision-making is much faster and quicker.
Questions 9.
Which community was relatively rich and powerful in Belgium?
(a) Dutch-speaking community
(c) French-speaking community
(b) English-speaking community
(d) German-speaking community
Answer:
(c) French-speaking community
Questions 10.
What is a major problem associated with coalition government?
(a) Formation of coalition government with regional powers.
(b) Problems to keep satisfied coalition partners in the government.
(c) Formation of coalition governments with small parties.
(d) Formation of coalition government with opposite ideological parties.
Answer:
(b) Problems to keep satisfied coalition partners in the government.
![]()
Questions 11.
Which one among the following pairs is correctly matched?
| List-I | List-II |
| (a) Metals | International resource |
| (b) Pasture lands | Community owned resource |
| (c) Wind energy | Renewable resource |
| (d) Village ponds | Abiotic resource |
Answer:
(c) Wind energy – Renewable resource
Questions 12.
In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): Not the entire service sector is growing equally well.
Reason (R): Services that employ highly skilled and educated workers are not producing more.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Answer:
(c) A is true, but R is false.
Questions 13.
Which among the following gives recognition to the political parties in India?
(a) Election Commission
(c) Parliament
(b) Reserve Bank of India
(d) Supreme Court
Answer:
(a) Election Commission
Questions 14.
Read the given data and find out which sector has maximum contribution in GDP?
| Year | Primary (Rupees) | Secondary (Rupees) | Tertiary (Rupees) |
| 2000 | 56,000 | 49,000 | 1,33,500 |
| 2013 | 8,20,500 | 11,74,500 | 38,68,000 |
(a) Primary Sector
(c) Tertiary Sector
(b) Secondary Sector
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Tertiary Sector
Questions 15.
Which of the following options best describes the ‘Globalisation’?
(a) The process of removing international borders by countries.
(b) The process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries.
(c) The process of abolishing own governments and letting United nation govern.
(d) The process of abolishing own currency and adopting dollar as only recognised currency.
Answer:
(b) The process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries.
Questions 16.
Find the odd one out from the following:
(a) Human beings, Flora and fauna, Fisheries, Livestock
(b) Solar energy, Wind energy, Water, Forests
(c) Houses, Plots, Burial grounds, Pasture lands
(d) Land, Salt, Rocks, Metals
Answer:
(c) Houses, Plots, Burial grounds, Pasture lands
Questions 17.
Fill in the blank:
| Company | Manufactured Item |
| Ford Motors | Automobiles |
| Cargill Foods | ? |
Options:
(a) Medicines
(b) Edible oil
(c) Chocolates
(d) Biscuits
Answer:
(b) Edible oil
Questions 18.
Ajay lives in Sadhupur, a village in India. Ajay has taken a loan for farming. The loan provider charges a low interest which cannot create burden on Ajay. All the activities of loan provider are monitored by RBI. RBI sees that the lender does not give loan only to businessmen or only to earn profit. If it fails to follow the norms it is penalised. Also lender has to submit a periodically report to RBI. Analyse the information given above, considering one of the following correct option:
(a) Cooperative society
(c) Commercial bank
(b) Money lender
(d) Traders
Answer:
(c) Commercial bank
![]()
Questions 19.
Which of the following cannot be used as collateral?
(a) Land titles
(c) God own taken on rent
(b) Deposits with banks
(d) Livestock
Answer:
(d) Livestock
Questions 20.
Identify the correct statement/s about Self Help Group (SHG):
I. A typical SHG has 25-30 members, usually belonging to one neighbourhood, who meet and save
regularly.
II. Saving per member varies from Rs 25 to Rs 100 or more, depending on the ability of the people to save.
III. Members can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs.
IV. The SHG helps borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
Options:
(a) I & II (b) I & 111
(c) HT & ¡V
(d) II, Ill & IV
Answer:
(d) 11, Ill & IV
Section – B
(Very Short Answer-Based Questions)
Questions 21.
Who brought the technology of woodblock printing to Europe? Who bought the woodblock printed books?
Answer:
In 1295, Marco Polo, a great Italian explorer, brought this technology from China to Italy. Soon this technology spread to other parts of Europe. Merchants and students in the university towns bought these cheaper printed books.
Questions 22.
Mention any two constitutional provisions that make India a secular state.
Answer:
The following constitutional provisions make India a secular state:
- There is no official religion for the indian state.
- The Constitution prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion.
Questions 23.
Analyze any two factors that were responsible for increasing the feeling of alienation among the Sri
Lankan Tamils.
OR
Distinguish between community government in Belgium and majoritarian government in Sri Lanka.
Answer:
- In 1956, Sinhala was recognised as the only official language in Sri Lanka.
- The governments followed preferential policies that favoured Sinhala applicants for university positions and government jobs.
OR
| Community Government in Belgium | Majoritarian Government in Sri Lanka |
| (i) The Belgian leaders adopted a policy of power sharing. | The Sri Lankan leaders adopted a policy of maj oritar ianism. |
| (ii) They gave equal powers to all communities no matter whether they are in majority or minority. | They gave preferences to the majority Sinhala community alone, thus disregarding the minority Tamil community. |
Questions 24.
Mention any two features of unorganized sector.
Answer:
- This sector is characterized by small and scattered units which are largely outside the control of the government
- There is no job security for workers.
- There is no provision for overtime, paid leave, holidays, leave due to sickness, etc. (Any two)
Section – C
(Short Answer-Based Questions)
Questions 25.
What is most important attributes for comparing countries and why?
OR
What is Human Development Report? Discuss its emergence.
Answer:
The most important attributes for comparing countries are:
(i) The income of the countries is considered to be one of the most important attributes for their
comparison.
(ii) Generally, countries which have higher income are considered more developed than the countries
which have less income.
(iii) This is based on the understanding that more income provides more of all things that human beings
need. People will be able to get whatever they required and want with greater income. That’s why
greater income itself is considered to be one important goal.
Emergency of Human Development Report:
When it is realised that the level of income alone is not able to reflect the true picture of the development of a country, other parameters on which development could be measured began to develop. A long list such criterion was thought but only small number of the most important things were selected which included health and education indicators. Over the past decade or so, health and education indicators have come to be widely used along with income as a measure of development. Human Development Report is one which uses these indicators.
OR
Human Development Report: Human Development Report is annual report which compares countries based on the educational levels of the people, their health status and per capita income. It is published by United Nations Development Programme.
![]()
Questions 26.
Analyse the various measures and practices introduced by the French revolutionaries that created a sense of collective identity amongst the French people.
Answer:
Following are the measures and practices introduced by the French revolutionaries that created a sense of collective identity amongst the French people:
- Equal rights were provided to all under the constitution and the ideas of la patrie (the fatherland) and le citoyen (the citizen) were promoted to represent all French as a united community.
- The former flag i.e., Royal standard flag was replaced with the new French flag, the tricolor.
- The Estates General was made an elected body by the active citizens and renamed as the National Assembly.
- New hymns were composed, oaths taken and martyrs commemorated, all in the name of the nation.
- A centralized administrative system was introduced. Uniform laws were formulated for all citizens within its territory. Internal customs duties and dues were abolished and a uniform system of weights and measures was adopted.
- French which was spoken and written in Paris selected as the common language of the nation and regional dialects were discouraged to use. (Any three)
Questions 27.
Differentiate between the unitary government and federal government?
Answer:
| Unitary Government | Federal Government |
| (i) In this system, there must be a Central government. State governments may or may not exist. | In this system, there must be a Central government and State governments. The third tier of government i.e., local government may or may not exist. |
| (ii) If the State government exists, it will be subordinate to the Central government and answerable to it. | State governments are not subordinate to the Central government. They are answerable to people. |
| (iii) Powers are not divided by the constitution. The central government allows State governments to administer on selected subjects. | Powers are divided by the constitution. They have separate powers independent to each others. |
| (iv) Central government can give orders to State government and its orders should be followed. | The central government cannot give orders to State government but if they do then, they have, no compulsion to follow it. |
Questions 28.
Discuss the various efforts made at international level for the conservation of natural resources.
Answer:
Efforts made at international level for the conservation of natural resources are as follows:
(i) The first effort at international level was made in 1968 with the Club of Rome which promoted resource conservation in a more systematic way. Then, in 1974, Schumacher in his book ‘Small is Beautiful’ argued about resource conservation in Gandhian philosophy.
(ii) The Brundtland Commission Report, 1987 made an influential contribution in resource conservation at the global level. The concept of ‘Sustainable Development was introduced by this report and promoted it as a way for resource conservation. After that, it was published in a book entitled ‘Our Common Future’.
(iii) The Earth Summit at Rio-de-Janeiro, Brazil in 1992 was another major contribution with respect to resource conservation.
Questions 29.
Why is credit taken in rural areas?
Answer:
In rural areas, credit is taken mainly for agricultural activities and crop production.
- Money is needed to buy high-cost seeds, fertilisers, pesticides, to pay water and electricity bills and to repair equipment etc.
- There is a long period of minimum three to four months between the procurement of these inputs by farmers and selling of the crop.
- Farmers usually take crop loans at the beginning of the season and repay the loan after harvest. The income from farming is an important determinant for repayment of the loan.
Section – D
(Long Answer-Based Questions)
Questions 30.
Why was there a conflict between the Sinhala and Tamils?
OR
Discuss the arrangements made under the Constitution of Belgium to solve the problem of community conflict.
Answer:
(i) After emerging of Sri Lanka as an independent country in 1948, the leaders of the Sinhala community looked to secure dominance over government because of their majority. Soon, a series of majoritarian measures were adopted by the democratically elected government to establish the supremacy of Sinhala.
(ii) With an Act passed by the Sri Lankan Parliament in 1956, Sinhala was recognized as the only official language ignoring Tamil. Also, the preferential policies followed by the Sri Lankan government used to favour Sinhala applicants for university positions and government jobs.
(iii) Protecting and promoting Buddhism was made the duty of state by the new constitution. As the government had adopted these measures step by step, the feeling of alienation among the Sri Lankan Tamils increased.
(iv) Tamils were begun to believe that all the major political parties led by the Buddhist Sinhala leaders were not sensitive to their language and culture.
(v) They felt that the constitution and government policies were not giving them equal political rights, discriminated against them in getting jobs and other opportunities and ignored their interests. Due to these, the relations between the Sinhala and Tamil communities spoiled over time.
OR
Following were the arrangements made under the constitution of Belgium to solve the problem of community conflict.
(i) According to the constitution, central government shall have the equal numbers of Dutch and French-speaking ministers.
(ii) Some special laws can only be passed with the support of majority of members from each linguistic group. These provisions ensure that no single community can make decisions unilaterally.
(iii) Many powers of the central government have been given to state governments of the two regions of the country. The state governments are not subordinate to the central government.
(iv) There is a separate government in Brussels in which both the communities have equal representation. Despite being majority community in Brussels, the French-speaking people accepted equal representation in government because the Dutch-speaking community has accepted equal representation in the central government in spite of being majority community in all over the country.
(v) Besides the Central and the State government, there is a third kind of government also i.e., Community government. It is elected by people belonging to one language viz., Dutch, French and German-speaking community irrespective of their living area. Community governments have the power regarding cultural, educational and language-related issues.
![]()
Questions 31.
How did Non-Cooperation Movement start with participation of middle class people in the city? Explain its impact on the economic front.
OR
How did the Colonial Government repress the ‘Civil Disobedience Movement? Explain.
Answer:
The Non-Cooperation Movement was launched on August 1920 by the Congress.
- Thousands of students, headmasters left the government schools and colleges and lawyers gave up their legal practices in courts.
- The Council Elections were boycotted in all provinces except Madras.
- The effects of non-cooperation on the economic front were more dramatic.
- Liquor shops were picketed and foreign cloths were burnt in large bonfires.
- The import of foreign cloth reduced to half between 1921 and 1922.
- A large number of places, merchants, peasants and traders refused completely to trade in foreign goods or finance foreign trade.
- Boycott movement spread like a fire and the people were aware of this movement.
- People started discarding imported clothes and wearing only Indian ones due to which production of Indian textile mill and handlooms went up.
- The Non-Cooperation Movement helped to boost the Indian economy.
OR
The ‘Civil Disobedience Movement’ initiated the boycott of foreign clothes and picketed liquor shops. Peasants showed their reluctance in paying revenues and taxes. At the same time, village officials resigned. The Colonial Government prevented the members from participating in national movements.
(i) In many places, forest people transgressed forest laws and prevented people from entering the reserved forests and grazing cattle. Enraged by the development, the colonial government started detaining the Congress leader one by one. This resulted in the outbreak of violent clashes in various places.
(ii) Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan, a staunch disciple of Mahatma Gandhi, was detained in April 1930. Various people were assassinated who protested the movement.
(iii) Mahatma Gandhi was detained. Industrial workers of Sholapur captured police post, municipal buildings and railway stations.
(iv) Being frightened by these developments, the British Government adopted a policy of brutal repression. The government adopted a policy of brutal repression.
(v) Peaceful demonstrators were attacked. Women and children were mercilessly beaten and about 1,00,000 people were detained.
Questions 32.
How are manufacturing industry classified on basis of capital investment, ownership and bulk, weight of raw material and finished goods?
OR
How industries contribute to the national economy of the country?
Answer:
Manufacturing industry are classified on basis of capital investment, ownership and bulk, weight of raw material and finished goods:
(i) On the basis of capital investment:
(a) Small-scale industries: These industries come under the maximum investment allowed on the assets of a unit bv the government. This investment limit keeps changing over a period of time. At present the maximum investment allowed is rupees one crore.
(b) Large scale industries: Industries having investment beyond the number of rupees one crore are considered to be a large scale industry for example, iron and steel industry.
(ii) On the basis of ownership:
(a) Public sector industries: These industries are owned and operated by government agencies e.g., BHEL, SAIL etc.
(b) Private sector industries: These industries are owned and operated by individuals or a group of individuals e.g., TISCO, Bajaj Auto Ltd., Dabur Industries.
(c) Joint sector industries: These industries are jointly run by the state and individuals or a group of individuals e.g., Oil India Ltd. (OIL) is jointly owned by public and private sector.
(d) Cooperative sector industries: These industries are owned and operated by the producers or suppliers of raw materials, workers or both. They collectively arrange resources and share the profits or losses proportionately e.g., the sugar industry in Maharashtra, the coir industry in Kerala.
(iii) Based on the bulk and weight of raw material and finished goods:
(a) Heavy industries: These industries manufacture bulky products e.g., iron and steel.
(b) Light industries: These industries use light raw materials and produce light goods, e.g., electrical goods industries.
OR
Contribution of industries to the national economy:
- Industries involve the production of goods and services. This has brought about substantial increase in the GDP of the country.
- Industries improve the living condition of people and also help in poverty eradication by providing employment.
- The industrial sector enhances the country’s growth and also offers a wide variety of choices to consumers.
- Manufactured goods are exported to other nations, thereby adding to the country’s foreign exchange.
- Industries also contribute significantly in improving the country’s infrastructure in various sectors and help in all-round development of the nation.
Questions 33.
Why are better public facilities needed for the development of the country?
Explain four public facilities.
OR
What does HDI stand for? Explain the main criteria of measuring HDI according to the UNDP Report of 1990.
Answer:
Public facilities are the facilities provided by the government either free of cost or at very low price for the welfare of people. Development of a country depends upon various facilities which are affordable when provided collectively by the state. Following are some of the public facilities required for development:
(i) Public Distribution System: Public Distribution System of a country distributes food articles to the people of a country. The better the PDS works, the better fed are the people of the country and the nutritional level of the people of the country also improves which ultimately contributes to the development of the country.
(ii) Education Facilities: Educated people are the base of any kind of development. It is the established fact that most developed countries are the most educated countries and the countries with high level of education have high rate of development.
(iii) Health Facilities: A person can contribute towards any development only when he is healthy. A person’s health is dependent upon the quality of food and the medical facilities available in the country. So the country’s medical system and food distribution needs to be very strong and effective so that the benefits of these facilities must reach to the last person.
![]()
(iv) Transportation and Communication: Transportation provides the mobility of resources from one part of the country to the other parts where they are more required. Communication helps in the timely flow of information. This mobility of resources and information is very much required for the balanced development of the country.
(v) Security: Development takes place only in a secure environment. So, a country’s internal and external security is very much required for the development of a country.
OR
HDI stands for Human Development Index. The main criteria of measuring HDI (Human Development Index) according to UNDP report of 1990 can be explained as follows :
- UNDP published HDI to compare different countries based on educational level, health status of the people and per capita income of the country.
- It (HDI) determines the rank of a country in three areas i.e., life expectancy, educational level and per capita income.
- Improvements has been suggested in calculating HDI.
- Now it is clear that what is important for development is all about health and well being of the people.
Section – E
(Case-Based Questions)
Questions 34.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows:
The Portuguese and Spanish conquest and colonisation of America was decisively under way by the mid-sixteenth century. European conquest was not just a result of superior firepower. In fact, the most powerful weapon of the Spanish conquerors was not a conventional military weapon at all. It was the germs such as those of smallpox that they carried on their person. Because of their long isolation, America’s original inhabitants had no immunity against these diseases that came from Europe. Smallpox in particular proved a deadly killer. Once introduced, it spread deep into the continent, ahead even of any Europeans reaching there. It killed and decimated whole communities, paving the way for conquest.
1. Which two nations were the earliest colonisers in America?
Answer:
Portugal and Spain were the earliest nations that colonised America around mid-sixteenth century.
2. What were some of the reasons due to which the colonisers easily established their control over several parts of America?
Answer:
The colonisers had superior firepower, military weapons and many advanced materials. But their most important weapon proved to be smallpox.
3. How smallpox turned into death of native people of America?
Answer:
The Spanish conquerors transmitted the disease of smallpox to a large number of the native people in America which spread rapidly in the continent. The native people did not have immunity towards this disease and due to which there was death of thousands of people because of this disease. It led to the eradication of number of communities and made the colonization easier.
Questions 35.
Read the given extract and answer the following questions.
Mahatma Gandhi declared Vinoba Bhave as his spiritual heir. He also participated in Satyagraha as one of the foremost satyagrahis. He was one of the votaries of Gandhi’s concept of gram swarajya. After Gandhiji’s martyrdom, Vinoba Bhave undertook padyatra to spread Gandhiji’s message covered almost the entire country. Once, when he was delivering a lecture at Pochampalli in Andhra Pradesh, some poor landless villagers demanded some land for their economic well-being.
Vinoba Bhave could not promise it to them immediately but assured them to talk to the Government of India regarding provision of land for them if they undertook cooperative farming. Suddenly, Shri Ram Chandra Reddy stood up and offered 80 acres of land to be distributed among 80 land-less villagers. This act was known as ‘Bhoodan’. Later he travelled and introduced his ideas widely all over India. Some zamindars, owners of many villages offered to distribute some villages among the landless. It was known as Gramdan. However, many land-owners chose to provide some part of their land to the poor farmers due to the fear of land ceiling act. This Bhoodan-Gramdan movement initiated by Vinoba Bhave is also known as the Blood-less Revolution.
1. With what objective ‘Padyatra’ was started by Vinoba Bhave?
Answer:
It was started to spread Gandhiji’s message of gram swarajya in the entire country.
2. What is meant by Land Ceiling Act?
Answer:
This Act states that a person will hold the maximum area limit of the land. If a person holding more than the maximum limit that land was taken away from him/her by the Government of India.
3. Analyse the reasons why Bhoodan-Gramdan movement is also known as the Bloodless Revolution.
Answer:
- There was no scope for violence in any form or at any level.
- Many zamindars and land-owners donated their lands or villages voluntarily.
Questions 36.
Read the given extract and answer the following questions.
Political parties are easily one of the most visible institutions in a democracy. For most ordinary citizens, democracy is equal to political parties. If you travel to remote parts of our country and speak to the less educated citizens, you could come across people who may not know anything about our Constitution or about the nature of our government. But chances are that they would know something about our political parties. At the same time this visibility does not mean popularity. Most people tend to be very critical of political parties. They tend to blame parties for all that is wrong with our democracy and our political life. Parties have become identified with social and political divisions.
1. What are the three main components of a political party?
Answer:
The three main components of a political party are :
- The leaders
- The active members
- The followers
2. Who is partisan?
Answer:
A person who is strongly committed to a party. A partisan person always take side of a group and is unable to give a balanced view.
![]()
3. Explain one merit and one demerit of the opposition party.
Answer:
Merit- It voices different views and criticises government for its failures or wrong policies. Demerit- In many cases, opposition party tends to hinder the work of ruling party which can led to delay in important decision-making.
Section – F
(MAP Skill-Based Questions)
Questions 37.
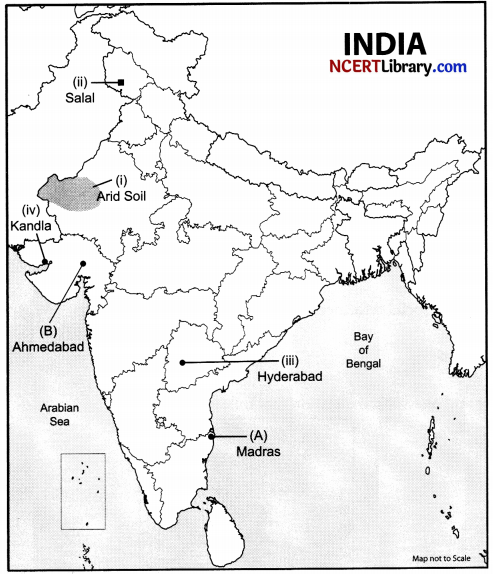
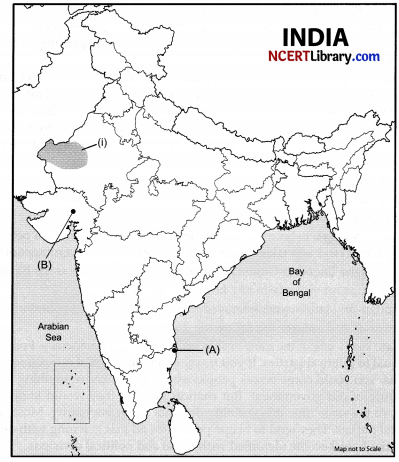
(a) Two places (A) and (B) have been marked on the given outline map of India. Identify them and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them:
A. Indian National Congress session at this place in 1927.
B. The place where Cotton Mill Workers organised Satyagraha.
(b) On the same outline map of India locate and label any three of the following with suitable symbols:
- Identify the soil type.
- Salal Dam.
- Hyderabad Software Technology Park.
- Kandla Port.
Answer: