Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions Set 1 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 1 with Solutions
Time : 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 objective type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts.
Section – A
Select and write one most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1-20
Question 1.
The change in colour of the moist litmus paper in the given set up is due to [1]
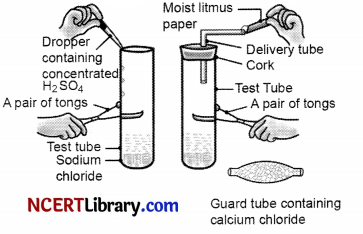
i. presence of acid
ii. presence of base
iii. presence of H+(aq) in the solution
iv. presence of Litmus which acts as an indicator
(a) i and ii
(b) Only ii
(c) Only iii
(d) Only iv.
Answer:
(c) Only iii
Explanation: The gas when passed through moist litmus paper will show colour change to red. It shows acidic properties because H+ ions are produced when HCl dissolves in water.
Question 2.
In the redox reaction [1]
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
(a) MnO2 is reduced to MnCl2 & HCl is oxidized to H2O
(b) MnO2 is reduced to MnCl2 & HCl is oxidized to Cl2
(c) MnO2 is oxidized to MnCl2 & HCl is reduced to Cl2
(d) MnO2 is oxidized to MnCl2 & HCl is reduced to H20
Answer:
(b) MnO2 is reduced to MnCl2 & HCl is oxidized to Cl2
Explanation: If a substance gains oxygen or loses hydrogen during a reaction, it is oxidised. If a substance loses oxygen or gains hydrogen during a reaction, it is reduced. Thus, MnCl2 is reduced in the reaction where as HCl is oxidized.
Question 3.
Which of the following is the correct observation of the reaction shown in the above set up? [1]
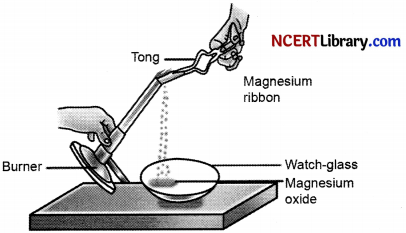
(a) Brown powder of Magnesium oxide is formed.
(b) Colourless gas which turns lime water milky is evolved.
(c) Magnesium ribbon bums with brilliant white light.
(d) Reddish brown gas with a smell of burning Sulphur has evolved.
Answer:
(c) Magnesium ribbon burns with brilliant white light.
Explanation: Magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling white flame and changes into a white powder. This powder is magnesium oxide. It is formed due to the reaction between magnesium and oxygen present in the air.
Question 4.
With the reference to four gases CO2, CO, Cl2 and O2, which one of the options in the table is correct? [1]

Answer:
(b) CO2, Cl2, CO2, CO
Explanation: When CO2 is dissolved in water it produces carbonic acid and solution turns blue litmus red. Litmus test of aqueous CO2 indicates acidic nature of carbon dioxide. Aerobic respiration occurs in mitochondria in presence of oxygen. The end products of this respiration are carbon dioxide, water and energy.
Chlorine is used in the treatment of drinking water to kill bacteria.
Incomplete combustion occurs when the supply of air or oxygen is poor. Water is still produced, but carbon monoxide and carbon are produced instead of carbon dioxide.
Question 5.
On placing a copper coin in a test tube containing green ferrous sulphate solution, it will be observed that the ferrous sulphate solution [1]
(a) turns blue, and a grey substance is deposited on the copper coin.
(b) turns colourless and a grey substance is deposited on the copper coin.
(c) turns colourless and a reddish-brown substance is deposited on the copper coin.
(d) remains green with no change in the copper coin.
Answer:
(d) remains green with no change in the copper coin.
Explanation:
Copper is less reactive metal. The standard reduction potential is positive. High standard reduction potential metals are unable to replace low standard reduction potential metals. Therefore, iron in ferrous sulphate solution cannot be replaced by copper. Therefore, nothing will change.
![]()
Question 6.
Anita added a drop each of diluted acetic acid and diluted hydrochloric acid on pH paper and compared the colors. Which of the following is the correct conclusion? [1]
(a) pH of acetic acid is more than that of hydrochloric acid.
(b) pH of acetic acid is less than that of hydrochloric acid.
(c) Acetic acid dissociates completely in aqueous solution.
(d) Acetic acid is a strong acid
Answer:
(a) pH of acetic acid is more than that of hydrochloric acid.
Explanation: The strength of acids and bases depends on the number of H+ ions and OH– ions produced, respectively. Hydrochloric acid and acetic acid of the same concentration, say one molar, produce different amounts of hydrogen ions. Acids that give rise to more H+ ions are said to be strong acids, and acids that give less H+ ions are said to be weak acids. Lower is the pH, greater is the hydrogen ion concentration and greater is the acid strength. HC1 is strong acid and is completely dissociated, Acetic acid is weak acid and is partially dissociated.
Question 7.
The formulae of four organic compounds are shown below. Choose the correct option
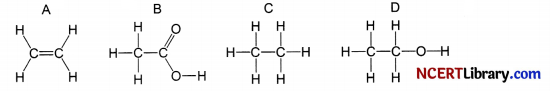
(a) A and B are unsaturated hydrocarbons
(b) C and D are saturated hydrocarbons
(c) Addition of hydrogen in presence of catalyst changes A to C
(d) Addition of potassium permanganate changes B to D
Answer:
(c) Addition of hydrogen in presence of catalyst changes A to C
Explanation: Ethene on catalytic hydrogenation in presence of Nickel catalyst gives ethane.

Question 8.
In the given transverse section of the leaf identify the layer of cells where maximum photosynthesis occurs. [1]
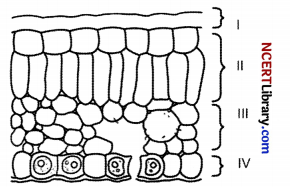
(a) I, II
(b) II, III
(c) III, IV
(d) I, IV
Answer:
(b) II, III
Explanation: The process of photosynthesis occurs in a middle layer called the mesophyll. The palisade mesophyll layer is where most of the photosynthesis occurs in the leaf. The palisade cells contain a lot of chloroplasts to help them perform this photosynthesis. The palisade cells are closely packed together to maximise the light absorption.
Question 9.
Observe the experimental setup shown below. Name the chemical indicated as ‘X’ that can absorb the gas which is evolved as a byproduct of respiration. [1]

Answer:
(b) KOH
Explanation: The potassium hydroxide is used to absorb carbon dioxide during the experiment.
Question 10.
If a tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf pea plant then, what percentage of FI and F2 generation respectively will be tall?
(a) 25%, 25%
(b) 50%, 50%
(c) 75%, 100%
(d) 100%, 75%
Answer:
(d) 100%, 75%
Explanation: In the F1 generation, only tall plants are formed (Tt). When F1 plant is subjected to self pollination, in the F2 generation, 3 tall plants and 1 dwarf plants are formed.
So in F1 generation 100% plants are tall, whereas in F2 75% plants are tall.
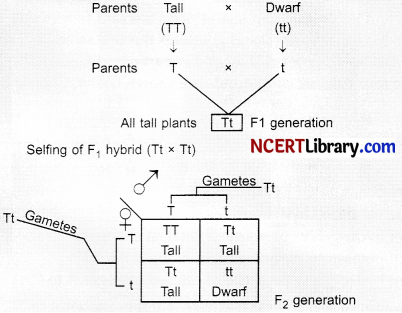
Question 11.
Observe the three figures given below. Which of the following depicts tropic movements appropriately?
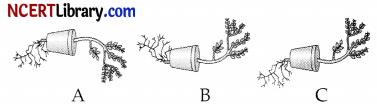
(a) B and C
(b) A and C
(c) B only
(d) C only
Answer:
(d) C only
Explanation: Plants show tropism in response to earth gravity. The roots of a plant always grow downwards while the shoots usually grow upwards and away from the earth. This upward and downward growth of shoots and roots, respectively, in response to the pull of earth or gravity is geotropism.
Question 12.
The diagram shown below depicts pollination. Choose the options that will show a maximum variation in the offspring. [1]
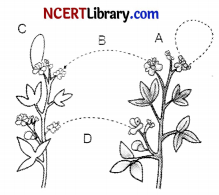
(a) A, B and C
(b) B and D
(c) B, C and D
(d) A and C
Answer:
(b) B and D
Explanation: When the pollen from one flower fertilises the ovum of another flower of a different plant or individual of the same species, it accounts for maximum genetic variation and recombination.
Question 13.
A complete circuit is left on for several minutes, causing the connecting copper wire to become hot. As the temperature of the wire increases, the electrical resistance of the wire
(a) decreases.
(b) remains the same.
(c) increases.
(d) increases for some time and then decreases.
Answer:
(c) increases.
Explanation: The resistance of all substances changes to some degree with temperature. In the case of pure metals, the resistance increases rapidly with a rise in temperature.
![]()
Question 14.
A copper wire is held between the poles of a magnet.
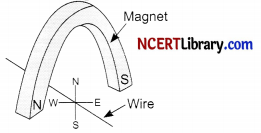
The current in the wire can be reversed. The pole of the magnet can also be changed over. In how many of the four directions shown can the force act on the wire?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2 (Either North or South)
Explanation: Out of the four directions shown, the force act on the wire in 2 directions. According to Fleming’s left hand rule, the force acting on the wire must be perpendicular to the current in the wire and the magnetic field.
So, the force on the wire due to the interaction of the magnetic fields of the bar magnet and current carrying wire can act only in upwards or downwards directions.
Question 15.
Plastic insulation surrounds a wire having diameter d and length 1 as shown above. A decrease in the resistance of the wire would be produced bv an increase in the [1]
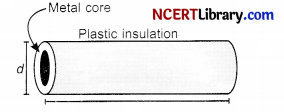
(a) length / of the wire
(b) diameter d of the wire
(c) temperature of the wire
(d) thickness of the plastic insulation
Answer:
(b) diameter d of the wire
Explanation: Resistance of tine conductor depends (i) on its length, (ii) on its area of cross-section, and (iii) on the nature of its material. The resistance of a uniform conductor is inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area. When cross-sectional area increases, resistance decreases.
R = ρ\(\frac { l }{ A }\)
Question 16.
Which of the following pattern correctlv describes the magnetic field around a long straight wire carrying current? [1]
(a) straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
(b) straight lines parallel to the wire.
(c) radial lines originating from the wire.
(d) concentric circles centred around the wire.
Answer:
(d) concentric circles centred around the wire.
Explanation: A metallic wire carrying an electric current has associated with it a magnetic field. The field lines about the wire consist of a series of concentric circles whose direction is given by the I right-hand rule.
Question number 17 to 20 are Assertion – Reasoning based questions.
These consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is False but R is true
Question 17.
Assertion: Silver bromide decomposition is used in black and white photography.
Reason: Light provides energy for this exothermic reaction. [1]
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false
Explanation: The chemical reactions of silver bromide is as follows:
2AgBr(s) → 2Ag(s) + Br2(g)
The areas of the photograph exposed to light (energy) becomes black due to the formation of Ag (Ag j is black in colour) and the parts which are not exposed to light are white in colour (AgBr is white in colour).
Light is absorbed in this reaction so it is an endothermic reaction. AgBr decompose into metal (Ag) and non- metal gas Br2.
Question 18.
Assertion: Height in pea plants is controlled by efficiency of enzymes and is thus genetically controlled.
Reason: Cellular DNA is the information source for making proteins in the cell. [1]
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: A series of bases make up DNA. This kind of sequence is also known as a “genome i sequence.” Transcription occurs on the genome sequence for each individual protein. During transcription, messenger RNA is created by duplicating the genome’s sequence (mRNA). The l ribosome converts this mRNA to an amino acid sequence. Then, a specific protein is created by altering this amino acid sequence.
Question 19.
Assertion: Amphibians can tolerate mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Reason: Amphibians are animals with two chambered heart [1]
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false
Explanation: Amphibians do not require much energy to perform their work and tolerate some I mixing of the oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood streams. In amphibians the body temperature 1 depends on the temperature in the environment. Amphibians have three-chambered hearts
Question 20.
Assertion: On freely suspending a current – carrying solenoid, it comes to rest in Geographical N-S direction.
Reason: One end of current carrying straight solenoid behaves as a North pole and the other end as a South pole, just like a bar magnet. [1]
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: A current carrying solenoid behaves like a bar magnet. When it is suspended freely, it interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field and aligns itself along the north-south direction.
The current-carrying linear electromagnet has one end that behaves as the North Pole and the ot end that behaves as the South Pole.
Section – B
Question number 21 to 26 are very short answer questions.
Question 21.
A clear solution of slaked lime is made by dissolving Ca(OH)2 in an excess of water. This solution is left exposed to air. The solution slowly goes milky as a faint white precipitate forms. Explain why a faint white precipitate forms, support your response with the help of a chemical equation.
OR
Keerti added dilute Hydrochloric acid to four metals and recorded her observations as shown in the table given below:
| Metal | Gas Evolved |
| Copper | Yes |
| Iron | Yes |
| Magnesium | No |
| Zinc | Yes |
Select the correct observation(s) and give chemical equation(s) of the reaction involved. [2]
Answer:
Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to produce slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) releasing a large amount of heat.
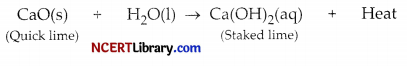
In this reaction, calcium oxide and water combine to form a single product, calcium hydroxide.
Calcium hydroxide reacts with Carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere to form Calcium carbonate which results in milkness and a white precipitate is formed.
![]()
OR
The reactions of metals with HCl are as follows:
1. When dilute HCl is added to iron fillings the reaction proceeds as:
2HCl + Fe → FeCl2 + H2(g)
In the reaction hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
2. Zinc reacts rapidly with hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas. It is a single displacement reaction where zinc metal displaces the hydrogen to form hydrogen gas and zinc chloride. The reaction is exothermic in nature and thus generates large amount of heat:
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
3. Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid according to the equation:
Mg(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Single displacement reaction occurs with generation of hydrogen gas.
4. Copper is below hydrogen in the reactivity series. This means that copper is less reactive than hydrogen and hence cannot displace it from the acidic solution, so, this is the reason copper does not react with hydrochloric acid.
Thus, the observations for Iron and Zinc are correct.
Question 22.
How is the mode of action in beating of the heart different from reflex actions? Give four examples. [2]
Answer:
The difference between beating of heart and reflex actions are:
| Beating of heart | Reflex actions |
| 1. Actions that are not under the control of our will are referred to as involuntary actions. The beating of the heart is an involuntary action | The instantaneous response to something is referred to as a reflex action. |
| 2. They can function without any form of stimuli. | They need a stimulus for it to act. |
| 3. The brain controls these actions. | The spinal cord controls these movements. |
| 4. They do not involve skeletal muscle. Other example of involuntary action is Salivating when food is put in the mouth. | They do involve skeletal muscle. Example of reflex action is immediate withdrawal of hands upon touching a hot cup of tea. Closing the eyes, when bright light is focused. |
![]()
Question 23.
Patients whose gallbladder are removed are recommended to eat less oily food. Why? [2]
Answer:
Gallbladder stores bile which helps in emulsification of lipids. The emulsification of fats will be hampered in the lack of stored bile, which will slow down fat digestion. Therefore the patients whose gallbladder are removed are recommended to eat less oily Food.
Question 24.
Name the substances other than water, that are reabsorbed during urine formation. What are the two parameters that decide the amount of water that is reabsorbed in the kidney? [2]
Answer:
Each kidney has large numbers of filtration units called nephrons packed close together. Some substances in the initial filtrate, such as glucose, amino acids, salts and a major amount of water, are selectively re-absorbed as the urine flows along the tube.
The amount of water re-absorbed depends on how much excess water is there in the body, and on how much of dissolved waste there is to be excreted out of the body.
Question 25.
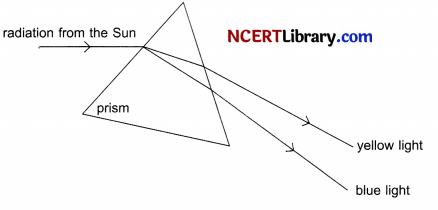
State the phenomena observed in the above diagram. Explain with reference to the diagram, which of the two lights mentioned above will have the higher wavelength? [2]
OR
How will you use two identical prisms so that a narrow beam of white lightincident on one prism emerges out of the second prism as white light? Draw the diagram.
Answer:
When white light is passed through a glass prism it splits into its spectrum of colours (in order violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red) and this process of white light splitting into its constituent colours is termed as dispersion of light.
All the constituent colours of a white light have same velocity in vacuum, but when it passes through a transparent medium like glass prism, their velocity changes. At the first face of the prism, different colours are deviated by different angles. Violet having the minimum speed gets deviated by maximum angle and red having the maximum speed gets deviated by minimum angle. On reaching the other face of the prism, these colours are refracted according to the laws of refraction. Thus, the dispersion of white light occurs on entering a prism.
Velocity is directly proportional to wavelength at a given constant frequency. So yellow will have greater wavelength than blue as the velocity of yellow light is greater than blue.
OR
When a narrow beam of white light is incident on one of two identical prisms arranged so that one is inverted relative to the other, the white light exits the second prism as white light. The two prisms’ angles of deflection are equal and opposing. The second prism mixes the spectrum along a single ray, and the colours once more combine to give white light as the emergent light, in contrast to the first prism, which separates the light into the seven colours due to varying degrees of deflection.
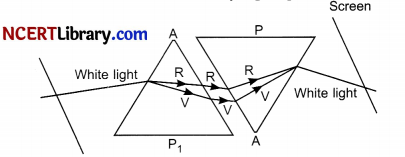
Question 26.
A lot of waste is generated in neighborhood. However, almost all of it is biodegradable. What impact will it have on the environment or human health? [2]
Answer:
Effects of biodegradable substances on the environment or human health are:
- Stagnant biodegradable wastes expels out foul smell which is very harmful to the environment.
- These wastes also emit some greenhouse gases such as methane, carbon dioxide etc. It also emits solids such as ammonia.
- It can be the breeding ground for germs that create unhygienic conditions.
Section – C
Question number 27 to 33 are short answer questions.
Question 27.
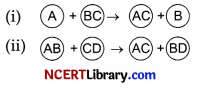
Identify the types of reaction mentioned above in (i) and (ii). Give one example for each type in the form of a balanced chemical equation. [3]
Answer:
(i) The reaction shown in (i) is displacement reaction.
A displacement reaction is the one wherein the atom or a set of atoms is displaced by another atom in a molecule A + B – C → A – C + B.
The above equation exists when A is more reactive than B.
For instance, when iron is added to a copper sulphate solution, it displaces the copper metal.
![]()
(ii) The reaction shown in (ii) is double displacement reaction.
In a double displacement reaction, atoms from two different compounds switch places. The reactants are two compounds and the products are two different compounds.
For example:
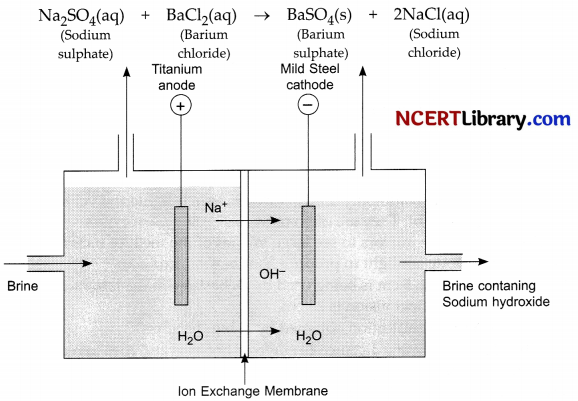
(a) Identify the gasses evolved at the anode and cathode in the above experimental set up.
(b) Name the process that occurs. Why is it called so?
(c) Illustrate the reaction of the process with the help of a chemical equation. [3]
Answer:
When electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride it decomposes to form sodium hydroxide. The process is called the chlor-alkali alkali process.
(a) Chlorine gas is given off at anode and hydrogen gas at cathode.
(b) The process is called the chlor-alkali process as the products obtained are alkali, chlorine gas and hydrogen gas
(c) An aqueous solution of sodium chloride is called brine.
2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) (Electric current) → 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) + H2(g).
Question 29.
The leaves of a plant were covered with aluminium foil, how would it affect the physiology of the plant?
OR
How is lymph an important fluid involved in transportation? If lymphatic vessels get blocked, how would it affect the human body? Elaborate. [3]
Answer:
When the leaves of a plant were covered with aluminium foil, it would affect the physiology of the plant as follows:
- When the leaves are covered with aluminum foil, the plants will not get sufficient carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and gaseous exchange will not take place.
- There will be no respiration due to lack of Oxygen.
- There will be no transpiration so there would be no upward movement of water or minerals from the soil as there will be no transpirational pull. Temperature regulation of leaf surface will be affected.
OR
Lymph or tissue fluid consists of plasma, proteins and blood cells that escape into intercellular spaces in the tissues through the pores present in the walls of capillaries. Lymph drains into lymphatic capillaries from the intercellular spaces, which join to form large lymph vessels that finally open into larger veins. Lymph carries digested and absorbed fat from intestine and drains excess fluid from extra cellular space back into the blood.
Blockage of lymphatic system will lead to water retention and poor fat absorption in the body.
![]()
Question 30.
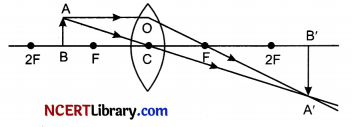
Rohit wants to have an erect image of an object using a converging mirror of focal length 40 cm. [3]
(a) Specify the range of distance where the object can be placed in front of the mirror. Justify.
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show image formation in this case.
(c) State one use of the mirror based on the above kind of image formation.
Answer:
(a) The object has to be placed at a distance between 0-40 cm. This is because image is virtual, erect and magnified when the object is placed between F and P.
(b)
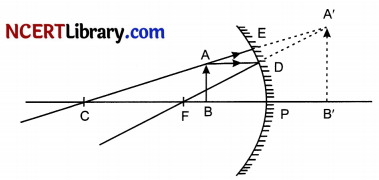
(c) Concave mirrors are commonly used in torches, search-lights and vehicles headlights to get powerful parallel beams of light. They are often used as shaving mirrors to see a larger image of the face. The dentists use concave mirrors to see large images of the teeth of patients. Large concave mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnaces.
Question 31.
(a) A lens of focal length 5 cm is being used by Debashree in the laboratory as a magnifying glass. Her least distance of distinct vision is 25 cm.
(i) What is the magnification obtained by using the glass?
(ii) She keeps a book at a distance 10 cm from her eyes and tries to read. She is unable to read. What is the reason for this? [3]
(b) Ravi kept a book at a distance of 10 cm from the eyes of his friend Hari. Hari is not able to read anything written in the book. Give reasons for this?
Answer:
Given, image distance = v = – 25 cm, focal length = f = 5 cm, magnification = m = ?
From lens formula, \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) ⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\)
\(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ -25 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) = \(\frac { -1-5 }{ 25 }\) = \(\frac { -6 }{ 25 }\)
Object distance = u = \(\frac { -25 }{6u }\) cm
We know that, m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac { -25×6 }{ -25 }\) = 6
(ii) Debashree is not able to read the book kept at 10 cm from her eyes, because the least distance of distinct vision is 25 cm.
(b) Hari is not able to read anything written in the book because the least distance of distinct vision is 25 cm.
Question 32.
A student fixes a white sheet of paper on a drawing board. He places a bar magnet in the centre and sprinkles some iron filings uniformly around the bar magnet. Then he taps gently and observes that iron filings arrange themselves in a certain pattern. [3]
(a) Why do iron filings arrange themselves in a particular pattern?
(b) Which physical quantity is indicated by the pattern of field lines around the bar magnet?
(c) State any two properties of magnetic field lines.
OR
A compass needle is placed near a current carrying wire. State your observations for the following cases and give reasons for the same in each case-
(a) Magnitude of electric current in wire is increased.
(b) The compass needle is displaced away from the wire.
Answer:
(a) When iron filings are placed in a magnetic field around a bar magnet, they behave like tiny magnets. The magnetic force experienced by these tiny magnets make them rotate and align themselves along the direction of field lines.
(b) The physical property indicated by this arrangement is the magnetic field produced by the bar magnet.
(c) (i) Inside the magnet, the direction of the magnetic field lines is from the South Pole to the North Pole.
(ii) Magnetic field lines never intersect with each other.
(iii) Magnetic field lines form a closed-loop.
(iv) Field lines have both direction and magnitude at any point on the field.
OR
(a) The magnetic field of the current-carrying wire is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, which causes the compass needle to deflect more.
(b) As the magnetic field is inversely proportional to the perpendicular distance from the wire, the deflection in the needle decreases.
Question 33.
Why is damage to the ozone layer a cause for concern? What are its causes and what steps are being taken to limit this damage? [3]
Answer:
The ozone layer is a gaseous blanket that surrounds the Earth. The ozone layer serves as a protective shield to block the ultra-violet rays of the sun which are harmful and can lead to skin cancer in humans, thus the damage to the ozone layer is concerning.
The primary cause of the ozone layer’s depletion is synthetic compounds like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which are used as refrigerants and in fire extinguishers.
Steps to be taken to limit this damage are:
1. A large number of developing and industrialised nations have endorsed and are adhering to UNEP’s (United Nations Environment Programme) directives to freeze or restrict the production and usage of CFCs at levels from 1986.
2. The release of CFCs into the atmosphere must be curtailed to limit the harm to the ozone layer. CFCs should be replaced with environmentally friendly replacements in refrigerants and fire extinguishers. In addition, the release of CFCs from industrial processes should be regulated.
Section – D
Question number 34 to 36 are long answer questions.
Question 34.
Shristi heated Ethanol with a compound A in presence of a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid and observed a sweet smelling compound B is formed. When B is treated with sodium hydroxide it gives back Ethanol and a compound C. [5]
(a) Identify A and C
(b) Give one use each of compounds A and B.
(c) Write the chemical reactions involved and name the reactions.
OR
(a) What is the role of concentrated Sulphuric acid when it is heated with Ethanol at 443 K. Give the reaction involved.
(b) Reshu by mistake forgot to label the two test tubes containing Ethanol and Ethanoic acid. Suggest an experiment to identify the substances correctly? Illustrate the reactions with the help of chemical equations
Answer:
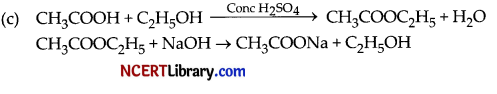
(a) When carboxylic acid and alcohol react, the product formed is known as an ester. The formation of an ester from the reaction of ethanoic acid with absolute ethanol in the presence of an acid as a catalyst is as follows :
![]()
Esters have a sweet fruity smell. They are mainly used for making perfumes and synthetic flavouring agents. The reaction of esters with alkalis gives carboxylic acid salt and alcohol. This reaction is used in the making of soaps and the process is called as saponification reaction.
CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH → C2H5OH + CH3COONa
A – Ethanoic acid or any other carboxylic acid,
C – Sodium salt of ethanoic acid, any other carboxylic acid or sodium ethanoate.
(b) Uses of A:
1. Ethanoic or acetic acid is used in making dyes, pigments, and paint and coating additives. It is used in printing on fabric. It is a component of wood glue and other sealants. Acetic acid is also used as a cleaning and degreasing solvent.
2. Acetic acid is utilised for more than just salad dressing. It is utilised as a natural preservative and antibacterial agent in the preservation of food, not only in vegetable pickling but also as an active component of edible films and in hurdle preservation technology.
Use of B – It is used for making perfumes and flavoring agent.
OR
(a) The balanced chemical equation for the reaction can be written as:
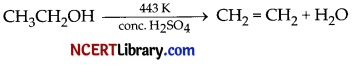
Therefore, concentrated sulphuric acid removes water from ethanol, thereby, acting as a dehydrating agent.
(b) By reaction with sodium carbonate or bicarbonate with the samples, ethanol will not react whereas ethanoic acid gives brisk effervescence.
Carbon dioxide, salt, and water are produced when ethanoic acid reacts with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates. Sodium acetate is usually produced as a salt when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate as shown in the reaction below:
CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
Question 35.
(a) Why is it not possible to reconstruct the whole organism from a fragment in complex multicellular organisms? [5]
(b) Sexual maturation of reproductive tissues and organs are necessary link for reproduction. Elucidate.
OR
(a) How are variations useful for species if there is drastic alteration in the niches?
(b) Explain how the uterus and placenta provide necessary conditions for proper growth and development of the embryo after implantation?
Answer:
(a) Since complex multicellular organisms have organ system level organisation, it is impossible to rebuild the entire organism from a piece. Their body’s organ systems all function as one integrated system. Many multicellular organisms are more than just a haphazard assembly of cells.
Organs are formed by the organisation of specialised cells as tissues and tissues as organs, which must then be situated in specific locations throughout the body. Cell-by-cell division is therefore impractical. Thus it is not possible to reconstruct the whole organism from a fragment in complex.
(b) Due to the requirement of specialised cells called germ-cells to participate in sexual reproduction, sexual maturation of reproductive organs is a crucial link for reproduction. The size of each organism’s body must increase until it reaches adulthood, at which point the pace of overall body growth starts to halt and reproductive tissues start to mature. The body goes through a whole new set of changes, such as altered body proportions and the emergence of new characteristics.
This stage of adolescence is known as puberty. Boys and girls experience various transformations at the same time. Breast size starts to grow in girls, and the nipples at the points of the breasts start to colour. Also, girls begin to menstruate at around this time. Boys begin to have new thick hair growth on the face and their voice begin to crack.
OR
(a) Variation is useful for the survival of species over time. If a population of reproducing organisms were suited to a particular niche and if the niche were drastically altered, the population could be wiped out. However, if some variations were to be present in a few individuals in these populations, there may be some chance of their survival.
Example: If the temperature of water increases by global warming, most bacteria would die. But a population of heat resistant bacteria could survive here. These few variants would be resistant to the heat and would survive and grow further.
(b) The placenta is an organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy.
- The uterine lining thickens and becomes well-supplied with blood to support the developing embryo.
- The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of placenta. It is embedded in the uterine wall.
- It contains villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue. On the mother’s side are blood spaces, which surround the villi.
- This offers a substantial surface area for the exchange of glucose and oxygen from mother to embryo.
- Additionally, the growing embryo will produce substances that should be eliminated by being transferred into the placenta through the mother’s blood.
- As a result of the muscles in the womb contracting rhythmically, the infant is bom.
Question 36.
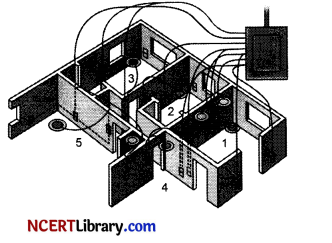
The diagram above is a schematic diagram of a household circuit. The house shown in the above diagram has 5 usable spaces where electrical connections are made. For this house, the mains have a voltage of 220 V and the net current coming from the mains is 22A. [5]
(a) What is the mode of connection to all the spaces in the house from the mains?
(b) The spaces 5 and 4 have the same resistance and spaces 3 and 2 have respective resistances of 20 G and 30 G. Space 1 has a resistance double that of space 5. What is the net resistance for space 5.
(c) What is the current in space 3?
(d) What should be placed between the main connection and the rest of the house’s electrical appliances to save them from accidental high electric current?
Answer:
(a) All spaces are connected in parallel.
A parallel circuit divides the current through the electrical gadgets. The total resistance in a parallel circuit is decreased. This is helpful particularly when each gadget has different resistance and requires different current to operate properly.
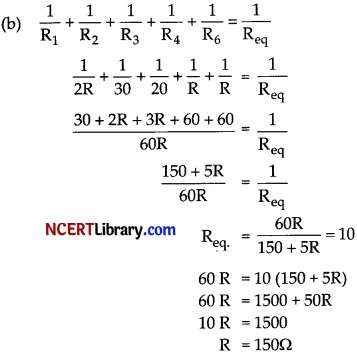
(b) Let Resistance of Space 5 and 4 be R Ω respectively
Resistance of Space 1 = 2 R Ω
Resistance of Space 2 = 30 Ω
Resistance of Space 3 = 20 Ω
Current = 22 A
V = 220 V
Total Resistance = V/I
(c) For space 3
V = IR
V = 220 V
R = 20 Ω
So I = 220/20 = 11 A
(d) Fuse wire is used in electric circuits to prevent the excess current flowing into the circuit and therefore preventing the appliances from getting damaged.
Section – E
Question number 37 to 39 are case – based/data -based questions with 2 to 3 short sub – parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Question 37.
Two students decided to investigate the effect of water and air on iron object under identical experimental conditions. They measured the mass of each object before placing it partially immersed in 10 ml of water. After a few days, the object were removed, dried and their masses were measured. The table shows their results. [4]
| Student | Object | Mass of Object before Rusting in g | Mass of the coated object in g |
| A | Nail | 3.0 | 3.15 |
| B | Thin plate | 6.3 | 6.33 |
(a) What might be the reason for the varied observations of the two students?
(b) In another set up the students coated iron nails with zinc metal and noted that, iron nails coated with zinc prevents rusting. They also observed that zinc initially acts as a physical barrier, but an extra advantage of using zinc is that it continues to prevent rusting even if the layer of zinc is damaged. Name this process of rust prevention and give any two other methods to prevent rusting.
OR
(b) In which of the following applications of Iron, rusting will occur most? Support your answer with valid reason.
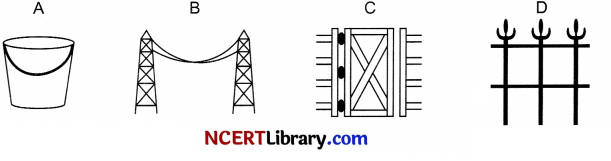
A – Iron Bucket electroplated with Zinc
B – Electricity cables having iron wires covered with aluminium
C – Iron hinges on a gate
D – Painted iron fence
Answer:
(a) Rusting occurs in both A and B so there is an increase in mass. As the surface area of B (thin plate) is more compared to nail, extent of rusting is more.
(b) Galvanization is a process used for the protection of steel or iron from rusting. In this process, a protective zinc coating is applied on the iron surface. The most common method of galvanizing is to dip the hot metal in a bath of molten zinc. Zinc is more reactive metal than iron, hence it reacts with oxygen to form a protective oxide layer, which prevents inner iron from getting in contact with oxygen.
OR
(b) C – Iron hinges on a gate
The exposure of iron (or an alloy of iron) to oxygen in the presence of moisture leads to the formation of rust.
![]()
Question 38.
Pooja has green eyes while her parents and brother have black eyes. Pooja’s husband Ravi has black eyes while his mother has green eyes and father has black eyes. [4]
(a) On the basis of the above given information, is the green eye colour a dominant or recessive trait? Justify your answer.
(b) What is the possible genetic makeup of Pooja’s brother’s eye colour?
(c) What is the probability that the offspring of Pooja and Ravi will have green eyes? Also, show the inheritance of eye colour in the offspring with the help of a suitable cross.
OR
(d) 50% of the offspring of Pooja’s brother are green eyed. With help of cross show how this is possible.
Answer:
(a) Yes, green eye colour is recessive as it will express only in homozygous condition.
(b) The possible genetic makeup of Pooja’s brother’s eye colour can be: BB, Bb
(c) bb*Bb
| B | b | |
| b | Bb | bb |
| b | Bb | bb |
50% of the offsprings can have green eye colour.
OR
(d) Brother is heterozygous (Bb) and wife is green (bb)
Wife bb*Bb brother
| B | b | |
| b | Bb | bb |
| b | Bb | bb |
50% of the offsprings can have green eye colour as per the cross shown.
Question 39.
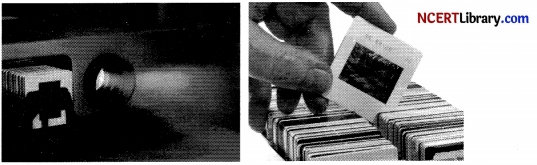
The above images are that of a specialized slide projector. Slides are small transparencies mounted in sturdy frames ideally suited to magnification and projection, since they have a very high resolution and a high image quality. There is a tray where the slides are to be put into a particular orientation so that the viewers can see the enlarged erect images of the transparent slides. This means that the slides will have to be inserted upside down in the projector tray.
To show her students the images of insects that she investigated in the lab, Mrs. Iyer brought a slide projector. Her slide projector produced a 500 times enlarged and inverted image of a slide on a screen 10 m away. [4]
(a) Based on the text and data given in the above paragraph, what kind of lens must the slide projector have?
(b) If v is the symbol used for image distance and u for object distance then with one reason state what will be the sign for v/u in the given case?
(c) A slide projector has a convex lens with a focal length of 20 cm. The slide is placed upside down 21 cm from the lens. How far away should the screen be placed from the slide projector’s lens so that the slide is in focus?
OR
(d) When a slide is placed 15 cm behind the lens in the projector, an image is formed 3 m in front of the lens. If the focal length of the lens is 14 cm, draw a ray diagram to show image formation, (not to scale)
Answer:
(a) Convex Lens is used in projector to get magnified image. Convex lens is placed in front of object such that object is between F and 2F. We get inverted image on the other side of lens at the distance beyond 2F.
(b) The image formed will be real and inverted so negative sign will be used.
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\)
\(\frac { 1 }{ 20 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ -21 }\)
\(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 20 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 21 }\)
= \(\frac { (21-20 }{ 420 }\)
= \(\frac { 1 }{420 }\)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 420 }\)
v = 420 cm