NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric.
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The rearing of silkworms for obtaining silk is called
(a) cocoon
(b) silk
(c) sericulture
(d) silviculture.
Solution:
(c) The breeding and management of silkworms for the production of silk is known as sericulture. Different types of silk, with different textures, are obtained from different varieties of silk moths.
Question 2.
Which of the following is not a type of silk?
(a) Mulberry silk
(b) Tassarsilk
(c) Mooga silk
(d) Moth silk
Solution:
(d) Mulberry silk, tassar silk, mooga silk and eri silk are different types of silk produced from cocoons of different types of silk moths. Moth silk is not a type of silk.
Question 3.
Paheli wanted to buy a gift made of animal fibre obtained without killing the animal. Which of the following would be the right gift
(a) Woollen shawl
(b) Silk scarf
(c) Animal fur cap
(d) Leather jacket
Solution:
(a): Wool can be obtained without killing the animal. It comes from the fleece/hair of wool yielding animals such as sheep, goat, yak, camel, rabbit, etc. Silk is obtained by killing the pupae. Fur and leather are animal products which are obtained from the skin of animals by killing them.
Question 4.
Silk fibre is obtained from
(a) fleece of sheep
(b) cotton ball
(c) cocoon
(d) shiny jute stalk.
Solution:
(c) Silk is a natural fibre which is obtained from the cocoons of silk moths.
Question 5.
Wool fibre cannot be obtained from which of the following?
(a) Goat
(b) Llama
(c) Alpaca
(d) Moth
Solution:
(d) Different wool yielding animals are sheep, goat, camel (Llama and Alpaca belong to camel family), rabbit, yak etc.
Question 6.
Selective breeding is the process of
(a) selecting the offsprings with desired properties
(b) selecting the parents with desired properties
(c) selecting an area for breeding
(d) selecting fine hair for good quality wool.
Solution:
(b) Selective breeding is the process of crossing of two selected varieties having different traits to produce a hybrid having good traits of both, e.g., some breeds of sheep possess only soft under-hair. Their parents are specially selected to give birth to sheep which have only soft under-hair.
Question 7.
The general process that takes place at a sheep shearing shed is
(a) removal of fleece
(b) separating hair of different textures
(c) washing of sheep fibre to remove grease
(d) rolling of sheep fibre into yarn.
Solution:
(a) Removal of the fleece from a sheep is called shearing. It can be done manually with a large razor or with a shearing machine.
Question 8.
The term sericulture is used for
(a) culture of bacteria
(b) rearing of silkworm
(c) making silk fabric from silk yarn
(d) production of sarees.
Solution:
(b) The breeding, rearing or management of silkworms for the production of silk is known as sericulture.
Question 9.
Reeling of silk is
(a) a process of making silk reels
(b) spinning of silk fibres
(c) weaving of silk cloth
(d) the process of taking silk threads from cocoon.
Solution:
(d) The process of unwinding the silk filaments from the cocoon and combining them together to make a thread of raw silk is called reeling. For commercial purpose 3-10 fine filaments are reeled together at a time to produce desired diameters of raw silk or reeled silk. The final viable length of reeled filament is 300-600 m.
Question 10.
Silkworms secrete fibre made of
(a) fat
(b) cellulose
(c) protein
(d) nylon.
Solution:
(c) Salivary gland of the silkworm secretes fibre made up of protein sericin and fibroin.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 11.
Fill in the blanks in the following statements.
(a) ______ and ______ fibres are obtained from animals.
(b) Silk fibres come from ______ of silk ______ .
(c) Wool yielding animals bear ______ on their body.
(d) Hair trap a lot of ______ , which is a poor ______ of heat.
Solution:
(a) Silk, wool
(b) cocoons, moths
(c) hair
(d) air, conductor
Question 12.
State whether the following statements are True or False. If false, correct them.
(a) Silkworms are caterpillars of silk moth.
(b) In India, camels and goats are generally reared for obtaining wool.
(c) The rearing of silkworms for obtaining silk is called silviculture.
(d) In the process of obtaining wool from fleece, sorting is done after scouring.
(e) Yak hair are not used to make woollen fabric.
Solution:
(a) True
(b) False – In India, sheep are generally reared for obtaining wool.
(c) False – The rearing of silkworms for obtaining silk is called sericulture.
(d) True
(e) False – Yak hair are used to make woollen fabric.
Question 13.
How do the hair of certain animals help in keeping their bodies warm?
Solution:
The hair of the body of the certain animals trap a lot of air. Since air is a poor conductor of heat, this shields the body from cold and keeps it warm.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 14.
Match the items of column I with the items given in column II.
| (a) | Yak wool | (i) | Sheared hair |
| (b) | Angora goats | (ii) | Silkworm |
| (c) | Mulberry leaves | (iii) | Tibet and Ladakh |
| (d) | Scouring | (iv) | Jammu and Kashmir |
Solution:
(a) (iii)
(b) (iv)
(c) (ii)
(d) (i)
Question 15.
Various steps involved to obtain wool from fleece are given here.
(i) Picking out the burrs
(ii) Dyeing in various colours
(iii) Shearing
(iv) Scouring
(v) Sorting
Write the above steps in the correct sequence in which they are carried out.
Solution:
(iii) Shearing
(iv) Scouring
(v) Sorting
(i) Picking out the burrs
(ii) Dyeing in various colours
Question 16.
Some words related with silk are jumbled up. Write them in their correct form.
(a) TURECULRISE
(b) WILSMORK
(c) BELMURRY
(d) RINGLEE
Solution:
(a) SERICULTURE
(b) SILKWORM
(c) MULBERRY
(d) REELING
Question 17.
Figure shows three rings of circles with letters in them. Some of these letters in each ring can form the name of one wool yielding animal. Find the names of these animals.
Solution:
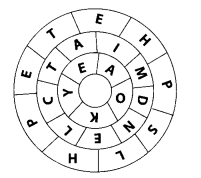
Yak, camel, sheep
Question 18.
Write a caption for each of the figures given as ( a-d )

Solution:
(a) Eggs of silk moth on mulberry leaves
(b) Silkworm
(c) Cocoon
(d) Cocoon with developing moth
Question 19.
Steps for the production of silk are given below in a jumbled order. Arrange them in their proper sequence.
(a) Eggs are warmed to a suitable temperature for the larvae to hatch from eggs.
(b) Fibres are taken out from the cocoon.
(c) After 25 to 30 days, the caterpillars stop eating and start spinning cocoons.
(d) The larvae/caterpillars or silkworms are kept in clean trays along with freshly chopped mulberry leaves.
(e) Female silk moths lay eggs.
(f) Cocoons are kept under the sun or boiled in water.
Solution:
(e) Female silk moths lay eggs.
(a) Eggs are warmed to a suitable temperature for the larvae to hatch from eggs.
(d) The larvae/caterpillars or silkworms are kept in clean trays along with freshly chopped mulberry leaves.
(c) After 25 to 30 days, the caterpillars stop eating and start spinning cocoons.
(f) Cocoons are kept under the sun or boiled in water.
(b) Fibres are taken out from the cocoon.
Question 20.
A wholesale woollen fibre dealer gets the woollen fibre of different textures sorted for various purposes. Match the items in column I with the woollen fibre in column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | Pashmina shawl | (i) | Camel wool |
| (b) | Woollen carpet | (ii) | Angora wool |
| (c) | Baby blanket | (iii) | Kashmir goat |
| (d) | Woollen sweater | (iv) | Sheep wool |
Solution:
(a) – (iii)
(b) – (i)
(c) – (ii)
(d) – (iv)
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 21.
Complete the paragraph related to the life history of silk moth by filling in the blanks.
The __(a)__ silk moth lays __(b)__, from which hatch called ___(c)___ or __(e)__. They grow in size and when the caterpillar is ready to enter the next stage of its life history called __(f)__ it first weaves a covering to hold itself, which is known as __(g)__.
Solution:
(a) female
(b) eggs
(c) larvae
(d)caterpillars
(e) silkworms
(f) pupa
(g) cocoon
Question 22.
Paheli went to the market to buy sarees for her mother. She took out a thread from the edge of the two sarees shown by the shopkeeper and burnt them. One thread burnt with a smell of burning hair and the other burnt with the smell of burning paper. Which thread is from a pure cotton saree and which one from a pure silk saree? Give reason for your answer.
Solution:
The thread which bums with the smell of burning hair is from pure silk saree and the thread which bums with the smell of burning paper is from pure cotton saree. It is because both silk and hair are protein fibres whereas both cotton and paper are carbohydrates.
Question 23.
Explain the phrase – “Unity is Strength” on the basis of the making of fabric from fibre.
Solution:
A fibre is a thin hair like strand. A large number of fibres are used to make fabric. The phrase – “Unity is strength” can be used in this regard because single fibre can be easily pulled and broken whereas fabric needs more energy to tear apart.
Question 24.
Write various steps for processing fibres into wool.
Solution:
Various steps for processing fibres into wool are:
(i) Shearing – The removal of wool or fleece from a sheep or other wool yielding animal is called shearing. It can be done manually with a large razor or with a shearing machine.
(ii) Scouring – The sheared hair is moved through tubs filled with soapy water to remove dust, dirt and grease. This is known as scouring. It is then passed through a series of rollers and dryers.
(iii) Sorting – Sorting consists of separating hair of different textures.
(iv) Removing burr – Burrs are soft fluffy fibres in wool. These are removed manually.
(v) Carding – During the process of carding, the clean selected wool fibres are passed through rollers that have thin wired teeth The teeth untangle the fibres and arrange them into a flat sheet called a web. The web is then formed into narrow untwisted fibres known as slivers.
(vi) Dyeing – The natural hair of sheep is white, brown or black. It is dyed in different colours.
(vii) Spinning – The fibres are straightened, combed and rolled into yam. The process of making yarn from fibres is called spinning.
Question 25.
Describe the life history of silk moth with the help of figures of various stages.
Solution:
The female silk moth lays eggs. When an egg hatches, a tiny caterpillar crawls out. This is the silkworm or larva. The silkworm feeds on mulberry leaves and grows. When it is ready to enter the next stage in its life cycle, it first weaves a net to hold itself. It then secretes a fibre made of proteins, which hardens on exposure to air. This is the silk fibre. It covers itself completely with this fibre, to form cocoon. At this stage, the larva is called a pupa. The pupa grows and changes inside the cocoon. A few weeks later, the cocoon opens and an adult moth comes out.

NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions
- Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Heat
- Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes
- Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Chapter 8 Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Chapter 9 Soil
- Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
- Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
- Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- Chapter 14 Electric Current and Its Effects
- Chapter 15 Light
- Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
- Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline
- Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric will help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.