Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions Set 1 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 1 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- Question paper comprises Six Sections -A, B, C, D, E, and F. There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A – From question 1 to 20 are MCQs of 1 mark each.
- Section B – Question no. 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words.
- Section C – contains Q.25 to Q.29 are Short Answer Type Questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 60 words
- Section D – Question no. 30 to 33 are long answer-type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section E – Questions no from 34 to 36 are case-based questions with three sub-questions and are of 4 marks each.
- Section F – Question no. 37 is map-based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 37a from History (2 marks) and 37b from Geography (3 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions has to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
Section – A
Multiple Choice Questions (1 × 20 = 20)
Question 1.
What helped in the colonization of Asian and African countries? Identify the correct statement from the
following options. [1]
A. Intergovernmental policies for the expansion of trade
B. Governmental invite to the mother countries for expansion
C. Technology, investments and improvement in transport
D. Capitalists of these regions wanted trade with colonial powers
Answer:
C. Technology, investments and improvement in transport
Explanation:
Industrialization had already occurred in Britain, and new technologies were available. New people were coming up with different inventions. They required markets for their goods as well as raw materials for their industries. British people were looking for locations from where they could purchase raw materials at a reasonable price as well as a market where goods could be sold. The development of means of transportation was another factor in capturing and exploiting the weaker nations.
![]()
Question 2.
Which of the following newspaper was started by Bal Gangadhar Tilak? [1]
A. Hindu
B. Kesari
C. Sudharak
D. Pratap
Answer:
B. Kesari
Explanation:
An important figure in the Indian Independence struggle, Lokmanya Tilak, started the Marathi newspaper ‘Kesari’ on January 4, 1881. The newspaper, which is still published by the Kesari Maratha Trust and Tilak’s heirs, served as a spokesman for the Indian national freedom cause.
Question 3.
Look at the picture given below. Identify the name of the painter of this painting from the following [1]

A. Abanindranath Tagore
B. Rabindranath Tagore
C. Raja Ravi Verma
D. Samant Das Gupta
Answer:
C. Raja Ravi Verma
Explanation:
Raja Ravi Verma mixed European and Indian elements to produce an original painting style. The renowned Indian epics Mahabharata and Ramayana, as well as ancient mythical tales from the Puranas, were all featured in the paintings of Raja Ravi Verma. Raja Ravi Verma distinguished himself from other artists of his era by fusing elements of Indian culture with special methods used in European academic art.
Question 4.
Arrange the following in chronological order: [1]
I. Print culture created the conditions for the French Revolution.
II. Martin Luther’s writings led to beginning of the Protestant Reformation.
III. Menocchio reinterpreted the message of the Bible.
IV. Johann Gutenberg invented printing press.
OPTIONS:
A. Ill, II, I & IV
B. I, II, III & IV
C. IV, III, II & I
D. IV, II, HI & I
Answer:
D. IV, II, III & I Explanation:
1. Around 1436, German goldsmith, Johannes Gutenberg is credited with creating the printing press.
2. On October 31, 1517, a teacher and monk named Martin Luther released a work he called Disputation on the Power of Indulgences, or Ninety-Five Theses, which marked the start of the Protestant Reformation.
3. Italian miller, Menocchio started reading the books that were available in his area in the sixteenth century. He developed a vision of God and Creation and reinterpreted the Bible’s message in a way that infuriated the Roman Catholic Church.
4. By the 1780s, there was a flood of literature that made fun of the royal family and their morals.
It caused controversy by raising issues with the current societal structure. It resulted in negative attitudes about the monarchy. Thus, print culture fostered the circumstances that led to the French Revolution.
Question 5.
Identify the crop with the help of the following information: [1]
- It is a crop that is used both as food and fodder.
- It is a kharif crop that requires a temperature between 21°C to 27°C.
- It grows well in old alluvial soil.
- Use of modern inputs has contributed to the increasing production of this crop.
Options:
A. Wheat
B. Maize
C. Rice
D. Sugarcane
Answer:
B. Maize
Explanation:
Maize is a crop that is used for both food and fodder. It is a kharif crop that grows best on old alluvial soil and requires temperature between 21 °C and 27°C. In some states, such as Bihar, maize is also planted during the rabi season.
Question 6.
Which of the following description of forest is NOT correct? [1]
A. Reserved Forest -Reservation of more than half of forests
B. Protected Forest- Reservation of 1/3 of the forests
C. Unclassed Forest-Reservation of forest under govt, and private individuals Permanent Forest-Reserved and D.unclassed forest for the production of timber Permanent Forest-Reserved and unclassed forest for the production of timber
Answer:
D.unclassed forest for the production of timber Permanent Forest-Reserved and unclassed forest for the production of timber
Explanation:
Reserved and protected forests are sometimes known as permanent forest estates, which are kept up for the purpose of producing wood and other forest products as well as for protective purposes. For example, Madhya Pradesh has the most land covered under permanent forests.
Question 7.
Match the following: [1]
| Resources | Examples |
| (a) Renewable Resources: | I. Forests and wildlife |
| (b) Non-Renewable Resources: | II. The oceanic resources |
| (c) National Resources: | III. Roads, canals and railway |
| (d) International Resources: | IV. Minerals and fossil fuels |
OPTIONS:
A. a-I, b-IV, c-III, d-II
B. a-II, b-I, c-IV, d-III Answer: A. a-I, b-IV, c-III, d-II
C. a-IV, b-I, c-IV, d-II
D. a-I, b-IV, c-II, d-III
Answer:
A. a-I, b-IV, c-III, d-II
Explanation:
- Renewable resources can replenish themselves at the pace of usage. E.g. Forests and wildlife.
- The supply of non-renewable resources is limited. E.g. Minerals and fossil fuel.
- All resources controlled by state or federal governments are referred to as national resources. E.g. Roads, canals, and railways.
- International Resources: These are organizations that govern all territories that do not belong to any particular nation. E.g. The oceanic resources.
![]()
Question 8.
Consider the following statements regarding power-sharing arrangements in Belgium and identify the
incorrect one from the following:
A. Equal number of members from Dutch and French community in the central government
B. Separate government for Brussels with equal representation of communities
C.The state government to be subordinate to the central government
D.Community government elected by people belonging to one language community
Answer:
C.The state government to be subordinate to the central government
Explanation:
In Belgium, the state government is not subjected to the central government.
Question 9.
Which one of the following subjects comes under the legislation of Centre and State in India? [1]
A. Education
B. Forests
C. Banking
D. Trade
Answer:
A. Education
Explanation:
The 42nd Amendment Act of 1976 shifted five issues from the State List to the Concurrent List. These were as follows:
Education, weights and measures, forests, administration of justice and wild animal and bird protection
Question 10.
Which of the following statements is true regarding Feminist Movements?
A. A group which favours giving more power to working women at rural and urban level.
B. A movement that believes in giving exclusive rights to female in urban areas.
C. Radical women’s movements aimed at equality in personal and family life as well.
D. It is the practice of placing a feminine and masculine point of view in decision making.
Answer:
C. Radical women’s movements aimed at equality in personal and family life as well.
Explanation:
The term “feminist movement” refers to groups or movements calling for improvements to the political and legal standing of women as well as their educational and employment prospects. Achieving equality for men and women is the primary goal of the feminist movement. It neither favours giving more power to working women at rural and urban level nor believes in giving exclusive rights to females in urban areas. Additionally, it has nothing to do with the practise of including both feminine and masculine viewpoints when making decisions.
Question 11.
Which one among the following pairs is correctly matched? [1]
| List I | List II |
| A. Bharatiya Janata Party | National Democratic Alliance |
| B. Congress Party | Left front |
| C. Communist Party of India | Regional Party |
| D. Mizo National Front | United Progressive Alliance |
Answer:
A. Bharatiya Janata Party – United Progressive Alliance
Explanation:
National Democratic Alliance (NDA) is a broad-based political coalition in India that is headed by the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP). It was established in 1998 and currently is in power at the national level including in 18 Indian states and one Union Territory.
Question 12.
There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided below: [1]
Assertion (A): Democracy is an accountable, responsive and legitimate government.
Reason (R): Democracies have regular, free and fair elections and decision-making is based on norms and procedures.
A. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
C. A is true but R is false.
D. A is false but R is true.
Answer:
A. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
A democratic government is said to be an accountable, responsive and legitimate government due to a plethora of reasons. It provides the chance to the people of the nation to choose their own representatives by conducting free and fair elections. The decisions are based on proper norms and procedures.
Question 13.
Which one of the following religions was protected and fostered by Sri Lankans in their constitution? [1]
A. Christianity
B. Hinduism
C. Buddhism
D. Islam
Answer:
C. Buddhism
Explanation:
Following is a list of actions that Sri Lanka took in accordance with the 1956 Act:
- Buddhism will be promoted and protected by the State.
- Policies were created favoring Sinhala applicants for posts in government and higher education.
- Sinhala was acknowledged as the only official language, while Tamil was entirely ignored.
Question 14.
Read the given data and find out children of which state have attained maximum elementary school education. [1]
| States | Per Capita Income For 2018-19 (in?) | Infant Mortality Rate per 1,000 live births (2018) | Literacy Rate % 2017-18 | Net Attendance Ratio (per 100 persons) secondary stage (age 14 and 15 years) 2017-18 |
| HARYANA | 2,36,147 | 30 | 82 | 61 |
| KERALA | 2,04,105 | 7 | 94 | 83 |
| BIHAR | 40,982 | 32 | 62 | 43 |
Sources:
Economic Survey 2020-21, P.A 157, National Sample Survey Organisation (Report No. 585), National Statistical Office, Government of India.
A. Haryana
B. Bihar
C. Haryana and Kerala both
D. Kerala
Answer:
D. Kerala
Explanation:
As per the table given above, 94% of children attained elementary school education in Kerala, whereas the percentage in Haryana and Bihar is 82 and 62 respectively.
![]()
Question 15.
Read the following data and select the appropriate option from the following. [1]
| Educational Achievement of Rural Population of Uttar Pradesh | ||
| Category | Male | Female |
| Literacy rate for rural population | 76% | 54% |
| Literacy rate for rural children in age group 10-14 years | 90% | 87% |
| Percentage of rural children aged 10-14 attending school | 85% | 82% |
How much percentage of girls are not attending school?
A. 81%
B. 61%
C. 69%
D. 18%
Answer:
D. 18%
Explanation:
According to the table given above, The percentage of rural children aged 10-14 attending school’ is 82% for females. Therefore, the remaining 18% of the females are not attending the school.
Question 16.
Find the odd one out from the following options: [1]
A. Tourist Guide, Barber, Tailor, and Potter
B. Teacher, Doctor, Vegetable Vendor and Lawyer
C. Postman, Cobbler, Soldier and Police Constable
D. Indian Railways, Jet Airways, Doordarshan and Metro
Answer:
D. Indian Railways, Jet Airways, Doordarshan and Metro
Explanation:
Option (A), (B), (C) are related to professions, whereas option (D) is related to the means of transportation/communication.
Question 17.
Fill in the blank: [1]
| SECTOR | CRITERIA USED |
| Primary, Secondary & Tertiary | Nature of economic activity |
| Organized & Unorganized | ? |
OPTIONS:
A. Nature of Employment activities
C. Nature of Production activities
B. Nature of Social activities
D. Nature of Political activities
Answer:
A. Nature of Employment activities
Explanation:
The economic activities are divided into organized and unorganized sectors based on employment circumstances or the type of employment activities.
Question 18.
Read the information given below and select the correct option: [1]
Rohan has taken a loan of ?5 lakhs from the bank to purchase a house on 12% rate of interest. He has to submit papers of new house and salary record to the bank. What is this process called as?
A. Interest Rate
C. Principal Amount
B. Collateral
D. Installments
Answer:
B. Collateral
Explanation:
A property or other type of physical wealth that the borrower holds, such as a home, livestock, a car, etc., is known as collateral. The bank provides money to the borrower based on these assets.
Question 19.
Which of the following international agencies allow free trade and work on mutual trade between countries?
A. WTO
B. IMF
C. UPU
D. FAO
Answer:
A. WTO
Explanation: The WTO’s main goal is to promote the elimination of trade restrictions and other trade-distorting regulations so that products and services can move more freely among its member nations.
Question 20.
Identify the correct statements about globalization. [1]
Answer:
I. Removal of barriers by the government II. Foreign companies are allowed to set up factories
III. Has enabled all companies to increase their investments
IV. Has lessened foreign investment and foreign trade OPTIONS:
A. I & II B. II & III C. I & HI D. II & IV
Answer:
A. I & II
Explanation:
Globalization entails the reduction of government restrictions. The government permits open trade contacts between all nations. According to globalization’s liberalization policy, this refers to the freedom of business owners to launch any type of industry, trade, or commercial enterprise, both domestically and internationally.
Section – B
(Very Short Answer-Based Questions)
Question 21.
Analyze any two factors that were responsible for the Great Depression in America during 1929. [2]
Answer:
- Agricultural overproduction remained a problem and it was made worse by falling agricultural prices.
- As prices slumped and agricultural incomes declined, farmers tried to expand production and bring a larger volume of produce to the market but it pushed down prices.
- In the mid-1920s, many countries financed their investments through loans from the US, it was extremely easy to raise loans in the US when the going was good.
- But in the first half of 1928, countries that depended crucially on US loans faced an acute crisis.
- The withdrawal of US loans affected the rest of the world in different ways. In Europe, it led to the failure of small major banks and the collapse of currencies such as the British pound sterling.
- Any other relevant point. (Any two points)
![]()
Question 22.
Mention the provisions that constitute India into a secular country. [2]
Answer:
- There is no official religion for the Indian state. Our Constitution does not give a special status to any religion.
- The Constitution provides to all individuals and communities freedom to profess, practice and propagate any religion, or not to follow any.
- The Constitution prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion.
- Secularism is an idea that constitutes one of the foundations of our country.
- At the same time, the Constitution allows the state to intervene in matters of religion in order to ensure equality within religious communities.
- Any other relevant point? (Any two points)
Question 23.
Suggest any two ways to conserve energy resources in India. [2]
OR
Suggest any two ways to improve the usage of Solar energy.
Answer:
Energy can be conserved in different ways. Some of them are as below:
- Promotion of energy conservation and increased use of renewable energy sources. The people should be made aware of the fact that energy should be conserved and used sustainably. They should use renewable energy sources.
- We have to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious use of our limited energy resources. A sustainable use of non-renewable energy resources are very important to conserve them.
- Use public transport systems instead of individual vehicles. People should use public transport instead of private vehicles to save excess use of fossil fuels.
- Switch off electricity when not in use. One should switch off electricity when one is not using it. It can save a huge amount of energy in the whole world.
- Using power-saving devices is another method to conserve energy.
- One should use non-conventional sources of energy.
- Any other relevant point. (Any two points)
OR
Some ways to improve the usage of solar energy are as follows:
- It can be improved by reducing the cost of solar panels.
- Use of efficient solar panel models is another method of improving the usage of solar energy.
- Rising awareness about the importance of renewable energy is very important. In society, people should be made aware of this fact.
- Easy installation process. The installation process of solar panels is very easy. People can easily install them in their houses on their own.
- One should buy the solar panels with High Concentrated Photovoltaic (CPV) Cells.
- One should avoid installing solar panels in shaded areas as it will act as a barrier in the production of solar energy.
- Any other relevant point. (Any two points)
Question 24.
In what ways Government can increase employment in the rural sector? [2]
Answer:
The Government can increase employment in the rural sector by adopting the following methods:
- By introducing mega projects. New dams are constructed and canals are dug to irrigate the agricultural land.
- By introducing tertiary facilities in an area.
- To identify, promote and locate industries and services in semi-rural areas.
- It is also possible to set up industries that process vegetables and agricultural produce like potato, sweet potatoes, etc.
- By promoting tourism, or regional craft industry, or new services like IT.
- Any other relevant point. (Any two points)
Section – C
Short Answer-Based Questions (3×5 = 15)
Question 25.
How was the social and political situation of India affected by the First World War? Explain. [3]
OR
How did the Indian merchants and industrialists relate themselves to the Civil Disobedience Movement?
Explain.
Answer:
- The war created a new economic and political situation.
- It led to a huge increase in defence expenditure which was financed by war loans and increasing taxes: customs duties were raised and income tax introduced.
- Through the war years prices increased, doubling between 1913 and 1918, leading to extreme hardship for the common people.
- Villages were called upon to supply soldiers, and the forced recruitment in rural areas caused widespread anger.
- Crops failed in many parts of India, resulting in acute shortages of food.
- This was accompanied by an influenza epidemic. Millions of people perished as a result of famines and the epidemic.
- Any other relevant point. (Any three points)
OR
- Indian merchants and industrialists were keen on expanding their business, and reacted against colonial policies that restricted business activities.
- They wanted protection against imports of foreign goods, and a rupee-sterling foreign exchange ratio that would discourage imports.
- To organise business interests, they formed the Indian Industrial and Commercial Congress in 1920 and the Federation of the Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industries (FICCI) in 1927.
- Led by prominent industrialists like Purshottamdas Thakurdas and G. D. Birla, the industrialists attacked colonial control over the Indian economy and supported the Civil Disobedience Movement.
- They gave financial assistance and refused to buy or sell imported goods.
- Most businessmen wanted to flourish trade without constraints.
- Any other relevant point. (Any three points)
Question 26.
Examine the factors that influence the distribution pattern of the railway network in India. [3]
Physical and economic factors have influenced the distribution pattern of the Indian Railways network in the following ways:
(i) Northern Plains: Level land, high population density and rich agricultural resources have favoured development of railways in these plains. However, a large number of rivers requiring construction of bridges across their wide river beds posed some obstacles.
(ii) Peninsular region: It is a hilly terrain. The railway tracks are laid through low hills, gaps or tunnels. So, it is very difficult to lay the railway lines.
(iii) Himalayan region: The Himalayan mountainous regions too are not favourable for the construction of railway lines due to high relief, sparse population and lack of economic opportunities.
(iv) Desert of Rajasthan: On the sandy plain of western Rajasthan too, it is very difficult to lay railway lines which has hindered the development of railways.
(v) Swamps of Gujarat, forested tracts of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Jharkhand; these are also not suitable for the development of railways.
(vi) The contiguous stretch of Sahyadri could be crossed only through gaps or passes. Although the Konkan railway along the west coast has been developed but it has also faced a number of problems such as sinking of track in some stretches and landslides.
(vii) Any other relevant point. (Any three points)
![]()
Question 27.
In what ways Multi-National Corporation (MNC) different from other companies? Explain with an example. [3]
(i) Domestic companies tend to restrict their operations to the country of origin, while multinational corporations operate in more than two countries. Ex- Infosys.
(ii) Companies (Infosys) expand globally for many reasons, mostly to obtain new markets, cheaper resources and reduction in operational costs, all of which significantly affect financial management. These benefits also increase the risks faced by multinational corporations.
(iii) Multinational (Infosys) financial management differs from domestic financial management in six essential ways.
(iv) Unlike their domestic financial management counterparts, multinationals are subject to exchange rates that differ based on the prevailing inflation rate in the foreign countries where they operate.
(v) Any other point. (Any three points)
Question 28.
Differentiate between democratic and non-democratic government. [3]
(i) Democratic goverment are transparent, legitimate and accountable whereas non-democratic governments are selected and formed at their own discretion
(ii) Democratic governments provides dignity and freedom to all without any discrimination whereas it is not possible to get it in a non-democratic government.
(iii) In a democratic government, conflicts are resolved through debate, discussions and negotiation rather than discretion. In a non-democratic government, the head of the government is the single person to resolve the conflicts.
(iv) Minority and majority cooperation is a common phenomenon in the democratic government. It can’t be seen in a non-democratic government.
(v) Democratic government enhances dignity of all without any discrimination.
(vi) Any other relevant point. (Any three points)
Question 29.
‘Tertiary sector is different from other sectors.’ Justify the statement with suitable arguments. [3]
- The tertiary sector is basic service sector, whereas primary and secondary sectors are the sectors that are engaged in producing goods.
- The tertiary sector supports and helps in the development of the primary and secondary sectors.
- Tertiary activities can be termed as an assistance for the production process.
- The tertiary sector provides services like transport, banking, communication, etc.
- It generates more employment than other sectors.
- Any other relevant point. (Any three points)
Section – D
(Long Answer-Based Questions) (5 × 4 = 20)
Question 30.
Highlight the various measures and practices that French revolutionaries introduced to create a sense of
collective identity amongst the French people. [5]
OR
Highlight the role of Otto von Bismarck in making of Germany.
Answer:
- The ideas of la patrie (the fatherland) and le citoyen (the citizen) emphasised the notion of a united community enjoying equal rights under a constitution.
- A new French flag, the tricolour, was chosen to replace the former royal standard.
- The Estates General was elected by the body of active citizens and renamed the National Assembly.
- New hymns were composed, oaths taken and martyrs commemorated.
- A centralized administrative system was put in place and it formulated uniform laws for all citizens within its territory.
- Internal customs duties and dues were abolished and a uniform system of weights and measures was adopted.
- Regional dialects were discouraged and French, as it was spoken and written in Paris, became the common language of the nation.
- Any other relevant point. (Any five points)
OR
(i) Prussia took on the leadership of the movement for national unification.
(ii) Its chief minister, Otto von Bismarck, was the architect of this process carried out with the help of the Prussian army and bureaucracy.
(iii) Three wars over seven years – with Austria, Denmark and France, ended in Prussian victory and completed the process of unification.
(iv) In January 1871, the Prussian king, William I, was proclaimed German Emperor in a ceremony held at Versailles.
(v) On 18 January 1871, an assembly comprising the princes of the German states, representatives of the army, important Prussian ministers including the Chief Minister Otto von Bismarck gathered in the Hall of Mirrors in the Palace of Versailles to proclaim the new German Empire headed by Kaiser William I of Prussia.
(vi) Any other relevant point. (Any five points)
Question 31.
‘Manufacturing sector is considered as the backbone of general and economic development/ Examine the statement in the context of India. [5]
OR
Examine the multi-pronged aspects of Information Technology and Electronics Industry.
Answer:
- Manufacturing industries help in modernising agriculture.
- It helps in reducing the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
- It helps in eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country.
- It helps in reducing regional disparties by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas.
- Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce.
- It helps in bringing foreign exchange.
- Any other relevant point (Any five points)
OR
Describe the necessity or utility of political parties in democratic countries.
Answer:
- Parties nominate candidates to run in elections. These candidates could be chosen by the party’s leaders or by its members.
- Voters can choose from a variety of policies and programmes put forth by the parties.
- The creation of legislation for a nation depends heavily on political parties. The legislature is typically where laws are discussed and adopted.
- Parties establish and control governments. They appoint leaders, educate them to serve as ministers, and then manage the government according to their preferences.
- The opposition is made up of losing parties. The opposition expresses diverse opinions and faults the administration.
- Public opinion is shaped by parties. They have thousands of members spread out around the nation, and they have a significant impact on how people think.
- Parties give the average person access to government resources and social programmes. A person can meet a local party leader more easily than a government representative.
- Any other relevant point. (Any five points)
![]()
OR
(i) Elected representatives will be accountable to their constituency for what they do in the locality. The rise of political parties is directly linked to the emergence of representative democracies. Thus, large scale societies need representative democracy.
(ii) As societies became large and complex, they also needed some agency to gather different views on various issues and to present these to the government.
(iii) They needed some way to bring various representatives together so that a responsible government could be formed.
(iv) They needed a mechanism to support or restrain the government, make policies, justify or oppose them. .
(v) Political parties fulfill these needs that every representative government has. We can say that parties are a necessary condition for a democracy.
(vi) Any other relevant point. (Any five points)
Question 33.
Explain the role of Self-Help Groups (SHGs) in the rural society. [5]
OR
Explain the significance of the Reserve Bank of India in the Indian economy.
Answer:
- The idea is to organize rural poor, in particular women, into small Self Help Groups (SHGs) and pool (collect) their savings.
- A typical SHG has 15-20 members, usually belonging to one neighborhood, who meet and save regularly. Saving per member varies from Rs 25 to Rs 100 or more, depending on the ability of the people to save.
- Members can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs.
- The group charges interest on these loans but this is still less than what the moneylender charges.
- After a year or two, if the group is regular in savings, it becomes eligible for availing loan from the bank.
- Loan is sanctioned in the name of the group and is meant to create self-employment opportunities for the members.
- Small loans are provided to the members for releasing mortgaged land, for meeting working capital needs.
- Most of the important decisions regarding the savings and loan activities are taken by the group members.
- The group decides as regards the loans to be granted — the purpose, amount, interest to be charged, repayment schedule etc. Also, it is the group which is responsible for the repayment of the loan.
- Any case of non-repayment of loan by any one member is followed up seriously by other members in the group.
- Any other relevant point. (Any five points)
OR
- It supervises the functioning of formal sources of loAnswer:
- The banks maintain a minimum cash balance out of the deposits they receive.
- Out of the deposits they receive, the RBI mandates commercial banks to maintain a minimum cash balance. The RBI keeps an eye on whether the banks truly keep a cash balance.
- The RBI makes sure that banks lend money to small farmers, small-scale businesses, small borrowers, SHGs, and other groups in addition to profitable companies and dealers.
- Banks are required to periodically provide the RBI with information on how much they are lending, to whom, at what interest rate, etc.
- The RBI establishes recommendations for commercial banks to follow for setting interest rates on deposits and loAnswer:
- Any other relevant point. (Any five points)
Section – E
(Case-Based Questions)
Question 34.
Read the source given below and answer the question that follows: [4]
Will Thome is one of those who went in search of seasonal work, loading bricks and doing odd jobs. He describes how job-seekers walked to London in search of work:
Thad always wanted to go to London, and my desire was stimulated by letters from an old workmate … who was now working at the Old Kent Road Gas Works. I finally decided to go in November, 1881. With two friends I started out to walk the journey, filled with the hope that we would be able to obtain employment, when we get there, with the kind assistance of my friend we had little money when we started, not enough to pay for our food and lodgings each night until we arrived in London.
Some days we walked as much as twenty miles, and other days less. Our money was gone at the end of the third day For two nights we slept out – once under a haystack, and once in an old farm shed On arrival in London we tried to find my friend but were unsuccessful. Our money was gone, so there was nothing for us to do but to walk around until late at night, and then try to find some place to sleep. We found an old building and slept in it that night. The next day, Sunday, late in the afternoon, we got to the Old Kent Gas Works, and applied for work. To my great surprise, the man we had been looking for was working at the time. He spoke to the foreman and I was given a job.’
Quoted in Raphael Samuel, ‘Comers and Goers’, in H.J. Dyos and Michael Wolff, eds, The Victorian City: Images and Realities, 1973.
1. Analyse the major factor which led London become an attractive place for the job seekers. [1]
Answer:
Due to the industrial revolution and availability of job opportunities in factories of London it became a hub for the migrant people in search of employment.
2. Analyse the reason for the appointment of Will Thorne by the Old Kent Gas works. [1]
Answer:
Gas work was the seasonal industry and they were in need to low wage workers for increasing their operating profits.
3.Examine the preference of hand labour over machines by the industrialists of the Victorian Britain. [2]
Answer:
- Machines needed huge capital investments.
- Machines were costly, ineffective, difficult to repair.
- Labour was available at low wages.
- In seasonal industries, only seasonal labour was required.
- Any other relevant point. (Any two points)
Question 35.
Read the given extract and answer following questions: [4]
Narmada Bachao Andolan or Save Narmada Movement is a Non-Governmental Organisation (NGO) that mobilized tribal people, farmers, environmentalists and human rights activists against the Sardar Sarovar Dam being built across the Narmada river in Gujarat. It originally focused on the environmental issues related to trees that would be submerged under the dam water. Recently it has re-focused the aim to enable poor citizens, especially the oustees (displaced people) to get full rehabilitation facilities from the government.
People felt that their suffering would not be in vain… accepted the trauma of displacement believing in the promise of irrigated fields and plentiful harvests. So, often the survivors of Rihand told us that they accepted their sufferings as sacrifice for the sake of their nation. But now, after thirty bitter years of being adrift, their livelihood having even being more precarious, they keep asking: “Are we the only ones chosen to make sacrifices for the nation?”
![]()
Source:
S. Sharma, quoted in In the Belly of the River. Tribal conflicts over development in Narmada valley. A. Baviskar. 1995.
1. With what objective ‘Sardar Sarovar Dam’ was built? [1]
Answer:
- To secure power – One of the main objectives of Sardar Sarovar dam was to secure electricity.
- Irrigation is another objective of this project. The lands near the dam would get a good irrigation supply for their crops.
- Drinking water for the drought-prone region – The project would also provide drinking water facilities in the drought-prone regions.
- Any other relevant point. (Anyone point)
2. Analyse the reason of protest by the tribal people. [1]
Answer:
- Huge displacement of people: Due to the construction of the dam, several villages would be submerged under the water and the people would need to move from that place leaving behind their property and livelihood.
- Demand for rehabilitation: The people who had to move from that place demanded an alternative area to live from the government.
- The harm of harvest: As their livelihood was based on agriculture and the agricultural lands could not be used now, they protested and raised their voice against this issue.
- Loss of livelihood: As they were displaced from their own land, they lost their livelihood. They demanded some alternatives for their survival.
- Any other relevant point? (Anyone point)
3. Highlight the issues on which ‘Save Narmada Movement’ worked on. [2]
Answer:
- Against huge displacement of people : They raised their voice for the people who were being displaced from their own lands.
- Environmental issue: There would be a significant environmental loss as a result of the construction of the dam.
- Demand for rehabilitation of tribal: They demanded for an alternative area for their rehabilitation as they lost all their properties in this process.
- To provide tribals the source of livelihood : They also demanded some alternative sources of livelihood for the tribals by which they could survive.
- Any other relevant point. (Any two points)
Question 36.
Read the given extract and answer following questions. [4]
Power sharing arrangements can also be seen in the way political parties, pressure groups and movements control or influence those in power. In a democracy, the citizens must have freedom to choose among various contenders for power. In contemporary democracies, this takes the form of competition among different parties. Such competition ensures that power does not remain in one hand. In the long run, power is shared among different political parties that represent different ideologies and social groups. Sometimes this kind of sharing can be direct, when two or more parties form an alliance to contest elections.
If their alliance is elected, they form a coalition government and thus share power. In a democracy, we find interest groups such as those of traders, businessmen, industrialists, farmers and industrial workers. They also will have share in governmental power, either through participation in governmental committees or bringing influence on the decision-making process.
1.’Power sharing is an essential component of democracy.’ Give one example to prove the statement. [1]
Answer:
- It helps in reducing the possibility of conflict between the social groups.
- Power sharing is a good way to ensure the stability of political order.
- Any other relevant point.
2. How is alliance building an example of power sharing? [1]
Answer:
- When two or more parties form an alliance to contest elections or to form a government is called sharing of power.
- Alliance could be between regional and national parties which is again an example of power sharing.
- Political ideas are shared in this process.
- Any other relevant point. (Any one point)
3. How Political parties, pressure groups and movements help in controlling or influencing those who are in power? [2]
Answer:
- Freedom of choice entails competition among the different parties.
- Such competition ensures that power does not remain in one hand, but is shared among different political parties representing different ideologies and social groups.
- Any other relevant point. (Any two points)
Section – F
(MAP Skill Based Question) (2 + 3 = 5)
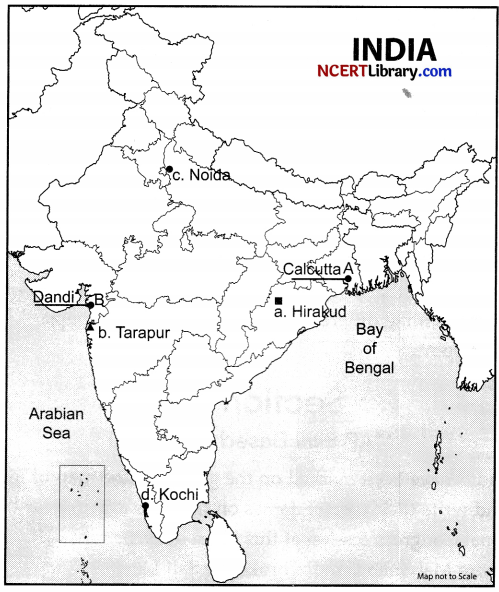
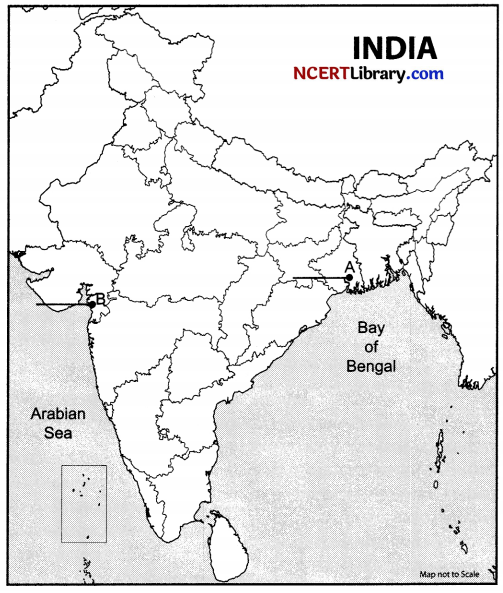
Question 37.
(a) Two places A and B have been marked on the given outline map of India. [2]
Identify them and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them.
A. Indian National Congress session at this place in 1920.
B. The place where Mahatma Gandhi broke the Salt Law.
(b) On the same outline map of India locate and label any THREE of the following with suitable symbols. [3]
a. Hirakud Dam.
b. Tarapur Atomic Power Station.
c. Noida Software Technology Park.
d. Kochi Port.
On the given outline map of India, identify the locations with the help of specified information.
Answer: