Students must start practising the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions Set 4 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 4 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- Question paper comprises Six Sections -A, B, C, D, E, and F. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From question 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Question no. 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words.
- Section C – contains Q.25 to Q.29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words
- Section D – Question no. 30 to 33 are long answer-type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section E – Questions no from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map-based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A
(Multiple Choice Questions) (1 × 20 = 20)
Question 1.
Mahatma Gandhi returned to India in
(a) 1920
(b) 1925
(c) 1915
(d) 1910
Answer:
(c) 1915
![]()
Question 2.
The political party having the main objective of upliftment of lower caste people:
(a) Communist Party of India
(c) Indian National Congress
(b) Bharatiya Janata Party
(d) Bahujan Samaj Party
Answer:
(d) Bahujan Samaj Party
Question 3.
Study the picture and answer the question that follows:
Identify the man who is sitting fifth from right.

(a) Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
(c) Subhash Chandra Bose
(b) Jawaharlal Nehru
(d) Mahatma Gandhi
Answer:
(c) Subhash Chandra Bose
Question 4.
Arrange the following in chronological order:
I. E.T. Pauli, a popular music publisher, published a picture announcing the ‘Dawn of the Century.
II. As the Swadeshi movement gathered momentum, nationalists mobilised people to boycott foreign cloth.
III. Till the First World War, European Managing Agencies controlled a large sector of Indian industries.
IV. Seth Hukumchand, a Marwari businessman, set up the first Indian jute mill in Calcutta.
Options:
(a) I, II, IV, III
(b) IV, I, II, III
(c) III, IV, II, I
(d) I, III, IV, II
Answer:
(a) I, II, IV, III
Question 5.
Identify the cropping season with the help of the following information:
- These crops are sown in winter from October to December and harvested in summer from April to June.
- Some of the major crops are wheat, gram, mustard, etc.
- The availability of precipitation during winter months helps in the success of these crops.
Options:
(a) Rabi
(b) Kharif
(c) Zaid
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Rabi
Question 6.
What is meant by the term ‘Feminist’?
(a) The qualities which are considered typical of women.
(b) A person who believes in equal rights and opportunities for women and men.
(c) The belief that men and women are unequal.
(d) The man who looks like the woman.
Answer:
(b) A person who believes in equal rights and opportunities for women and men.
Question 7.
Match the following:
| Soils | Major Crops |
| A. Black Soil | I. Sugarcane |
| B. Laterite Soil | II. Tobacco |
| C. Alluvial Soil | III. Cashew nut |
| D. Red and Yellow Soil | IV. Cotton |
Options:
(a) A-I, B-IV, C-II. D-III
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(b) A-II, B-iII, C-IV, D-I
(d) A-IIi, B-I, C-I’?, D-II
Answer:
(c) A-IV, B-II!, C-I, D-II
Question 8.
Consider the following statements regarding non-democratic regimes and identify the incorrect one
from the following?
(a) These types of governments do not have to bother about public opinion.
(b) These types of governments take less time to arrive at a decision.
(c) Principle of individual dignity has legal force in non-democratic regimes.
(d) These often suppress internal social differences.
Answer:
(c) Principle of individual dignity has legal force in non-democratic regimes.
Question 9.
Which of the following is a ‘National Political Party”?
(a) Samajwadi Party
(c) Rashtriya Lok Dal
(b) Rashtriya Janata Dal
(d) Bahujan Samaj Party
Answer:
(d) Bahujan Samaj Party
Question 10.
Consider the following statements regarding the language policy of Indian Federation.
- Hindi was identified as the official language.
- Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as scheduled languages.
- English can be used along with Hindi for official purpose.
Choose the right option from the following:
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 1 and 2
(c) Only I
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer:
(d) 1, 2 and 3
![]()
Question 11.
Which one among the following pairs is correctly matched?
| List-I | List-II |
| (a) Vienna Peace Treaty | 1866-1871 |
| (b) Unification of Italy | 1859-1870 |
| (c) Unification of Germany | 1814-1815 |
| (d) Napoleonic Wars | 1900-1905 |
Answer:
(b) Unification of Italy -1859-1870
Question 12.
In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the
statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A): After primary and secondary, there is a third category of activities that falls tinder tertiary
sector.
Reason (R): Because it is a service sector.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is true.
(d) A is false, hut R is false.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 13.
Which one of the following options describe ‘Coalition’?
(a) Power usually changes between two main parties.
(b) An alliance of several parties to form the government.
(c) Several parties competing to win elections and form the government.
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(c) Several parties competing to win elections and form the government.
Question 14.
Read the bar graph given below and find out which sector, as compared to 1973-74, has seen maximum improvement in GDP contribution in the year 2013-2014.
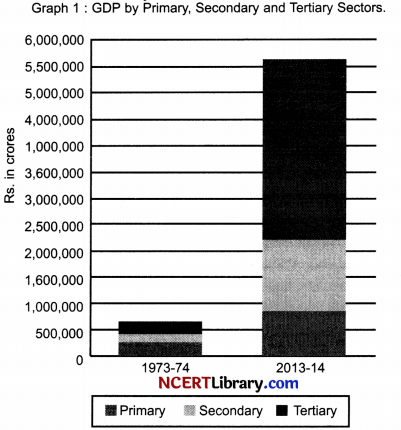
(a) Primary Sector
(c) Tertiary Sector
(b) Secondary Sector
(d) Equal Growth in all sectors
Answer:
(a) Primary Sector
Question 15.
What are the different things that people seek in the society besides good income?
(a) Equal treatment in the society
(c) Respect in the society
(b) Freedom and security in the society
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 16.
Find the odd one out from the following:
(a) Wheat, Rice, Jowar, Maize
(c) Groundnut, Linseed, Gram, Sesamum
(b) Pineapples, Apricots, Apples, Mangoes
(d) Moong, Urad, Peas, Lentil
Answer:
(c) Groundnut, Linseed, Gram, Sesamum
Question 17.
Fill in the blank:
| Company | Manufactured Item |
| Parakh Foods | Edible oil |
| Sundaram Fasteners | 7 |
Options:
(a) Medicines
(b) Automobiles
(c) Paints
(d) Nuts and bolts
Answer:
(d) Nuts and bolts
Question 18.
Kamlesh has taken a loan of ? 8 lakhs from the bank to purchase a car. The annual interest rate on the loan is 12.5 per cent and the loan is to be repaid in 2 years in monthly instalments. The bank retained the papers of the new car as collateral, which will be returned to Kamlesh only when he repays the entire loan with interest.
Analyse the loan information given above, considering one of the following correct option.
(a) Mode of re-payment
(c) Interest on loan
(b) Terms of credit
(d) Deposit criteria
Answer:
(b) Terms of credit
![]()
Question 19.
As per Human Development Report 2006, which neighbouring country has the highest income following:
(a) India
(b) Pakistan
(c) Nepal
(d) Sri Lanka
Answer:
(d) Sri Lanka
Question 20.
Identify the correct statement/s about Reserve Bank of India (RBI):
I. In India, it issues currency notes on behalf of the central government.
II. It supervises the functioning of informal sources of loAnswer:
III. It monitors the SHGs in actually maintaining cash balance.
IV. It sees that banks give loans only to profit-making businesses and traders.
Options:
(a) Only I
(b) I & III
(c) III & IV
(d) I, II & III
Answer:
(a) Only I
Section – B
(Very Short Answer-Based Questions)
Question 21.
Mention any two industrial organisations which were established by Indian merchants and industrialists to protect their business interests.
Answer:
The following organisations were established by them to protect their business interests:
- The Indian Industrial and Commercial Congress in 1920
- The Federation of Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (FICCI) in 1927
Question 22.
What is the difference between a state party and a national party?
Answer:
| State Party | National Party |
| (i) The influence of state party is confined to one more state. | The national parties have influence all over the country. |
| (ii) The state parties are interested in promoting the interests of only their state/states. | The national parties are interested in promoting the intersts of the entire country and help in promoting international issues. |
| (iii) The state parties seek autonomy of their state/ states. | The national parties are interested in integrating the entire country and in promoting the interests all of state. |
(Any two)
Question 23.
Mention any two roles of the Reserve Bank of India.
OR
What are demand deposits?
Answer:
The two roles of the Reserve Bank of India are:
- The RBI issues currency notes in India on the behalf of the central government.
- It regulates the cash balances of the banks and regulates their formal operations as well.
OR
People also have the provision to withdraw the money as and when they require it. Since the deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn on demand, these deposits are called demand deposits.
Question 24.
Why is tourism considered as a trade?
Answer:
Some of the reasons due to which tourism is considered as a trade are:
- The arrival of lakhs of tourists every year is a great source of foreign exchange and helps in the economic prosperity of several industries related to tourism.
- There are several categories of tourism like medical tourism, eco-tourism and adventure tourism in India.
Section – C
(Short Answer-Based Questions)
Question 25.
Highlight any three benefits of industrialisation on the society.
OR
Describe any three major problems faced by Indian cotton weavers in the nineteenth century.
Answer:
The three benefits of Industrialisation on the society are enumerated as follows:
- The emergence of railway stations and expansion of railway lines.
- Building activities augmented in the cities, engendering greater opportunities of employment for youth.
- Widening of roads for facilitating transport.
OR
The problems faced by the cotton weavers in India during mid-nineteenth century were as follows:
- A huge decline of textile exports from India. The local markets shrank due to deluge of Manchester imports.
- Produced by machines at lower costs, the imported cotton goods were so cheap that the hand-spun cotton materials made by Indian weavers could not easily compete with them.
- The Indian weavers failed to achieve sufficient supply of raw cotton of good quality.
Question 26.
“India is rich in certain types of resources and deficient in some others.” Support your answer with
examples.
Answer:
Resources in our country are not evenly distributed. For example:
- Arunachal Pradesh has an abundance of water resources but lacks in infrastructure. On the other hand, Rajasthan is gifted with solar and wind energy but lacks in water resources.
- Most of northeast states are rich in natural vegetation, but lack in fertile soil.
- Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh are rich in minerals and coal deposits but lack in industrialisation.
Question 27.
Explain the role of judiciary in the federal system of India.
Answer:
Judiciary plays an important role in ensuring the implementation of various laws and procedure:
- The Supreme Court of India has the exclusive authority of settling disputes between the government of India and one or more states or between two states.
- The High Court stands at the head of state’s judicial administrations.
- The Union Territories come under the jurisdiction of different State High Courts.
![]()
Question 28.
Why there is a need to supervise the banking system by the RBI?
Answer:
The Reserve bank of India supervises the Banking system due to the following reasons:
- The RBI monitors that the banks maintain a minimum cash balance.
- The RBI ensures that the banks give loans not just to the profit-making businessmen and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries and small borrowers.
- Banks have to submit the information to the RBI on how much they are lending, to whom, at what interest rates etc.
Question 29.
Explain the reasons for the growth of the service sector (tertiary sector) in India.
Answer:
The tertiary sector in India has been growing rapidly for a number of reasons:
- The development of agriculture and industry leads to the development of services such as trade, transport, storage etc. The greater the development of the primary and secondary sectors the more would be the demand for such services.
- As income levels rise, certain sections of people start demanding more services, such as eating out, tourism, shopping, private hospitals; private schools, professional training etc. This change was quite sharp in cities, especially in big cities.
- Over the past decade, services, such as those based on information and communication technology and software export, have created a boom for call centres.
- The government policy of privatisation has also led to the growth of this sector. The liberalisation of the financial environment has boosted the growth in the financial sector.
Section – D
(Long Answer-Based Questions)
Question 30.
The first clear expression of nationalism came with the French Revolution in 1789. Elucidate.
OR
What was the status of people in Europe during economic hardships in the 1830s?
Answer:
France was a full-fledged territorial state in 1789 under the rule of an absolute monarchy. The estate general, renamed as General Assembly, became an elected body.
- The revolution proclaimed that it was the people who would henceforth constitute the nation and shape its destiny. A new French flag, the Tricolour, was chosen to replace the former royal standard.
- A centralised administrative system was put in place, and it formulated uniform laws for all citizens within its territory. Internal customs duties and dues were abolished and a uniform system of weights and measures was adopted.
- Regional dialects were discouraged and French, as it was spoken and written in Paris, became the common language of the nation.
- The revolutionaries further declared that it was the mission and the destiny of the French nation to help other people of Europe to become independent nations.
- With the outbreak of revolutionary wars, the French armies began to carry the idea of nationalism abroad.
Thus, France became a nation-state, and the world got a clear expression of nationalism through the French revolution.
OR
In the 1830s, the employment rate in the economy was lower. People migrated from rural areas to urban areas in search of jobs. Small producers faced stiff competition due to imported cheap machines which were produced in England, where industries were much more advanced. Textile industry faced a major set-back as the production used to be carried out in small workshops or homes. The regions of Europe where the aristocracy was still prevalent had peasants who struggled from burden of feudal dues and obligations. The economy suffered from widespread poverty on account of price inflation and bad harvest season.
Question 31.
Discuss the expected outcomes of democracy. .
OR
Describe some of the recent efforts and suggestions made in India to reform political parties and their leaders.
Answer:
The expected outcomes of democracy are as follows:
- It enables the people to choose their representatives through a fair and free system.
- People get varied option of opinion through a multi-party system, where they can select their representatives as per their choice.
- It helps in establishing a government which is accountable to the people.
- The elected government is responsive to the needs and expectations of the people.
- It is a legitimate form of government which runs according to the rules and regulations provided by the constitution.
- There is transparency in the system i.e., people have the right to examine the process of decision-making.
- People get freedom of expression.
- People are provided with fundamental rights which help in ensuring equality among people.
- The judiciary is impartial and independent to safeguard the rights of the people.
- There is a strong opposition party or parties which act as a watchdog to keep the ruling party on track.
- There is freedom of media and press.
- The constitution has written set of rules to demarcate the powers of the Centre and the States,
- The integrity, unity and sovereignty of the country is maintained.
- People are watchful and participate actively in the decision-making process. (Any five)
OR
Some of the recent efforts and suggestions in India to reform political parties and its leaders are:
- The constitution was amended to prevent elected MLAs and MPs from changing parties.
- If an MLA or MP changes parties, he or she will lose the seat in the legislature. This new law has helped bring defection down.
- The Supreme Court passed an order to reduce the influence of money and criminals. It is mandatory for every candidate who contests elections to file an affidavit giving details of his property and criminal cases pending against him.
- The new system has made a lot of information available to the public about every candidate contesting the elections.
- The Election Commission passed an order making it necessary for political parties to hold their organisational elections and file their income tax returns.
Question 32.
Describe the significance of pipelines in India.
OR
Classify the pollution created by industries.
Answer:
The significance of pipelines in India are stated as follows:
- They are used for transporting crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from oil fields and natural gas fields to refineries, fertiliser factories and big thermal power plants.
- Solids can also be transported through a pipeline when converted into slurry.
- Because of pipelines, refineries at Barauni, Mathura, Panipat and gas based fertiliser plants, could be located in the interiors of India.
- Initial cost of laying pipelines is high but subsequent running costs are minimal.
- Pipelines rules out trans-shipment (during transportation) losses or delays.
![]()
OR
Industries pollute the environment by polluting air, water and land. They also cause noise pollution. They have increased pollution and resulted in a degraded environment. The pollution created by industries can be classified as:
(i) Land pollution: It is caused by dumping of non-biodegradable solid waste from industries in landfill sites.
(ii) Air pollution: Industries cause air pollution by the emission of gases from industrial complexes and power generation units. Leakage of poisonous gases and chemicals from chemical industries and burning of fossil fuels in big and small factories also leads to air pollution.
(iii) Water pollution: It is caused when industrial effluents both organic and inorganic are discharged into rivers or other water bodies. Some other common pollutants of the water pollution are fertilisers, pesticides, dyes, soaps, etc.
(iv) Noise pollution: Undesirable noise pollution from industries like construction, running of generators to generate power, electrical drill, etc., is responsible for disturbing our environment.
(v) Thermal pollution: It occurs when hot water from factories and thermal plants is drained into rivers and ponds before cooling.
Question 33.
Is income a sufficient factor for development? What other factors do you think are significant for development?
OR
What does sustainability of development mean? How can sustainable development be achieved?
Answer:
Income is generally considered to be an important factor on which the development of a country’s people depends. This is based on the understanding that more income results into more of all those things that the human beings need. But income is not the only factor on which the development and welfare of the people depends.
Following are some of the factors:
(i) Equality of Income: An important factor which is must for development is the equality of income. A country cannot be considered developed if only a section of the society enjoys all the benefits while the other section suffers poverty.
(ii) Health facilities: A person’s health is dependent upon the quality of food and the medical facilities available in the country. So, the country’s medical system and food distribution need to be very strong and effective so that the benefits of these facilities must reach to the last person.
(iii) Education: Education enhances the understanding of the world around a person. Knowledge makes the discovery of new ideas, items and technology possible which makes the lives of the people easier.
(iv) Clean Environment: Clean environment is equally important for people as health is. The absence of clean environment results into poor health which again is worse for the people of any county.
(v) Security: A person can feel or sense development only when he has the sense of security, internal as well as external.
OR
The concept of sustainable development or sustainability underlines the importance of these words “We have not inherited the world from our forefathers-we have borrowed it from our children.” So, this concept tells us that the present generation must utilise all the resources in such a judicious manner that the future generation may also enjoy the benefits of these resources in the same manner as the present generation is enjoying today. Following are certain steps which can be taken to achieve sustainable development:
(i) Judicious Use of Natural Resources: The very first step that can be taken is the judicious use of the natural resources. Natural resources are limited. So they must be utilised by keeping economic priorities in mind and in such a manner which may provide the maximum benefits to the people.
(ii) Penalty for Wastage: Another step that can be taken to stop the wastage of natural resources is to penalise people responsible for wastage of natural resources. For this purpose government must frame necessary policies and implement them so that wastage of at least non-renewable resources may be stopped.
(iii) Alternative Resources: Efforts must be made to generate alternatives of the natural resources. Though it is very difficult but the technology has made it possible to generate alternative resources. But such technologies must be made commonly available for their maximum use.
Section – E
(Case-Based Questions)
Question 34.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows:
Gutenberg was the son of a merchant and grew up on a large agricultural estate. From his childhood, he had seen wine and olive presses. Subsequently, he learnt the art of polishing stones, became a master goldsmith, and also acquired the expertise to create lead moulds used for making trinkets. Drawing on this knowledge, Gutenberg adapted existing technology to design his innovation. The olive press provided the model for the printing press, and moulds were used for casting the metal types for the letters of the alphabet. By 1448, Gutenberg perfected the system. The first book he printed was the Bible. About 180 copies were printed and it took three years to produce them. By the standards of the time this was fast production.
1. Who was Gutenberg?
Answer:
Gutenberg was a German inventor, printer and goldsmith who invented the first-known printing press in the 1430s.
2. What were some of the professional skills acquired by Gutenberg?
Answer:
Gutenberg acquired the skills of polishing stones, and also attained expertise in the creation of lead moulds used for making trinkets. He became a master goldsmith and designed several jewels.
3. What contribution was made by Gutenberg in the field of press?
Answer:
Gutenberg led to the invention of the printing press. In his design, he made the use of the casting metal types for the letters of the alphabet. The first book which was printed by the use of this technology was the Bible. There were more than 180 copies that got printed by this technique.
Question 35.
Read the given extract and answer the following questions.
The denudation of the soil cover and subsequent washing down is described as soil erosion. The processes of soil formation and erosion go on simultaneously and generally there is a balance between the two. Sometimes, this balance is disturbed due to human activities like deforestation, over-grazing, construction and mining etc., while natural forces like wind, glacier and water lead to soil erosion. The running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies. The land becomes unfit for cultivation and is known as bad land.
In the Chambal basin such lands are called ravines. Sometimes water flows as a sheet over large areas down a slope. In such cases the top soil is washed away. This is known as sheet erosion. Wind blows loose soil off flat or sloping land known as wind erosion. Soil erosion is also caused due to defective methods of farming. Ploughing in a wrong way i.e. up and down the slope form channels for the quick flow of water leading to soil erosion.
Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes. This is called contour ploughing. Steps can be cut out on the slopes making terraces. Terrace cultivation restricts erosion. Western and central Himalayas have well developed terrace farming. Large fields can be divided into strips. Strips of grass are left to grow between the crops. This breaks up the force of the wind.
This method is known as strip cropping. Planting lines of trees to create shelter also works in a similar way. Rows of such trees are called shelter belts. These shelter belts have contributed significantly to the stabilisation of sand dunes and in stabilising the desert in western India.
1. The balance of soil formation and erosion is disturbed due to human activities. Give one example to prove the statement.
Answer:
This balance is disturbed due to overgrazing in states like Gujarat, Rajasthan and Maharashtra.
2. What is soil conservation?
Answer:
Soil conservation refers to the efforts made to prevent soil from getting eroded.
![]()
3. Differentiate between gully erosion and sheet erosion.
Answer:
Gully erosion occurs when the running water aits through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies.
Sheet erosion occurs when the top soil gets eroded from very large areas due to the running water.
Question 36.
Read the given extract and answer the following questions.
Belgium and Sri Lanka both are democracies. Yet, they dealt with the question of power-sharing differently. In Belgium, the leaders have realised that the unity of the country is possible only by respecting the feelings and interests of different communities and regions. Such a realisation resulted in mutually acceptable arrangements for sharing power. Sri Lanka shows us a contrasting example. It shows us that if a majority community wants to force its dominance over others and refuses to share power, it can undermine the unity of the country.
1. How was the power-sharing arrangement in Belgium different from that of in Sri Lanka?
Answer:
In Belgium, the leaders amended the constitution four times in order to enable everyone to live together within the same country, whereas in Sri Lanka, the Sinhala community adopted majoritarian measures to establish its supremacy over the Sri Lankan Tamils.
2. Explain why power sharing is desirable.
Answer:
Prudential Reason: Power sharing ensures stability of political order. Moral Reason: A democratic rule involves sharing power with those affected by its exercise, and who have to live with its effects.
3. List any two steps taken by the leaders of Belgium to accommodate all the communities.
Answer:
- The Constitution prescribes that the number of Dutch and French-speaking ministers shall be equal in the central government.
- Some special laws require the support of majority of members from each linguistic group. Thus, no single community can make decisions unilaterally.
Section – F
(MAP Skill-Based Question)
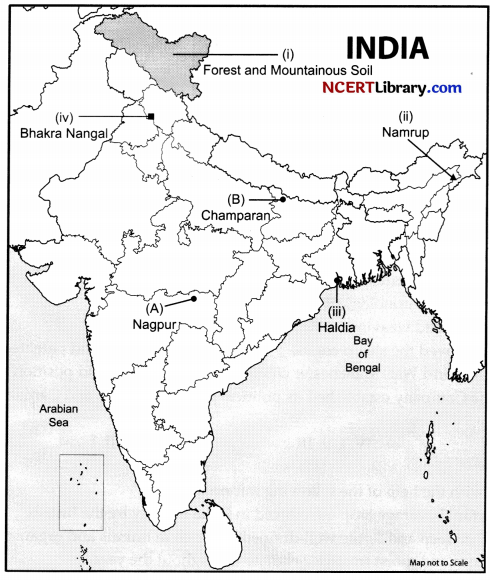
Question 37.
(a) Two places (A) and (B) are marked on the outline political map of India. Identify these places
with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked near them.
(A) The place where the Indian National Congress Session was held in December 1920.
(B) Mahatma Gandhi organised a Satyagraha Movement at this place for indigo planters.
(b) Locate and label any three of the following with appropriate symbols on the same given outline political map of India.
- Identify the major soil type.
- Namrup Thermal Power Plant
- Haldia Port.
- Bhakra Nangal Dam.
Answer: