Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions Set 3 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 3 with Solutions
Time : 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 objective type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts.
Section – A
Select and write one most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1-20
Question 1.
When you focus the image of a distant flag, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image as it appears on the screen is:
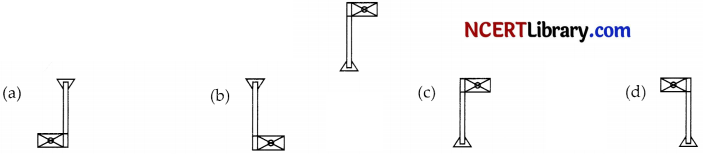
Answer:

Explanation: As image is focused on the screen, then the image formed is real. And real images are inverted.
Question 2.
Dominant alleles are expressed exclusively in a heterozygote, while recessive traits are expressed only if the organism is _________ for the recessive allele.
(a) Homozygous
(b) Heterozygous
(c) Normal
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Homozygous
Explanation: Mendel’s law of dominance states that in a heterozygote, one trait will cancel the presence of another trait for the same characteristic.
Rather than both alleles contributing to a phenotype, the dominant allele will be expressed exclusively. The recessive allele will remain “latent,” but will be transmitted to offspring by the same manner in which the dominant allele is transmitted. The recessive trait will only be expressed by offspring that have two copies of this allele.
Question 3.
The image formed on the retina of the human eye is :
(a) Virtual and erect
(b) Real and inverted
(c) Virtual and inverted
(d) Real and erect
Answer:
(b) Real and inverted
Explanation: The image formed on the retina of the human eye is real and inverted. On retina, the image is converted into electrical impulses and sent to the brain. The brain flips that image into a virtual and erect image.
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following salts do not contain water of crystallisation?
(a) Blue vitriol
(b) Baking soda
(c) Washing soda
(d) Gypsum
Answer:
(b) Baking soda
Explanation:
- Baking soda: It is sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) in anhydrous form without any water of crystallisation.
- Blue Vitriol: It is hydrated salt of copper sulphate containing 5 molecules of water of crystallisation (CuSO4. 2H2O).
- Washing soda: It is hydrated salt of sodium carbonate containing 10 molecules of water of crystallisation (Na2CO3.10H2O)
- Gypsum: It is hydrated salt of calcium sulphate containing 2 molecules of water of crystallisation (CaSO4 2 H2O).
Question 5.
Identify A, B and C in the given diagram and match the labelling referred in column I and correlate with the function in column II.
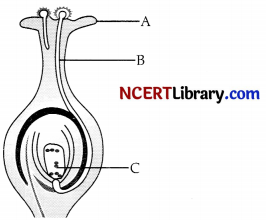
| Column I | Column II |
| A. | (i) Special reproductive female sex cell which combines with male gamete to form zygote. |
| B. | (ii) A male gamete moves down though it towards the female gamete in the ovary. |
| C. | (iii) Receiving the pollen grains from the anther of stamen during pollination. |
Answer:
(a) A-(iii), B-(ii), C-(i)
(b) A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iii)
(c) A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iii)
(d) A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii)
Answer:
(a) A-(iii), B-(ii), C-(i)
Explanation:
- A – Stigma. The top part of carpel is called stigma. Stigma is for receiving the pollen grains from the anther of stamen during pollination.
- B – Pollen tube. When a pollen grain falls on the stigma, it bursts open and grows a pollen tube downward through the style towards the female gamete in the ovary. A male gamete moves down the pollen tube.
- C – Female gamete (ovum). It is a special reproductive female sex cell which combines with male gamete to form zygote.
Question 6.
Offspring formed as a result of sexual reproduction exhibit more variations because:
(a) Sexual reproduction is a lengthy process.
(b) Genetic material comes from two parents of the same species.
(c) Genetic material comes from two parents of different species.
(d) Genetic material comes from many parents.
Answer:
(b) Genetic material comes from two parents of the same species.
Explanation: Sexual reproduction is a process in which two individuals of the same species collaborate to produce two distinct gametes, one male and one female. The fusion of gametes results in the mixing of genetic material, resulting in the formation of a diploid cell with new combinations. An electric fuse is connected with :
Question 7.
An electric fuse is connected with
(a) live wire
(b) earthing
(c) neutral wire
(d) parallel to the line wire
Answer:
(a) live wire
Explanation: An electric fuse is connected with live wire because it gets blown up when an excess current tries to pass through it in order to save the electrical appliances by restricting the flow of that current.
Question 8.
Characters transmitted from parents to offspring are present in:
(a) Cytoplasm
(b) ribosome
(c) Golgi bodies
(d) genes
Answer:
(d) genes
Explanation: Characters are transmitted from parents to offspring through genes. Genes are the heredity units of the body in living organisms. Chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell contain information for the inheritance of features from parents in the form of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid). This DNA contains genes.
Question 9.
Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit?
(a) I²R
(b) IR²
(c) VI
(d) V²/R
Answer:
(b) IR²
Explanation:
We know that,
Where,
P = VI … (i)
P = Power
Where,
V = Potential difference
I = Current
V = IR … (ii)
On substituting equation (ii) in equation (i), we get
P = I²R … (iii)
Again, from Ohm’s law
I = \(\frac { V }{ R }\) … (iv)
On substituting equation (iv) in equation (i), we get,
P = \(\frac{\mathrm{V}^2}{\mathrm{R}}\)
Hence, option (b) IR² does not represent power.
Question 10.
Which statement is not true about Thyroxine?
(a) Thyroxine regulates the basal metabolism of our body.
(b) Iodine is an important component required for synthesis of Thyroxine.
(c) Under secretion of Thyroxine causes simple goitre.
(d) Iron is essential for synthesis of Thyroxine.
Answer:
(d) Iron is essential for synthesis of Thyroxine.
Explanation: Iodine, not iron, is required for the synthesis of Thyroxine. It controls the glucose, protein, and fat metabolism of the body. The thyroid gland produces Thyroxine, which is also known as thyroid hormone.
Question 11.
Let us consider the flow of the current through a metallic wire, if the temperature of the entire system increases. What will happen from the following options?
(a) Potential difference (V) increases
(b) Resistance (R) decreases
(c) Potential difference (V) decreases
(d) V and R remain the same
Answer:
(c) Potential difference (V) decreases
Explanation: If the temperature of the entire system increases when the current is flowing through a metallic wire, the power (VI) is dissipated in the form of heat. Hence the potential difference (V) decreases.
Question 12.
Axon is:
(a) Impulse
(b) Cytoplasmic extension
(c) Muscle parts
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) Cytoplasmic extension
Explanation: Axons are one of two forms of cytoplasmic protrusions from a neuron’s cell body; dendrites are the other. In vertebrates, an axon is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell that conducts electrical impulses.
![]()
Question 13.
Which of the following properties of aluminium makes it suitable for making cooking utensils?
(i) Good thermal conductivity
(ii) Good electrical conductivity
(iii) Ductility
(iv) High melting point
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(d) (i) and (iv)
Explanation: Good thermal conductivity and high melting point of aluminium are the properties that makes it suitable for making cooking utensils.
Question 14.
A current flows in a wire, running between the S and N poles of a magnet lying horizontally as shown in the figure below:
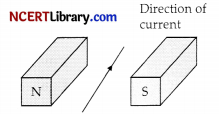
The force on the wire due the magnet is directed.
(a) From N to S
(b) From S to N
(c) Vertically downwards
(d) Vertically upwards
Answer:
(c) Vertically downwards
Explanation: Force on conductor is calculated using Fleming’s left hand rule.
Question 15.
What branch of biology focuses on the study of patterns of inheritance?
(a) Genetics
(b) Immunology
(c) Evolution
(d) Ecology
Answer:
(a) Genetics
Explanation: Genetics is the branch of biology that deals with questions of inheritance. It uses techniques from various disciplines like Molecular biology, Cell biology, and many more to understand the basis of inheritance.
Question 16.
Mutual induction is a process in which current is induced in the neighbouring coil if current flows in a coil. In the figure shown below:
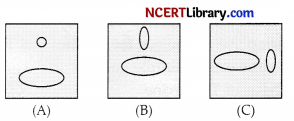
(a) Maximum in situation (A)
(b) Maximum in situation (B)
(c) Maximum in situation (C)
(d) Same in all situation
Answer:
(a) Maximum in situation (A)
Explanation: As both the coils are in the same plane and induced current is found to be highest when the direction of the coil is at right angle to the magnetic field.
Question number 17 to 20 are Assertion – Reasoning based questions.
These consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question 17.
Assertion: Diabetes mellitus is caused due to lack of insulin in the body.
Reason: Insulin helps in utilisation of glucose in the body.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Insulin is a hormone released by the beta cells of the pancreas. It maintains the blood glucose level in the body, by its proper utilisation. So, lack of insulin causes accumulation of glucose in the blood and hence a disease called diabetes mellitus is caused. Thus, both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 18.
Assertion: Electric current flowing through a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends.
Reason: Ohm’s law expression V = IR, where R (resistance) of the wire is always varying.
Answer:
(c) A is true, but R is false.
Explanation: Ohm’s law states that the electric current flowing through a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference across its two ends. The expression is written as :
V = IR
Here, R (resistance of the wire) is constant value then only the statement will be valid.
V ∝ I only if \(\frac { V }{ I }\) = constant
Thus, assertion is true, but reason is false.
Question 19.
Assertion: Lumen of fallopian tube is lined by ciliated epithelium.
Reason: Ciliated epithelium helps in moving the zygote towards the uterus for implantation.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: Lumen of Fallopian tube is lined by ciliated epithelium as cilia have a rhythmic waving and beating motion that helps substances to travel from one place to another. Thus, both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Question 20.
Assertion: Hydrogen peroxide is kept in coloured bottles.
Reason: Hydrogen peroxide is a moderately reactive metal that can react with light or heat slowly to produce water.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false
Explanation: Hydrogen peroxide is a highly reactive metal that can react with light or heat to produce water. It decomposes into water and oxygen in the presence of sunlight. To prevent this reaction with light and heat it is stored in coloured bottles so that light cannot pass through it. Thus, assertion is true, but reason is false.
Section – B
21 to 26 are very short answer questions.
Question 21.
Write the essential functions performed by ozone at the higher levels of the Earth’s atmosphere? How is it produced? Name the synthetic chemicals mainly responsible for the drop of amount of ozone in the atmosphere. How can the use of these chemicals be reduced?
Answer:
Ozone layer absorbs most of the harmful ultraviolet radiations from the sun to the earth. It is formed high up in the atmosphere by the action of ultraviolet radiation on oxygen gas. Chlorofluorocarbons are the synthetic chemicals responsible for the drop of amount of ozone in the atmosphere.
The use of these chemicals can be reduced by:
- Replacement of chloroflurocarbons with hydrochlorofluorocarbons because it breaks down more quickly.
- Safe disposal of old appliances such as refrigerators and freezers.
Question 22.
Answer the following questions:
(i) Define power of a lens.
(ii) Name the lens that has:
(a) Negative power.
(b) Positive power.
Answer:
(i) The ability of a lens to converge the rays of light falling on it is called the power of lens.
(ii) (a) The focal length of a concave lens is negative, so its power is negative.
(b) The focal length of a convex lens is positive, so its power is positive.
Question 23.
Draw a diagram of excretory system in human beings and label the following terms given below. Aorta, Vena cava, Urinary bladder, Urethra.
OR
List two vital functions of the kidneys.
Answer:
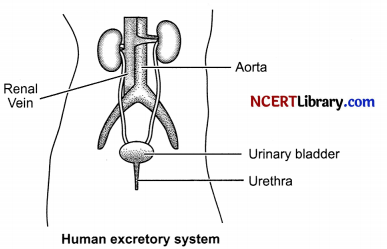
Two vital functions of kidneys are:
- They help in the removal of waste products that are harmful for the body. It is called excretion.
- They maintain the proper level of salts and water concentration in the body. It is called osmoregulation.
Question 24.
The diagram shows one layer of carbon atom in graphite.
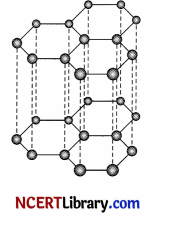
(i) Identify the type of bonding in graphite.
(ii) Which property of graphite make it suitable for use as a dry lubricant? Explain.
Answer:
(i) Between the carbon atoms in each layer covalent bond is found and Van Der Waal’s forces are found between the layers of carbon atoms in graphite.
(ii) Graphite is soft which make it suitable for use as a dry lubricant. Between the carbon atoms in each layer covalent bond is found and weak Van Der Waals forces are found between the layers of carbon atoms in graphite. So the layers can slide over one another making it a relatively soft substance.
Question 25.
Guinea pig having black colour when crossed with guinea pig having same colour produced 80 offspring, out of which 60 were black and 20 were white. Now find out:
(i) What is the possible genotype of the guinea pigs?
(ii) Which trait is dominant and which trait is recessive?
(iii) What is this cross called as and what is its phenotype ratio?
OR
Why do all the gametes formed in human females have an X-chromosome?
Answer:
(i) The possible genotype of the guinea pigs is Bb x Bb.
(ii) Black colour is dominant and white colour is recessive.
(iii) This is an example of monohybrid cross and its phenotypic ratio is 3:1.
OR
The sex chromosome in human female is homomorphic i.e., they contain same chromosome XX. During meiosis process at the time of gamete formation all egg cell will get one copy of X chromosome, hence all the gametes formed in human females have an X-chromosome.
![]()
Question 26.
State the various characteristics of chemical reactions.
Answer:
Some of the characteristics of chemical reactions are:
- Formation of a precipitate
- Change in colour
- Change in temperature
- Change in the state.
- Evolution of a gas
Section – C
Question number 27 to 33 are short answer questions.
Question 27.
B1, B1 and B3 are three identical bulbs connected as shown in figure. Ammeters A1, A2 and A3 are connected as shown. When all the bulbs glow, the current of 3 A is recorded by ammeter A.
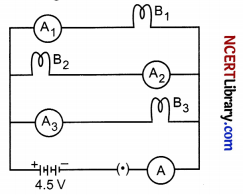
(i) What happens to the glow of the other two bulbs when bulb Ba gets fused?
(ii) What happens to the reading of A1, A2, A3 and A when the bulb B2 gets fused?
(iii) How much power is dissipated in the circuit when all the three bulbs glow together?
Answer:
Resistance of combination of three bulbs in parallel,
\(\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{eq}}=\frac{\mathrm{V}}{\mathrm{I}}=\frac{4.5}{3}=1.5 \Omega\)
If R is the resistance of each wire, then
\(\frac{1}{R_{e q}}=\frac{1}{R}+\frac{1}{R}+\frac{1}{R}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{eq}}}=\frac{3}{\mathrm{R}}\)
⇒ R = 3Req
⇒ R = 3 x 1.5 = 4.5 Ω
Current in each bulb,
I = \(\frac { V }{ R }\) = \(\frac{4.5 \mathrm{~V}}{4.5 \Omega}\) = 1 A
(i) When bulb B1 gets fused, the currents in B2 and B3 remain same I2 = I3 = 1 A, as the voltage across them remains same so their glow remains unaffected.
(ii) When bulb B2 gets fused, the current in B2 becomes zero and currents in B1 and B3 remains 1 A.
Total current I = I1 + I2 + I3
= 1 + 0 + 1 = 2A
Current in ammeter A1 = 1 A
Current in ammeter A2 = 0
Current in ammeter A3 = 1 A
Current in ammeter A = 2 A
(iii) When all the three bulbs are connected in the circuit:
Power dissipitated, P = \(\frac{\mathrm{V}^2}{\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{eq}}}\)
⇒ P = \(\frac{(4.5)^2}{1.5}\) = 13.5 W
Question 28.
Obtain an expression for magnification of an image formed by a concave mirror.
Answer:
Consider the formation of the image A’B’ of an object AB by a concave mirror. As shown in given figure, the right angled triangles ABP and A’B’P are similar triangles, hence
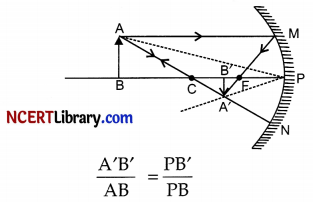
As per sign convention followed, PB = – u, PB’ = – v, PB’ = – v, AB = size of the object = + h and A’B’ = size of the image = -h’
Hence, we have
\(\frac{-h^{\prime}}{h}=\frac{-v}{-u}\)
or \(\frac{-h^{\prime}}{h}=\frac{-v}{u}\)
Thus, by definition of magnification of image, we have
Magnification, m = \(\frac{h^{\prime}}{h}=-\frac{v}{u}\)
Question 29.
(i) Define activity series of metals. Arrange the metals gold, copper, iron and magnesium in order of their increasing reactivity.
(ii) What will you observe when:
(a) Some zinc pieces are put in copper sulphate solution.
(b) Some silver pieces are put into green coloured ferrous sulphate solution.
Answer:
(i) The series of metals in which metals are arranged in decreasing order of their reactivity is called activity series of metals. The increasing order of reactivity will be:
Au < Cu < Fe < Mg.
(ii) (a) The blue solution will become colourless and reddish brown copper metal will be deposited.
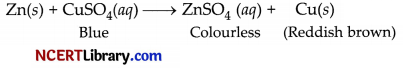
(b) When some silver pieces are put into green coloured ferrous sulphate solution, there will be no reaction because Ag is less reactive than iron.
Ag(s) + FeSO4(aq) → No reaction
Reaction will not take place because Ag is less reactive than iron.
Question 30.
How do Mendel’s experiment show that traits are inherited independently?
OR
The given box diagram represents the ratio of females to males or the sex ratio in our country for 10 decades (1901 to 2001). Answer the following questions in the light of your knowledge of sex determination and the data presented in the box diagram.
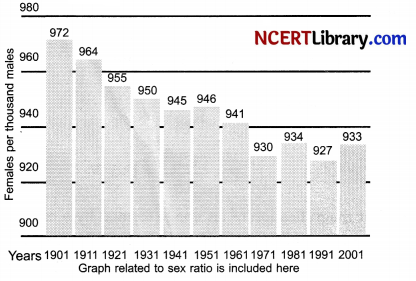
(i) What does the bar diagram show?
(ii) As per scientific knowledge regarding sex determination, what should be the sex ratio or the male to female ratio at a given point of time?
(iii) Assign one reason to the trend showing deviation from the expected sex ratio.
(iv) Suggest a way by which such a trend can be stopped.
Answer:
Mendel’s experiment show that:
- When a cross was made between a tall pea plant with round seeds and a short pea plant wrinkled seeds, the F1 progeny plants are all tall with round seeds. This indicates that tall and round seeds are the dominant traits.
- When the F1 plants are self pollinated and the F2 progeny show that some progencies tall with round seeds and some progencies are short plants with wrinkled seeds which are the traits visible in the F2 generation.
- There were also some progencies with new combinations like tall plants with wrinkled seed short plants with round seeds.
OR - Bar diagram shows the proportion of females in the population over a decade.
- 1:1 should be the sex ratio or the male to female ratio at a given point of time.
- Female foeticide is the main reason to this trend showing deviation from the expected sex ratio.
- Banning sex tests of unborn baby; increasing awareness and education will help to stop such trends.
Question 31.
Define:
(i) Food chain
(ii) Food web
(iii) Biological magnification.
Answer:
(i) Food chain: The series or organism taking part at various trophic level for the flow of energy is called a food chain.
(ii) Food web: Food web represents many interlinked food chains as each organism is generally eaten by two or more other kind of organisms. It cannot represented by a straight line.
(iii) Biological magnification: The accumulation of harmful chemicals at each trophic level with the help of various biotic and abiotic factors is called biological magnification.
Question 32.
(i) Define the term alloy and amalgam. Name the alloy used for welding electric wires together. What are its constituents?
(ii) Name the constituents of the following alloys:
(a) Brass
(b) Stainless steel
(c) Bronze
OR
Write difference between calcination and roasting.
Answer:
(i) An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of a metal with a metal or a non-metal. Amalgam is an alloy of a metal with mercury.
The alloy used for welding electric wires together is Solder. Its constituents are lead and Tin.
(ii) (a) Brass: Brass alloy is made of zinc (Zn) and copper (Cu).
(b) Stainless steel: It contains chromium (12.14%), molybdenum (0.21 %), nickel (less than 2%), and carbon (about 0.11%).
(c) Bronze: It is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12% tin and often with the addition of other metals (such as aluminium, manganese, nickel or zinc) and sometimes non-metals or metalloids such as arsenic, phosphorus or silicon.
OR
| Calcination | Roasting |
| 1. In this process, the ore is heated in a limited supply of air below its melting point. The process involves the removal of volatile impurities, moisture and the decomposition of any carbonate ore into oxide. | The process of heating the ore in the excess supply of air below its melting point is called roasting. This process is employed when oxidation of the ore is required. As a result of roasting, moisture is driven away, volatile impurities are removed, the impurities like sulphur, phosphorus, arsenic are removed as their oxides and the ore undergoes oxidation to form metal oxide or sulphate. |
| 2. Moisture organic impurities are removed and the ore becomes porous and more reactive. | Volatile impurities are removed as oxides (SO2, P2O5, As2O3) and the ore becomes porous and more reactive. |
| 3. Carbonate and hydrated ores are calcined and CO2 or water vapour is given off. ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2 |
Sulphide ores are roasted, and SO2 is given off. |
Question 33.
State one characteristic each of the chemical reaction which takes place when:
(i) Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium carbonate.
(ii) Lemon juice is added gradually to potassium permanganate solution.
(iii) Dilute sulphuric acid is added to barium chloride solution.
Answer:
(i) Carbon dioxide gas is released.
(ii) Colour changes from purple to colourless
(iii) White precipitate of barium sulphate is formed
Section – D
Question number 34 to 36 are long answer questions.
Question 34.
Explain the nutrition process in amoeba.
OR
(i) Explain the statement “Bile does not contain any enzyme but it is essential for digestion”.
(ii) Explain the process of breathing in human beings.
Answer:
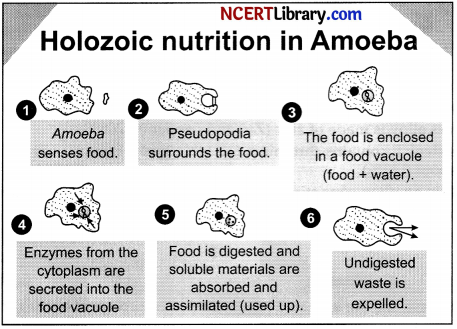
Amoeba follows holozoic nutrition.
It involves the following steps:
1. Ingestion – Amoeba engulfs the food by using its temporary finger like projections called pseudopodia. This process is called ingestion.
2. By phagocytosis process it engulfs its food.
3. Digestion – The food which is taken inside the amoeba forms a food vacuole. Many enzymes are secreted into the food vacuole and the complex food molecule is converted into simple and diffusible form.
4. Absorption and assimilation – The digested food is absorbed by the cell by diffusion process.
5. Egestion – The undigested residue which remains in vacuole is expelled out.
OR
(i) Though bile juice secreted by liver has no enzymes in it but still it is essential for digestion because:
1. It makes the medium alkaline in the small intestine so that intestinal juice can perform its functions because the food from stomach which enters into the small intestine is acidic in nature.
2. It emulsifies fats so that enzymes like lipase can act upon fats to convert them into fatty acids and glycerol.
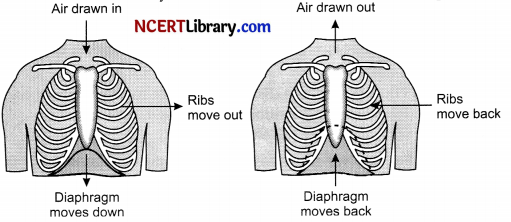
(ii) Breathing process occurs by inhalation and exhalation.
1. Inhalation: It is the process by which oxygen is taken in through nostrils. During inhalation process, the ribs move upwards and outwards due to contraction of intercostal muscles. The diaphragm is lowered so that the volume of thoracic cavity increases. As a result air is forced inside the lungs through nostrils.
2. Exhalation: ¡lis the process by which carbon dioxide is exhaled out from lungs through nostrils.
During this process the ribs moves inwards and diaphragm comes back to its original position.
The volume of thoracic cavity decreases so air is forced out through the lungs.
Question 35.
(i) Observe the given figure and answer the following:
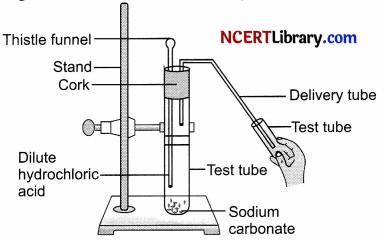
(a) Identify the gas evolved.
(b) How will you test the presence of gas evolved?
(c) What is the nature of the gas evolved?
(d) What will happen to the lime water when the gas evolved is passed through it? Give chemical equation.
(e) What happens to the lime water when this gas is passed for a longer period of time?
(ii) Account for the following:
(a) State the relation between hydrogen ion concentration of an aqueous solution and its pH.
(b) An aqueous solution has a pH value of 7.0. Is this solution acidic, basic or neutral?
(c) Which has a higher pH, 1 M HC1 or 1 M NaOH solution?
(d) Tooth enamel is one of the hardest substance in our body. How does it undergo damage due to eating chocolates and sweets? What should we do to prevent it?
(e) How do H+ ions exist in water?
Answer:
(i) (a) Carbon dioxide gas is evolved.
(b) Carbon dioxide gas is non-supporter of combustion so when a burning splinter is brought near this gas, it get extinguished.
(c) This gas is acidic in nature as it turns blue litmus red.
(d) Lime water will turn milky.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(e) When this gas is passed through lime water for longer period of time, the milky lime water disappears.
CO2 + CaCO3 + H2O → Ca(HCO3)2
(ii) (a) Hydrogen ion concentration of an aqueous solution is inversely proportional to its pH.
(b) The solution is neutral.
(c) 1 M NaOH solution has higher pH because base have higher pH value than acids.
(d) Tooth enamel gets corroded slowly when pH in the mouth is below 5.5. Acid is produced in mouth due to degradation of food which is partially hydrolysed by saliva. But if excess acid is produced, it causes tooth decay. It can be prevented by using tooth paste which are generally basic.
(e) H+ ions exist in water as H3O+ ions.
![]()
Question 36.
(i) “A convex lens can form a magnified erect as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it.” Draw ray diagram to justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the lens in each case.
(ii) An object of height 4 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave lens of focal length 10 cm. Use lens formula to determine the position of the image formed.
OR
(i) To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List two such rays and state the path of these rays after reflection in case of concave mirrors. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror.
(ii) A concave mirror produces three times magnified image on a screen. If the object is placed 20 cm in front of the mirror, how far is the screen from the object?
Answer:
(i) Case I: Image formed is magnified and erect when object is placed between optical centre and focus on a convex lens.
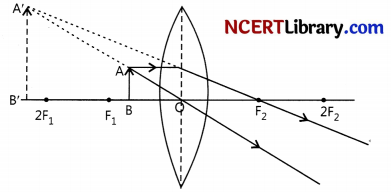
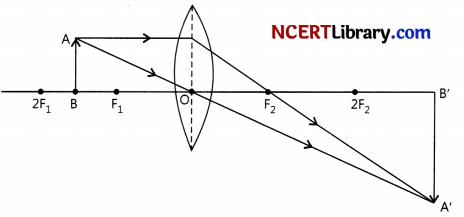
Case II: Image formed is magnified and inverted when the object is placed between F and 2F of a convex lens.
(ii) Given: u = – 20 cm, f = – 10 cm.
Using lens formula,
\(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ υ }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\)
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ υ }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\)
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ υ }\) = – \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 20 }\)
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ υ }\) = \(\frac { -2-1 }{ 20 }\) = \(\frac { -3 }{ 20 }\)
⇒ υ = \(\frac { -20 }{ 3 }\) cm
OR
(i) The following rays of light are usually used to locate the images formed by a spherical mirror : The incident ray passing through the centre of curvature: In this case, light after reflecting from the spherical mirror moves back along the same path.
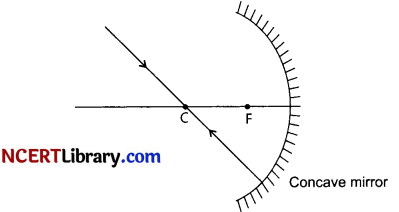
The ray incident obliquely to the principal axis: In this case, the incident ray will be reflected back by the reflecting surface of the spherical mirror obliquely, making equal angles with the principal axis.
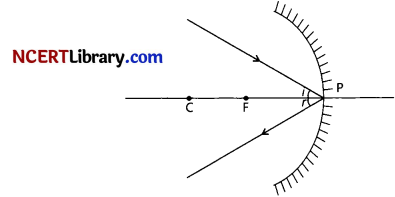
When the object is placed between pole and focus of the concave mirror, image is formed behind the mirror and is virtual, erect and magnified.
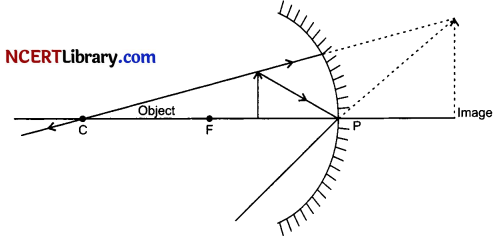
(ii) Given, Magnification, m = – 3 (As image is real), Object distance, u = – 20 cm
We have, m = – \(\frac { υ }{ u }\)
⇒ – 3 = -(\(\frac { υ }{ -20 }\))
⇒ υ = – 60 cm
The image is located at a distance of 60 cm in front of the mirror.
Thus, the screen is at a distance of 40 cm from the object.
Section – E
Question number 37 to 39 are case – based/data -based questions with 2 to 3 short sub – parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Question 37.
Mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. That is, the total mass of the elements present in the products of a chemical reaction has to be equal to the total mass of the elements present in the reactants. In other words, the number of atoms of each element remains the same, before and after a chemical reaction. Hence, we need to balance a skeletal chemical equation.
To make a chemical equation more informative, the physical states of the reactants and products are mentioned along with their chemical formulae. The gaseous, liquid, aqueous and solid states of reactants and products are represented by the notations (g), (1), (aq) and (s), respectively. The word aqueous (aq) is written if the reactant or product is present as a solution in water.
Usually physical states are not included in a chemical equation unless it is necessary to specify them. Sometimes the reaction conditions, such as temperature, pressure, catalyst, etc., for the reaction are indicated above and/or below the arrow in the equation. For example,
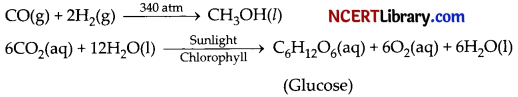
(a) Balance the chemical equation for given reaction with proper physical state.
Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
(b) Which law is demonstrated above?
OR
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation for reaction of Barium chloride and Aluminium sulphate to give Barium sulphate and aluminium chloride.
Answer:
(a) The balanced chemical equation for given reaction is;
3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
(b) Law of Conservation of Mass is demonstrated in the above equation.
OR

Question 38.
Stomata are tiny pores present on the surface of the leaves. Massive amounts of gaseous exchange takes place in the leaves through these pores for the purpose of photosynthesis. But it is important to note here that exchange of gases occurs across the surface of stems, roots and leaves as well. Since large amounts of water can also be lost through these stomata, the plant closes these pores when it does not need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The opening and closing of the pore is a function of the guard cells. The guard cells swell when water flows into them, causing the stomatal pore to open. Similarly the pore closes if the guard cells shrink.
1. Take two healthy potted plants which are nearly the same size.
2. Keep them in a dark room for three days.
3. Now place each plant on separate glass plates. Place a watch-glass containing potassium hydroxide by the side of one of the plants.
4. The potassium hydroxide is used to absorb carbon dioxide.
5. Cover both plants with separate bell-jars.
6. Use Vaseline to seal the bottom of the jars to the glass plates so that the set-up is air-tight.
7. Keep the plants in sunlight for about two hours.
8. Pluck a leaf from each plant and check for the presence of starch as in the above activity.
(a) What can be concluded from the activity?
(b) What is the function of stomata?
(c) How guard cells controls the opening and closing of stomata?
OR
(d) In the above activity, do both the leaves show the presence of the same amount of starch?
Answer:
(a) It shows that the amount of carbon dioxide affects the process and outcome of photosynthesis.
(b) Massive amounts of gaseous exchange takes place in the leaves through these pores for the purpose of photosynthesis.
(c) The guard cells swell when water flows into them, causing the stomatal pore to open. Similarly the pore closes if the guard cells shrink.
OR
(d) No, both the leafs shows presence of different amount of starch in the given activity.
Question 39.
The given table shows that the resistivity of an alloy is generally higher than that of its constituent metals. Alloys do not oxidise (burn) readily at high temperatures. For this reason, they are commonly used in electrical heating devices, like electric iron, toasters etc. Tungsten is used almost exclusively for filaments of electric bulbs, whereas copper and aluminium are generally used for electrical transmission lines.
| Material | Resistivity (Ω m) | |
| Conductors | Silver Copper Aluminium Tungsten Nickel Iron Chromium Mercury Manganese |
1.60 x 10-8 1.62 x 10-8 2.63 x 10-8 5.20 x 10-8 6.84 x 10-8 10.0 x 10-8 12.9 x 10-8 94.0 x 10-8 1.84 x 10-8 |
| Alloys | Constantan (alloy of Cu and Ni) Manganin (alloy of Cu, Mn and Ni) Nichrome (alloy of Ni, Cr, Mn and Fe) |
49 x 10-6 44 x 10-6 100 x 10-6 |
| Insulators | Glass Hard rubber Ebonite Diamond Paper(dry) |
1010 – 1014 1013 – 1016 1015 – 1017 1012 – 1013 1012 |
(a) How much current will an electric bulb draw from a 200 V source, if the resistance of the bulb filament is 1500 Ω?
(b) Why alloys are used in heating devices?
(c) Which alloy is used exclusively for filaments of electric bulbs?
OR
(c) Write the composition of Nichrome.
Answer:
(a) Given that V = 200V; R = 1500Ω.
Therefore, current I = 200 V/1500 Ω = 0.13 A.
(b) Alloys do not oxidise (burn) readily at high temperatures. For this reason, they are commonly used in electrical heating devices, like electric iron, toasters etc.
(c) Tungsten
OR
(c) Nichrome is an alloy of Ni, Cr, Mn and Fe.