Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions Set 2 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 2 with Solutions
Time : 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 objective type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts.
Section – A
Select and write one most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1-20
Question 1.
Pentane has the molecular formula C5H12. It has:
(a) 5 covalent bond
(b) 12 covalent bonds
(c) 16 covalent bonds
(d) 17 covalent bonds
Answer:
(c) 16 covalent bonds
Explanation: Structural formula of pentane is:
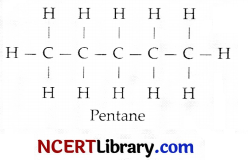
Number of C – C covalent bonds = 4
Number of C – H covalent bonds = 12
Hence, the total number of covalent bonds in the structure of pentane is 16.
Question 2.
A student learns that magnetic field strength around a bar magnet is different at every point which diagram shows the correct magnetic field lines around a bar magnet?
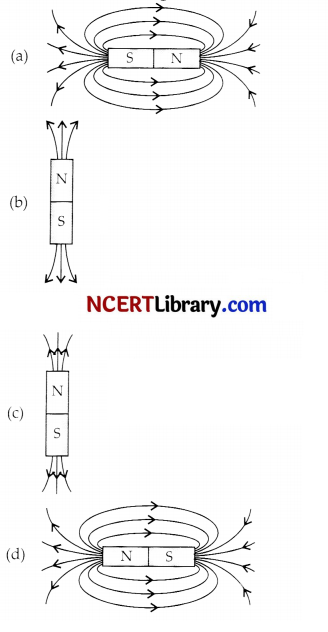
Answer:
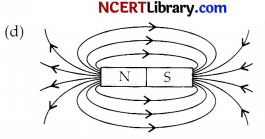
Explanation: As magnetic lines of forces are continuous curves and originate from N-pole and ends at the S-pole
Question 3.
A few drops of iodine solution were added to rice water. The solution turned blue-black in colour. This indicates that rice water contains :
(a) Complex proteins
(b) Simple proteins
(c) Starch
(d) Fats
Answer:
(c) Starch
Explanation: Due to the presence of starch, when iodine solution was added to rice water, the solution becomes blue- black. Iodine forms Starch Iodide complex when it comes in contact of the amylose structure of starch. The blue-black colour comes from the starch iodide complex.
Question 4.
By removing the inducing magnets, the induced magnetism is:
(a) Finished after sometime
(b) Finished just after
(c) Non-finished for a long time
(d) Not charged
Answer:
(b) Finished just after
Explanation: As induced magnetism takes place, as long as the induced magnet is present.
Question 5.
CNS consists of:
(a) brain
(b) spinal cord
(c) only cerebrum
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) both (a) and (b)
Explanation: The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The spinal cord is a long, tubular bundle of neurons that connects the brain to the rest of the body and transmits information.
![]()
Question 6.
Which among the following is not the function of testes at puberty?
(i) Formation of germ cells
(ii) Secretion of testosterone
(iii) Development of placenta
(iv) Secretion of estrogen
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(c) (iii) and (iv)
Explanation: Development of placenta and secretion of estrogen are related to female reproductive I system, hence are not the function of testes at puberty.
Question 7.
A copper wire is held between the poles of a magnet:
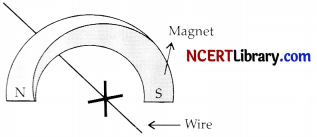
The current in the wire can be reversed. The pole of the magnet can also be changed over. In how many of the four directions shown can the force act on the wire?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
Explanation: By Fleming’s left hand rule, we know that the force on the wire is perpendicular to the current in the wire and the magnetic field.
Question 8.
The process where characteristics are transmitted from parent to offsprings is called:
(a) Variation
(b) Heredity
(c) Gene
(d) Allele
Answer:
(b) Heredity
Explanation: Characteristics from parents are passed down to offspring during sexual reproduction. These are the combinations of female and male parent. This is known as heredity.
Question 9.
On which of the given factors, resistance does not depend?
(a) Length of conductor
(b) Area of cross-section
(c) Temperature
(d) Density
Answer:
(d) Density .
Explanation: The resistance of wire can be expressed as:
R = ρ\(\frac { L }{ A }\)
Where, A = Area of cross-section of the conductor
L = Length of the conductor
ρ = Resistivity
From the above relation, we can see that resistance of a wire is directly proportional to its length and inversely proportional to the area of cross-section. Hence, resistance does not depend on the density.
Question 10.
In a double displacement reaction such as the reaction between sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution:
(i) exchange of atoms takes place.
(ii) exchange of ions takes place.
(iii) a precipitate is produced.
(iv) an insoluble salt is produced.
The correct option is :
(a) (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) only (ii)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Explanation: In a double displacement reaction such as the reaction between sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution, sodium sulphate chemically reacts with barium chloride in the form of their aqueous solution to form an insoluble white precipitate of barium sulphate and sodium chloride.
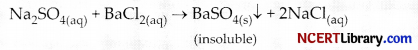
Here, exchange of ions takes place.
Question 11.
Which is the first enzyme to mix with food in the digestive tract?
(a) Amylase
(b) Pepsin
(c) Trypsin
(d) Cellulase
Answer:
(a) Amylase
Explanation: Amylase is the first enzyme in the digestive tract to mix with food. It is secreted in the mouth and acts on starch to break it down into smaller molecules.
Question 12.
Which of the following obeys Ohm’s law?
(a) Filament of a bulb
(b) LED
(c) Nichrome
(d) Transistor
Answer:
(c) Nichrome
Explanation: In conductors, resistance remains constant when the current passing through them is increased, they are known as Ohmic conductors. Nichrome which is an alloy is made in such a way that its resistance remains constant for a wide range of temperature. Hence, nichrome obeys Ohm’s Law. Whereas, transistor, LED, bulb filament do not obey Ohm’s law because with the varied change in temperature their resistance changes.
Question 13.
Which of the following statements are correct ?
(i) Pvurvate can be broken down into ethanol and carbon dioxide by yeast.
(ii) Fermentation takes place in aerobic bacteria.
(iii) Fermentation takes place in mitochondria.
(iv) Fermentation is a form of anaerobic respiration.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer:
(c) (i) and (iv)
Explanation: Fermentation is an anaerobic process in which sugar is converted to acids or alcohol in the absence of oxygen. This process occurs in yeast, bacteria, and oxygen-depleted muscle cells in the same way that lactic acid fermentation does, but it takes place in the cytoplasm rather than in the mitochondria.
![]()
Question 14.
Electrical resistivity of an alloy of copper and nickel is when compared with the electrical resistivity of an allov of copper, manganese and nickel.
(a) same
(b) double
(c) more
(d) less
Answer:
(c) more
Explanation: Electrical resistivity of an alloy of copper and nickel is more when compared with the electrical resistivity of an alloy of copper, manganese and nickel. The electrical resistivity of Cu-Ni alloys with increasing temperature rises steeply. At 200°C, the electrical resistivity of Cu-Ni alloy is 49 x 10-8Ω-m whereas of copper, manganese and nickel 44 x 10-8Ω-m.
Question 15.
The xylem in plants are responsible for :
(a) transport of water
(b) transport of food
(c) transport of amino acids
(d) transport of oxygen
Answer:
(a) transport of water
Explanation: In vascular plants, xylem is a type of tissue that transports water and some nutrients from the roots to the leaves. The other type of transport tissue is phloem, which is responsible for transporting sucrose and other nutrients throughout the plant. The xylem acts as a conducting tissue to transport water and some soluble nutrients such as minerals and inorganic ions from the roots to the rest of the plant.
Question 16.
A student has traced the path of a ray of light through a glass slab as follows. If you are asked to label 1,2, 3 and 4, the correct sequencing of labeling ∠i, ∠e, ∠r and lateral displacement respectively is :
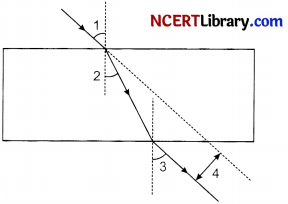
(a) 2, 1, 3, 4
(b) 1, 2, 3, 4
(c) 1, 3, 2, 4
(d) 1, 3, 4, 2
Answer:
(c) 1, 3, 2, 4
Explanation: Here, 1 is angle of incidence, 3 is angle of emergence, 2 is the angle of refraction and 4 is the lateral displacement.
Question number 17 to 20 are Assertion – Reasoning based questions.
These consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is False but R is true.
Answer:
Question 17.
Assertion: Plants raised by vegetative propagation can bear flower and seed earlier than those produced from seeds.
Reason: Plants which have lost the capacity to bear viable seeds, can propagate through vegetative propagation.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
Explanation: The plant which are unable to produce seed reproduce by the means of vegetative propagation. This process is a type of asexual reproduction which is much faster than sexual reproduction. Thus, both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 18.
Assertion: It is possible to correct the refractive defects with contact lenses or through surgical interventions. Reason: The eye lens is composed of fibrous jelly-like material.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
Explanation: The refractive defects can be corrected by contact lenses and eye lens is composed of fibrous jelly-like material. Thus, both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Question 19.
Assertion: Colour of copper sulphate solution changes when an iron nail is kept immersed in it.
Reason: The colour of copper sulphate solution changes when iron nail is kept immersed in it due to the decomposition reaction taking place between iron and copper leading to formation of iron sulphate.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false
Explanation: The colour of copper sulphate solution changes when iron nail is kept immersed in it due to the displacement reaction iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution leading to the formation of iron sulphate. Thus, assertion is true but reason is false.
Question 20.
Assertion: The rate of photosynthesis will be lowered if the leaves are coated with oil.
Reason: Stomata gets blocked and thus gaseous exchange is affected.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: Stomata is a tiny pore in leaves that help in gaseous exchange, so if the stomata gets blocked due to oil, gaseous exchange will be affected and hence rate of photosynthesis gets lowered. Thus, both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Section – B
Question number 21 to 26 are very short answer questions.
Question 21.
(i) State two reasons for the following facts:
(a) Sulphur is a non-metal.
(b) Magnesium is a metal
(ii) Compound X and aluminium are used to join railway tracks.
(a) Identify the compound X
(b) Name the reaction
(c) Write down its reaction.
OR
(i) What type of oxides are formed when non-metals react with oxygen? Explain with an example.
(ii) What type of oxides are formed when metals combine with oxygen? Explain with the help of an example.
Answer:
(i) (a) Sulphur is a non- metal because:
- It is a poor conductor of electricity.
- Sulphur is neither malleable nor ductile.
(b) Magnesium is a metal because:
- It is a good conductor of electricity.
- Magnesium is malleable nor ductile.
(ii)
- Compound χ = Fe2O3
- Thermite reaction.
- Fe2O3 + 2Al → 2Fe + Al2O3.
OR
(i) When non-metals react with oxygen, they form acidic oxides or neutral oxides.
Example: Carbon reacts with oxygen to form an acidic oxide called carbon dioxide.
(ii) When metals combine with oxygen, they form basic oxides.
Example: Sodium reacts with oxygen to form a basic oxide called sodium oxide.
![]()
Question 22.
(i) One half of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm is covered with a black paper. Can such a lens produce an image of a complete object placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer.
(ii) 4 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find the nature, position and size of the image.
Answer:
Yes, it can produce an image of a complete object placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens.
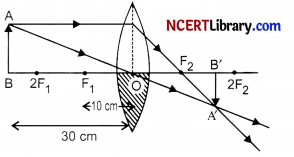
(ii) Given: h1 = 4 cm, f = + 20 cm, u = – 15 cm
We know that,
\(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ υ }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\)
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ υ }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 20 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 15 }\) = \(\frac { 3-4 }{ 60 }\) = \(\frac { -1 }{ 60 }\)
∴ Image distance, υ = – 60 cm. Image will be virtual and erect.
Now, Magnifiction, m = \(\frac{h_2}{h_1}=\frac{v}{u}\)
⇒ h2 = \(\frac{v}{u} \times h_1=\frac{-60}{-15}\) x 4 = + 16 cm
Hence, a erect and virtual image is formed having size 16 cm.
Question 23.
Write the chemical equation of the reaction in which the following changes have taken place with an example of each:
(i) Change in colour
(ii) Change in temperature
Answer:
(i) Change in colour
Cu (s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag
The solution will become blue in colour and shiny silver metal will be deposited.
(ii) Change in temperature
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O + Heat
The temperature will increase because heat will be evolved.
Question 24.
A student is viewing under a microscope a permanent slide showing various stages of asexual reproduction by budding in yeast. Draw diagram of what he observes in proper sequence.
Answer:
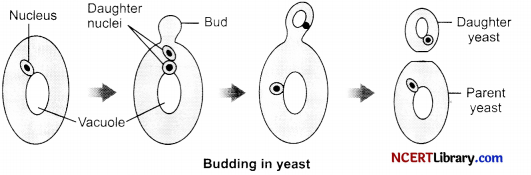
Question 25.
How many X chromosomes can be found in the cells of the body of (i) a boy, and (ii) a girl?
OR
“The maximum concentration of harmful chemicals accumulates in human beings.” State the phenomenon involved and justify this statement.
Answer:
(i) Males have one X chromosome.
(ii) Females have two X chromosomes.
OR
Human beings are always placed at the top of a food chain. The concentration of harmful chemicals [non-biodegradable substance] goes on increasing at every trophic level as human beings are placed at the apex of every food chain so maximum concentration of harmful chemicals get accumulated in their body. This phenomenon is called biomagnification.
Question 26.
What is ozone and how does it affect any ecosystem?
Answer:
Ozone is a triatomic molecule made of three oxygen atoms. It is present as a layer in stratosphere which prevents the harmful UV radiations of sun from entering the earth’s surface, thus protecting us from skin cancers, genetic mutations, eye diseases like cataract etc. Ozone is a molecule made from three atoms of oxygen.
The harmful chemicals like CFCs which are used as coolants in refrigerators, air conditioners when released into atmosphere break down the ozone thus leading to depletion of ozone layer. Hence harmful UV rays can easily pass through ozone layer and cause various types of disorders in humans, plants and animals.
Section – C
Question number 27 to 33 are short answer questions.
Question 27.
(i) A person needs a lens of power – 5.5 dioptre for correcting his distinct vision. For correcting his near vision he needs a lens + 1.5 dioptre. What is the focal length of the lens required for correcting
(a) distinct vision
(b) near vision?
(ii) What do you mean by Presbyopia?
Answer:
(i) (a) Power of lens needed for correction distant vision of the person (P) = – 5.5 D
Focal length of lens required for correcting distant vision
(f) = \(\frac { 1 }{ P }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ -5.5 }\) m = 0.18 m = 18 cm.
(b) For correcting near vision the power of lens required (P) = + 1.5 D
Focal length of lens required for correcting near vision
(f) = \(\frac { 1 }{ P }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 1.5 }\) m = 0.67 m = 66.7 cm.
(ii) Presbyopia is the defect of human eye in which a person is unable to see the nearby as wTell as far off objects clearly.
Question 28.
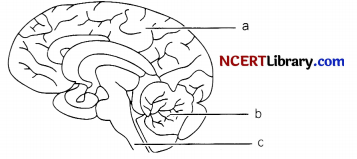
The figure represents human brain. Study the figure given below and answer the following:
(i) Name the parts labeled (a), (b) and (c)
(ii) Give one function of parts (a), (b) and (c)
(iii) The largest part of the brain comprising two hemispheres is known as ……………..
OR
Study the diagrams given below and answer the following questions:
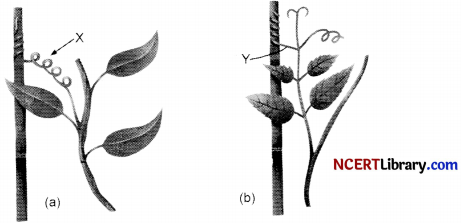
(i) Name the structures shown as X and Y in the figures (A) and (B), respectively.
(ii) Write the functions performed by the structures X and Y.
(iii) Name the phenomenon depicted and define it.
(iv) How do the structures X and Y differ from each other?
(v) Give examples of the plants which show the said phenomenon.
Answer:
(i)
- – Cerebrum
- – Cerebellum
- – Medulla oblongata
(ii)
- Cerebrum is the seat of intelligence, memory, will power, consciousness. It controls voluntary actions. It is the largest portion of the brain. It is divided into two halves called cerebral hemispheres which are connected by a sheet of fibres called corpus callosum.
- Cerebellum controls and coordinates muscular activity and maintains the posture and balance of the body.
- Medulla oblongata controls functioning of internal organs and involuntary actions like beating of heart, breathing movement, peristalsis movement etc.
(iii) The largest part of the brain comprising two hemispheres is known as Cerebrum.
OR
- χ : Stem tendrils, Y: Leaf tendrils.
- Functions of X and Y: Stem and leaf tendrils enable the plant to climb up a support.
- Thigmotropism is depicted here in the figure. It is the growth movement of plant touch stimulus.
- Stem tendrils (X) arise from the stem while leaf tendrils (Y) arise from the leaf of the
- Sweet pea, vines and Cuscuta.
Question 29.
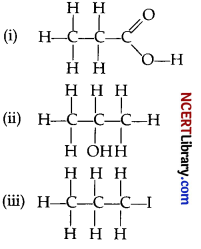
Draw the structure of the following :
(i) Propanoic acid
(ii) 2-propanol
(iii) 1-iodopropane
Answer:
Question 30.
Why does micelle formation takes place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle is formed in other solvents such as ethanol also?
Answer:
Soap may be represented by the formula RCOONa where R is an alkyl group which represents long chain of carbon with fifteen or more atoms. Oil drops containing dirt particles and water do not mix. Soap helps in their mixing by reducing interfacial tension or friction. Actually it forms a sort of bridge between oil drops and water in which the alkyl portion (hydrophobic end) point towards oil drop while other portion (hydrophilic end) is directed towards water. This is known as micelle formation. Thus, soap helps in the formation of a stable emulsion between oil and water. Ethanol and other similar solvents which are of organic nature and they do not help in micelle formation because soap is soluble in them.
![]()
Question 31.
(i) Give reasons for the following observations:
(a) Ionic compounds in general have high melting and boiling points.
(b) Highly reactive metals cannot be obtained from their oxides by heating them with carbon.
(c) Copper vessels get a green coat when left exposed to air in the rainy season.
(ii) Choose the metal (from the list given below) which can displace zinc from zinc sulphate solution – Lead, copper, magnesium, silver. Write the equation of the chemical reaction involved.
Answer:
(i) (a) Ionic compounds in general have high melting and boiling points as their ions are held together by stronger electrostatic force of attraction.
(b) Highly reactive metals cannot be obtained from their oxides by heating them with carbon as they have more affinity for oxygen than as compared to carbon.
(c) Copper vessels get a green coat when left exposed to air in the rainy season as it reacts with C02 and H20 to form a green coating of basic copper carbonate.
(ii) Magnesium can displace zinc from zinc sulphate solution.
Mg(s) + ZnSO4(aq) → MgSO4(aq) + Zn(s)
Question 32.
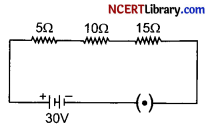
(i) How will you infer with the help of an experiment that the same current flows through every part of a circuit containing three resistors in series connected to a battery?
(ii) Consider the given circuit and find the current flowing in the circuit and potential difference across the 15 Ω resistor when the circuit is closed.
OR
(i)
- Draw a graph of potential difference (V) versus current (I) for an ohmic resistor.
- How can you find the resistance of the resistor from this graph?
(ii) Three resistors are connected to a 12 V battery as shown in the figure given below:
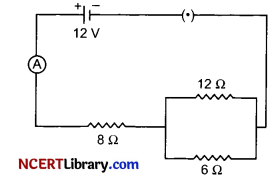
(a) What is the current through the 8 ohm resistor?
(b) What is the potential difference across the parallel combination of 6 ohm and 12 ohm resistor?
(c) What is the current through the 6 ohm resistor?
Answer:
(i) Let three resistors R1, R2 and R3 are connected in series which are also connected with a battery, an ammeter and a key as shown in figure.
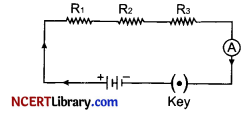
When key is closed, electric circuit is completed and current starts flowing through the circuit. Take the reading of ammeter. Now change the position of ammeter to anywhere in between the resistors and take its reading. We will observe that in both the cases reading of ammeter will be same showing same current flows through every part of the electric circuit.
(ii) Given, R1 = 5 Ω, R2 = 10 Ω, R3 = 15 Ω, V = 30 V
Total resistance, R = R1 + R2 + R3 [As 5 Ω, 10 Ω and 15 Ω are connected in series]
⇒ R = 5 + 10 + 15
⇒ R = 30 Ω
Potential difference, V = 30V
Current in the circuit, I = ?
From Ohm’s law, I = \(\frac { V }{ R }\)
⇒ I = \(\frac { 30 }{ 30 }\)
⇒ I = 1 A
Therefore,
Current flowing in the circuit = 1 A
Potential difference across 15 Ω resistors = IR3 = 1 A x 15 Ω
= 15 V
OR
(i) (a) X-axis denotes potential difference (V) and y-axis denotes current (I) flowing in the circuit.
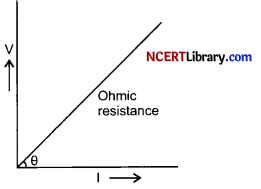
(b) The slope of the V-I graph shown in the figure gives the resistance of the resistor or R = \(\frac { V }{ I }\).
(ii) (a) We know,
Equivalent resistance for 12 Ω and 6 Ω = \(\frac{\mathrm{R}_1 \mathrm{R}_2}{\mathrm{R}_1+\mathrm{R}_2}\)
Resistance of 12 Ω-6 Ω parallel combination = \(\frac { 12×6 }{ 18 }\) = 4 Ω
Equivalent resistance for 8Ω and 4Ω = R3 + R4
The combined resistance of the circuit = 8 + 4 = 12 Ω
∴ Current through 8 ft resistance = \(\frac { 12 }{ 12 }\) = 1 A
(b) We know, Potential difference V = IR
Potential difference across the resistor 12Ω and 6 Ω in parallel combination
= 4 x 1 = 4V
(c) Current through 6 Ω resistor I = \(\frac { V }{ R }\)
⇒ I = \(\frac { 4V }{ 6Ω }\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) A
Question 33.
Answer the following:
(i) What are decomposers? What will be the consequence of their absence in an ecosystem?
(ii) Describe how decomposers facilitate recycling of matter in order to maintain balance in the ecosystem?
Answer:
(i) Decomposers are the microbes that feed on dead and decay organisms. Dead plants and animals will get accumulated in the ecosystem as there would be no decomposers to decompose them. The decomposers will act upon dead and decayed organisms into simpler forms and get mixed in the soil which is used by producers again. But in the absence of decomposers this whole process would not occur and the dead organisms will get accumulated in the ecosystem.
(ii) Decomposers act upon dead and decay organisms to convert them into simpler forms. These simple substances get mixed up in the soil and are used as nutrients by the producers. From producers it goes to consumers and so on. Thus there is recycling of matter which is done by decomposers that maintain the balance in the ecosystem.
Section – D
Question number 34 to 36 are long answer questions.
Question 34.
(i) A 10 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 12 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 18 cm. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
(ii) The absolute refractive index of Ruby is 1-7. Find the speed of light in Ruby. The speed of light in vacuum is 3 x 108 m/s.
OR
A 6 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 30 cm. The distance of the object from the mirror is 45 cm. Use mirror formula to determine the position, nature and size of the image formed. Also draw labelled ray diagram to show the image formation in this case
Answer:
(i) Height of object, h1 = + 10 cm
Focal length, f = + 12 cm
Object distance, u = – 18 cm \(\frac { υ }{ u }\) = [lat
From the lens formula,
\(\frac { 1 }{ υ }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\)
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ υ }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ -18 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 12 }\)
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ υ }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 18 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 12 }\)
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ υ }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 12 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 18 }\)
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ υ }\) = \(\frac { 3-2 }{ 36 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 36 }\)
υ = 36 cm
⇒ Magnifiction, m = ex]\frac { 36 }{ -18 }[/latex] = -2
The position of image formed is at distance of 36 cm from convex lens.
(ii) We know that,

Thus, speed of light in ruby is 1.76 x 108 ms-1
OR
Given, Height of the object = 6 cm
Focal length, f = – 30 cm
Object distance, u = – 45 cm
Image distance, v =?
Height of image, hi = ?
We have,
\(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{-30}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{-45}\)
⇒ \(\frac{-1}{30}+\frac{1}{45}=\frac{1}{v}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{-3+2}{90}\)
⇒ υ = – 90 cm
Thus, image position is at 90 cm in the same side of the mirror where object is placed.
Also, we have magnification (m),
⇒ m = \(\frac{h_i}{h_o}=\frac{-v}{u}\)
⇒ \(\frac{h_i}{6}=\frac{-(-90)}{-45}\)
⇒ \(\frac{h_i}{6}=-2\)
⇒ hi = – 12 cm
Thus, height of image formed is 12 cm.
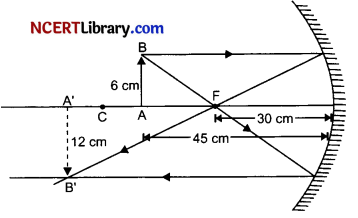
Image formed is real and inverted.
Question 35.
Answer the following questions:
(i) Explain the process of preparation of soap in laboratory.
(ii) Why is common salt (sodium chloride) added during the preparation of soap?
(iii) Why is soap not suitable for washing clothes when the water is hard?
(iv) What are detergents chemically? List merits and demerits of using detergents for cleansing.
Answer:
(i) Soap can be prepared in the laboratory as follows:
- Take about 20 ml of castor oil (cottonseed oil, linseed oil or soya bean oil) in a beaker.
- Add 30 ml of 20% sodium hydroxide solution to it.
- Heat the mixture with constant stirring till a paste of soap is formed.
- Then add 5 to 10 grams of common salt (sodium chloride).
- Stir the mixture well and allow it to cool. On cooling the solution, solid soap separates out.
- When the soap sets, it can be cut into pieces called ‘soap bars’.
(ii) Common salt is added to the mixture to make the soap come out of solution. Though most of the soap separates out on its own but some of it remains in solution. Common salt is added to precipitate out all the soap from the aqueous solution.
(iii) When soap is used for washing clothes with hard water, a large amount of soap in water reacts with the calcium and magnesium ions of hard water to form an insoluble precipitate called scum, before it can be used for the real purpose of washing.
(iv) Detergents are chemically sodium or potassium salts of sulphonic acid of benzene or alkene.
Merits of detergents for cleansing:
- Detergents can work well with both hard water and soft water.
- Detergents are more effective than soaps.
- Detergents contain synthetic chemical so they tend to provide more cleaning power.
- Detergents are made with chemical substances so they can be modified for specific purposes such as laundry detergents etc.
- Detergents are more easily soluble in water.
Demerits of detergents for cleansing:
- They are expensive.
- They can create water pollution.
- Detergents are formed with synthetic chemicals with few natural sources therefore they are usually non-biodegradable.
- They can cause soil pollution.
![]()
Question 36.
Describe the alimentary canal of human beings.
OR
Describe the internal structure of human heart.
Answer:
The alimentary canal of human beings start with mouth and ends at anus.
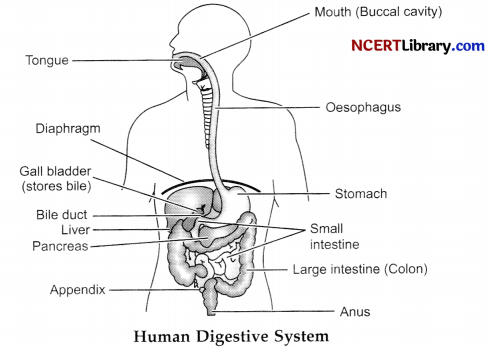
(1) Mouth: We ingest food through the mouth. Teeth are present in mouth which helps in chewing and mastication of food. Tongue helps in mixing food with saliva. Mouth has salivary glands which secrete saliva. Saliva contains the enzyme ptyalin or salivary amylase which help in breaking down complex food (starch) into simpler substances.
(2) Oesophagus: The food in form of bolus passes from mouth to stomach through oesophagus by peristalsis. It acts as a passage of food from mouth to the stomach.
(3) Stomach: Stomach is a J shaped bag like structure. Gastric glands present in stomach secrete gastric juice. Gastric juice contains HC1, mucus and enzyme pepsin. Pepsin is a protein digestive enzyme. Food in form of chime passes to small intestine.
(4) Small intestine: It is the longest part of the alimentary canal with many folds. It is a coiled like structure. It secretes intestinal juice which contains many enzymes like amylase, lipase, maltase, lactase etc. The complete digestion of food occurs in small intestine. It contains finger like projections called villi which absorbs the digested food. It receives pancreatic juice from pancreas and bile juice from liver for digestion of fats, carbohydrates and proteins.
(5) Large intestine: It receives the undigested and unabsorbed food from small intestine. Most of the water is absorbed here and the remaining is converted into a semi-solid waste material called faecus. The faecal matter is stored in rectum and is removed through anus from time to time.
OR
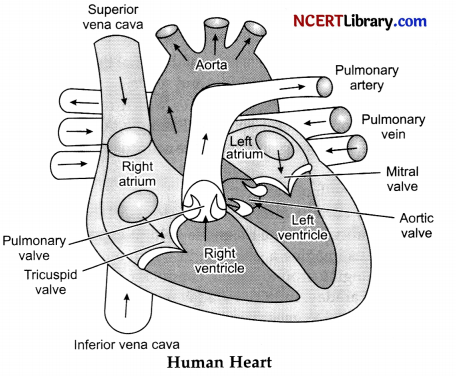
(1) Human heart is four chambered. It consists of two upper chambers called auricles or atrium and two lower chambers called ventricles.
(2) The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body through two venacava – superior and inferior venacava. The opening between right atrium and right ventricle is guarded by tricuspid valve which prevents back flow of the blood.
(3) Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to the lungs for oxygenation.
(4) Left atrium receives oxygenated blood from lungs through pulmonary veins. The opening of left atrium and left ventricle is guarded by bicuspid valve.
(5) From left ventricle, aorta arises which carries oxygenated blood to the whole parts of the body.
(6) Human heart is enclosed by pericardium membrane.
Section – E
Question number 37 to 39 are case – based/data -based questions with 2 to 3 short sub – parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Question 37.
The process of dissolving an acid or a base in water is a highly exothermic one. Care must be taken while mixing concentrated nitric acid or sulphuric acid with water. The acid must always be added slowly to water with constant stirring. If water is added to a concentrated acid, the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and cause bums. The glass container may also break due to excessive local heating. Look out for the warning sign on the can of concentrated sulphuric acid and on the bottle of sodium hydroxide pellets. Mixing an acid or base with water results in decrease in the concentration of ions (H3O+/OH–) per unit volume. Such a process is called dilution and the acid or the base is said to be diluted.
- Take 10 mL water in a beaker.
- Add a few drops of concentrated H2SO4 to it and swirl the beaker slowly.
- Touch the base of the beaker.
(a) What happens to concentration of ions when a solution is diluted?
(b) Is the process of mixing of acid or base in water exothermic or endothermic?
OR
(b) Are all bases soluble in water?
Answer:
(a) Mixing an acid or base with water results in decrease in the concentration of ions (H3O+/OH–) per unit volume.
(b) The process of dissolving an acid or a base in water is a highly exothermic in nature.
OR
(b) All bases do not dissolve in water. An alkali is a base that dissolves in water.
Question 38.
When growing plants detect light, a hormone called auxin, is synthesised at the shoot tip, which helps the cells to grow longer. When light is coming from one side of the plant, auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. This concentration of auxin stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light. Thus, the plant appears to bend towards light. Another example of plant hormones are gibberellins which, like auxins, help in the growth of the stem.
Cytokinins promote cell division, and it is natural then that they are present in greater concentration in areas of rapid cell division, such as in fruits and seeds. These are examples of plant hormones that help in promoting growth. But plants also need signals to stop growing. Abscisic acid is one example of a hormone which inhibits growth. Its effects include wilting of leaves. What are effects of adrenaline hormone on heart?
(a) What is the function of Cytokinins?
(b) What are plant growth inhibitors? Give an example.
(c) Where is auxin synthesised?
OR
(d) What is the function of gibberellins?
Answer:
(a) Cytokinins promote cell division, and it is natural then that they are present in greater concentration in areas of rapid cell division, such as in fruits and seeds.
(b) Plant growth inhibitors are regulating substances which retard such processes as root and stem elongation, seed germination, and bud opening. Example, Abscisic acid.
(c) Auxin is synthesised at the shoot tip and helps the cells to grow longer.
OR
(d) Gibberellins help in the growth of the stem.
Question 39.
We have studied that when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field such that the direction of current is perpendicular to the magnetic field, it experiences a force. This force causes the conductor to move. Now let us imagine a situation in which a conductor is moving inside a magnetic field or a magnetic field is changing around a fixed conductor. What will happen? This was first studied by English physicist Michael Faraday.
In 1831, Faraday made an important breakthrough by discovering how a moving magnet can be used to generate electric currents.
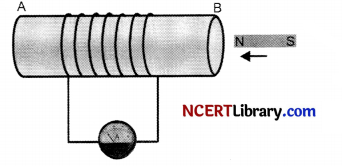
To observe this effect, let us perform the following activity.
1. Take a coil of wire AB having a large number of turns. Connect the ends of the coil to a galvanometer as shown. Take a strong bar magnet and move its north pole towards the end B of the coil. Do you find any change in the galvanometer needle?
2. There is a momentary deflection in the needle of the galvanometer, say to the right. This indicates the presence of a current in the coil AB. The deflection becomes zero, the moment the motion of the magnet stops.
3. Now withdraw the north pole of the magnet away from the coil. Now the galvanometer is deflected toward the left, showing that the current is now set up in the direction opposite to the first.
4. Place the magnet stationary at a point near to the coil, keeping its north pole towards the end B of the coil. We see that the galvanometer needle deflects toward the right when the coil is moved towards the north pole of the magnet. Similarly the needle moves toward left when the coil is moved away.
(a) What happens when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field such that the direction of current is perpendicular to the magnetic field?
(b) What is a galvanometer?
(c) When the coil is kept stationary with respect to the magnet, the deflection of the galvanometer drops to zero. What do you conclude from this activity?
OR
(c) Which important discovery was made by Faraday in 1831?
Answer:
(a) When a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field such that the direchon of current is perpendicular to the magnetic field, it experiences a force. This force causes the conductor to move.
(b) A galvanometer is an instrument that can detect the presence of a current in a circuit. The pointer remains at zero (the centre of the scale) for zero current flowing through it. It can deflect either to the left or to the right of the zero mark depending on the direction of current.
(c) This activity shows that the motion of a magnet with respect to the coil produces an induced potential difference which sets up an induced electric current in the circuit.
OR
(c) In 1831, Faraday made an important breakthrough by discovering how a moving magnet can be used to generate electric currents.