Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions Set 5 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 5 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- Question paper comprises Six Sections -A, B, C, D, E, and F. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From question 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Question no. 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words.
- Section C – contains Q.25 to Q.29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words
- Section D – Question no. 30 to 33 are long answer-type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section E – Questions no from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map-based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A
(Multiple Choice Questions) 1 × 20 = 20
Question 1.
Where did Mahatma Gandhi make salt out of the seawater?
(a) Sabarmati
(b) Champaran
(c) Dandi
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Dandi
![]()
Question 2.
Which of the following social reformers fought against caste system?
(a) Jyotiba Phule
(c) B. R. Ambedkar
(b) Mahatma Gandhi
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 3.
Study the picture and answer the question that follows:
Which of the following options best depicts the above image?

(a) Female working for food
(c) The Irish potato famine
(b) Child labor
(d) Poverty in Europe
Answer:
(c) The Irish potato famine
Question 4.
Arrange the following in chronological order:
I. The IMF and the World Bank started their financial operations.
II. The US became a colonial power by taking over some colonies which earlier held by Spain.
III. Due to the efforts of Indian nationalist leaders, the system of indentured labour was abolished.
IV. The big European powers met in Berlin to complete the carving up of Africa between them.
Options:
(a) I, III, IV, II
(b) II, IV, III, I
(c) IV, II, III, I
(d) I, II, III, IV
Answer:
(c) IV, II, III, I
Question 5.
Identify the crop with the help of the following information:
- It is a tropical as well as a subtropical crop.
- It grows well in hot and humid climate with a temperature of 21 °C to 27°C.
- It can be grown on a variety of soils needs manual labour from sowing to harvesting.
- India is the second largest producer of this crop only after Brazil.
Options:
(a) Coffee
(b) Tea
(c) Rice
(d) Sugarcane
Answer:
(d) Sugarcane
Question 6.
Which subjects are included in the Concurrent List?
(a) National Importance
(c) Both national and state importance
(b) State importance
(d) Local Importance
Answer:
(c) Both national and state importance
Question 7.
Match the following:
| Dams | Rivers |
| A. Nagarjuna Sagar | I. Kaveri |
| B. Mettur | II. Damodar |
| C. Bhakra Nangal | III. Krishna |
| D. Panchet | IV. Satluj |
Options:
(a) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(c) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
(b) A-II, B-iII, C-IV, D-I
(d) A-III, B-L C-IV, D-II
Answer:
(d) A-III. B-I, C-IV, D-II
Question 8.
Consider the following statements regarding caste in politics and identify the incorrect one from the following:
(a) Caste in politics always produces positive results.
(b) Caste factor played important role in the formation of Central Government.
(c) Social reformers and laws have played important role to reduce casteism.
(d) Routes of casteism are visible in our society from ancient time.
Answer:
(a) Caste in politics always produces positive results.
Question 9.
Which among the following is the correct meaning of ‘Alliance’?
(a) Two parties together form the government.
(b) Leftists and Rightists together form the government.
(c) When state and national parties together form the government.
(d) When several parties in a multi-party system join for the purpose of contesting elections and
winning power.
Answer:
(d) When several parties in a multi-party system join for the purpose of contesting elections and
winning power.
Question 10.
‘Coming together federation’ is not found in which of the following country?
(a) India
(b) U.S.A.
(c) Switzerland
(d) Australia
Answer:
(a) India
![]()
Question 11.
Which one among the following pairs is correctly matched?
| List-I | List-II |
| (a) January 1921 | Labore Congress Session |
| (b) December 1929 | Second Round Table Conference |
| (c) March 1930 | SaIt March |
| (d) December 1931 | Khilafat Movement |
(c) March 1930-Salt March
In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the
statements and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): Workers in organized sectors enjoy security of employment.
Reason (R): Organised sector is registered by the government and have to follow the rules and regulations
which are given in laws such as Factories Act, and Minimum Wages Act.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 13.
Which of the following are the main components of a political party?
(a) Leaders
(c) Active members
(b) Followers
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 14.
Arrange the following in the correct sequence:
(i) Transporting paper to factory
(iii) Printing of pages
(ii) Sale of books in bookstore
(iv) Compilation of pages
Options:
(a) (iv), (iii), (i), (ii)
(b) (i), (iii), (iv), (ii)
(c) (ii), (i), (iii), (iv)
(d) (iii), (ii), (iv), (i)
Answer:
(b) (i), (iii), (iv), (ii)
Question 15.
Which of the following belongs to taking loan from an organized sector?
(a) Bank
(c) Local money lenders
(b) Relatives
(d) Friends
Answer:
(a) Bank
Question 16.
Find the odd one out from the following:
(a) Iron ore, Manganese, Nickel, Cobalt
(c) Gold, Silver, Iridium, Platinum
(b) Copper, Lead, Tin, Bauxite
(d) Coal, Petroleum, Limestone, Natural gas
Answer:
(d) Coal, Petroleum, Limestone, Natural gas
Question 17.
Fill in the blank:
| Sector | Related Economic Activity |
| Tertiary | Banking |
| Primary | ? |
Options:
(a) Fishing
(b) Weaving
(c) Teaching
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Fishing
Question 18.
Shivangi took a loan of? 9 lakhs from the bank to purchase a car. The annual interest rate on the loan is 12.5 percent and the loan is to be repaid in 4 years in monthly installments. The bank retained the papers of the new car as collateral, which will be returned to Rita only when she repays the entire loan with interest. Analyze the loan information given above, considering one of the following correct options:
(a) Interest on loan
(c) Mode of repayment
(b) Deposit criteria
(d) Terms of credit
Answer:
(d) Terms of credit
Question 19.
Which of the following department measures the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country?
(a) Central Government
(c) Department of Income Affairs
(b) Department of External Affairs
(d) World Trade Organisation (WTO)
Answer:
(a) Central Government
Question 20.
Identify the correct statement/s about Multinational Corporation (MNC):
I. A Multinational Corporation (MNC) is a company that owns or controls production in more than one nation.
II. It sets up offices and factories for production in regions where it can get cheap labour and other resources.
III. In addition, it might look for government policies that look after its interests.
IV. Infosys is an Indian MNC that provides business consulting, information technology and outsourcing services.
Options:
(a) I & II
(b) I & III
(c) III & IV
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Section – B
(Very Short Answer-Based Questions)
Question 21.
Give two examples from history to show the impact of technology on food availability.
Answer:
In the late 19th century, the impact of technology on food availability was multifarious.
- Faster railways, lighter wagons and larger ships helped move food more cheaply and quickly from faraway farms to final markets.
- Refrigerated ships enabled the transport of perishable foods over long distances.
![]()
Question 22.
What is federalism? Explain with an example.
Answer:
Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government. For example, in India, the jurisdictions of the respective levels of government are specified in the Constitution.
Question 23.
Differentiate between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals.
OR
Differentiate between conventional and non-conventional sources of energy.
Answer:
| Ferrous Minerals | Non-Ferrous Minerals |
| (i) These minerals have iron content. | (i) These minerals do not have iron content. |
| (ii) For example, iron ore, manganese. cobalt, etc. | (ii) For example, copper, lead, bauxite, etc. |
OR
| Conventional Sources of Energy | Non-Conventional Sources of Energy |
| (i) These are the traditional sources of energy such as, fossil fuels, firewood, cattle dung cake, etc. | (i) These are the recently developed sources of energy such as, solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy, etc. |
| (ii) They are exhaustible. | (ii) They are non-exhaustible. |
| (iii) They pollute the environment on a large scale. | (iii) They are environment-friendly. |
(Any two)
Question 24.
Mention any two common developmental goals of the people.
Answer:
The two common developmental goals of the people are:
- Freedom and security
- Better living conditions
Section – C
(Short Answer-Based Questions)
Question 25.
Why did Gandhiji decide to launch a nationwide Satyagraha against the proposed Rowlatt Act 1919? Explain any three reasons.
OR
Analyze any three reasons for slowdown of the Non-Cooperation Movement in cities.
Answer:
In 1919, Mahatma Gandhi aimed to initiate a nationwide Satyagraha against the proposed nefarious Rowlatt Act (1919). The citizens of India vehemently protested against the Black Act. Nevertheless, the Act was passed and it empowered the government to subdue political activities.
- On 6th April, 1919, Gandhiji started a nationwide Satyagraha that garnered huge response. People from various cities supported the movement.
- Most of the leaders were selected from Amritsar. Gandhiji was prevented from entering Delhi.
- The colonial government detained the political prisoners without trial for two years.
OR
The Non-Cooperation Movement initiated with the participation of the middle-class stratum in cities and gained momentum. In the cities, the pace of movement subsequently slowed down. The few reasons are enumerated as follows:
- Khadi cloth was relatively more expensive than mass-produced mill cloth. As a matter of fact, poor people could not afford to buy it.
- The boycott of British institutions posed a serious problem as substitute Indian institutions were unavailable.
- Students and teachers began to take positions in colonial government schools. At the same time, lawyers resumed their work in government courts.
Question 26.
What is the significance of the title ‘Lifelines of National Economy?
Answer:
The pace of development of any country depends upon the production of goods and services as well as their movement over space. Movement of these goods and service can be over three domains of earth i.e., land, water and air. Therefore, efficient means of transport are prerequisites for fast development. They connect one part of the country to the other part and help the industries to get the raw materials as well as the finished products. It also develops a nexus among different cultures and religions. Agriculture also depends on transportation. Thus, they are known as the lifeline of an economy.
Question 27.
Which feature of the Panchayati Raj do you like most and why?
Answer:
Panchayati Raj is a system of governance in which Gram Panchayats are the basic unit of administration.
- Gram Panchayat is a council consisting of several ward members known as Panch and Sarpanch. They are directly elected by all the adult population living in that ward or village.
- This feature of Gram Panchayat is very significant. People in a particular village elect their representatives who are very much acquainted or familiar with the local issues.
- Thus, they can solve the problem of people easily and effectively. This is the feature that I liked the most in our country of the Panchayati Raj.
Question 28.
Discuss the difficulties faced by a borrower when a loan is taken from an informal sector.
Answer:
The difficulties faced by a borrower when a loan is taken from an informal source are:
- Compared to the formal money lenders, most of the informal money lenders charge a much higher interest rate on loans. The cost to the borrower of informal loans is much higher.
- The higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loan as a result borrowers have less income left with them. This can lead to an increasing debt and debt trap.
- People who might wish to start an enterprise by borrowing may not do so because of the high cost
of borrowing.
![]()
Question 29.
Describe any three characteristics of the WTO.
Answer:
The three characteristics of WTO are:
- World Trade Organisation (WTO) is a powerful international organization. It aims at liberalizing international trade.
- It establishes rules regarding international trade and sees that these rules are obeyed. Nearly 162 countries of the world are currently the members of the WTO, as on 30th November 2015.
- WTO is supposed to allow free trade for all countries. But in practice, it is seen that the developed countries have unfairly retained trade barriers.
Section – D
(Long Answer-Based Questions)
Question 30.
Discuss the various factors that led to the rise of nationalism in Europe.
OR
Describe the cause of the Silesian weaver’s uprising. Comment on the viewpoint of the journalist Wilhelm Wolff.
Answer:
The factors that led to the rise of Nationalism in Europe are:
(i) The decline of Feudalism: Feudal lords were a disruption in the way of the rising nationalism feelings among the people. But the wars and crusades weakened them.
(ii) The weakness of Papacy and the Roman Empire: The reformation and renaissance movements led to the awakening of the people and weakened authority of the Holy Roman Empire and the Pope. As a result, national states and national churches were established in many countries.
(iii) Foreign Rule: Foreign rule also played a significant part in the growth of nationalism in certain countries.
(iv) The reaction against Injustice: The reactions against the rule of unjust monarchs gave rise to the feeling of nationalism.
(v) Contribution of great writers: The writings of politicians, great poets and philosophers like J.S. Mill, Machiavelli, Garibaldi, Fitch, Mazzini, etc., contributed strongly in rousing national spirit and political consciousness among the people.
OR
The perspectives of the journalist Wilhelm Wolff are as follows:
- The main reason behind the Silesian weaver’s uprising was lower payment for the accomplishment of job.
- Contractor who manufactured raw materials and procured finished textiles from the weavers paid less money for the service of the weavers.
- The weavers were tortured mercilessly if they asked for their dues. This resulted in logical agitation and uprising by the weavers against the contractor.
- The perspective of the journalist Wilhelm Wolff was that the hardship of the workers was a colossus and the contractor made their lives infernal. In this context, the viewpoint of journalists was apposite and logical.
Question 31.
Explain the advantages of decentralization of industries in India.
OR
What does the sustainability of development mean? Flow can sustainable development be achieved?
Answer:
The decentralization of industries reduces the regional disparities of development. Citizens of a nation living in different parts of a country should get equal opportunities for development.
- The decentralization of industries solves the problem of unemployment. People are able to get employment.
- The decentralization of industries assures the uninterrupted flow of goods and services in the market.
- Decentralization solves the problem of the centralization of the population. Due to industrialization, some cities are densely populated, but due to the decentralization of industries, the problems of overcrowded cities are solved. It makes people get work in their homelands.
- The decentralization of industries is helpful for the fair use of resources of underdeveloped areas.
OR
Sustainability of development means that the development should take place without damaging the environment and development in the present should not compromise with the needs of future generations.
Here the natural resources should be used in such a way that environmental balance is also maintained. Sustainable development can be achieved in the following ways:
- By scientific and proper use of resources.
- By finding out the way to reduce environmental pollution.
- By developing renewable sources of energy like water, wind, and solar energy.
Question 32.
Write the difference between vertical division of power-sharing and horizontal division of power-sharing.
OR
What do you mean by a political party? Describe the three components of a political party.
Answer:
The difference between vertical division of power-sharing and horizontal division of power-sharing.
| Vertical Division of Power-sharIng | Horizontal Division of Power sharing |
| (i) In the vertical division of power-sharing, power is divided among the different levels of the government like the State government, Union government and Lower levels. | In the horizontal division of power, the power is shared between different organs of the government like Executive, Legislature and Jciary. |
| (ii) Different levels of government exercise power. | Different organs of the government exercise power. |
| (iii) There is no specification of the system of balance and checks. | It specifies the concept of balance and check. |
| (iv) It ensures the concept of deepening of democracy. | It ensures the concept of the expansion of democracy. |
| (v) State government, Central government and Panchayati Raj are examples of the vertical; division of power-sharing. | For examples: Executive, Legislature and Judiciary are the organs of the Government of India. |
OR
A political party is a group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the government. Political parties take some policies and programs for society intending to promote the collective good. Three components of a political party are:
- The Leaders: Every political party has some prominent leaders who formulate policies and programmes of the party and choose candidates for contesting elections.
- The Active Members: They are involved in different committees of the party and participate directly in their activity.
- The Followers: They believe in the party’s ideology and support the party by casting their votes in favor of the party at the time of the election.
Question 33.
How far is it correct to say that disguised unemployment can also be called underemployment? Explain.
OR
What are the ways to increase more employment for the people in rural India?
Answer:
It is a situation in which more workers are working in an activity than required. The people who are actually engaged in such activity appear to be employed but are not fully employed. For example, if for the cultivation of one-hectare land, 10 workers are required, but instead of 10 workers, 15 workers are working. In this case, 5 workers are disguised unemployed. In such cases, even if the surplus workers are removed, the production will not suffer. This type of unemployment is basically found in agriculture and can also be called underemployment because workers perform below their productivity level.
OR
Unemployment is a very serious problem that is being faced by India since the advent of the British and especially since independence. The government has to take many effective steps to increase the employment in the country.
Following are the various steps that can be taken by the government to increase employment:
1. The government may provide cheap credit facilities to the people so that they can buy necessary equipment for their occupation. The farmers may build wells or tube wells, buy tractors or other equipment for farming. They may also purchase better seeds, fertilizers and other nutrients for the agriculture. These all are employment-generating effects.
![]()
2. The government may build better infrastructure in terms of transportation, electricity and communication etc. This will help in better and assured production and easier movement of goods from one place to another. This encourages the farmers and producers to expand the market for their products.
3. The government must identify the potential industries in rural areas which may utilise the agricultural crops produced there and invite the entrepreneurs to start such industries there.
4. Government may improve irrigation facilities so that farmers may harvest two or three crops in a year. This will increase employment.
5. Government may initiate some more employment programs which require mental work rather than physical work like elder education programme etc.
Section – E
(Case-Based Questions)
Question 34.
Read the source given below and answer the question that follows:
The earliest kind of print technology was developed in China, Japan and Korea. This was a system of hand printing. From AD 594 onwards, books in China were printed by rubbing paper – also invented there – against the inked surface of woodblocks. As both sides of the thin, porous sheet could not be printed, the traditional Chinese ‘accordion book’ was folded and stitched at the side.
Superbly skilled craftsmen could duplicate, with remarkable accuracy, the beauty of calligraphy. The imperial state in China was, for a very long time, the major producer of printed material. China possessed a huge bureaucratic system which recruited its personnel through civil service examinations. Textbooks for this examination were printed in vast numbers under the sponsorship of the imperial state. From the sixteenth century, the number of examination candidates went up and that increased the volume of print.
1. Name the nations where the earliest print technology was developed.
Answer:
The earliest print technology was developed in China, Japan and Korea.
2. How the books were printed in China from 594 AD?
Answer:
The books in China were printed by rubbing paper against the inked surface of woodblocks.
3. Discuss the relationship between the bureaucratic system of China and the production of printed materials.
Answer:
China had a large bureaucratic system in which the recruitment was made through the medium of civil service examinations. For this examination, textbooks were printed in large numbers. From the 16th century, the number of examination candidates increased and that raised the demand of printed textbooks.
Question 35.
Read the given extract and answer the following questions.
This type of farming is practised in areas of high population pressure on land. It is labor-intensive farming, where high doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation are used for obtaining higher production. Though the ‘right of inheritance’ leading to the division of land among successive generations has rendered land-holding size uneconomical, the farmers continue to take maximum output from the limited land in the absence of alternative source of livelihood. Thus, there is enormous pressure on agricultural land.
The main characteristic of this type of farming is the use of higher doses of modem inputs, e.g. high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides in order to obtain higher productivity. The degree of commercialization of agriculture varies from one region to another. For example, rice is a commercial crop in Haryana and Punjab, but in Odisha, it is a subsistence crop. Plantation is also a type of commercial farming. In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area. The plantation has an interface of agriculture and industry. Plantations cover large tracts of land, using capital-intensive inputs, with the help of migrant labourers. All the produce is used as raw material in respective industries.
1. With what objective ‘Intensive Subsistence Farming’ is practiced?
Answer:
To obtain higher production with the help of high doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation.
2. Mention any one feature of commercial farming.
Answer:
- Crops are grown specifically for sale in the market.
- Higher doses of modem inputs are used in order to obtain higher productivity. (Anyone)
3. What is plantation farming? Name some important plantation crops which are grown in India.
Answer:
In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area. Tea, coffee, rubber, banana, sugarcane, etc. are important plantation crops in India.
Question 36.
Read the given extract and answer the following questions.
Democracies are based on political equality. All individuals have equal weight in electing representatives. Parallel to the process of bringing individuals into the political arena on an equal footing, we find growing economic inequalities. A small number of ultra-rich enjoy a highly disproportionate share of wealth and incomes. Not only that, their share in the total income of the country has been increasing. Those at the bottom of the society have very little to depend upon. Their incomes have been declining. Sometimes they find it difficult to meet their basic needs of life, such as food, clothing, house, education and health.
1. “Democracy ensures reduction of inequalities and poverty”. Explain the statement.
Answer:
Democracy ensures equal distribution of goods, income and opportunities. A democratic government always tries to reduce poverty ratio and works for welfare of people.
2. List the factors that affect economic growth.
Answer: These are : population size, global situation, cooperation and economic priorities.
![]()
3. How can the accommodation of social diversity work in a democracy?
Answer:
- In a democracy, the majority needs to work with minority so that the government functions to represent the general view.
- Every citizen has a chance of being in majority at some point of time.
Section – F
(MAP Skill-Based Question)
Question 37.
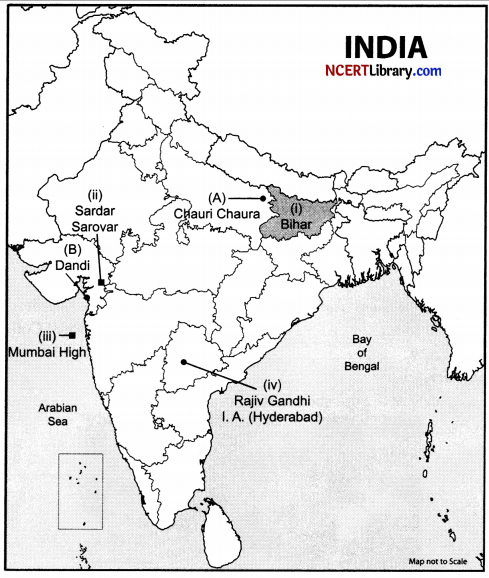
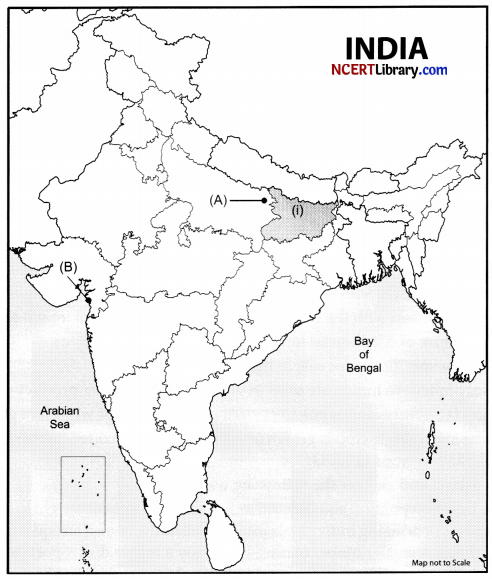
(a) Two places (A) and (B) are marked on the outline political map of India. Identify these places with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked near them.
(A) The place associated with the calling off the Non-Cooperation Movement.
(B) The place where the Civil Disobedience Movement was started.
(b) On the same outline map of India locate and label any three of the following:
- Identify the major rice-producing state.
- Sardar Sarovar Dam.
- Mumbai High.
- Rajiv Gandhi International Airport.
Answer: