Students must start practising the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions Set 3 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 3 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- Question paper comprises Six Sections -A, B, C, D, E, and F. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From question 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Question no. 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words.
- Section C – contains Q.25 to Q.29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words
- Section D – Question no. 30 to 33 are long answer-type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section E – Questions no from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map-based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A
(Multiple Choice Questions) (1 × 20 = 20)
Question 1.
What was the main purpose behind the passing of the Vernacular Press Act in India in 1878?
(a) The Vernacular Press Act regulated the publications in the English language.
(b) The Vernacular Press Act aimed to curb growing political dissent by banning many political parties.
(c) The Vernacular Press Act aimed to control trade controlled by Indian merchants and imposed high tariffs on their goods.
(d) The Vernacular Press Act aimed to control the freedom of the ‘native press’ by imposing stringent control over what they published.
Answer:
(d) The Vernacular Press Act aimed to control the freedom of the ‘native press’ by imposing stringent control over what they published.
![]()
Question 2.
Who among the following published ‘Kesari’?
(a) Balgangadhar Tilak
(b) Mahatma Gandhi
(c) Jyotiba Phule
(d) B.R. Ambedkar
Answer:
(a) Balgangadhar Tilak
Question 3.
Study the picture and answer the question that follows:

What does the above image depict?
(a) A poster hung on wall
(b) Postage stamp with picture of Marianne
(c) Picture of Germania, Philip Veit
(d) Caricature of Otto van Bismarck
Answer:
(b) Postage stamp with picture of Marianne
Question 4.
Arrange the following in chronological order:
I. The first spinning and weaving mill of Madras began production.
II. James Watt improved the steam engine produced by NJewcomen and patented the new one.
III. After the First World War, Manchester could never recapture its old position in the Indian market.
IV. The East India Company established its political power in Bengal and Carnatic.
Options:
(a) I, II, III, IV
(b) IV, I, II, III
(c) III, IV’, II, I
(d) I, III, IV, II
Answer:
(b) IV, I, II, III
Question 5.
Identify the crop with the help of the following information:
- It is an important beverage crop introduced in India initially by the British.
- It grows well in deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter.
- It requires warm and moist frost-free climate throughout the year.
- In India, Assam is the largest producer of this crop.
Options:
(a) Coffee
(b) Tea
(c) Rice
(d) Sugarcane
Answer:
(b) Tea
Question 6.
Ruling party means:
(a) Political party that runs government.
(c) Opposition party.
(b) Political party that competes in election.
(d) Non-Political party.
Answer:
(a) Political party that runs government.
Question 7.
Match the following:
| Name of Crops | Classification of Crops |
| A. Jute | I. Fibre crop |
| B. Coffee | II. Oilseed crop |
| C. Sesamum | III. Horticulture crop |
| D. Apricot | IV. Beverage crop |
Options:
(a) A-I, B-IV, C-II. D-III
(b) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(d) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
Answer:
(a) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
Question 8.
Consider the following statements regarding democracy and identify the incorrect one from the
following?
(a) Promotes equality among citizens
(b) Enhances the dignity of the individual
(c) Provides a method to resolve conflicts
(d) Does not provide room to correct mistakes
Answer:
(d) Does not provide room to correct mistakes
Question 9.
Which one of the following is a major caste group of Sri Lanka?
(a) Christian and Tamil
(b) Buddhist and Hindu
(c) Sinhali and Tamil
(d) Sinhali and Christian
Answer:
(c) Sinhali and Tamil
Question 10.
Which of the following regions has the highest representation of women in their national parliaments?
(a) Asian
(b) American
(c) African
(d) Nordic
Answer:
(d) Nordic
![]()
Question 11.
Which one among the following pairs is correctly matched?
| List-I | List-II |
| (a) Union Government | Chief Minister |
| (b) State Government | President |
| (c) Municipal Corporation | Mayor |
| (d) Gram Panchayat | Governor |
Answer:
(c) Municipal Corporation – Mayor
Question 12.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes
provided below:
Assertion (A): Moneylenders can lend loan at whatever interest rate they choose.
Reason (R): Moneylenders do not follow the rules and regulations set for them by the RBI.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Answer:
(c) A is true, but R is false.
Question 13.
Which of the following outlines the prudential reason for power sharing?
(a) Power sharing is good for democracies.
(b) Power sharing is the spirit of democracy.
(c) Power sharing reduces the chances of social conflicts.
(d) A democratic rule involves power sharing.
Answer:
(c) Power sharing reduces the chances of social conflicts.
Question 14.
Read the given data and find out the percentage of rural girls attending school.
| Education Achievement of Rural Population of Uttar Pradesh | ||
| Category | Male | Female |
| Literacy rate for rural population | 70% | 54% |
| Literacy rate for rural children in age group 10-14 years | 90% | 87% |
| Percentage of rural children aged 10-14 attending school | 85% | 82% |
(a) 85%
(b) 82%
(c) 81%
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) 82%
Question 15.
Which region of the world has the maximum amount of crude oil reserves?
(a) USA
(b) Middle East
(c) China
(d) Japan
Answer:
(b) Middle East
Question 16.
Find the odd one out from the following:
(a) Bokaro, Jamshedpur, Vadodara, Vijaynagar
(b) Mohali, Pune, Bengaluru, Indore
(c) Kanpur, Rajkot, Chennai, Moradabad
(d) Kolkata, Delhi, Hyderabad, Gurugram
Answer:
(a) Bokaro, Jamshedpur, Vadodara, Vijaynagar
Question 17.
Fill in the blank:
| Source of Credit | Example |
| Formal Sector Loans | Banks |
| Informal Sector Loans | ? |
Options:
(a) Cooperatives
(b) Commercial Banks
(c) Traders
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Traders
Question 18.
Assume there are four families in a country. The average per capita income of these families is i0.
If the income of three families is ‘ 5000, 8000, and 4000 respectively, what is the income of the fourth
family?
(a) 5500
(b) 2000
(c) 300
(d) 7000
Answer:
(d) 7000
Question 19.
Public Sector stands for:
(a) Most of the assets owned by big companies
(b) Assets owned by Government.
(c) Most of the assets owned by a group of people.
(d) Most of the assets owned by an individual.
Answer:
(b) Assets owned by Government.
![]()
Question 20.
Identify the correct statement/s about World Trade Organisation (VTO):
I. It is one such organization whose aim is to liberalize international trade.
II. It establishes rules regarding international trade.
III. At present, 169 countries of the world are currently its members.
IV. Its rules have forced the developed countries to remove trade barriers.
Options:
(a) I & II
(b) I & III
(c) III & IV
(d) I, II & III
Answer:
(a) I & II
Section – B
(Very Short Answer-Based Questions)
Question 21.
Today the world has become a global village. “Justify this statement”.
Answer:
Today the world has become a “large village” because of:
- Efficient and fast means of transport.
- Development of telecommunication and satellite communication systems.
Question 22.
Differentiate between one-party and two-party systems.
Answer:
One-party system:
There is the domination of only one political party in the country that forms the government on every occasion.
Example:
The Communist Party of China
Two-Party system:
In the two-party system, the major competition for political power is between two parties.
Example:
USA and U.K.
Question 23.
How did the Non-Cooperation Movement unfold in the cities and towns of India?
OR
Why was the Inland Emigration Act of 1859 troublesome for plantation workers?
Answer:
The Non-Cooperation Movement was adopted enthusiastically by the people in towns and cities. Some of the actions taken by the people were:
- Thousands of students left government schools and colleges.
- Middle-class people participated enthusiastically in the movement, and thousands of teachers and I lawyers left their jobs and practices respectively.
OR
The Inland Emigration Act of 1859 was troublesome for plantation workers because they were not permitted to leave the tea gardens without official permission. In fact people rarely got such permissions. They were also not allowed to go to their homes.
Question 24.
How do demand deposits share the essential features of money?
Answer:
Demand deposits share the essential features of money because:
- With demand deposits, we can directly settle payments without the use of cash. The facility of cheques helps in this manner.
- Along with currency, demand deposits are commonly accepted as a means of payment. Thus, they constitute money in the modem economy.
Section – C
(Short Answer-Based Questions)
Question 25.
What is resource planning? Give three phases of resource planning.
OR
Write a short note on reserve.
Answer:
Resource planning is proper and judicious planning of resources.
The phases of resource planning are:
- Resource identification and inventory in different parts of the country. This includes the assessment, mapping, qualitative and quantitative estimation and resource measurement.
- Development of a planning structure with the necessary technical skills and institutional capacity to implement resource development plans
- Matching the resource development with the overall plans of national development.
OR
Reserves are the subset of stocks, that may be utilized with the aid of existing technical expertise, but their use has not been started. These can be used for meeting future requirements. Water from the river can be used for hydroelectric power generation but currently is only used to a very restricted level. So, the water in the dams, forests etc., is a reserve which can be used in the future.
Question 26.
Mention three reasons by which the rich peasant communities took active participation in the Civil Disobedience Movement.
Answer:
Three reasons by which the affluent peasant communities took part in the Civil Disobedience Movement are enumerated as follows:
- Being producers of cash crops, they were dismayed by the global economic depression and subsequent falling prices of 1930s.
- As their cash income abated, they found it difficult to meet the revenue demand of government.
- There was a popular resentment among the rich peasants and they enthusiastically bolstered the movement.
![]()
Question 27.
Write any three differences between organized and unorganized sector.
Answer:
| Organized Sector | Unorganized Sector |
| (i) They are registered with Government. | They are not registered with government. |
| (ii) Fixed work times and extra payment facilities for overtime | Work time is normally very long and no extra payment facilities for overtime. |
| (iii) Job security is there. | Job security is not there. |
Question 28.
Explain the majoritarianism in Sri Lanka.
Answer:
Majoritarianism is practiced in Sri Lanka in the following ways:
- In 1956, an Act was passed to recognise Sinhala as the only official language, thus disregarding Tamil.
- The governments followed preferential policies that favoured Sinhala applicants for university positions and government jobs.
- A new constitution stipulated that the state shall protect and foster Buddhism.
Question 29.
What do you mean by MNC? Give an example of a MNC in India. What is the basic function of foreign trade?
Answer:
MNC is a company that owns or controls production in more than one nation. Toyota is an example of a MNC in India. Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets, i.e., markets of their own countries.
Section – D
(Long Answer-Based Questions)
Question 30.
Define federalism. Write two merits and demerits of federalism.
OR
The real success of federalism in India can be attributed to the nature of democratic politics in India. Explain.
Answer:
Federalism is the form of government in which different layers of government exist and power is shared among them.
Merits of Federalism:
- Governmental activities have been becoming easier.
- Federalism enables citizens to make the choice of their preferable place for living.
Demerits of Federalism:
- the Possibility to have a conflict between federations or different layers of government.
- It is very confusing and inconsistent system. Differential laws for different states may be confusing at all.
OR
(i) Linguistic States after independence: In 1950, the boundaries of several old states were
changed in order to create new states. This was done to ensure that the people who spoke the same language, share common culture, ethnicity or geography could live in the same state.
(ii) Language Policy: The Indian Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one of the languages. Though Hindi was identified as the optional language, but the central government has not imposed Hindi on states where people speak a different language. Besides Hindi, there are 22 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Indian Constitution.
(iii) Centre-State relations: Improving the center-state relations is one more way in which federalism has been strengthened in practice. Though Indian Constitution has demarcated the powers of the Union and the state governments but still the Union government can have influence over the state in many ways. In the past, the Central government has often misused the Constitution to dismiss the state governments that were controlled by rival parties. This undermined the spirit of federalism, and that of democracy.
Question 31.
Describe the process of unification of Germany.
OR
Describe the process of unification of Britain.
Answer: In the mid-nineteenth century, Germany was a coalition of smaller states that were inextricably intertwined as a German confederation. Austria dominated this confederation. In the 1860s, the dominant position of Austria was challenged by Prussia and the process of unification and codification of German law started. In the 1840s, nationalist feelings were rampant in the hearts of the middle-class GermAnswer: In 1848, the bourgeois intelligentsia united to form a nation-state out of the several German states.
However, the monarchy and the military combined to subdue them and they also achieved independence from the landowners of Prussia (the Junkers). Subsequently, Prussia became the leader of the German unification movement. Its chief minister Otto von Bismarck was the architect of the unification movement, supported by the Prussian army and Prussian bureaucracy. The unification process was accomplished after Prussia triumphed over Austria, Denmark and France over seven years’ time. On January 1871, the Prussian King, Kaiser William I was proclaimed the German Emperor in a ceremony held at the Palace of Versailles.
OR
In Britain, the establishment of the nation-states was the culmination of long persistent process. Principal identities of the people were ethnic ones. All ethnic groups like English, Welsh, Scot or Irish had their own cultural and political traditions. The English nation continued to grow in wealth and power. It was able to expand its influence over other nations. The Act of Union of 1707 between England and Scotland culminated in the development of the United Kingdom of Great Britain. The British parliament was dominated by the English. On the other hand, the Scottish influence began to wither away. These conditions resulted in many revolts. At the same time, the older nations were curbed to being subordinate partners in the arrangement. British flag and anthem were propagated in Britain.
Question 32.
Write any two non-material things on which the quality of our life depends? Define the following concepts:
(a) Infant Mortality Rate (or IMR)
(b) Literacy Rate
(c) Net Attendance Ratio
OR
Kerala with lower per capita income has a better human development ranking than Maharashtra. Hence, per capita income is not an useful criterion at all and should not be used to compare states. Do you agree? Discuss.
Answer:
- A safe and secure environment.
- Quality friends and relatives.
Definitions:
(a) Infant Mortality Rate (or IMR) refers to the number of children that die before the age of one year as a proportion of 1000 live children bom in that particular year.
(b) Literacy Rate is the measure of the proportion of literate population in the 7 and above age group.
(c) Net Attendance Ratio is the total number of children of age group 6-10 attending school as a percentage of total number of children in the same age group.
OR
The per capita income is a simple criterion which is easy to calculate and understand. So it is useful but it is not a comprehensive measure of human development. It only reflects the average income per person of the country but there are two limitations with this criterion.
(i) The first limitation is that this criterion is very much influenced by the extreme upper and lower values and fails to represent the level of equality of income.
![]()
(ii) Secondly, it does not represent the other indicators of quality of life like level of health and education which are equally or rather more important objectives for human development on which the magnitude of income depends. Kerala has Low Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) and better level of education than those of Maharashtra that is why Kerala, though with lower per capita income has a better human development ranking than Maharashtra.
Question 33.
What is soil conservation? Explain the methods of soil conservation suitable to Indian conditions
OR
Define resources. How are resources classified?
Answer:
Soil conservation includes all those measures which help in protecting the soil from erosion or degradation.
(i) Crop rotation: If the same crop is sown in the same field, year after year, this consumes certain nutrients from the soil making it infertile. Crop rotation can check this type of erosion.
(ii) Settled agriculture: Checking and reducing shifting agriculture by persuading the tribal people to switch over to settled agriculture.
(iii) Terracing and contour bunding: Terracing and contour bunding across the hill slopes is a very effective, and one of the oldest methods of soil conservation. Hill slope is cut into a number of terraces having horizontal top and steep slopes on the back and front. Contour bunding involves the construction of bank along the contour.
(iv) Strip cropping: Large fields can be divided into strips. Strips of grass are left to grow between the crops. This breaks the force of the wind. This method is known as strip cropping.
(v) Shelter Belt: Planting lines of trees to create shelter also works in a similar way. Rows of such trees are called shelter belts. These belts have contributed significantly to the stabilisation of sand dunes and in establishing the desert in western India.
OR
Anything which can be used to satisfy our needs is technologically accessible, economically, feasible and culturally acceptable can be termed as a ‘Resource’.
The resources can be classified into various categories:
- On the basis of origin – biotic and abiotic
- On the basis of exhaustibility – renewable and non-renewable
- On the basis of ownership – individual, community, national and international
- On the basis of status of development – potential, developed stock and reserves.
Section – E
(Case-Based Questions)
Question 34.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows:
However, once the East India Company established political power, it could assert a monopoly right to trade. It proceeded to develop a system of management and control that would eliminate competition, control costs, and ensure regular supplies of cotton and silk goods. This it did through a series of steps.
First: the Company tried to eliminate the existing traders and brokers connected with the cloth trade, and establish a more direct control over the weaver. It appointed a paid servant called the gomastha to supervise weavers, collect supplies, and examine the quality of cloth. Second: it prevented Company weavers from dealing with other buyers. One way of doing this was through the system of advances. Once an order was placed, the weavers were given loans to purchase the raw material for their production. Those who took loans had to hand over the cloth they produced to the gomastha. They could not take it to any other trader.
1. How did the East India Company establish monopoly over trade?
Answer:
To establish monopoly over trade in India, the Company developed a system of management and control that would eliminate competition, control costs, and ensure supplies of cotton and silk goods.
2. Who were gomasthas?
Answer:
Gomasthas were the paid servants of the East India Company who were given the responsibility to supervise weavers, collect supplies and examine the quality of cloth.
3. How the East India Company controlled the textile industry in India?
Answer:
The East India Company controlled the textile industry in India by several ways:
- The Company made policies to ensure the eradication of the traders and brokers who were connected with the cloth trade.
- They also appointed gomasthas to regulate the people related to the textile industry.
- The weavers were forced to do agreements with the Company and after that they could not make agreements with the other traders and this led to the uncompetitive prices for their production. (Any two points)
Question 35.
Read the given extract and answer the following questions.
You have studied the physical diversities and plurality of cultures in India. These are also reflected in agricultural practices and cropping patterns in the country. Various types of food and fibre crops, vegetables and fruits, spices and condiments, etc. constitute some of the important crops grown in the country. India-has three cropping seasons-rabi, kharif and zaid. Rabi crops are sown in winter from October to December and harvested in summer from April to June. Some of the important rabi crops are wheat, barley, peas, gram and mustard.
Though, these crops are grown in large parts of India, states from the north and north-western parts such as Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh are important for the production of wheat and other rabi crops. Availability of precipitation during winter months due to the western temperate cyclones helps in the success of these crops. However, the success of the green revolution in Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan has also been an important factor in the growth of the above-mentioned rabi crops.
Kharif crops are grown with the onset of monsoon in different parts of the country and these are harvested in September-October. Important crops grown during this season are paddy, maize, jowar, bajra, tur (arhar), moong, urad, cotton, jute, groundnut and soyabean. Some of the most important rice-growing regions are Assam, West Bengal, coastal regions of Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Maharashtra, particularly the (Konkan coast) along with Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. Recently, paddy has also become an important crop of Punjab and Haryana.
In states like Assam, West Bengal and Odisha, three crops of paddy are grown in a year. These are Aus, Aman and Boro. In between the rabi and the Kharif seasons, there is a short season during the summer months known as the Zaid season. Some of the crops produced during ‘zaid’ are watermelon, muskmelon, cucumber, vegetables and fodder crops. Sugarcane takes almost a year to grow.
1 Name some important zaid crops.
Answer:
These are: watermelon, muskmelon, cucumber, vegetables and fodder crops.
2. Analyse the reason of precipitation during winter months.
Answer:
It occurs due to western temperate cyclones and helps in the success of rabi crops.
3. State any two characteristics of Kharif cropping season.
Answer:
- In this season, crops are grown with the onset of monsoon and harvested in September-October.
- Some of the important kharif crops are paddy, maize, jowar, bajra, groundnut, etc.
Question 36.
Read the given extract and answer the following questions.
We have seen how crucial political parties are for the working of democracy. Since parties are the most visible face of democracy, it is natural that people blame parties for whatever is wrong with the working of democracy. All over the world, people express strong dissatisfaction with the failure of political parties to perform their functions well. This is the case in our country too. Popular dissatisfaction and criticism has focused on four problem areas in the working of political parties. Political parties need to face and overcome these challenges in order to remain effective instruments of democracy.
![]()
In order to face these challenges, political parties need to be reformed. The question is: Are political parties willing to reform? If they are willing, what has prevented them from reforming so far? If they are not willing, is it possible to force them to reform? Citizens all over the world face this question. This is not a simple question to answer. In a democracy, the final decision is made by leaders who represent political parties. People can replace them, but only by another set of party leaders. If all of them do not wish to reform, how can anyone force them to change?
1. How can you say that there is lack of internal democracy within political parties?
Answer:
- The concentration of power is in the hands of one or few leaders at the top.
- Ordinary members of the party do not get sufficient information about party decisions and those who disagree with the decisions find it difficult to continue in the party. (Anyone)
2. List any one major challenge which the political parties face in the present era?
Answer:
- Lack of internal democracy
- Dynastic succession
- The growing role of money and muscle power
- Parties do not seem to offer a meaningful choice to the voters. (Anyone)
3. “Defection makes democracy weak” Explain the steps taken by our leaders to end defection.
Answer:
The Constitution was amended to prevent elected MLAs and MPs from changing parties. This was done because many elected representatives were indulging in defection in order to become ministers or for cash rewards. Now the law states that if any MLA or MP changes parties, he or she will lose the seat in the legislature. This new law has helped bring defection down.
Section – F
(MAP Skill-Based Question)
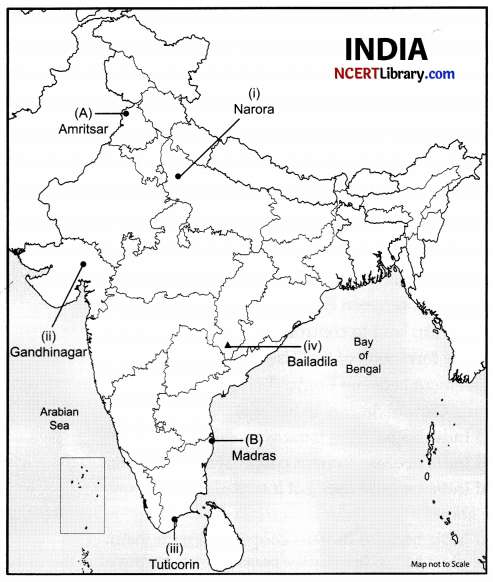
Question 37.
(a) Two places (A) and (B) have been marked on the given outline map of India. Identify them and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them.
(A) The place where the Jallianwala Bagh incident took place.
(B) The place where the session of Indian National Congress was held in 1927.
(b) On the same outline map of India locate and label any three of the following:
- Narora Nuclear Power Plant.
- Gandhinagar Software Technology Park.
- Tuticorin Seaport.
- Identify the iron ore mine.
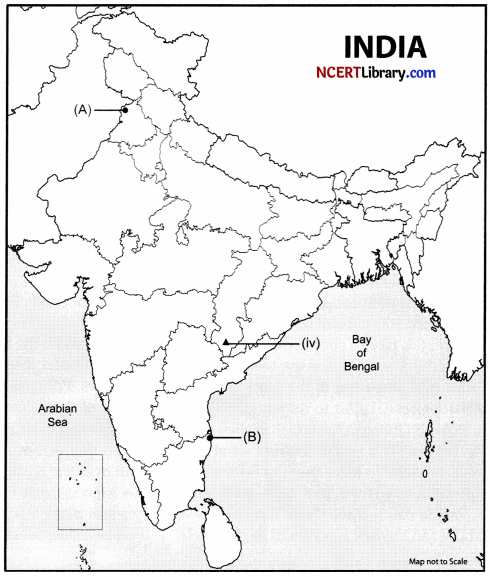
Answer: