Practicing the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Maths Basic Set 7 allows you to get rid of exam fear and be confident to appear for the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Maths Basic Set 7 with Solutions
Time Allowed : 3 hours
Maximum Marks : 80
General Instructions:
- This Question Paper has 5 Sections A, B, C, D, and E.
- Section A has 20 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B has 5 Short Answer-I (SA-I) type questions carrying 2 marks each.
- Section C has 6 Short Answer-Il (SA-II) type questions carrying 3 marks each.
- Section D has 4 Long Answer (LA) type questions carrying 5 marks each.
- Section E has 3 Case Based integrated units of assessment (4 marks each) with sub-parts of the values of 1,1 and 2 marks each respectively.
- All Questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice in 2 Qs of 2 marks, 2 Qs of 3 marks and 2 Questions of 5 marks has been provided. An internal choice has been provided in the 2 marks questions of Section E.
- Draw neat figures wherever required. Take n = \(\frac{22}{7}\) wherever required if not stated.
Section – A
(Section A consists of 20 Questions of 1 marks each.)
Question 1.
If an event that cannot occur, then its probability is : [1]
(A) 1
(B) \(\frac{3}{4}\)
(C) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(D) 0
Answer:
(D) 0
Explanation:
An event that cannot occur has 0 probability, such an event is called impossible event.
![]()
Question 2.
Consider the following data
| Class | 65-85 | 85-105 | 105-125 | 125-145 | 145-165 | 165-185 | 185-205 |
| Frequency | 4 | 5 | 13 | 20 | 14 | 7 | 4 |
The difference of the upper limit of the median class and the lower limit of the modal class is : [1]
(A) 0
(B) 19
(C) 20
(D) 38
Answer:
(C) 20
Explanation:
| Class | Frequency | Cumulative frequency |
| 65-85 | 4 | 4 |
| 85-105 | 5 | 9 |
| 105-125 | 13 | 22 |
| 125-145 | 20 | 42 |
| 145-165 | 14 | 56 |
| 165-185 | 7 | 63 |
| 185-205 | 4 | 67 |
Hence, n = 67 (odd)
So, Median = \(\frac{67 + 1}{2}\) = 34
34 lies in class 125-145.
So, median class is 125-145 and upper limit is 145.
Now, the maximum frequency is 20 and it lies in class 125-145 (modal class).
Lower limit of modal class = 125
Hence, the required difference 145 – 125 = 20
Question 3.
It is proposed to build a single circular park equal in area to the sum of areas of two circular parks of diameters 16 m and 12 m in a locality. The radius of the new park would be : [1]
(A) 10 m
(B) 15 m
(C) 20 m
(D) 24 m
Answer:
(A) 10 m
Explanation :
Area of first circular park whose diameter is 16 m,
= π(\(\frac{16}{2}\))²
= π(8)² = 6471 m²
Area of second circular park whose diameter is 12 m,
= π(\(\frac{12}{2}\))²
= π(6)²
= 36π m²
According to question,
Area of single circular park = Area of first circular park + Area of second circular park
πr² = 64π + 36π
πr² = 100π
r = 10 m
Question 4.
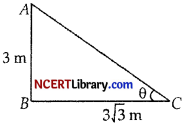
A pole 3 m high casts a shadow 3\(\sqrt{3}\) m long on the ground, then the Sun’s elevation is : [1]
(A) 60°
(B) 45°
(C) 30°
(D) 90°
Answer:
(C) 30°
Explanation :
In AABC, ∠B = 90°
tan θ = \(\frac{3}{3 \sqrt{3}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) = tan 30°
⇒ θ = 30°
Question 5.
What is the Greatest Common Divisor of 5 and 15? [1]
(A) 10
(B) 20
(C) 5
(D) 1
Answer:
(C) 5
Explanation:
We know that Greatest common divisor = HCF
So, HCF(5, 15) = GCD(5, 15) = 5
![]()
Question 6.
The product of a non-∠ero rational and an irrational number is : [1]
(A) always irrational
(B) always rational
(C) rational or irrational
(D) one
Answer:
(A) always irrational
Explanation:
The product of a non-zero rational and an irrational number is always an irrational number
Question 7.
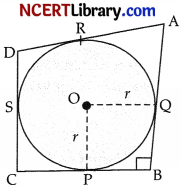
In figure, a circle with centre O is inscribed in a quadrilateral ABCD such that, it touches the sides BC, AB, AD and CD at points P, Q, R and S respectively. If AB = 29 cm, AD = 23 cm, ∠B = 90° and DS = 5 cm, then the radius of the circle (in cm.) is : [1]
(A) 11
(B) 18
(C) 6
(D) 15
Answer:
(A) 11
Explanation :
Since DS = DR = 5 cm
(tangents of a circle from same external point)
Now, AR = AD – DR
= 25 – 5 = 18 cm
Similarly, AR = AQ = 18 cm (tangents)
Now, QB = AB -AQ
= 29 -18 = 11 cm
Similarly, QB = PB = 11 cm
Given, ∠B = 90°
So, ∠POQ = 90°
Hence, OQBP is square
∵ QB = 11 cm
∴ Side of square = 11 cm
So the radius =11 cm
Question 8.
If the common difference of an A.E, is 5, then what is a18 – a13? [1]
(A) 5
(B) 20
(C) 25
(D) 30
Answer:
(C) 25
Explanation :
In the given A.E, d = 5
Thus, a18 – a13 = a +17d – a – 12d = 5d = 25
Question 9.
If the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial ax2 + bx + c, a ^ 0 are equal, then : [1]
(A) c and a have opposite sign
(B) c and b have opposite sign
(C) c and a have the same sign
(D) c and b have the same sign
Answer:
(C) c and a have the same sign
Explanation:
or equal roots b² – 4ac = 0 or b2 = 4ac.
b² is always positive, so 4ac must be positive, i.e., product of a and c must be positive, i.e., a and c must have same sign either positive or negative.
Question 10.
The sum of square of two consecutive natural numbers is 13, then the numbers are : [1]
(A) 1,2
(B) 1, 3
(C) 2, 3
(D) 2, 4
Answer:
(C) 2, 3
Explanation:
Let the two consecutive natural numbers be x and (x + 1).
Given that,
x² + (x + 1)² = 13
On simplifying, we get
⇒ 2x² + 2x-12 = 0
or x² + x – 6 = 0
⇒ x² + 3x-2x-6 = 0
⇒ x(x + 3) – 2(x + 3) = 0
⇒ (x + 3)(x – 2) = 0
⇒ x = 2, -3
As – 3 is not a natural number so rejecting it
We get the required consecutive natural numbers as 2,3.
![]()
Question 11 .
In the following figure, Q is a point on PR and S is a point on TR. QS is drawn and ∠RPT = ∠RQS. [1]
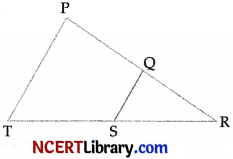
Which of these criteria can be used to prove that ARSQ is similar to ARTP ?
(A) AAA similarity criterion
(B) SAS similarity criterion
(C) SSS similarity criterion
(D) RHS similarity criterion
Answer:
(A) AAA similarity criterion
Explanation:
In ARQS and ∠RPT,
∠RQS = ∠RPT (Given)
∠R = ∠R (common)
So, by using the theorem,
If the corresponding angles are equal, then their corresponding sides are proportional and the triangles are similar.
Question 12 .
If the difference of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 20°, then the angles are : [1]
(A) 100° and 80°
(B) 150° and 30°
(C) 120° and 60°
(D) 160° and 20°
Answer:
(A) 100° and 80°
Explanation:
We know that,
Sum of opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral = 180°
Given, difference = 20°
So, x + y =180° and x – y = 20°
On solving, we get, x = 100°
and y = 80°
Question 13.
The minute hand of a clock is 84 cm long. The distance covered by the tip of minute hand from 10:10 am to 10:25 am is : [1]
(A) 44 cm
(B) 88 cm
(C) 132 cm
(D) 176 cm
Answer:
(C) 132 cm
Explanation:
Length of minute hand = Radius of the quadrant/sector so formed = 84 cm.
In 1 minute, minute hand makes an angle of 6°.
Therefore, in 15 minutes it makes an angle of 15 × 6° = 90°
Distance covered by the tip of the minute hand = Length of arc
= \(\frac{θ}{360°}\) × 2 × 2πr
= \(\frac{90°}{360°}\) × 2 × 2 × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 84
= 132 cm
Question 14 .
If two solid hemispheres of same base radius V are joined together along their bases, then curved surface area of this new solid is : [1]
(A) 4πr²
(B) 6πr²
(C) 3πr²
(D) 8πr²
Answer:
(A) 4πr²
Explanation:
When two hemispheres of equal radii are joined base to base, new solid becomes sphere and curved surface area of sphere is 4πr²
![]()
Question 15.
If one root of 9x² + 16x + k = 0 is the reciprocal of the other root, then the value of k is: [1]
(A) 9
(B) 16
(C) 7
(D) 5
Answer:
(A) 9
Explanation :
Let α and \(\frac{1}{α}\) be the roots of the a
given quadratic polynomial.
α\(\frac{1}{α}\) = \(\frac{k}{9}\) = 1
⇒ k = 9
Question 16.
The angle of depression of a car parked on the road from the top of 150 m high tower is 30°. The distance of the car from the tower (in metres) is : [1]
(A) 50\(\sqrt{3}\)
(B) 150\(\sqrt{3}\)
(C) 150\(\sqrt{3}\)
(D) 75
Answer:
(B) 150\(\sqrt{3}\)
Explanation:
In ∆ABC, ∠B=90°
tan θ = \(\frac{CB}{AB}\)
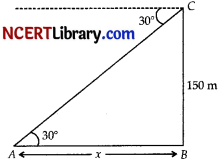
tan 30° = \(\frac{150}{x}\)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{150}{x}\)
x = 150\(\sqrt{3}\)
Question 17.
The zeroes of quadratic polynomial x² + 99x + 127 are :
(A) both negative
(B) both positive
(C) one positive and one negative
(D) reciprocal of each other
Answer:
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: p(x) = x² + 99x + 127 b
zeroes = \(\frac{c}{a}\) = 127
Since, product of zeroes is positive and sum is negative, it is possible only when both the zeroes are negative.
Therefore, both the zeroes are negative.
Question 18.
The value of x for which 2x, (x + 10) and (3x + 2) are the three consecutive terms of an A.E, is [1]
(A) 6
(B) -6
(C) 18
(D) -18
Answer:
(A) 6
Option (A) is correct.
Explanation:
2x, (x + 10) and (3x + 2) are in A.P
∴ (x + 10) – 2x = (3x + 2) – (x + 10)
⇒ -x + 10 = 2x – 8
⇒ -x – 2x = – 8 -10
⇒ -3x = -18
⇒ x = 6
Directions for question 19 and 20: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Choose the correct option.
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is NOT the correct explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false and (R) is true.
Question 19.
Assertion (A): AABC with vertices A(-2,0), B(2,0) and C(0,2) is similar to ADEF with vertices D(-4, 0), E(4,0) and F(0,4).
Reason (R): A circle has its centre at the origin and a point P(5,0) lies on it. The point Q(6,8) lies outside the circle. [1]
Answer:
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is NOT the correct explanation of (A).
Explanation:
In case of assertion:
By using Distance Formula,
Distance between A (-2,0) and B (2,0)

Here, we see that sides of ∆ABC and ∆FDE are proportional.
Therefore, by SSS similarity rule, both the triangles are similar.
∴ Assertion is correct.
In case of reason:
Point Q (6,8) will lie outside the circle if its distance from the centre of circle is greater than the radius of the circle.
Distance between centre O (0,0) and P (5, 0),
OP = \(\sqrt{(5-0)^2+(0-0)^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{5^2+0^2}\)
= 5
As, point P lies at the circle, therefore, OP = Radius of circle.
Distance between centre O (0,0) and Q (6,8),
OQ = \(\sqrt{(6-0)^2+(6-0)^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{6^2+8^2}\)
= \(\sqrt{36+64}\)
= \(\sqrt{100}\)
= 10
As OQ > OR therefore, point Q (6, 8) lies outside of the circle.
∴ Reason is correct.
Hence, both assertion and reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion.
Question 20.
Assertion (A): For all real values of c, the pair of equations x-2y = 8 and 5x -10y = c have a unique solution.
Reason (R): Two lines a\x + by + q = 0 and a2x + by + c2 = 0 are given to be parallel, then [1]
Answer:
(D) (A) is false and (R) is true.
Explanation:
In case of assertion:
x – 2y = 8 …(i)
5x – 10 = c …(ii)
∴ \(\frac{a_1}{a_2}=\frac{1}{5}, \frac{b_1}{b_2}=\frac{-2}{-10}=\frac{1}{5} \text { and } \frac{c_1}{c_2}=\frac{-8}{-c}=\frac{8}{c}\)
As \(\frac{a_1}{a_2}=\frac{b_1}{b_2}\), so system of linear equations can never have unique solution.
∴ Assertion is incorrect.
In case of reason:
We know that if two lines a1x + b1y + c1 = 0 and a2x + b1y + c2 = 0 are parallel, then
\(\frac{a_1}{a_2}=\frac{b_1}{b_2} \neq \frac{c_1}{c_2}\)
∴ Reason is correct
Hence, assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
![]()
Section – B
Section B consists of 5 Questions of 2 marks each.
Question 21.
Find a rational number between \(\sqrt{2}\) and \(\sqrt{3}\) .
Answer:
Since,
\(\sqrt{2}\) = 1.414
and \(\sqrt{3}\) = 1.732
Now, we can write ‘ri rational number between those e.g., just greater than 1.414 and less than 1.732 and it should be terminating or not e.g, 1.415659,1.416893,1.715644, ……… .
Therefore, one rational number between \(\sqrt{2}\) and \(\sqrt{3}\) is 1.416893.
Question 22.
In the adjoining figure, if AABC is circumscribing a circle, then find the length of BC.
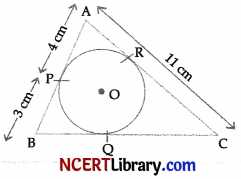
Answer:
∵ AP and AR are tangents to the circle from external point A.
∴ AP = AR = 4 cm
Similarly, PB and BQ are tangents.
∴ BP = BQ = 3 cm
Now, CR = AC – AR = 11 – 4 = 7 cm
Similarly, CR and CQ are tangents.
∴ CR = CQ = 7cm
Now, BC = BQ + CQ = 3 + 7 = 10 cm
Hence, the length of BC is 10 cm.
Question 23.
The points A( 1, – 2), B(2,3), C(k, 2) and D(- 4, – 3) are the vertices of a parallelogram. Find the value of k. 2
Answer:
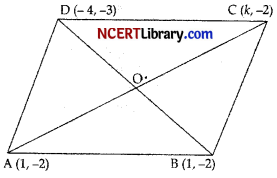
Diagonals of parallelogram bisect each other
⇒ midpoint of AC = midpoint of BD
⇒ \(\left(\frac{1+k}{2}, \frac{-2+2}{2}\right)=\left(\frac{-4+2}{2}, \frac{-3+3}{2}\right)\)
⇒ \(\frac{1+k}{2}=\frac{-2}{2}\)
⇒ k = -3
Question 24.
For what value of T, the system of equations kx + 3y = 1,12x + ky = 2 have no solution.
OR
Find the value of k for which the roots of the quadratic equation 2x² + kx + 8 = 0 will have the equal roots ?
Answer:
The given equations can be written as
kx + 3y – 1 = 0 and 12r + ky – 2 = 0
Here, a, = k, bj = 3, Cj = -1
and a2 = 12, b2 = k, c2 = – 2
The equation for no solution
\(\frac{a_1}{a_2}=\frac{b_1}{b_2} \neq \frac{c_1}{c_2}\)
\(\frac{k}{12}=\frac{3}{k} \neq \frac{-1}{-2}\)
\(\frac{k}{12}=\frac{3}{k}\)
\(\frac{3}{k} \neq \frac{1}{2}\)
or, k² = 36
and k ≠ 6
or, k = ±6
Hence, k = -6
OR
For equal roots,
D = 0
∴ b² – 4ac = 0
⇒ k² = 4 × 2 × 8
k² = 64
k² = 64
k = ± \(\sqrt{64}\)
∴ k = ± 8
![]()
Question 25.
Find the value of:
sin 30°. cos 60° + cos 30°. sin 60°
Is sin 90° is equal to cos 90° ?
OR
Prove that: \(\frac{\left(\sin ^4 \theta+\cos ^4 \theta\right)}{1-2 \sin ^2 \theta \cos ^2 \theta}=1\)
Answer:
sin 30°. cos 60° + cos 30°. sin 60°
= \(\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{1}{2}+\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \times \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
= \(\frac{1}{4}+\frac{3}{4}\)
= \(\frac{4}{4}\) = 1
Since, sin 90° = 1 but not equal to cos 90° as cos 90° = 0.
OR
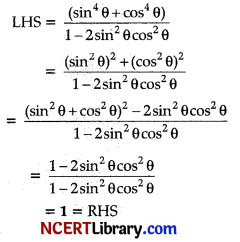
Hence Proved.
Section – C
Section C consists of 6 Questions of 3 marks each.
Question 26.
Explain whether 3 × 12 × 101 + 4 is a prime number or a composite number. [3]
Answer:
3 × 12 × 101 + 4 = 4(3 × 3 × 101 + 1)
= 4(909 + 1)
= 4(910)
= 2 × 2 × 2 × 5 × 7 × 13 = a composite number
[∵ Product of more than two prime factors]
Question 27.
Find the ratio in which y-axis divides the line segment joining the points A(5, -6) and B(-1, -4). Also find the coordinates of the point of division. [3]
Answer:
Let the point on y-axis be (0, y) and AP: PB = k: 1.
Therefore \(\frac{5-k}{k+1}\) = 0 gives k = 5
Hence, required ratio is 5 :1
y = \(\frac{-4(5)-6}{6}=\frac{-13}{6}\)
Hence, point on y- axis is (0, \(\frac{-13}{6}\))
Question 28.
Find the roots of the quadratic equation :
a²b²x² + b²x – a²x – 1 = 0 [3]
OR
Find the values of a and b, if they are the zeroes of polynomial x² + ax + b.
Answer:
Given, a²b²x² + b²x – a²x – 1 = 0
⇒ b²x(a²x + 1) – 1(a² + 1) = 0
⇒ (b²x – 1)(a²x + 1) = 0
x = \(\frac{1}{b²}\) or x = –\(\frac{1}{a²}\)
Hence, roots = \(\frac{1}{b²}\) or –\(\frac{1}{a²}\)
OR
Sum of zeroes = \(\frac{\text { Coefficient of x }}{\text { Coefficient of x² }}\)
∴ a + b = -a
⇒ 2a + b = 0
and product of zeroes = \(\frac{\text { Constant term }}{\text { Coefficient of x² }}\)
∴ ab = b
or, a = 1
Substituting a = 1 in 2a + b =0, we get b = – 2
Question 29.
ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC which is circumscribed about a circle as shown in the figure. Show that BC is bisected at the point of contact. [3]
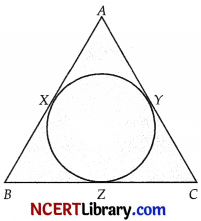
Answer:
AX = AY …(i)
BX = BZ …(ii)
CZ = CY …(iii)
(Tangents from an external point to a circle are equal)
AB = AC, (Given)
or, AX + XB = AY + YC
or, XB = YC [From eq (i)]
or, BZ = CZ
[From eqs. (ii) and (iii)]
∴ Z is the mid-point of BC and Z is the point of contact.
Hence, BC is bisected at the point of contact.
![]()
Question 30.
A man on the top of a vertical observation tower observes a car moving at uniform speed coming directly towards it. If it takes 12 minutes for the angle of depression to change from 30° to 45°, how long will the car take to reach I the observation tower from this point ? [3]
OR
Two tangents PA and PB are drawn from an external point P to a circle with centre O, such that ∠APB = x and ∠AOB = y. Prove that opposite angles are supplementary.
Answer:
Let the speed of car by x m/min.
In ∆ABC,
\(\frac{h}{y}\) = tan 45°
⇒ h = y
In ∆ABD,
\(\frac{h}{y+12}\) = tan 30°
⇒ h\(\sqrt{3}\) = y + 12
y \(\sqrt{3}\) – y = 12x
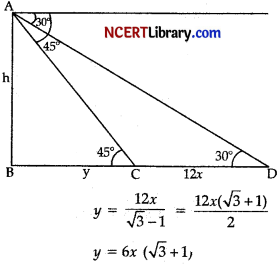
Hence, time taken from C to B = 6 (\(\sqrt{3}\) +1) minutes
Detailed Answer:
Let AB be the tower of height h and x be the distance between two cars
∠AQB = 45°
Now, in ∆ABQ,
tan 45° = \(\frac{A B}{B Q}\)
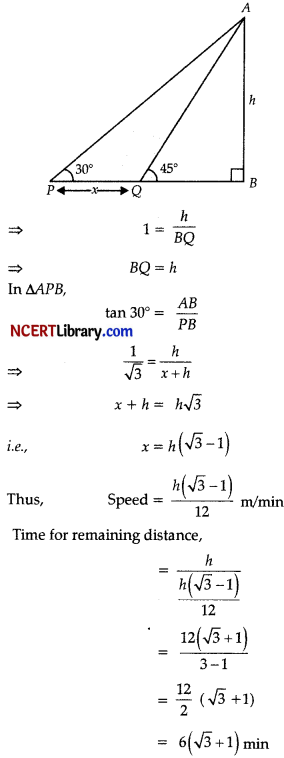
OR
Since, AOBP is a quadrilateral.
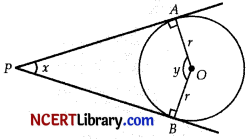
So, ∠A + ∠B + x + y = 360°
90° + 90° + x + y = 360°
180° + r + y = 360°
x + y = 180°
Hence, opposite angle are supplementary
Question 31 .
An electric pole is 12 m high. A steel wire tied to top of the pole is affixed at a point on the ground to keep the pole upright. If the wire makes an angle of 60° with the horizontal through the foot of the pole, find the length of the i’ wire.
Answer:
Let OA be the electric pole and B be the point on the ground to fix the wire.
Let BA be x m.
AO
In ∆ABO,
\(\frac{A O}{A B}\) = sin 60°
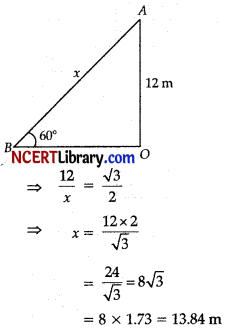
Hence, the length of wire = 13.84 m.
![]()
Section – D
Section D consists of 4 Questions of 5 marks each.
Question 32.
The numerator of a fraction is 3 less than its denominator. If 2 is added to both the numerator and the denominator, then the sum of the new fraction and original fraction is \(\frac{29}{20}\). Find the original fraction. [5]
OR
The 14th term of an A.R is twice its 8th term. If the 6th term is -8, then find the sum of its first 20 terms.
Answer:
Let the denominator be x, then numerators = x – 3
So, the fraction = \(\frac{x – 3}{x}\)
By the given condition, new fraction
= \(\frac{x – 3 + 2}{x + 2}\)
= \(\frac{x – 1}{x + 2}\)
Then, \(\frac{x – 3}{x}\) + \(\frac{x – 1}{x + 2}\) = \(\frac{29}{20}\)
⇒ 20[(x -3)(x + 2) + x(x – 1)] = 29(x² + 2x)
⇒ (x² -x – 6 + x²-x) = 29x² + 58x
⇒ 11x² – 98x – 120 = 0
⇒ 11x² – 110x + 12x – 120 = 0
(11x + 12) (x -10) = 0 or x = 10
The fraction is \(\frac{7}{10}\).
OR
Let first term be a and common difference be d.
Here, a14 = 2a8
or, a + 13d = 2(s + 7d)
a + 13d =2a + 14d
a = – d …(i)
Again, a6 = – 8
or, a + 5d = – 8 …(ii)
Solving (i) and (ii), we get
a = 2,
d = -2
S20 = \(\frac{20}{2}\) [2 × 2 + (20 – 1)(-2)]
= 10[4 + 19 × (-2)]
= 10(4-38)
= 10 × (-34) = -340
Question 33.
Prove that: \(\frac{\tan \theta+\sin \theta}{\tan \theta-\sin \theta}=\frac{\sec \theta+1}{\sec \theta-1}\)
Answer:
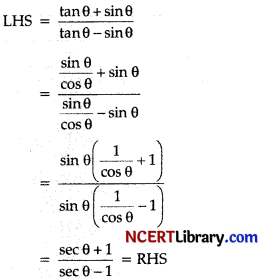
Hence Proved.
Question 34.
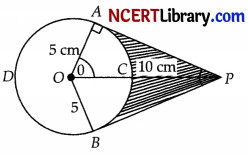
An elastic belt is placed around the rim of a pulley of radius 5 cm. From one point C on the belt, elastic belt is pulled directly away from the centre O of the pulley until it is at P, 10cm from the point O. Find the length of the belt that is still in contact with the pulley. Also find the shaded area. (Use π = 3.14 and \(\sqrt{3}\) = 1.73) [5]
The largest possible sphere is cut out from a wooden solid cube of side 7 cm. Find the volume of the wood left. (Use π = \(\frac{22}{7}\))
Answer:
cos θ = \(\frac{OA}{OP}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) or, θ = 60°
Reflex ∠AOB = 240°
∴ length of arc ADB = \(\frac{2 \times 3.14 \times 5 \times 240^{\circ}}{360^{\circ}}\)
= 20.93 cm
Hence length of elastic in contact = 20.93 cm
Now, AP = 5\(\sqrt{3}\) cm
Area (∆OAP + ∆OBP) = 25\(\sqrt{3}\) = 43.25 cm²
Area of sector OACB = \(\frac{2 \times 3.14 \times 240^{\circ}}{360^{\circ}}\)
= 26.16 cm²
Shaded Area = 43.25 – 26.16
= 17.09 cm²
OR
Given, the side of cube a = 7 cm
Since, the diameter of the largest possible sphere = Side of the cube
Hence, the radius of sphere = \(\frac{7}{2}\) cm.
Volume of the wood left = Volume of cube – Volume of sphere
= a³ – \(\frac{4}{3}\)πr<sup>3</sup>
= 7 × 7 × 7 – \(\frac{4}{3}\) × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × \(\frac{7}{2}\) × \(\frac{7}{2}\) × \(\frac{7}{2}\).
= 7 × 7 × 7(1 – \(\frac{11}{21}\))
= 7 × 7 × 7 × \(\frac{10}{21}\)
= \(\frac{490}{3}\)
Hence, volume of wood left = 163.3 cm³.
![]()
Question 35.
The mean of the following distribution is 48 and sum of all the frequencies is 50. Find the missing frequencies x and y.
| Class | 20-30 | 30-40 | 40-50 | 50-60 | 60-70 |
| Frequency | 8 | 6 | x | 11 | y |
Answer:
| C.I. | fi | xi | ui=\(\frac{x_i-a}{h}\) | fiui |
| 20-30 | 8 | 25 | -2 | -16 |
| 30-40 | 6 | 35 | -1 | -6 |
| 40-50 | X | 45 = a | 0 | 0 |
| 50-60 | 11 | 55 | 1 | 11 |
| 60 – 70 | y | 65 | 2 | 2y |
| Total | Σfi = 25 + x + y | Σfiui = 2y – 11 |
\(\text { Mean }=a+\left[\frac{Σf_iu_i}{Σf_i}\right] h\)
⇒ 48 = \(=45 +\left[\frac{2y-11}{50}\right] × 10\)
⇒ 48 – 45 = \(\frac{2y-11}{5}]\) = 3 × 5 = 2y – 11
⇒ 15 = 2y – 11
⇒ y = 13
Aslo, Σfi = 25 + x + y = 50
⇒ x + y = 25
⇒ x = 25 – 13 = 12
∴ x = 12 and y = 13.
Section – E
Case study based questions are compulsory.
Question 36.
On a weekend Rani was playing cards with her faniilv. The deck has 52 cards. If her brother drew one card.

Find the probability of getting a king of red colour.
Find the probability of getting a face card.
Find the probability of getting a red face card.
OR
Find the probability of getting a spade.
Answer:
I. No. of cards of a king of red colour = 2
Total no. of cards = 52
Probability of getting a king of red colour
= \(\frac{\text { No. of king of red colour }}{\text { Total number of cards }}\)
= \(\frac{2}{52}\) = \(\frac{1}{26}\)
II. No. of face card = 12
Total no. of cards = 52
Probability of face cards = \(\frac{12}{52}\) = \(\frac{3}{13}\)
III. No. of red face cards = 6
No. of face card = 13
Total no of cards = 52
Probability of getting a face card
= \(\frac{\text { No. of red face cards }}{\text { Total no. of cards }}\)
= \(\frac{12}{52}\) = \(\frac{3}{13}\)
No. of face card = 13
Total no of cards = 52
Probability of getting a face card
= \(\frac{\text { No. of red face cards }}{\text { Total no. of cards }}\)
= \(\frac{13}{52}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
![]()
Question 37.
It is common that Governments revise travel fares from time to time based on various factors such as inflation (a general increase in prices and fall in the purchasing value of money) on different types of vehicles like Auto¬Rickshaws, Taxis, Radio cab etc. The Auto charges in a city comprise of a fixed charge together with the charge for the distance covered. Study the following situations.

| Name of the city | Distance travelled (km) | Amount paid (₹) |
| City A | 10 | 75 |
| 15 | 110 | |
| City B | 8 | 91 |
| 14 | 145 |
Situation 1: In city A, for a journey of 10 km, the charge paid is ₹ 75 and for a journey of 15 km, the charge paid is ₹ 100.
Situation 2: In a city B, for a journey of 8 km, the charge paid is ₹ 91 and for a journey of 14 km, the charge paid is ₹ 145.
Refer situation 1
I. If the fixed charges of auto rickshaw be ₹ x and the running charges be ₹ y km/hr, then frame the linear
equations. Refer situation 2 1
II. Refer what will a person have to pay for travelling a distance of 30 km ?
III. Refer situation 1 a person travels a distance of 50 km. How much amount he has to pay?
OR
Plot the lines of situation 1 and situation 2 on the graph.
Answer:
I. According to given situation, we have
x + 10y = 75
x + 15y = 110
II. So let fixed charge is x.
then x + 8y = 91
x + 14y = 145
Solving (i) and (ii),
x = 19
y = 9
30 km trailing charge = x + 30y
= 19 + 30 x 9
= ₹ 289
III. Solving two equations,
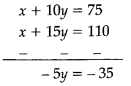
y = 7
Now, putting y = 7 in equation (i)
x + 10 × 7 = 75
x + 70 = 75
x = 75 – 70
x = 5
Now, if a person travels a distance of 50 km
then, amount = x + 50y
= 5 + 50 × 7
= 5 + 350
= ₹ 355
OR
![]()
Question 38.
ABCD is a playground. Inside the playground a circular track is present such that it touches AB at point P, BC at Q, CD at R and DA at S.
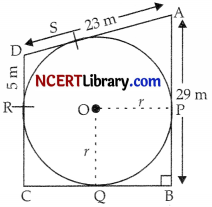
See the above figure and give answer of the following questions:
I. If DR = 5 m, then find DS.
II. What is the angle of OQB.
III. Find the length of AS.
OR
Find the length of PB.
Answer:
DR = 5 cm
DR = DS
(Length of tangents are equal)
i.e., DS = 5 m.
II. ∠OQB = 90° (Radius is ⊥ to tangent)
III. We have AD = 23 m.
and DS = 5 m (Proved in Q.I)
AS = AD – DS
= (23 – 5) m = 18 m
OR
We have, AB = 29 m
But AS = AP (lengths of tangents are equal)
and AS = 18 m
AP = 18 m (Proved in Q.II)
Now, PB = AB- AP
= (29- 18) m
= 11m.