Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions Set 4 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 4 with Solutions
Time : 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 objective type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts.
Section – A
Select and write one most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1-20
Question 1.
Select from the following the best experimental set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass slab:
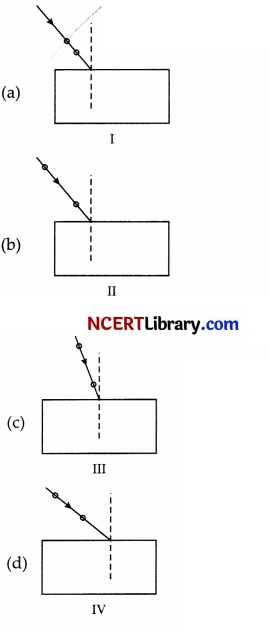
Answer:
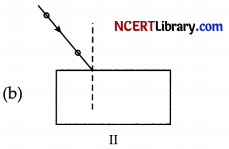
Explanation: To achieve best experimental set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass slab, the point of incidence should be in the middle of the glass slab and the incident angle should be close to 45°.
Question 2.
Which law should be kept in mind while we balance chemical equations?
(a) Conservation of momentum
(b) Conservation of mass
(c) Conservation of energy
(d) Conservation of frequency
Answer:
(b) Conservation of mass
Explanation: The law of conservation of mass states that “mass can neither be created nor destroyed.” So, both the sides of the chemical reactions have to be balanced to ensure that this law is followed and thus the number of the reactant and the product molecules remains same on both sides of the equation.
Question 3.
A rectangular loop carrying a current I is situated near a long straight wire such that the wire is parallel to one of the sides of the loop and is in plane of the loop. If steady current I is created in wire as shown in figure below, then the loop:
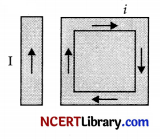
(a) Rotate about an axis parallel to the wire
(b) Move towards the wire
(c) Move away from the wire or towards right
(d) Remains stationary
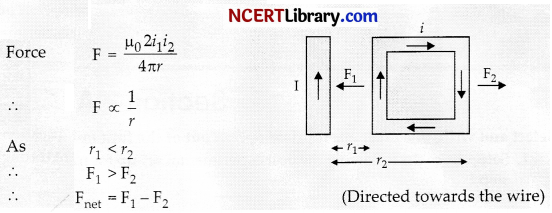
Answer:
(b) Move towards the wire
Explanation:
Question 4.
Choose the function of pancreatic juice from the following.
(a) Trypsin digests proteins and lipase digests carbohydrates.
(b) Trypsin digests emulsified fats and lipase digests proteins.
(c) Trypsin and lipase digest fats.
(d) Trypsin digests proteins and lipase digests emulsified fats.
Answer:
(d) Trypsin digests proteins and lipase digests emulsified fats.
Explanation: Pancreatic juice contains the digestive enzymes amylases, lipases, and trypsin, which I are secreted by the pancreas. Amylase degrades starch, trypsin degrades proteins, and lipase degrades emulsified lipids.
Question 5.
Which of the following is used for dissolution of gold?
(a) Hydrochloric acid
(b) Sulphuric acid
(c) Nitric acid
(d) Aqua regia
Answer:
(d) Aqua regia
Explanation: Aqua regia is a mixture of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid in the ratio 3 :1 and it can I dissolve noble metals such as gold, palladium, and platinum, which however, not soluble in either I of the acids alone.
Question 6.
An electric bulb is rated 220 V and 100 W. When it is operated on 110 V, the power consumed will be:
(a) 100 W
(b) 75 W
(c) 50 W
(d) 25 W
Answer:
(d) 25 W
Explanation:
We know that,
P = \(\frac{\mathrm{V}^2}{\mathrm{R}}\)
Where,
P = Electric Power
V = Potential difference in a circuit
R = Resistance
Now, R = \(\frac{\mathrm{V}^2}{\mathrm{P}}\)
R = \(\frac{220 \times 220}{100}\) = 484 Ω
As the voltage drop across the bulb is 110 V. The power consumed by the bulb is:
Pb = \(\frac{\mathrm{V}^2}{\mathrm{R}}\)
= \(\frac{110 \times 110}{484}\)
Pb = 25 W
Hence, the power consumed will be 25 W.
![]()
Question 7.
Offspring formed by asexual method of reproduction have greater similarity among themselves because:
(i) Asexual reproduction involves only one parent.
(ii) Asexual reproduction does not involve gametes.
(iii) Asexual reproduction occurs before sexual reproduction.
(iv) Asexual reproduction occurs after sexual reproduction.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(a) (i) and (ii)
Explanation: Offspring have greater similarity as only one parent is involved in asexual reproduction thus no gametes are formed. The basis of asexual reproduction is mitosis (division of a nucleus into two identical daughter nuclei). Each daughter nucleus has same genetic make up because of replication of parental DNA. The new offspring produced are called clones.
Question 8.
Name the process shown in the above diagram of getting back a full organism from its body parts.
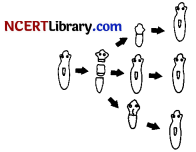
(a) Regeneration
(b) Budding
(c) Fragmentation
(d) Fission
Answer:
(a) Regeneration
Explanation: The process of getting back a full organism from its body parts is called regeneration. The simple animals like hydra and planaria show regeneration. If the body of planaria gets cut into a number of pieces, then each body piece can regenerate into a complete planaria by growing all the missing parts.
The regeneration of an organism from its cut body part occurs by the process of growth and development. The cells of cut body part divide rapidly to make a ball of cells. The cells then become specialised to form different types of tissues which again form various organs and body parts.
Question 9.
What is the colour of the ash formed when a magnesium ribbon is burnt in the air?
(a) White
(b) Black
(c) Yellow
(d) Pink
Answer:
(a) White
Explanation: When the magnesium ribbon is burned in the air it bums with the white dazzling flame leading to the formation of the white colour ash which is magnesium oxide.
Question 10.
The equivalent resistance of a series combination of two resistances is χ ohm. If the resistances are of 10 Ω and 40 Ω respectively, the value of χ will be:
(a) 10 Ω
(b) 20 Ω
(c) 50 Ω
(d) 40 Ω
Answer:
(c) 50 Ω
Explanation: We know that Total Resistance
R = R1 + R2
= 10 + 40
= 50 Ω
Hence, the value of χ is 50 Ω.
Question 11.
In which of the following groups of organisms, food material is broken down outside the body and absorbed ?
(a) Mushroom, green plants, amoeba
(b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
(c) Paramecium, amoeba, cuscuta
(d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
Answer:
(b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
Explanation: Yeast, mushrooms, and bread mould all exhibit a saprophytic mode of nutrition. They use digestive enzymes secreted outside their body to break down complex organic substances and absorb basic molecules as nutrition.
Question 12.
In Spirogyra, asexual reproduction takes place by:
(a) breaking up of filaments into smaller bits.
(b) division of a cell into two cells.
(c) division of a cell into many cells.
(d) formation of young cells from older cells.
Answer:
(a) breaking up of filaments into smaller bits.
Explanation: In Spirogyra, asexual reproduction takes place by fragmentation, i.e., the organism simply breaks up into smaller pieces upon maturation. Each piece grows into new individual without forming any gametes.
Question 13.
A cylindrical conductor of length T and uniform area of cross-section A’ has resistance ‘R’. The area of cross-section of another conductor of same material and same resistance but of length ‘ll’ is :
(a) 0.5 A
(b) 1.5 A
(c) 2 A
(d) 3 A
Answer:
(c) 2 A
Explanation: A cylindrical conductor of length T and uniform area of cross-section A’ has resistance ‘R’. The area of cross-section of another conductor of same material and same resistance but of length ‘2l’ will be 2 A. This can be explained as:
R = ρ\(\frac { l }{ A }\)
\(\frac{\mathrm{R}_1}{\mathrm{R}_2}=\left(\frac{\mathrm{L}_1}{\mathrm{~L}_2}\right) \times\left(\frac{\mathrm{A}_2}{\mathrm{~A}_1}\right)\)
A2 = \(\left(\frac{\mathrm{R}_1}{\mathrm{R}_2}\right) \times\left(\frac{\mathrm{L}_2}{\mathrm{~L}_1}\right)\) x A1
A2 = \(\left(\frac{\mathrm{R}}{\mathrm{R}}\right) \times\left(\frac{2 l}{l}\right)\) x A
A2 = 2A
Question 14.
Dominant alleles are expressed exclusively in a heterozygote, while recessive traits are expressed only if the organism is ___________ for the recessive allele.
(a) Homozygous
(b) Heterozygous
(c) Normal
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Homozygous
Explanation: Mendel’s law of dominance states that in a heterozygote, one trait will conceal the presence of another trait for the same characteristic. Rather than both alleles contributing to a phenotype, the dominant allele will be expressed exclusively. The recessive allele will remain “latent,” but will be transmitted to offspring by the same manner in which the dominant allele is transmitted. The recessive trait will only be expressed by offspring that have two copies of this allele.
Question 15.
The figure given below shows the magnetic field produced by a currents carrying wire. Which of the diagram shows it correctly?
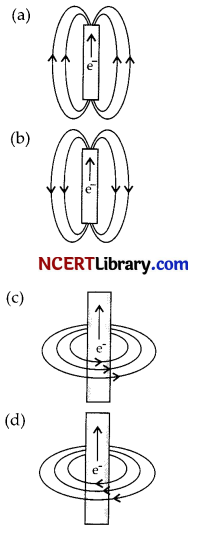
Answer:
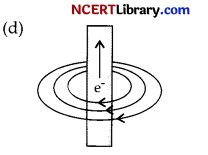
Explanation: As when current flows through and current-carrying wire, then direction of magnetic field is calculated by right hand thumb rule.
Question 16.
The Ratio of Number of Chromosomes in a Human Zygote and a Human Sperm is:
(a) 2:1
(b) 3:1
(c) 1:2
(d) 1:3
Answer:
(a) 2:1
Explanation: The number of chromosomes in a human sperm is half the number of chromosomes in a zygote i.e., their ratio is 2 :1.
Question number 17 to 20 are Assertion – Reasoning based questions.
These consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is False but R is true.
![]()
Question 17.
Assertion: A current carrying rod is suspended between U-shaped magnet, the rod deflects.
Reason: A force is exerted on the rod due to magnetic field.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: A force is always exerted due to magnetic field in the same way electric current flowing through any conductor produces magnetic field. And in this case, Fleming’s left-hand rule is used to predict directions of the magnetic field, current and displacement. Thus, assertion and reason both are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 18.
Assertion: Mendel selected the pea plant for his experiments.
Reason: Pea plant is cross-pollinating and has unisexual flowers.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: The flowers of pea plant are bisexual and they are self-pollinating, and thus, self and cross-pollination can easily be performed. They have a shorter life span and are the plants that are easier to maintain. Thus, Mendel chose the pea plant. Thus, both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 19.
Assertion: Sometimes, the eye may gradually lose its power of accommodation.
Reason: The crystalline lens of people at old age becomes milky and cloudy.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
Explanation: The person cannot see the objects distinctly and comfortably because of accommodation. The vision becomes blurred due to the refractive defects of the eye. Thus assertion is correct but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 20.
Assertion: XX chromosome give rise to female child whereas XY give rise to male child.
Reason: The Y chromosome in males is smaller than X chromosome.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
Explanation: Smaller Y chromosome, does not decide the gender of the child. Its presence is important not the size. Thus, both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Section – B
Question number 21 to 26 are very short answer questions.
Question 21.
The refractive indices of kerosene, turpentine and water are 1.44,1.47 and 1.33, respectively. In which of these materials does light travel the fastest?
OR
Why a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror gets reflected among the same path after reflection?
Answer:
We know that,

It is obvious from the above relation that the speed of light will be the maximum in that medium which has the lowest refractive index. Now, out of kerosene, turpentine and water, water has the lowest re¬fractive index of 1.33. So, the light will have maximum speed in water.
OR
The ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror gets reflected among the same path after a reflection because the angle of incidence is 0°. That is the ray passing through the centre of curvature is incident normally to the mirror. The angle of reflection should also be 0°.
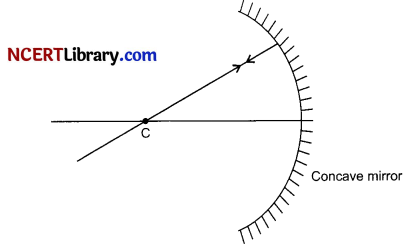
Question 22.
Differentiate between acids and bases.
Answer:
| Acids | Bases |
| 1. Acids are sour in taste. | Bases are bitter in taste. |
| 2. Acids turns blue litmus to red. | Bases turns red litmus to blue. |
| 3. An acid is a substance which gives H+ ions in water solution. | A base is a substance which gives OH– ions in water solution. |
| 4. The orange colour of Methyl orange Indicator changes to red in acidic medium. | The orange colour of Methyl Orange Indicator changes to yellow in bases. |
| 5. pH value of acid is less than 7. | pH value of base is greater than 7. |
| 6. When non-metallic oxides are dissolved in water they form acids. SO3 + H2O → H2SO4 |
When metallic oxides are dissolved in water they form bases.
CaO + H2O → Co(OH)2 |
Question 23.
Given below is a reaction which occurs in the stratosphere.
O3⇌ O2 + [O]
(i) Name the two reactions which are in equilibrium thereby maintaining steady concentration of ozone in the ozonosphere.
(ii) What is being absorbed by the ozone for the occurrence of above two reactions?
Answer:
(i) Photo-dissociation of ozone and generation of ozone are the two reactions which are in equilibrium thereby maintaining steady concentration of ozone in the ozonosphere.
(ii) Ultraviolet radiations from sun are being absorbed by the ozone for the occurrence of given two reactions
Question 24.
What step of digestion takes place in the stomach?
OR
Answer the following questions:
(i) What is translocation? Why is it essential for plants?
(ii) Where do the substances in plants reach as a result of translocation?
Answer:
Partly digested food called bolus passes through the oesophagus and enters the stomach. The stomach is a large bag-like muscular organ present on the left side of the body. The stomach expands when food enters it. The muscular walls of the stomach helps in mixing the food thoroughly with more digestive juices.
The gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach helps in further digestion of food. They release hydrochloric acid, pepsin and mucus. The hydrochloric acid makes the medium acidic which facilitates the action of pepsin. The mucus protects the inner lining of stomach from the action of the acid under normal conditions.
OR
(i) The transport of food from leaves to other parts of the plant is called translocation. Translocation is essential for plants because without it food prepared by the leaves cannot reach other parts of the plant for their growth and development.
(ii) The substances in plants reach to other tissues in plants from the leaves as a result of translocation.
Question 25.
List two different functions performed by pancreas in our body.
Answer:
Different functions performed by pancreas in our body are:
- Pancreas makes two hormones i.e., insulin and glycogen that regulates blood sugar level.
- It secretes pancreatic juice that aids in the digestion of food.
Question 26.
Write the structural formulae of all the isomers of hexane.
Answer:
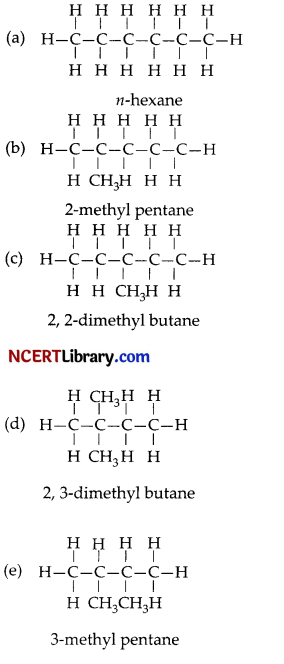
Section – C
Question number 27 to 33 are short answer questions.
Question 27.
How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
Answer:
When Mendel crossed pure pea plants with round, yellow seeds with pure plants with wrinkled, green seeds in F1 generation all pea plants with round and yellow seeds were produced. This shows that round and yellow are dominant characters whereas green and wrinkled are recessive characters. Again when these F1 plants were crossed round, yellow pea plants as well as green, wrinkled seeds pea plants were produced. But in addition to these two new characters were produced i.e. round and green, wrinkled and yellow seeds pea plants were produced.
This shows that two pair of characters combines in F3 generation but they get separated and behave independently in F2 generation.
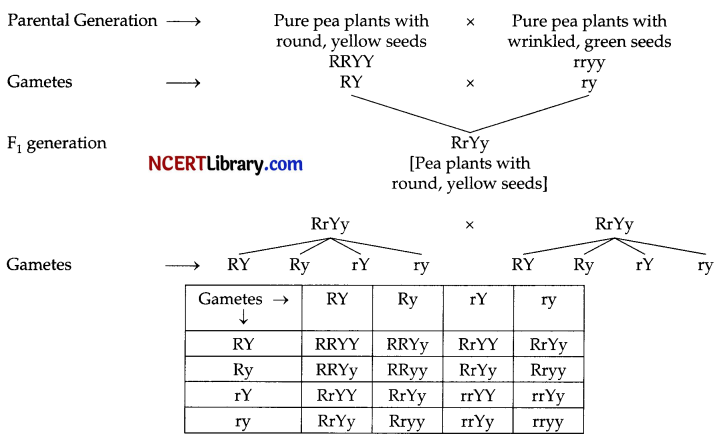
Round-yellow, round-green, wrinkled-yellow, wrinkled-green-9:3:3:1
Question 28.
Three resistors of 2 Ω, 3 Ω and 4 Ω are connected in (i) series, (ii) parallel. Find the equivalent resistance in each case.
Answer:
Given: R1 = 2 Ω, R2 = 3 Ω, R3 = 4 Ω
(i) In series, the equivalent resistance is
R1 = R2 + R2 + R3
= 2 + 3 + 4
= 9 Ω
(ii) In parallel, if the equivalent resistance is Rp, then
\(\frac{1}{R_p}=\frac{1}{R_1}+\frac{1}{R_2}+\frac{1}{R_3}\)
OR \(\frac{1}{R_p}=\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{3}+\frac{1}{4}=\frac{13}{12}\)
or \(R_p=\frac{12}{13}=0.92 \Omega\)
Question 29.
Give reasons:
(i) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
(ii) Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
(iii) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking.
Answer:
(i) Platinum, gold, and silver are used to make jewellery because they are very lustrous. Also, they are very less reactive and do not corrode easily.
(ii) Sodium, potassium, and lithium are stored in kerosene because they are very reactive metals and react very vigorously with air as well as water. They are kept immersed in kerosene oil in order to prevent their contact with air and moisture.
(iii) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal but it is resistant to corrosion. The reason for this is that aluminium reacts with oxygen present in air to form a thin layer of aluminium oxide. This oxide layer is very stable and prevents further reaction of aluminium with oxygen. It is light in weight and a good conductor of heat. Therefore, it is used to make utensils for cooking.
Question 30.
What are the characteristics of energy transfer in biosphere?
Answer:
The characteristics of energy transfer in biosphere are:
- The ultimate source of energy is sun and is converted from one form to another.
- Energy gets continuously transferred through food chain and energy flow is unidirectional.
- There is loss of some energy during transfer from one trophic level to the next.
- Only 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next. The solar energy trapped by producers does not revert back to the sun.
- At each trophic level, some of the energy is utilised by organisms, rest is lost to environment and only 10% is available to the next trophic level.
![]()
Question 31.
Explain how the following metals are obtained from their compounds by reduction process:
(i) Metal X which is lower in reactivity series.
(ii) Metal Y which is in middle of reactivity series.
(iii) Metal Z which is high in the reactivity series.
OR
When metal P is treated with a dilute acid Q, then a gas G is evolved which burns readily by making a little explosion.
(i) Name any two metals which can behave like metal P.
(ii) Name any two acids which can behave like acid Q.
(iii) Name the gas G.
(iv) Is the gas G lighter than or heavier than air?
(v) Is the reaction between metal P and dilute acid Q exothermic or endothermic?
Answer:
(i) Metals low in reactivity series are obtained by the method of heating their oxides with carbon.
(ii) Y is in the middle of the series, it can be obtained by heating with a reducing agent like carbon or highly reactive metals like Na, Ca, Al.
(iv) Metal Z is high up in the reactivity series. It can be obtained by electrolytic reduction.
OR
(i) Zinc and Iron.
(ii) Dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute sulphuric acid.
(iii) Hydrogen
(iv) Lighter than air
(v) Exothermic
Question 32.
(i) State a law which determines the direction of magnetic field around a current carrying wire.
(ii) Name and state the law which is used to determine the direction of force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field?
(iii) State condition when magnitude of force on a current carrying conductor placed in magnetic field is (a) zero (b) maximum.
OR
Answer the following questions:
(i) What do you mean by Overloading?
(ii) Define an electromagnet.
(iii) What is a galvanometer?
Answer:
(i) Right hand thumb rule which states that if we hold the current carrying conductor in our right hand such that the thumb points in direction of flow of current, then the fingers encircle the wire in the direction of magnetic field.
(ii) The direction of force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is obtained by the Fleming’s left hand rule. This rule states that ” When forefinger, central finger and thumb of left hand are stretched in such a way that they are mutually perpendicular to each other, if the forefinger indicates direction of magnetic field, central finger indicates the direction of current, then thumb will indicate the direc¬tion of motion of conductor i.e., force on the conductor.
(iii) No force acts on a current carrying conductor when current in conductor is parallel to the magnetic field.
Maximum force is exerted on the current carrying conductor if it is perpendicular to the direction of magnetic field.
OR
(i) Overloading is the process of overheating of a wire due to excess current drawn by all the appliances than the permitted limit for that wire.
(ii) An electromagnet is a magnet consisting of a long coil of insulated copper wire wrapped around a soft iron core that is magnetized only when electric current is passed through the coil.
(iii) A galvanometer is an instrument which can detect the presence of electric current in a circuit.
Question 33.
(i) Name the property of baking soda responsible for the following uses:
(a) As an antacid
(b) baking industry
(c) soda-acid fire extinguisher
(ii) Acids when reacts with metals release hydrogen gas but there is one acid which when reacts with metals does not release hydrogen gas except for two metals. Prove this statement.
Answer:
(i) (a) It is alkaline in nature as it neutralises the excess acid produced in our stomach and gives us relief from acidity. So, it is used as an antacid.
(b) Baking soda releases carbon dioxide gas which makes the cake or bread soft and spongy. So it is used in baking industry.
(c) Baking soda and sulphuric acid present in soda-acid fire extinguisher reacts to release carbon dioxide gas and this gas is a non-supporter of combustion thus cutting air supply and fire gets extinguished.
(ii) Acids like HC1 and sulphuric acid react with metals to liberate hydrogen gas.
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Mg + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H2
But nitric acid does not react with metals to liberate hydrogen gas as it is a strong oxidising agent. But magnesium and manganese metal when react with very dilute nitric acid they liberate hydrogen gas.
Zn + 4HNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + 2H2O + NO2
Mg + 2HNO3 → Mg(NO3)2 + H2
Mn + 2HNO3 → Mn(NO3)2 + H2
Section – D
Question number 34 to 36 are long answer questions.
Question 34.
(i) What happens when:
(a) Planaria gets cut into two pieces.
(b) A mature Spirogyra filament attains considerable length.
(c) On maturation sporangia bursts.
(ii) Students were asked to observe the permanent slides showing different stages of budding in yeast under high power of a microscope.
(a) Which adjustment screw were you asked to move to focus the slides?
(b) Draw diagrams in correct sequence to show budding in yeast.
(iii) What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
OR
What is placenta? Describe its structure. State its functions in case of a pregnant human female.
Answer:
(i) (a) Each piece regenerates into a new Planaria.
(b) When a mature Spirogyra filament attains considerable length it breaks into two or more fragments and each fragments grow into a new individual.
(c) On maturation when sporangia bursts, spores are liberated and they are dispersed. On getting a suitable substratum and under favourable conditions each spore germinates into new mycelium.
(ii) (a) Fine adjustment screws were moved to focus the slides.
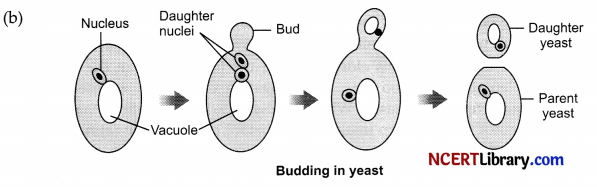
(iii) The advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction are :
1. Variations are produced due to sexual reproduction which helps in better survival of offsprings to the changing environment.
2. More diversity is seen in case of sexual reproduction as compared to asexual reproduction.
3. Due to recombination and crossing over in meiosis process during formation of gametes and as there is mixing of male and female gametes, genetic variations are seen which is the main cause of evolution.
OR
Placenta: It is physical barrier connecting the embryo in the mother’s womb to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste removal etc.
Structure: In human placenta is 22 cm in length 2-2.5 cm in thickness, weight 500 g. It has a dark reddish-blue or crimson colour. It is discoidal in shape.
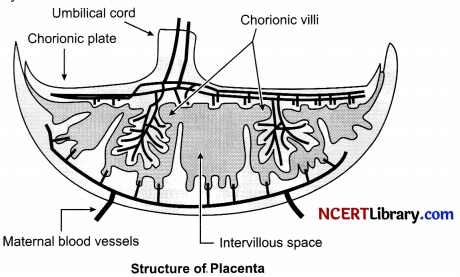
Functions: This provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother to the embryo, and the developing embryo will also generate waste substances which can be removed by transferring them into the mothers blood through the placenta.
Thus, it provides nourishment to the embryo, helps in the excretion and provides immunity to the foetus.
Question 35.
(i) 2 g of ferrous sulphate crystals are heated in a dry boiling tube. Answer the following:
(a) List any two observations.
(b) Name the type of chemical reaction taking place.
(c) Write the chemical equation of the reaction.
(ii) (a) What happens when an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of barium chloride? State the physical conditions of reactants in which reaction between them will not take place. Write the chemical equation to show the reaction and what is the type of reaction?
(b) What happens if iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution for half an hour?
Answer:
(i) (a) Two observations are:
- Green colour ferrous sulphate crystals will first turn into dirty white solid and then into a brown residue.
- A gas is evolved with pungent, suffocating smell.
(b) It is a thermal decomposition reaction.
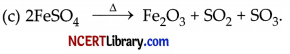
(ii) (a) When an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of barium chloride, the product formed is barium sulphate i.e., a white precipitate. The reaction will not take place if the reactants are in a solid state. It is a double displacement type of reaction.
BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
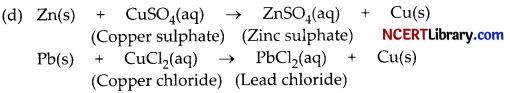
(b) When iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution for half an hour, iron sulphate solution and copper metal is formed.
CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
This reaction occurs because iron is more reactive than copper. Also a brown substance will be deposited on the iron nails. The deposited substance is nothing but copper.
![]()
Question 36.
The cause of myopia are the eyeball gets elongated and the focal length of the eye lens became too short or power of eye lens becomes too high. By elongation of eye ball we mean that the distance between the eye lens and retina is increased. When the distance becomes more than the focal length of the lens, the eye lens cannot form a sharp image of the distant object on the retina but forms an image in front of it as shown in the figure.
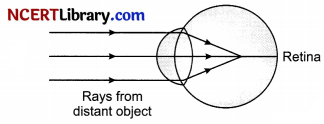
If focal length of the eyelens is short, it will form a sharp image of the distant object in front of the retina and not over it.
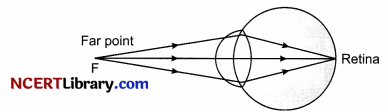
(i) Is eye lens made of glass?
(ii) A myopic person uses specs of power – 0.2 D, What is the distance of far point of his eye?
(iii) Which lens is used for correcting a myopic eye?
(a) Convex lens
(b) Concave lens
(c) Bifocal lens
(d) None of the above
(iv) The human eye forms the image of an object at its:
(a) Cornea
(b) Pupil
(c) Iris
(d) Retina
Answer:
(i) No, eye lens is not made of glass, it is made of fibrous jelly like material.
(ii) We know,
P = – 0.2 D
f = \(\frac { 1 }{ P }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ -o.2 }\) = – 5m
Distance of far point of his eye is 5 m.
(iii) (b) Concave lens
(iv) (d) Retina
Section – E
Question number 37 to 39 are case – based/data -based questions with 2 to 3 short sub – parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Question 37.
All human chromosomes are not paired. Most human chromosomes have a maternal and a paternal copy, and we have 22 such pairs. But one pair, called the sex chromosomes, is odd and is not always being a perfect pair. Women have a perfect pair of sex chromosomes, both called X. But men have a mismatched pair in which one is a normal-sized X while the other is a short one called Y. So women are XX, while men are XY.
As the figure shows, half the children will be boys and half will be girls. All children will inherit an X chromosome from their mother regardless of whether they are boys or girls. Thus, the sex of the children will be determined by what they inherit from their father. A child who inherits an X chromosome from her father will be a girl, and one who inherits a Y chromosome from him will be a boy.
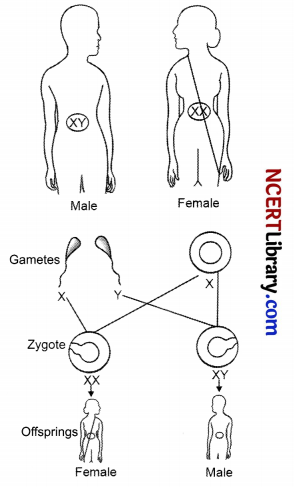
(a) Who determines the sex of a child; mother or father?
(b) What will be the gender of a child if it inherits Y chromosome from father?
OR
(b) How many pairs of chromosomes are present in humans?
Answer:
(a) Father
(b) A boy (Male)
OR
(b) 23 pairs out which twenty-two of these pairs, are called autosomes, they look the same in both males and females. One pair called sex chromosomes are different in both male and female.
Question 38.
1. Take three iron nails and clean them by rubbing with sand paper.
2. Take two test tubes marked as (A) and (B). In each test tube, take about 10 mL copper sulphate solution.
3. Tie two iron nails with a thread and immerse them carefully in the copper sulphate solution in test tube B for about 20 minutes.
4. Keep one iron nail aside for comparison.
5. After 20 minutes, take out the iron nails from the copper sulphate solution.
6. Compare the intensity of the blue colour of copper sulphate solutions in test tubes.
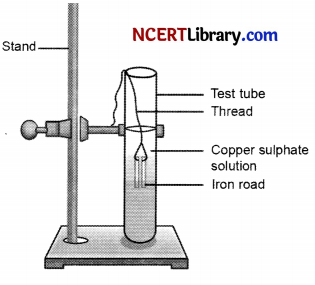
(a) What is shown in the above activity?
(b) The iron nail become brownish in colour and the blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades? Why?
(c) Is the reaction possible? Give reason.
Cu(s) + ZnSO4(aq) → CuSO4(aq) + Zn(s)O
OR
(d) Give any two examples of Displacement reaction.
Answer:
(a) The above activity shows Displacement reaction.
(b) The reason for this can be understood with the help of following reaction,
![]()
In this reaction, iron has displaced or removed another element, copper, from copper sulphate solution. Therefore, the iron nail becomes brownish in colour and the blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades.
(c) Zinc is more reactive element than copper. Therefore, copper cannot displace zinc from its solution. Hence, the given reaction is not possible.
OR
Question 39.
In our homes, we receive supply of electric power through a main supply (also called mains), either supported through overhead electric poles or by underground cables. One of the wires in this supply, usually with red insulation cover, is called live wire (or positive). Another wire, with black insulation, is called neutral wire (or negative).
In our country, the potential difference between the two is 220 V. At the meter-board in the house, these wires pass into an electricity meter through a main fuse. Through the main switch they are connected to the line wires in the house. These wires supply electricity to separate circuits within the house.
Often, two separate circuits are used, one of 15 A current rating for appliances with higher power ratings such as geysers, air coolers, etc. The other circuit is of 5 A current rating for bulbs, fans, etc. The earth wire, which has insulation of green colour, is usually connected to a metal plate deep in the earth near the house.
This is used as a safety measure, especially for those appliances that have a metallic body, for example, electric press, toaster, table fan, refrigerator, etc. The metallic body is connected to the earth wire, which provides a low-resistance conducting path for the Thus, it ensures that any leakage of current to the metallic body of the appliance keeps its potential to that of the earth, and the user may not get a severe electric shock.
(a) What is the potential difference between red wire and black wire?
(b) Why two separate circuits are used in homes?
(c) How is earth wire connected in homes?
OR
(c) How earth wire acts as safety device?
Answer:
(a) 220 V
(b) Two separate circuits are used, one of 15 A current rating for appliances with higher power ratings such as geysers, air coolers, etc. The other circuit is of 5 A current rating for bulbs, fans, etc.
(c) The earth wire, which has insulation of green colour, is usually connected to a metal plate deep in the earth near the house.
OR
(c) It is used as a safety measure, especially for those appliances that have a metallic body, for example, electric press, toaster, table fan, refrigerator, etc. The metallic body is connected to the earth wire, which provides a low-resistance conducting path for the current. Thus, it ensures that any leakage of current to the metallic body of the appliance keeps its potential to that of the earth, and the user may not get a severe electric shock.