Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions Set 7 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 7 with Solutions
Time : 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 objective type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts.
Section – A
Select and write one most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1-20
Question 1.
When white light enters a glass prism from air, the angle of deviation is maximum for:
(a) blue light
(b) yellow light
(c) red light
(d) violet light
Answer:
(d) violet light
Explanation: The white light consists of seven colours in which the violet has least wavelength and red colour has the maximum wavelength.
Question 2.
The reaction which decomposes after the supply of heat is called:
(a) Thermal decomposition
(b) Combination reaction
(c) Redox reaction
(d) Displacement reaction
Answer:
(a) Thermal decomposition
Explanation: A thermal decomposition reaction occurs when heat is applied to a compound causing it to decompose (break down) into multiple different chemical substances. An example is when baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) is heated.
2NaHCO3(s) CO2(g) + H2O(g) + Na2CO3(s)
Question 3.
The defect of vision in which a person cannot see the distant objects clearly but can see nearby objects clearly is called:
(a) myopia
(b) hypermetropia
(c) presbyopia
(d) bifocal eye
Answer:
(a) myopia
Explanation: A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see distant objects distinctly. Myopia is also known as short-sightedness.
Question 4.
Which part of alimentary canal receives bile from the liver?
(a) Stomach
(b) Small intestine
(c) Large intestine
(d) Oesophagus
Answer:
(b) Small intestine
Explanation: Small intestine represents the largest portion of our alimentary canal and is known to comprise three different parts – jejunum, duodenum, and ileum. The small intestine receives bile from liver. This bile is later stored within the gall bladder which executes two different functions – making food alkaline and breaking down its fats content. The partially digested food is absorbed by the duodenum of the small intestine along with the digestive juices from the liver, pancreas and its own walls.
Question 5.
Consider the room temperature is 24°C in summer, the electrical resistance of thermo coil which is used in the AC unit is 150 Ω. Then calculate the temperature of the thermo coil if the electrical resistance is 175 Ω. Given the temperature coefficient of the thermo coil is 2.98 x 10<-4 °C-1.
(a) 597°C
(b) 583°C
(c) 546°C
(d) 512°C
Answer:
(b) 583°C
Explanation:
Rt = R0 (1 + ∝ ∆ T)
175 = 150 (1 + 2.98 x 10-4 ∆ T)
\(\frac { 25 }{ 150 }\) = 2.98 x ∆ T x 10-4
∆ T = 559.28°C
T – 24° = 559.28°C
T = 559.28°C + 24°
T = 583.28°C
Hence, the temperature of the thermo coil is 583°C.
Question 6.
Which of the following property is generally not shown by metals?
(a) Electrical conduction
(b) Sonorous in nature
(c) Dullness
(d) Ductility
Answer:
(c) Dullness
Explanation: Metals have the quality of reflecting light from its surface and can be polished. They are not dull but lustrous.
Question 7.
The values of mA and pA are :
(a) 10-6 and 10-9 A respectively
(b) 10-3 and 10-6 A respectively
(c) 10-3 and 10-6 A respectively
(d) 10-6 and 10-3 A respectively
Answer:
(b) 10-3 and 10-6 A respectively
Explanation:
An ampere is the SI unit of electric current.
1 A = 1000 mA or 1 mA = \(\frac { 1 }{ 1000 }\) A = 10-3 A
∴ IμA = 10-3 x 10-3 A = 10-6 A
![]()
Question 8.
Name the layer of brain from inside towards the outside:
(a) Duramater, Arachnoid and Piamater
(b) Arachnoid, Duramater and Piamater
(c) Piamater, Arachnoid and Duramater
(d) Arachnoid, Piamater and Duramater
Answer:
(c) Piamater, Arachnoid and Duramater
Explanation: The brain is protected by cranial meninges, which are made up of three layers: an outside layer called duramater, a very thin middle layer called arachnoid, and an inner layer called piamater (which is in contact with the brain tissue). Thus, the layer of brain from inside towards the outside is: Piamater, Arachnoid and Duramater.
Question 9.
The resistance of a resistor is reduced to half of its initial value. In doing so, if other parameters of the circuit remain unchanged the heating effects on the resistor will become:
(a) two times
(b) half
(c) one – fourth
(d) four times
Answer:
(a) two times
Explanation: Resistance of a resistor R Ω
New resistance of a resistor \(\frac { R }{ 2 }\) Ω.
All other parameters of the circuit remain unchanged

By applying Joule’s law of heating H = I² Rt
As per Ohm’s law V = IR
or I = \(\frac { V }{ R }\)
∴ H = \(\frac { V }{ R }\) x \(\frac { V }{ R }\) x R x t
= \(\frac{\mathrm{V}^2}{\mathrm{R}}\) x t
Case -I
H = \(\frac{\mathrm{V}^2}{\mathrm{R}}\) x t
Case -II
H’ = \(\frac{\mathrm{V}^2}{\frac{\mathrm{R}}{2}} \times t\)
= \(\frac{\mathrm{V}^2 \times 2}{\mathrm{R}}\) x t
H’ = H x 2
Hence, the heating effect in the resistor will become two times if all other parameter of the circuit remain same.
Question 10.
Characters that are transmitted from parents to offspring during reproduction show:
(a) Only similarities with parents.
(b) Only variations with parents.
(c) Both similarities and variations with parents.
(d) Neither similarities nor variations.
Answer:
(c) Both similarities and variations with parents.
Explanation: In sexual reproduction, the offspring are not identical to the parents or to one another. This is because the offspring receive some genes from mother and some from father. Due to the mixing of genes on re-establishment of number of chromosome in various different combinations, the offspring show both similarities and variations with characters of parents.
Question 11.
The accumulator which is used for the domestic purpose has the electromotive force of 10 V and with an internal resistance of 0.8 Ω is externally charged by 150 V of the direct current power supply using a series resistor 18 Ω. Calculate the terminal voltage of the accumulator during using.
(a) 16.8 V
(b) 17.1 V
(c) 11.3 V
(d) 15.9 V
Answer:
(d) 15.9 V
Explanation:
E = V – Ir
V = E + Ir
= 10 + \(\left(\frac{150-10}{18+0.8}\right)\) x 0.8
= 15.9 V
Question 12.
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) Gene is a sequence of nucleotides.
(b) During the process of gene expression, DNA is first copied into RNA.
(c) Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence.
(d) Genes cannot acquire mutations in their sequence,
Answer:
(d) Genes cannot acquire mutations in their sequence.
Explanation: Genes can acquire mutations. A gene mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that makes up a gene that is permanent and differs from the sequence found in most people.
Question 13.
The process shown in the diagram below is:
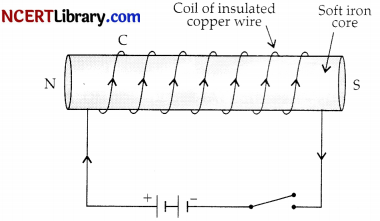
(a) Electromagnetism
(b) Electric generator
(c) Electric Motor
(d) Electric fuse
Answer:
(a) Electromagnetism
Explanation: An electromagnet produces a magnetic field so long as current flows in its coil.
Question 14.
Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding asexual reproduction in plants?
(a) Plants that reproduce asexually reach maturity faster than those who reproduce sexually.
(b) Plants that reproduce asexually have greater genetic diversity than those who reproduce sexually.
(c) Plants that reproduce asexually are more stable than those who reproduce sexually.
(d) Plants that reproduce asexually create offspring that are identical to the parent plant.
Answer:
(b) Plants that reproduce asexually have greater genetic diversity than those who reproduce sexually.
Explanation: Sexual reproduction provides genetic diversity because the sperm and egg that are produced contain different combinations of genes than the parent organisms. Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, does not need sperm and eggs since one organism splits into two organisms that have the same combination of genes.
Question 15.
The figure below shows the Fleming’s left hand rule. Identify the correct label with the function?
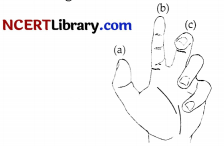
(a) Thumb force
(b) Fore finger magnetic field
(c) Middle finger-current
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Explanation: According to Fleming’s left hand rule stretch the thumb, fore finger and middle finger of your left hand side that they are mutually perpendicular. If the first finger points in the direction of magnetic field and second finger in the direction of current, then thumb will point in the direction of force.
Question 16.
Which of the following statements is true?
(a) The characteristics or traits of parents are transmitted to their progeny (offspring) through genes present on their chromosomes during the process of sexual reproduction.
(b) The genes which dominate other genes are called dominant genes and the genes which get dominated are called recessive genes.
(c) The progeny inherits two genes for each trait from its parent but the traits shown by the progeny depends on which inherited gene is dominant of the two.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Explanation: The characteristics or traits of parents are transmitted to their progeny (offspring) through genes present on their chromosomes during the process of sexual reproduction. The genes which dominate other genes are called dominant genes and the genes which get dominated are called recessive genes. The progeny inherits two genes for each trait from its parent but the traits shown by the progeny depends on which inherited gene is dominant of the two. Thus all the given statements are correct.
Question number 17 to 20 are Assertion – Reasoning based questions.
These consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the
appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is False but R is true.
Question 17.
Assertion: Carbon and its compounds are used as fuels.
Reason: They give lot of heat and light when burnt in air.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: Carbon and its compounds are used as fuels for most applications because most of the carbon compounds give a lot of heat and light when burnt in air. Saturated hydrocarbons bum with a clean flame and no smoke is produced. The carbon compounds, used as a fuel, have high calorific values. Thus, both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
![]()
Question 18.
Assertion: The testes descend into the scrotum just before birth.
Reason: Human males have 2 testes in the body.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
Explanation: Human males have 2 testes and the testes descend into the scrotum just before the birth for the movement of the foetus in the canal. Thus, both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 19.
Assertion: Mendel self-crossed F1 yellow with round seeds to obtain F2 generation.
Reason: F2 progeny of a yellow with round seeds and a green with wrinkled seeds are all green and wrinkled seeds.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false
Explanation: Mendel took two contradicting traits together for crossing i.e. colour and shape of seeds. He chose a round yellow seed and a wrinkled green seed and crossed them. He obtained only round yellow seeds in the F1 generation. Then, F1 progeny was self-pollinated, which gave four different combinations of seeds i.e. round-yellow, wrinkled-yellow, round green and wrinkled green seeds in the F2 generation. Thus, assertion is true but reason is false.
Question 20.
Assertion: Damage to the medulla oblongata causes death.
Reason: Medulla oblongata controls involuntary functions of the body.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: Medulla controls circulation, respiration, reflexes like swallowing, coughing, peristaltic movement of gut. So, damage to the medulla will stop circulation and respiration and eventually causes death. Thus, both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Section – B
Question number 21 to 26 are very short answer questions.
Question 21.
What is carpel? Write the function of its various parts.
OR
(i) Trace the path of the sperms from where they are produced in the human body to the exterior?
(ii) Write the functions of seminal vesicles and prostate glands in human male reproductive system?
Answer:
The flask-shaped organ in the centre of a flower is called carpel. It is also called as female reproductive organ of the plant. It is made up of three parts:
- Stigma: It is the top part of carpel and is sticky. So, it receives the pollen from the anther of stamen.
- Style: It connects stigma to ovary.
- Ovary: It contains female gametes of the plant and helps in reproduction.
OR - Seminiferous tubules → Epididymis → Sperm duct → Urethra This path is followed by sperm in the human body to the exterior.
- Seminal vesicles secretion serves as a medium for transportation of sperms and also they activate and nourish the sperms. The secretion of prostate gland makes the medium alkaline and neutralises the acidic medium of female vagina.
Question 22.
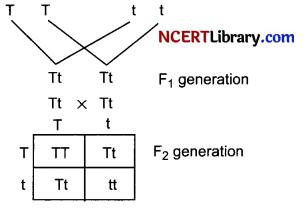
Name the plant Mendel used for his experiment. What type of progeny was obtained by Mendel in F1 and F2 generations when he crossed the tall and short plants? Write the ratio he obtained in F2 generation plants.
Answer:
Mendel used pea plant (Pisum sativum) when he crossed tall and short plants the progeny obtained in F1 generation were tall. When the F1 plants were selfed the F2 generations showed three tall and one dwarf plant. The genotypic ratio of F2 generation is 1: 2:1.
(TT: Tt: Tt: tt)
The phenotypic ratio 3:1 (Tall: Dwarf)
Question 23.
Give an example of a metal which:
(i) Is a liquid at room temperature?
(ii) Can be easily cut with a knife.
(iii) Is the best conductor of heat?
(iv) Is a poor conductor of heat?
Answer:
(i) Metal that exists in liquid state at room temperature is Mercury.
(ii) Metal that can be easily cut with a knife are Sodium and Potassium.
(iii) Metal that is the best conductor of heat are Silver and gold.
(iv) Metals that are poor conductors of heat are Mercury and lead.
Question 24.
How is sodium hydroxide manufactured in industries? Name the process. In this process a gas X is formed as by-product. This gas reacts with lime water to give a compound Y, which is used as a bleaching agent in the chemical industry. Identify X and Y and write the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
OR
A sanitary worker uses a white chemical having strong smell of chlorine gas to disinfect the water tank:
(i) Identify the chemical compound, write its chemical formula.
(ii) Give chemical equations for its preparation.
(iii) Write its two uses other than disinfection.
Answer:
Sodium hydroxide is manufactured by the electrolysis of concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride.
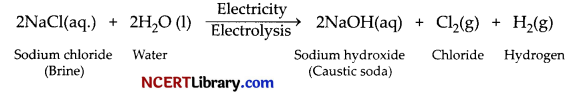
The process of manufacture of sodium hydroxide by electrolysis process is called chlor-alkali process. Gas X is chlorine gas and compound Y is calcium oxychloride (Bleaching powder).
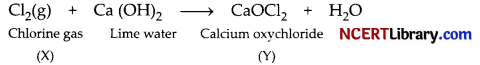
OR
(i) The compound is bleaching powder and its chemical formula is CaOCl2.
(ii) Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
(iii) (1) It is used as bleaching agent in textile industry.
(2) It is also used in paper industry.
Question 25.
When we increase the distance of an object from the eye, what happens to the image distance in the eye?
Answer:
For a normal eye, image distance in the eye is fixed, being equal to distance of retina from the eye lens. When we increase the distance of an object from the eye, the focal length of eye lens is changed on account of accommodation power of the eye, so as to keep the image distance constant.
Question 26.
What is biological magnification? Will the levels of this magnification be different at different levels of the ecosystem?
Answer:
The increase in concentration of harmful toxic substances in the body of organisms at each trophic level of a food chain is called biological magnification. Yes, the levels of this magnification will be different at different levels of the ecosystem because the concentration of chemicals goes on increasing at different trophic levels. It is maximum at higher trophic levels and minimum at lower trophic levels. Suppose a food chain is Grass → Rabbit → Eagle, it will be the highest in eagle and minimum in grass.
Section – C
Question number 27 to 33 are short answer questions.
Question 27.
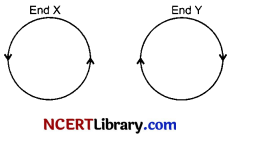
The directions of current flowing in the coil of an electromagnet at its two ends X and Y are as shown in given figure.
(i) What is the polarity of end X ?
(ii) What is the polarity of end Y ?
(iii) Name the rule which you have used to determine the polarities.
Answer the following questions:
(i) Define electromagnetic induction.
(ii) What is a permanent magnet? Give one use of it.
(iii) Define a compass.
Answer:
(i) Since current at end X is anticlockwise, the polarity at that end is North pole.
(ii) Current at end Y is clockwise, hence polarity at that end is South pole.
(iii) Clock-face rule is used to determine the polarities of the two faces of a current carrying circular loop.
OR
(i) The production of electricity from magnetism is called electromagnetic induction.
(ii) A permanent magnet is a magnet made from steel such that once magnetized, it does not lose its magnetism easily.
(iii) A compass is a device used to show magnetic field direction at a point. It consists of a tiny pivoted magnet usually in the form of a pointer which can turn freely in the horizontal plane.
![]()
Question 28.
Briefly describe different methods of wastes disposal?
Answer:
The various methods of waste disposal are:
- Land-fills: In urban areas wastes are filled or deposited in low lying areas. These are also known as dumping grounds where wastes are buried.
- Recycling of wastes: Some wastes like papers, plastics, metals etc., which can be recycled are sent to special recycling treatment plants so that new substances can be made from them.
- Preparation of compost: Biodegradable wastes like kitchen wastes, peels of fruits and vegetables etc., can be used to prepare compost which serves as a good manure to the plants.
- Incineration: Some wastes like medical wastes, chemical wastes are burnt at very high temperature in an incinerator and the ashes left behind are disposed by landfills.
- Production of biogas: Biodegradable wastes can be used in biogas plants to produce biogas which is used for several purposes like as a fuel.
Question 29.
Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Answer:
Carbon has 4 valence electrons. It completes its octet by sharing its four electrons with other carbon atoms or with atoms of other elements as it can neither lose four of its electrons nor gain four electrons as both the processes require extra amount of energy and would make the system unstable. Such bonds that are formed by sharing of electrons are known as covalent bonds. In covalent bonding, both the atoms share the valence electrons, i.e., the shared electrons belong to the valence shells of both the atoms.
In the formation of CH3Cl, carbon requires 4 electrons to complete its octet, while each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete its duplet. Also, chlorine requires an electron to complete the octet.
Therefore, all of these share the electrons and as a result, carbon forms 3 bonds with hydrogen and one with chlorine.
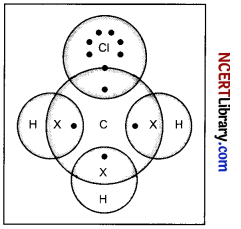
Question 30.
For making cake, baking powder is taken. If at home your mother uses baking soda instead of baking powder in cake.
(i) How will it affect the taste of the cake and why?
(ii) How can baking soda be converted into baking powder?
(iii) What is the role of tartaric acid added to baking soda?
OR
Answer the following questions:
(i) How is pH paper used to find the pH of a solution?
(ii) The pH value of water is 7. What will be the pH value of?
(a) Aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide.
(b) Dil. HCl.
Answer:
(i) Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate, on heating, it is converted into sodium carbonate which is bitter in taste. Thus, if baking soda is used, the taste of cake changes.
NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
(ii) Baking powder is a mixture of baking soda, cream of tartar (a dry acid), and sometimes com starch. Therefore, baking soda can be converted into baking powder by the addition of appropriate amount of tartaric acid to it.
(iii) Tartaric acid is added to neutralise the sodium carbonate formed on heating by the decomposition of NaHCO3. If it is not added, the cake would taste bitter due to the presence of sodium carbonate in it. Also, CO2 produced during the reaction causes cake to rise making them soft and spongy.
OR
(i) A few drops of solution are taken on the strip of pH paper. Then the colour obtained on the paper is compared with colour and corresponding pH value given on the chart of the pH paper.
(ii) (a) Aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide is basic in nature. Therefore, its pH will be greater than 7.
(b) Dil. HCl is acidic in nature, so its pH will be less than 7.
Question 31.
Answer the following questions:
(i) Write the electron-dot structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
(ii) Show the formation of Na2O and MgO by the transfer of electrons.
(iii) What are the ions present in these compounds
Answer:
(i) Electron – dot structure for Sodium (2, 8,1)
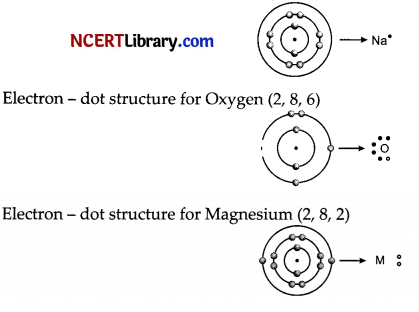
(ii) Formation of Na2O by transfer of electron:
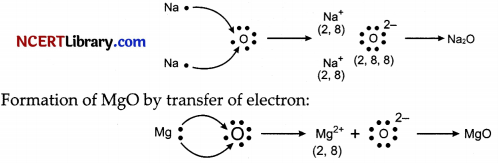
(iii) Ions present in these compounds are Mg2+, O2- and Na+.
Question 32.
How do the guard cells regulate opening and closing of stomatal pores?
Answer:
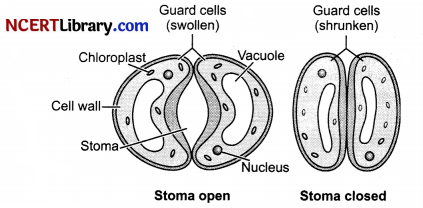
Guard cells are kidney shaped cells which contain thicker inner walls and thin outer walls. During day time they perform photosynthesis process due to presence of chloroplasts in them. Due to increase in solute concentration inside the guard cells, water from subsidiary cells rushes inside by osmosis process as a result guard cells swell up. The thin outer wall bulges out and thick inner wall is pulled inside thus stomata opens. During night time reverse happens, water rushes out from the guard cells and they become flaccid closing the stomatal pore. Thus turgour pressure of guard cells helps in closing and opening of stomata.
Question 33.
Answer the following questions:
(i) What is persistence of vision?
(ii) Define the term angle of deviation.
(iii) Define the term power of accommodation. Write the modification in the curvature of the eye lens which enables us to see the nearby objects clearly?
Answer:
(i) The image of any object formed on the retina persists for about 1/16 of a second. This continuance of sensation of eye for sometime even after the removal of the object is called persistence of vision.
(ii) The angle between the incident ray produced forward and the emergent ray produced backward is called angle of deviation.
(iii) The ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length, is called the power of accommodation. There should be a contraction of ciliary muscles, that will increase the curvature of the eye lens and becomes thicker, so the focal length of the eye lens will decrease. It will thus enable us to see the objects clearly.
Section – D
Question number 34 to 36 are long answer questions.
Question 34.
Define a chemical reaction. State four observations which help us to determine that a chemical reaction has taken place. Write one example of each of the observations with a balanced chemical equation.
OR
When two or more substances react and form some new substance, it is called a chemical reaction. As we know, all chemical reaction obeys law of chemical combination. Therefore, chemical reactions need to be balanced. It is done by hit and trial method. The chemical reactions can be classified into different types such as combination reaction, decomposition reaction, displacement reaction, double displacement reaction. The reactions take place in solution is precipitation reactions and neutralization reactions.

(i) Detine a chemical reaction.
(ii) Which law is followed by all chemical reactions?
(iii) Name four types of chemical reactions.
(iv) Give example of precipitation reactions.
Answer:
Chemical reaction is the transformation of chemical substance into another chemical substance. Only a rearrangement of atoms takes place in a chemical reaction. Old bonds are broken and new bonds are formed.
Some of the characteristics of chemical reactions are:
1. Change in colour: In some reactions, there is change in colour after the reaction. For example, the chemical reaction between potassium iodide solution and lead nitrate solution is characterised by the change in colour from colourless to the appearance of yellow colour due to the formation of lead iodide.

2. Change in state: In some reactions, change of state takes place during the reaction. The reaction might start with gaseous or liquid reactants but it will end up with a solid product and vice-versa. For example: Ammonia gas reacts with hydrogen chloride gas to produce solid ammonium chloride.
NH3 (g) + HCl (g) → NH4Cl(S)
3. Change in temperature: Temperature change is the characteristic of many reactions. For example, the chemical reaction between quicklime and water to form slaked lime. In this reaction, temperature of the reaction is increased due to the evolution of heat.
CaO (s) + H2O(Q) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) + Heat
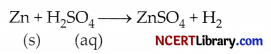
4. Evolution of gas: Some reactions are characterised by evolution of gas as a result of chemical reaction. For example, the chemical reaction between zinc and dilute sulphuric acid is characterised by the evolution of hydrogen gas.
OR
(i) A chemical reaction is defined as the reaction in which two or more substances react to form a new substance.
(ii) The law of chemical combination is followed by all chemical reactions.
(iii) Combination reactions, displacement reactions, double displacement reactions and decomposition reactions are four types of chemical reactions.
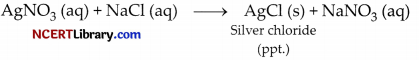
(iv) The reaction between silver nitrate and sodium chloride that forms precipitate of silver chloride and sodium nitrate is an example of precipitation reactions.
Question 35.
What is hydrotropism? Design an experiment to demonstrate this phenomenon.
OR
The brain directs our body’s internal functions. It also integrates sensory impulses and information to form perceptions, thoughts and memories. The brain gives us self-awareness and the ability to speak and move in the world.
(i) The brain is divided into three major subparts. Name these subparts.
(ii) Name the part of the brain that is responsible for maintaining body posture?

(iii) Name the part of the brain that has the reflex centers for sneezing and vomiting?
(iv) The brain is the part of which system?
Answer:
The movement of root of plants towards water is called hydrotropism. Take two glass troughs A and B, fill each one of them two-thirds with soil. In trough A plant a tiny seedling figure (a). In trough B plant a similar seedling and also place a small ‘clay pot’ inside the soil figure (b). Water the soil in trough A daily and uniformly. Do not water the soil in trough B but put some water in the clay pot buried in the soil. Leave both the troughs for a few days.
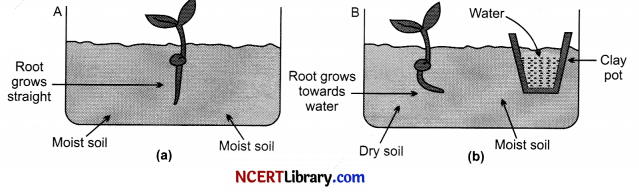
Now, dig up the seedlings carefully from both the trough without damaging their roots. We will find that the root of seedling in trough A is straight. On the other hand, the root of seedling in trough B is found to be bent to the right side (towards the clay pot containing water) figure (b). This can be explained as follows.
In trough A, the root of seedling gets water from both sides (because the soil is watered uniformly) in trough B, the roots gets water oozing out from the clay pot which is kept on the right side. So, the root of seedling in trough B grows and bends towards the source of water to the right side. This experiment shows that the root of a plant grows towards water. In other words, the root of a plant is positively hydrotropic.
OR
(i) The brain is divided into three main subparts: the forebrain, the midbrain and the hindbrain. The structure present towards the lower back of the skull is the hindbrain. The narrow region that links the hindbrain with the forebrain is the midbrain. The structure in front of the brain is the forebrain.
(ii) The cerebellum controls the body posture and coordinates motor activity for moving limbs.
(iii) The medulla oblongata is the region which regulates the breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure, and consists of reflex centers for sneezing, vomiting, defecating, coughing, hiccupping, and swallowing.
(iv) The nervous system present in vertebrates is divided into the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. The brain and spinal cord are found in the central nervous system. Thus, the brain is part of the central nervous system.
Question 36.
Answer the following questions:
(i) Define focal length of a divergent lens.
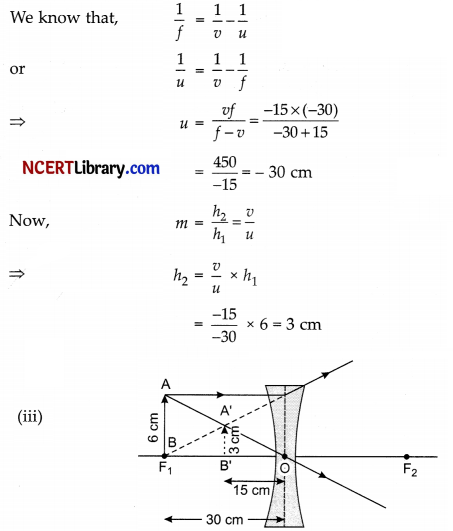
(ii) A divergent lens of focal length 30 cm forms the image of an object of size 6 cm on the same side as the object at a distance of 15 cm from its optical centre. Use lens formula to determine the distance of the object from the lens and the size of the image formed.
(iii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in the above situation.
Answer:
(i) The point from which parallel rays of light, after refraction from a lens, appear to diverge is called focus of divergent lens, and the distance between optical centre and this focus of a divergent lens is called focal length of divergent lens.
(ii) Focal length of divergent lens,
f = – 30 cm
Image distance, v = – 15 cm
Object height, h1 = 6 cm
Section – E
Question number 37 to 39 are case – based/data -based questions with 2 to 3 short sub – parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Question 37.
Most dirt is oily in nature and as you know, oil does not dissolve in water. The molecules of soap are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. The ionic-end of soap interacts with water while the carbon chain interacts with oil. The soap molecules, thus form structures called micelles where one end of the molecules is towards the oil droplet while the ionic-end faces outside. This forms an emulsion in water. The soap micelle thus helps in pulling out the dirt in water and we can wash our clothes clean.
The following process is carried out:
1. Take about 10 mL of distilled water (or rain water) and 10 mL of hard water (from a tube well or hand-pump) in separate test tubes.
2. Add a couple of drops of soap solution to both.
3. Shake the test tubes vigorously for an equal period of time and observe the amount of foam formed.
4. It is observed that quantity of foam is different in both the test tubes.
(a) What could be reason for difference in quantity of foam in both the test tubes?
(b) Which test tube shows less quantity of foam and why?
OR
(b) If detergent is used in place of soap, is there any difference in quantity of lather?
Answer:
(a) The reason for difference in quantity of foam in both the test tubes is the type of water sample taken in test tubes.
(b) Test tube having hard water shows less quantity of foam because hard water contains dissolved calcium and magnesium salts. These salts react with soap to form insoluble compounds resulting in the decrease of lather. Hence, hard water does not lather well.
OR
(b) If detergent is used in place of soap, yes there will be change because the charged ends of detergents do not form insoluble precipitates with the calcium and magnesium ions in hard water. Thus, they remain effective in hard water.
The food material taken in during the process of nutrition is used in cells to provide energy for various life processes. Diverse organisms do this in different ways – some use oxygen to break-down glucose completely into carbon dioxide and water, some use other pathways that do not involve oxygen. In all cases, the first step is the break-down of glucose, a six-carbon molecule, into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm.
Further, the pyruvate may be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide. This process takes place in yeast during fermentation. Since this process takes place in the absence of air (oxygen), it is called anaerobic respiration. Break- down of pyruvate using oxygen takes place in the mitochondria. This process breaks up the three-carbon pyruvate molecule to give three molecules of carbon dioxide. The other product is water. Since this process takes place in the presence of air (oxygen), it is called aerobic respiration.
The following process is carried out:
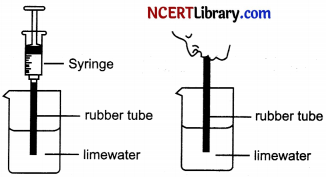
1. Take some freshly prepared lime water in a test tube.
2. Blow air through this lime water.
3. Note how long it takes for the lime water to turn milky.
4. Use a syringe or pichkari to pass air through some fresh lime water taken in another test tube.
5. Note how long it takes for this lime water to turn milky.
6. It is observed that syringe takes more time to turn lime water milky
(a) Explain why lime water turn milky instantaneously?
(b) Why syringe takes more time to turn lime water milky?
(c) Name the process through which carbon dioxide is released?
OR
(d) Name the process in which carbon dioxide is absorbed?
Answer:
(a) Our body cells produce carbon dioxide through oxidation of food. This gas is exhaled outside through the lungs. Lime water reacts with CO2 to form an insoluble precipitate. This turns lime water milky.
(b) Syringe takes more time to turn lime water milky because syringe push atmospheric air through the lime water. Atmospheric air has less quantity of carbon dioxide. Therefore, it takes more time.
(c) Through the process of Respiration carbon dioxide is released.
OR
(d) Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in the form of sugar. Thus in this process carbon dioxide is absorbed.
Question 39.
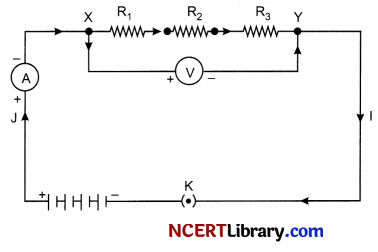
In various electrical gadgets, we often use resistors in various combinations. We now therefore intend to see how Ohm’s law can be applied to combinations of resistors. There are two methods of joining the resistors together. The resistors can be joined in series or in parallel.
The arrangement of three resistors joined in series with a combination of cells (or a battery) is shown in figure below:
(a) Give a general equation for resistance connected in series.
(b) Write any one disadvantage of series combination of resistance?
(c) Draw schematic diagram to show resistances connected in parallel.
OR
(c) What is the correct way of connect ammeter and voltmeter in the circuit to determine the equivalent resistance of two resistors in series?
Answer:
(a) When several resistors are joined in series, the resistance of the combination Rs equals the sum of their individual resistances, i.e., Rx = R1 + R2 + R3
(b) In a series circuit the current is constant throughout the electric circuit. Thus, it is obviously impracticable to connect an electric bulb and an electric heater in series, because they need currents of widely different values to operate properly.
(c)
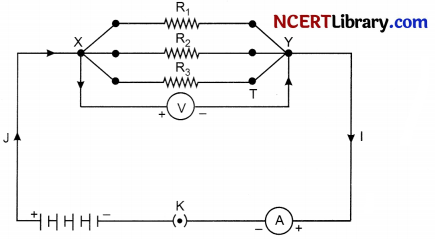
The correct way of connecting ammeter and voltmeter in the circuit to determine the equivalent resistance of two resistors is connecting ammeter in series and voltmeter in parallel. Ammeter is connected in series, so that whole current passes through it and voltmeter is connected in parallel to so that it could measure the complete voltage of the circuit.